Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Blue Dot network
Mains level: Paper 2- Indo-Pacific region
Context
The visit by United States Secretary of State Antony J. Blinken to Southeast Asia in December 2021 underscores the importance that is being accorded to this region by the Joe Biden administration.
Take aways from the visit
[1] Projecting the US as reliable partner
- The idea was to present the U.S. as a reliable partner in meeting the challenges that the Indo-Pacific region is facing.
- For instance, completely aware that the Southeast Asian nations are averse to choosing sides in this U.S.-China competition, Mr. Blinken made it a point to mention that “individual countries will be able to choose their own path and their own partners.
[2] Tackling China challenge
- Both China and the U.S. are trying to lure the Association of Southeast Asian Nation (ASEAN) countries to their side — China with its grand economic infrastructure investment deals and the U.S. through recent high profile official visits as well as through the Build Back Better World initiative and Blue Dot Network.
- In Southeast Asia, the U.S.-China competition is most visible in two areas; one is the South China Sea and the second is the investment in fulfilling the infrastructure development needs of Southeast Asian countries.
- The U.S. has continued its Freedom of Navigation operations in the disputed waters of the South China Sea.
- In his remarks in Indonesia, Mr. Blinken stressed America’s determination “to ensure freedom of navigation in the South China Sea, where Beijing’s aggressive actions there threaten the movement of more than $3 trillion worth of commerce every year”.
[3] Closing the gap on infrastructure
- Southeast Asia has been one of the top recipients of Chinese investments under its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- How these investments have driven countries such as Cambodia and Laos to do China’s bidding in the ASEAN even at the cost of compromising ASEAN’s unity is a known fact.
- Mr. Blinken reiterated that the U.S. remains committed to help close the gap on infrastructure.
- The infrastructure coordination group launched by the Quad members is seeking to catalyse even more investment and is looking to partner with Southeast Asia on infrastructure and many other shared priorities.
- Washington is promising to do more under the Build Back Better World initiative and the Blue Dot Network.
Way forward
- The ASEAN countries, even after the release of the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific, do not have a uniform approach when it comes to dealing with the U.S. and China.
- These differing approaches are also challenging the much vaunted ASEAN centrality in the Indo-Pacific.
- Though external players will have a limited role in ensuring that the unity within ASEAN is restored, providing proper alternative models of investments for development in sectors such as infrastructure, digital economy, supply chain, and health for the Southeast Asian nations will be critical.
Conclusion
The economic framework, investment plans and promises outlined need to be made operational quickly if Washington is to show that it is indeed serious about sustained commitment toward the Indo-Pacific.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Regulatory challenges faced by civil society organisations
Context
Recently, the Missionaries of Charity established by Nobel Laureate Mother Teresa was in the news for the cancellation of its permission under the FCRA.
Detailed scrutiny delaying permission for grant
- The levels of due diligence and the information sought on the one hand and the annual declarations to be given by the board members of civil society organisations on the other have increased significantly.
- The mandatory opening of bank accounts for foreign contributions has been centralised in one branch of the State Bank of India.
- The linking of Permanent Account Number (PAN), Aadhaar number and mapping it with the bank account/s of the individual board members are happening.
- The registrations under Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA) have been long necessitated in order to undertake due diligence of the causes for which the organisation is working for and also to have a handle on the traceability of funds.
- The dashboard shows a little under 17,000 active organisations — which have either got permission or will know their fate by March 2022, while around 33,000 organisations have either lost their permission or it has expired.
Various restrictions
- Restriction on sub-grant: In the past, the amendments in the FCRA that restricted the ability to sub-grant, killed many of the niche organisations working in very remote areas which had no direct access to international funding but were doing it through larger non-governmental organisations.
- Restriction on administrative expenses: The other amendment restricting the proportion of expenses on administration almost choked organisations that worked for the rights of the disposed.
- The increasing level of surveillance type of data sought has resulted in many organisations losing people on their governance structure and resulting in problems in funding.
Why do we need Civil Society Organisations?
- We need them because they usually work on what can be called an unreasonable agenda.
- This unreasonableness falls in three large verticals.
- [1] Ensuring efficiency and accountability from state: The first is that they ask for greater efficiency, delivery and accountability from the state.
- Whether is it about rehabilitation and compensation in the case of land acquisition or setting up a great accountability framework as was done through the movement led by the Mazdoor Kisan Shakti Sangathan for the Right to Information.
- [2] Correcting extractive nature of market: The second vertical is in correcting the extractive nature of markets.
- The groups asking for environmental accountability are looking at inter-generational justice on a matter that is not very precisely measurable but is palpable.
- [3] Picking up niche causes: The third is basically picking up causes that are so niche that it is beyond the capability of the state to come up with such initiatives.
