Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INSTC
Mains level: Paper 2- India-Iran relations
Context
Iran’s Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian’s three-day visit to India, last week, was the first ministerial-level visit from Iran since Ebrahim Raisi assumed the Iranian presidency in August last year.
Background
- Bilateral relations between India and Iran span millennia marked by meaningful interactions.
- Both countries shared borders until 1947 and share several common features in their language, culture and traditions.
- The diplomatic links were established on 15th March 1950, when both countries signed a Treaty of Friendship and Perpetual Peace.
- However, Iran’s joining of Baghdad pact in 1954 and the Cold War politics prevented both countries from having closer relations until the 1990s.
- Islamic Revolution of 1979, hostage of US diplomats, Iran-Iraq War and Tehran’s support for Hezbollah and Hamas among others resulted in a range of political and economic sanctions, leading to Iran being isolated at a global level
- In the 1990s, both countries’ interests converged around energy, Central Asia and security, mostly around the Pakistan-Afghan region.
- This resulted in the signing of ‘The Delhi Declaration’, which provided the vision of the countries’ defence and strategic partnership and “Tehran Declaration”, which set forth the areas of possible cooperation
India-Iran relations: A shared vision for equitable, pluralistic and co-operative international order
- The “Tehran Declaration” signed during former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s visit to Iran affirmed the shared vision of the two countries for an “equitable, pluralistic and co-operative international order”.
- It recognised then Iranian President Mohammad Khatami’s vision of a “dialogue among civilisations” as a paradigm of international relations based on principles of tolerance, pluralism and respect for diversity.
- Advancing the standing in global order: Two decades later, as India strengthens new partnerships within its regional vision centred on the Indo-Pacific, both countries remain driven by the goals of advancing their standing at the regional and global level.
- Both are keen to project themselves as independent strategic actors determined to play a role in shaping a new multipolar order in their shared Eurasian neighbourhood and also at the global level.
Why does India need Iran?
- Energy security: Conventionally, for energy security
- Iran is amongst India’s top oil suppliers
- Strategic importance: Since the 1990s, Iran’s importance has become ‘strategic’
- Security reasons: Iran’s cooperation is critical for India’s security given that
- Pak supports terrorism in India
- Influence in Afghanistan: India’s influence in Afghanistan is marginal.
- Countering Pakistan: India needs Iran to moderate Pak’s influence in West Asia
- Iran is a leader in the Muslim world.
- Access to Afghanistan and Central Asia
Significance of Iran for India
- Geopolitical logic in relations: The sanctions imposed by the US on Iran after it withdrew from the nuclear deal in 2018 may have virtually destroyed India-Iran trade, especially India’s energy imports from Iran, but the geopolitical logic underpinning relations between the two countries remains firm.
- Land bridge to Central Asia and Eurasia: Iran has sought to leverage its crossroad geographical location straddling the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea, India has come to see it as its land bridge to Central Asia and Eurasia.
- INSTC: Despite the difficulties posed by decades of American sanctions, Iran has, along with India, Russia and a few other countries in the Eurasian region, continued to work on the multi-modal International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- During Raisi’s visit to Moscow, the two sides had pledged to redouble their efforts to build the railway line between Iran’s Caspian port of Rasht and Astara on the Iran-Azerbaijan border.
- Alternative Caspian Sea Route: The activation of an alternative Caspian Sea route speaks volumes about the positive outlook of Iran, India and Russia on this corridor despite a variety of geopolitical challenges.
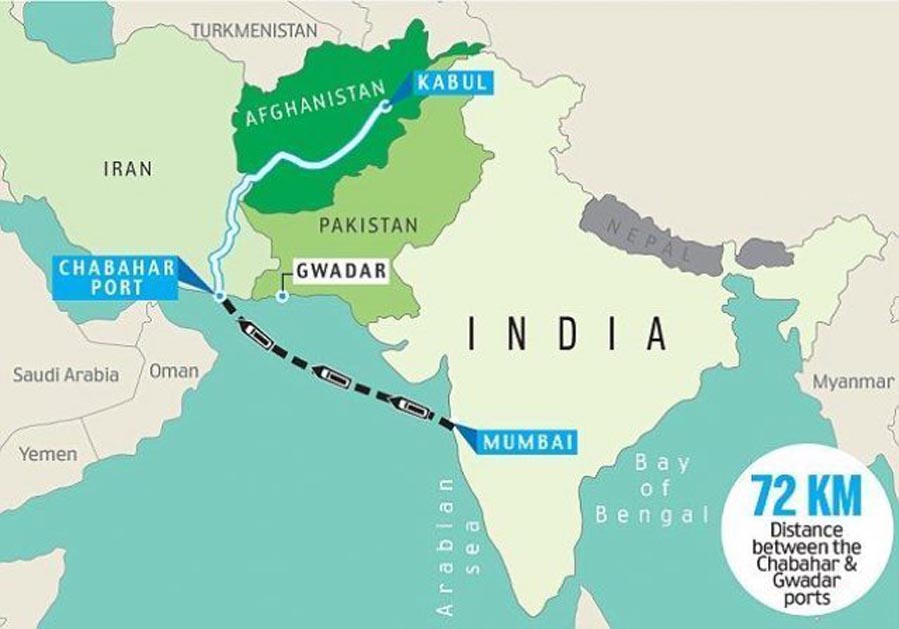
- Iran’s Chabahar port, where India is developing two berths that it will lease for commercial operations for 10 years, is also a story of perseverance in the ties between the two countries.
