| Smash 2025 FLT 09 Q7. Discuss the geological processes involved in the formation of different types of islands. How does global warming threaten the islands across the world? |
| PYQ. Explain the formation of thousands of islands in Indonesian and Philippines archipelagos. (2014) |
| Samachar Manthan: Article name: United Nations World Water Development Report, 2025 Source: Samachar Manthan March 2025 Details: – This report highlited mass displacements due to rising sea levels in small islands. – Approximately 300 families were relocated from the island of Gardi Sugdub in Panama’s Guna Yala province. |
The IPCC AR6 (2021) projects a sea level rise of 0.28–1.01 metres by 2100, threatening the very existence of low-lying island nations by endangering their land, livelihoods, and sovereignty.
Impacts of Climate Change & Sea Level Rise on Island Nations
- Geophysical Dimension
- Loss of Land and Habitable Area – Rising seas cause coastal erosion and submergence. Eg- Maldives, average elevation 1.5 m, risks total submergence
- Saltwater Intrusion into Freshwater – Contaminates groundwater and reduces potable water.
- Rising temperatures and ocean acidification endanger coral reefs—vital for fisheries, tourism, coastal protection, and carbon storage—while also heightening drought and freshwater scarcity in SIDS.
- Economic Dimension
- As per UNDP, from 1970 to 2020, SIDS lost US$153 billion due to weather extremes
- Threat to Food Security – Loss of arable land, coral reef degradation, and decline in fisheries.
- Vulnerability to Extreme Weather – Intensified storms, cyclones, and floods. Eg- Cyclone Pam (2015) in Vanuatu caused losses equal to 64% of GDP.
- Disproportionate Losses: SIDS face 3–5 times higher climate losses relative to revenues than other nations
- Debt and Fiscal Strain: Recovery costs push debt burdens. Eg- Dominica’s debt-to-GDP reached 150% after Hurricane Maria.
- Social Dimension
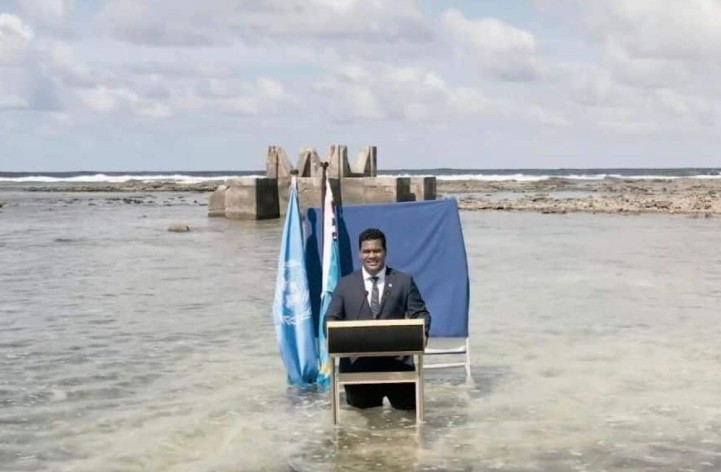
- Displacement and Climate Refugees – Rising seas force migration and create climate refugees. Eg- Kiribati purchased land in Fiji to resettle population
- Panama became the first nation to relocate an island community, moving 300 Guna families from Gardi Sugdub to the mainland due to rising sea levels.
- Cultural Dimension – Submergence of sacred sites, burial grounds, and landscapes. Eg- Marshall Islands heritage sites at risk of erasure.
- Political & Legal Dimension
- Sovereignty and Legal Challenges – Threat to statehood, EEZ rights, and maritime boundaries. Eg- Tuvalu’s appeal at the UN to preserve statehood despite land loss.
Way Forward
- Mitigation Strategies (Addressing root causes – emission reduction)
- Promote Renewable Energy: Expand solar, wind, geothermal, and ocean energy. Example: SIDS Lighthouses Initiative
- Blue Carbon Solutions: Protect and restore mangroves, seagrasses, coral reefs that act as carbon sinks and natural barriers.
- Global Emission Cuts: Major emitters must honor Paris Agreement commitments to limit warming below 1.5°C.
- Adaptation Strategies (Enhancing resilience and coping capacity)
- International Financing: Operationalise Loss and Damage Fund (COP27) and initiatives like the Bridgetown Initiative (2022) to help debt-stressed SIDS adapt
- Planned Relocation: Develop migration frameworks to manage climate-induced displacement with dignity.
- Community-Centric Approaches and nature based solutions: Use traditional knowledge and local innovations in adaptation strategies.
To confront the triple planetary crisis of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution, island nations must be supported through global solidarity to secure their survival and sustainable future.


