| Smash 2025 FLT 07Q15. How far can the theory of plate tectonics be used to explain the origin and distribution of major geological features across the Earth’s surface? |
| PYQQ. Why are the world’s fold mountain systems located along the margins of continents? Bring out the association between the global distribution of Fold Mountains and the earthquakes and volcanoes. (2014) |
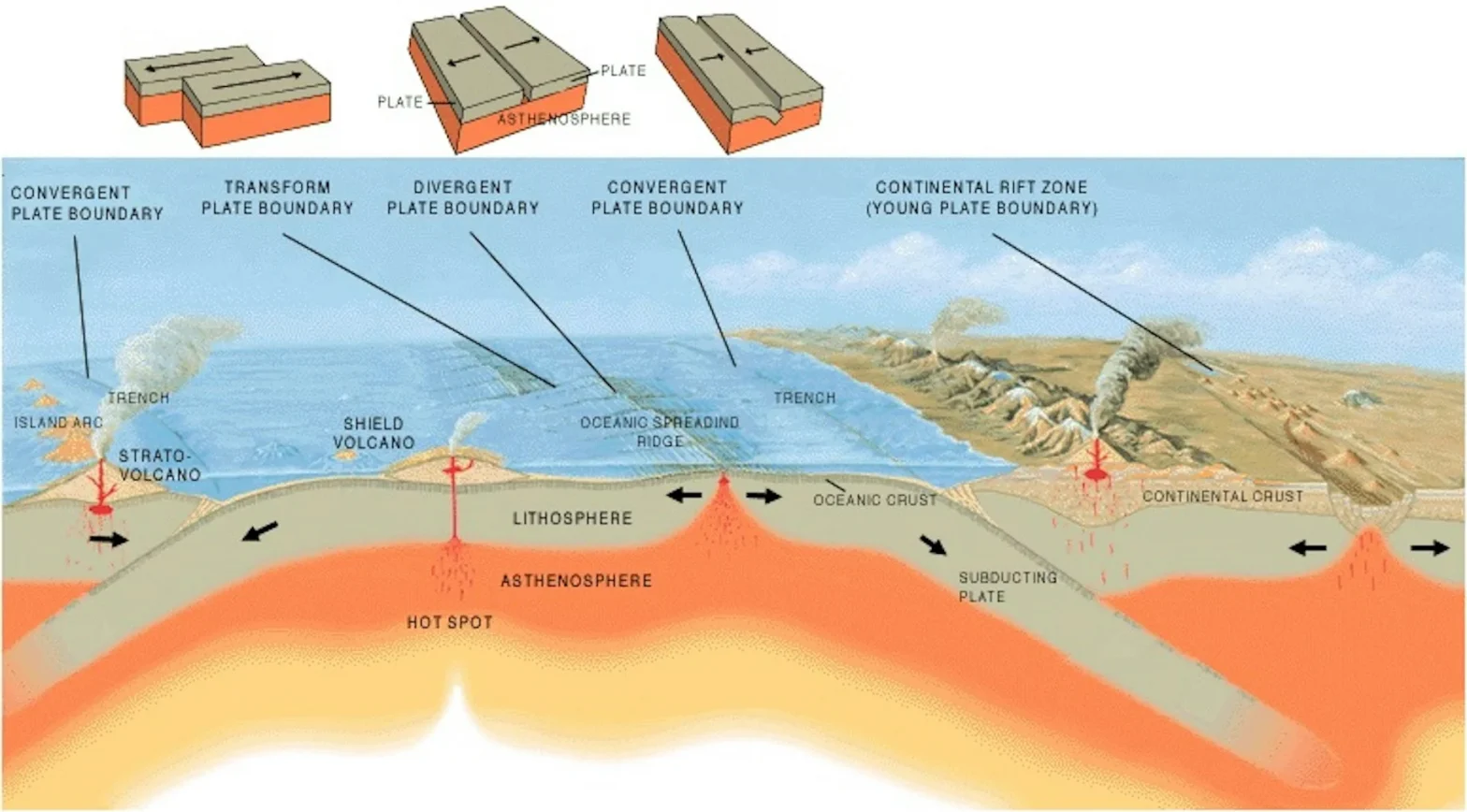
The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates that float over the asthenosphere. Their movements – divergence, convergence, and transform – continually reshape the continents and ocean basins. This dynamic process is explained by Plate Tectonic Theory
Changes in Shape and Sizes of Continents and Ocean Basins due to Tectonic Movements
- Divergent Boundaries
- Seafloor Spreading – New crust forms as plates move apart, widening oceans. Eg– Mid-Atlantic Ridge causing expansion of the Atlantic Ocean.
- Rifting – Continental divergence forms rift valleys, potential new oceans. Eg– East African Rift may split Africa, creating a new ocean.
- Formation of Ridges & Fracture Zones – Oceanic ridges rise above seafloor, altering basin topography. Eg– East Pacific Rise.
- Volcanic Island Chains – Magma upwelling creates new islands and redefines ocean shape. Eg– Iceland on Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
- Convergent Boundaries
- Subduction & Trench Formation – Oceanic crust sinks, shrinking basins. Eg– Mariana Trench, deepest point on Earth.
- Mountain Building (Orogeny) – Collisions fold crust, raising mountains. Eg– Himalayas (India–Eurasia), Andes (Nazca–South America).
- Volcanic Arcs – Subduction creates volcanic island chains altering ocean basin outlines. Eg– Japan, Philippines.
- Closing of Seas – Prolonged convergence closes small basins. Eg– Tethys Sea closed during India–Asia collision.
- Transform Boundaries
- Lateral Displacement of Crust – Plates sliding alter margins. Eg– San Andreas Fault shifting California coastline.
- Long-Term Continental Drift
- Breakup & Drift of Supercontinents – Continents drift, altering shapes and positions. Eg– Breakup of Pangaea ~200 million years ago.
- Future Supercontinents – Projections suggest continents may reunite. Eg– “Amasia” or “Pangaea Proxima.”
- Opening & Closing of Oceans (Wilson Cycle) – Oceans form and vanish over geologic cycles. Eg– Iapetus Ocean closed before Atlantic formed.
Other Factors Affecting Shape & Size of Continents and Ocean Basins
- Volcanism (Hotspots & Intra-plate activity) – Builds volcanic islands and oceanic plateaus, altering coastlines. Eg- Hawaiian Islands (Pacific), Iceland (Mid-Atlantic Ridge hotspot).
- Glaciation & Isostatic Rebound – Ice sheets depress crust; post-glacial rebound uplifts land and shifts coastlines. Eg- Scandinavia, Canadian Shield uplift.
- Sea Level Changes (Eustasy) – Due to climate change, glacial melting, thermal expansion, exposing or submerging shelves. Eg- Maldives, Tuvalu threatened by sea-level rise.
- Mantle Plumes & Superplume Events – Massive mantle upwellings lead to rifting or flood basalts, fragmenting land. Eg- Deccan Traps (India), Siberian Traps (Russia).
Understanding these processes not only explains Earth’s past but also prepares us to visualize its future landscapes and evolving continental order.