- For example, a drama school set up in a village called Heggodu, Karnataka, or an idea of distributing clothing for work as done by Goonj.
- These initiatives cannot be put into specific business plans, spreadsheets or government schemes.
- They, therefore, need a grant-based, cause-based revenue stream model.
Should these organisations accept foreign funding?
- Causes have no boundaries: “Causes” have no boundaries and funding for such socially desirable belief systems could come from beyond borders.
- Some causes carried out by organisations such as Doctors Without Borders, or Reporters Without Borders are by definition international in nature.
- Similar is the case with the Jaipur foot provided by the Bhagwan Mahaveer Viklang Sahayata Samiti.
- The humanitarian work by the Missionaries of Charity is beyond the capability of a state.
- Such causes do not have a rational basis to be explained in terms of a financial model; how do you put a price tag to press freedom?
- The niche funding will happen from agencies that may be beyond the borders.
- The duality of welcoming foreign investments (which takes away capital gains and dividends) while actively discouraging foreign aid to charities is staring us in the face.
Conclusion
The government needs to ensure that the regulations do not create hurdles for the civil society organisations in their functioning and receiving fundings.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Commitment to net-zero emission targets
Mains level: Paper 3- Transition towards clean energy
Context
At a time when our planet faces an existential crisis, there is little doubt that we need innovative, scientific and urgent steps to secure humanity’s future.
India’s climate commitment
- We need to act decisively to reach global net-zero, restricting future cumulative emissions to the remaining carbon budget — as COP26 noted — if the rise in temperature is to remain within the limits of the Paris Agreement.
- At COP26, India announced its climate commitments — the “Panchamrit”, including a commitment to reach net-zero by 2070.
- India’s announcement of its net-zero goal is a major step considering that our country is not the cause of global warming.
- Its historical cumulative emissions are a mere 4.37 per cent of the world’s total.
India’s steps to achieve the targets
[1] India’s renewable energy targets and achievements
- India’s renewable energy targets have steadily become more ambitious, from the 175 GW by 2022 declared at Paris, to 450 GW by 2030 at the UN Climate Summit, and now 500 GW by 2030, announced at COP26.
- India has also announced the target of 50 per cent installed power generation capacity from non-fossil energy sources by 2030, raising the existing target of 40 per cent, which has already been almost achieved.
- Renewable technologies: India will not lag in terms of new cutting-edge renewable technologies and has already announced a Hydrogen Energy Mission for grey and green hydrogen.
- In energy efficiency, the market-based scheme of Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT) has avoided 92 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent emissions during its first and second cycles.
[2] India’s E-mobility transtion
- FAME: India is accelerating its e-mobility transition with the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles Scheme to support the electric vehicle market development and enable its manufacturing ecosystem to achieve self-sustenance.
- Incentives for customers and companies: The government has also announced a slew of incentives for customers and companies to promote e-vehicles.
- Adoption of BS-VI: India leapfrogged from Bharat Stage-IV (BS-IV) to Bharat Stage-VI (BS-VI) emission norms by April 1, 2020.
- Scrapping policy: A voluntary vehicle scrapping policy to phase out old and unfit vehicles now complements these schemes.
- Electrification of railway routes: Indian Railways is charging ahead, targeting the full electrification of all broad-gauge routes by 2023.
[3] Ujjwala Yojana and UJALA
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana has benefitted 88 million households with LPG connections.
- More than 367 million LED bulbs have been distributed under the UJALA scheme, leading to energy savings of more than 47 billion units of electricity per year and a reduction of 38.6 million tonnes of CO2 per year.
- With these and many other initiatives, India has already achieved a reduction of 24 per cent in the emission intensity of its GDP between 2005 and 2016, and is on track to meet its target of 33 to 35 per cent by 2030.
Role of private sector
- Since industries also contribute to GHG emissions, any climate action will need to reduce or offset emissions that emerge from industrial and commercial activity.
- The public and private sectors in India are already playing a key role in meeting the climate challenge, helped by growing customer and investor awareness, as well as increasing regulatory and disclosure requirements.
- Enterprises are well-positioned to not just adapt to but also gain from the low-carbon transition.
- The low-carbon transition challenge is bigger for companies that are largely coal-powered and contribute more than half of our country’s emissions.
- The business fraternity must make the best possible use of this opportunity to invest in climate technologies and expand the use of renewable energy sources.
- The Indian cement industry has taken pioneering measures and achieved one of the biggest sectoral low carbon milestones worldwide.
Way forward
- India’s journey on the low-carbon pathway towards net-zero requires the active participation of all stakeholders.
- Sustainable lifestyles and climate justice are at the core of this journey.