Irritants in Indo-Iran ties
- India’s relations with Saudi Arabia, US and Israel: Growing Saudi-India-US-Israel relations have irked Iran.
- In retaliation, Iran, for the first time, has linked the plight of Muslims in Gaza, Yemen, and Bahrain, with those in Kashmir
- Iran-Pak-China ties: Warming Iran-Pak-China ties have annoyed India.
- Sluggish Chabahar port development: Slow Chabahar port development has annoyed Iran.
- China-Iran strategic partnership:
- An economic and security partnership deal between Iran and China was recently made public, creating a global alarm, especially for India and the US.
- The foundation for this deal was laid during Chinese President Xi Jinping’s visit to Iran in 2016
- The draft agreement involves Chinese investments worth $400 billion into the Iranian economy over 25 years.
- Of this, $280 billion will be allocated for the oil and gas sector and the remaining funding will be for other core sectors like banking, telecommunications, ports and railways.
- In return, China would get a steady supply of Iranian oil at a heavily discounted rate during the same period.
- This deal creates a win-win situation for both countries.
- It lifts Iran’s sanction-hit economy and helps China set a firm foothold in the Middle East.
US sanctions:
- Iran’s aim to develop nuclear weapons has come under strong criticism from Trump Administration since the beginning.
- Thus, the US has withdrawn from the Iran nuclear deal in 2018 after it was signed in 2015 and imposed unilateral sanctions on Iran.
- The US’ sanctions and aggressive policies have created a situation of economic and geostrategic uncertainty.
- Indian investors are wary of having businesses in Iran for the fear of the US.
- Also, India deviated from the policy of not abiding by unilateral sanctions by ceasing to purchase Iranian oil.
- Due to this, Iran did not back India’s bid to mobilise international support against Beijing’s aggression in the Ladakh.
Other issues:
- Iran is against India’s decision to abrogate Article 370 and 35A.
- It has called on India and Pakistan to show restraint and prevent the killing of innocent Kashmiris, revealing possible close ties between Pakistan and Iran.
- Iran also voiced against “extremist Hindus and their parties” during the 2020 Delhi riots.
- Apart from these issues, Iran also sidelined India’s ONGC from exploration rights at its Farzad B Gas field, stating that it will engage the company at a later date.
Way forward
- As India is treading a fine line in balancing relations with the US, China and Iran while striving to augment its political influence in West Asia, embracing one country over the other is not an option for India.
- Therefore, a multilateral foreign policy is a way forward.
- India must retain its involvement in the Chabahar port development because of the geostrategic significance.
- In the immediate term, India should improve its multi-alignment credentials to absorb investments into the port projects from the public and private sector, boost maritime cooperation among littoral countries to enhance the transit of goods, and foster regional partnership for the Chabahar port development.
- Based on the mutual geostrategic and energy interests, India could collaborate with Japan under the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor.
- Japan’s participation would enhance the multilateral characteristics of the transit hub in the region, unlike the China-owned Gwadar port. This will further enhance multilateral investments to solidify regional economic partnerships that enable the sustainability of the port.
- Also, India needs to evolve a better strategy on Iran beyond waiting to see how the US may react, beyond having to issue a clarification in response to Iran’s sudden provocations and beyond allowing voids of partnerships that China may fill.
- In order to do so, India must create a new alliance of countries having similar geostrategic interests, which are also facing issues with US’ unrealistic and aggressive foreign policy strategy and China’s expansionistic policies.
Conclusion
While the revival of the nuclear deal could give a fillip to India’s economic ties with Iran, India’s interests in continental Asia will be served well by heeding to the calls for developing a long-term roadmap for bilateral relations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