Conclusion
With cooperation from the private sector, India will be able to responsibly use its fair share of the global carbon space and contribute to reaching the global net-zero goal to build a more environmentally sustainable planet.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Western Disturbances
Mains level: Not Much
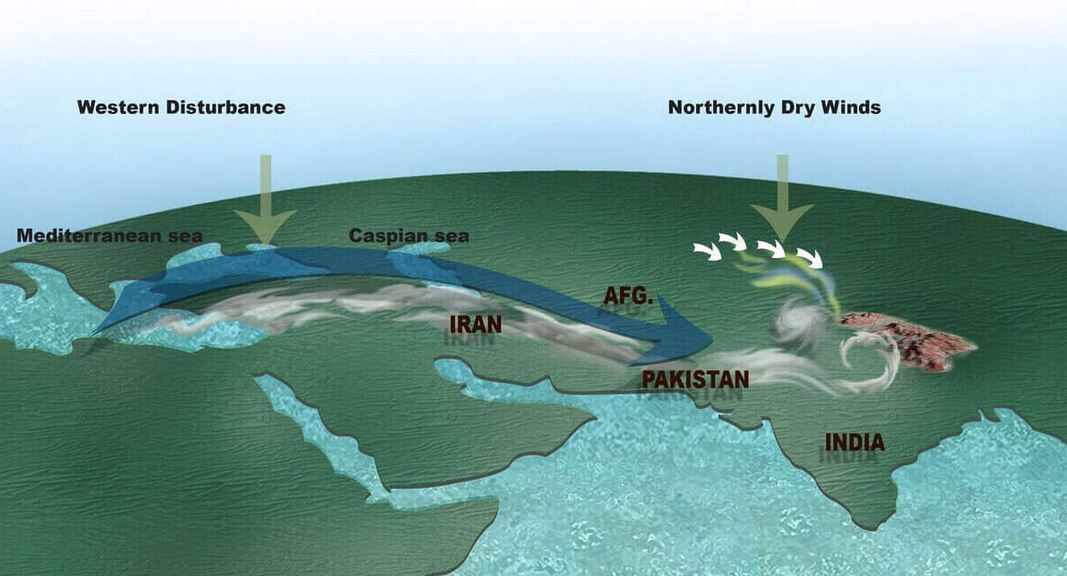
Under the influence of two consecutive western disturbances, New Delhi is in for a wet spell.
Western Disturbances
- A western disturbance is an extratropical storm originating in the Mediterranean region that brings sudden winter rain to the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent.
- It is a non-monsoonal precipitation pattern driven by the westerlies.
- The moisture in these storms usually originates over the Mediterranean Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea.
- Extratropical storms are global phenomena with moisture usually carried in the upper atmosphere, unlike their tropical counterparts where the moisture is carried in the lower atmosphere.
- In the case of the Indian subcontinent, moisture is sometimes shed as rain when the storm system encounters the Himalayas.
- Western disturbances are more frequent and strong in the winter season.
Impact: Winter Rainfall and Extreme Cold
- Western disturbances, specifically the ones in winter, bring moderate to heavy rain in low-lying areas and heavy snow to mountainous areas of the Indian Subcontinent.
- They are the cause of most winter and pre-monsoon season rainfall across northwest India.
- An average of four to five western disturbances forms during the winter season.
Its significance
- Precipitation during the winter season has great importance in agriculture, particularly for the rabi crops.
- Wheat among them is one of the most important crops, which helps to meet India’s food security.
Try this PYQ:
Q. Consider the following statements:
- The winds which blow between 30°N and 60°S latitudes throughout the year are known as westerlies.
- The moist air masses that cause winter rains in the North-Western region of India are part of westerlies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MAC, NATGRID
Mains level: Counter-terrorism ops and security agencies
The Union government has asked the States to share more intelligence inputs through the Multi Agency Centre (MAC), a common counter-terrorism grid under the Intelligence Bureau (IB).
Why in news?
- States are often reluctant to share information on the platform.
- There are several gaps in sharing critical information at the right time.
- Plans are afoot for more than a decade to link the system up to the district level.
About MAC
- The Multi-Agency Centre (MAC) was formed in December 2001 following the Kargil intrusion and the subsequent overhaul of the Indian national security apparatus suggested by the Kargil Review Committee report.
- Accordingly, the Intelligence Bureau (IB) was authorized to create a multi-agency centre (MAC) in New Delhi.
- Now functioning 24×7 as the nodal body for sharing intelligence inputs, MAC coordinates with representatives from numerous agencies, different ministries, both central and state.
- Various security agencies share real-time intelligence inputs on the MAC.
- The state offices have been designated as subsidiary MACs (SMACs).
- As many as 28 organisations, including the Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), armed forces and State police, are part of the platform.
Back2Basics: NATGRID
- NATGRID is an intelligence-sharing network that collates data from the standalone databases of the various agencies and ministries of the Indian government.
- It collects and collates a host of information from government databases including tax and bank account details, credit/debit card transactions, visa and immigration records and itineraries of rail and air travel.
- It came into existence after the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
- It is accessible to only authorized people from 10 security agencies on a case-to-case basis for investigations into suspected cases of terrorism.
- It will also have access to the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems, a database that links crime information, including First Information Reports, across 14,000 police stations in India.
Note: NATGRID data will be made available to 11 central agencies, which are: Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), Intelligence Bureau (IB), National Investigation Agency (NIA), Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), Enforcement Directorate (ED), Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC), Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) and Directorate General of GST Intelligence.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IC15 Crypto Index
Mains level: Cryptocurrencies market in India

Superapp CryptoWire recently launched India’s first cryptocurrency index, IC15, which will measure the performance of the 15 most widely traded cryptocurrencies listed on leading crypto exchanges by market capitalization.
What is IC15?
- CryptoWire constituted an Index Committee of domain experts, industry practitioners, and academicians that will select cryptocurrencies from the top 400 coins in terms of market capitalization.
- The eligible cryptocurrency should have traded on at least 90% of the days during the review period and be among the 100 most liquid cryptocurrencies in terms of trading value.
- Also, the cryptocurrency should be in the top 50 in terms of the circulating market capitalization.
- The committee will then select the top 15 cryptocurrencies. The index will be reviewed quarterly.
What is its significance?
- IC15 can be replicated for creating index-linked products such as index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- Usually, the performance of a mutual fund scheme is assessed with reference to a benchmark, which could be a total return index of the Nifty or the Sensex.
- IC15 is the first index in India that can act as a benchmark of the underlying cryptocurrency market and the performance benchmark for fund managers.
- Moreover, robo-advisors, which provide financial advice with moderate to minimal human intervention, can use this index to create investment products at lower costs.
How does IC15 correlate with other market indicators?
- IC15’s base value as on 1 April 2018 was 10,000.
- It would mean that the index has gained 615% in absolute terms to 71,475.48 till 31 December 2021.
Can index-based crypto investment reduce risks?
- Index investing can be an effective way to diversify against risks as a fund invests in a basket of assets against a few limited coins.
- However, index-based investing may not fully remove risks associated with investing in crypto assets.
- Case in point: IC15 saw a 50% plunge in 2018, whereas other asset classes have seen a maximum drop in the range of 3-4%.
- Further, bitcoin and ethereum have a combined weightage of 77% in the index, making it highly vulnerable to any volatility in these two coins.
Can crypto funds be launched in India?
- SEBI has recently asked mutual fund houses not to launch crypto-based funds until the Centre comes out with clear regulations.
- This means asset management companies for now won’t be able to launch crypto funds based on IC15.
- However, in the absence of any regulations, crypto platforms can offer products based on the index.
- Global crypto investment platform Mudrex last year launched Coin Sets—crypto funds based on themes such as decentralized finance or market cap.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nai Talim
Mains level: Not Much
The Vice President of India has said that the New Education Policy follows the ‘Nai Talim’ of Mahatma Gandhi by giving importance to the mother tongue as the medium of instruction at the school level.
What is Nai Talim?
- The phrase Nai Talim is a combination of two words- Nai Means ‘New’ and Talim – a Urdu word-means ‘Education’.
- In 1937, Gandhiji introduced the concept of Nai Talim in India. It aimed to achieve Gram Swaraj (liberation of villages).
- In short, Gandhiji dreamed to make all villages independent; and self-reliant.
- It is an approach to the total personality development of body, mind and spirit and was based on four principles namely:
- Education or learning in mother tongue along with handicraft work,
- Work should be linked with most useful vocational needs of the locality,
- Learning should be linked with vocational work, and
- Work should be socially useful and productive needed for living.
Gandhiji and Education
- Gandhi’s first experiments in education began at the Tolstoy Farm ashram in South Africa.
- It was much later, while living at Sevagram (Wardha) and in the heat of the Independence struggle, that Gandhi wrote his influential article in Harijan about education.
- In it, he mapped out the basic pedagogy (or teaching) with focus on:
- Lifelong character of education,
- Social character and
- A holistic process
- Thus, for Gandhi, education is ‘the moral development of the person’, a process that is by definition ‘lifelong’.
- He believed the importance of role of teacher in the learning process.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2020:
Q. One common agreement between Gandhism and Marxism is
(a) The final goal of a stateless society
(b) Class struggle
(c) Abolition of private property
(d) Economic determinism
Post your answers here:
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now


