| Smash 2025 FLT 07 Q5. India has significant potential to lead the global renewable energy transition. Discuss the major opportunities and barriers in scaling up renewable energy infrastructure in India. |
| PYQ Q. India has immense potential of solar energy though there are regional variations in its development. Elaborate. (2020) |
India, being a tropical country with 300 sunny days annually and high solar insolation (4–7 kWh/m²/day), has immense potential for solar energy.
| Fact File: India ranks 3rd in Solar Power capacity, (IRENA RE Statistics 2025) with capacity of 1.08 GWhTotal solar energy potential stands at 748 GWh |
Ecological Benefits
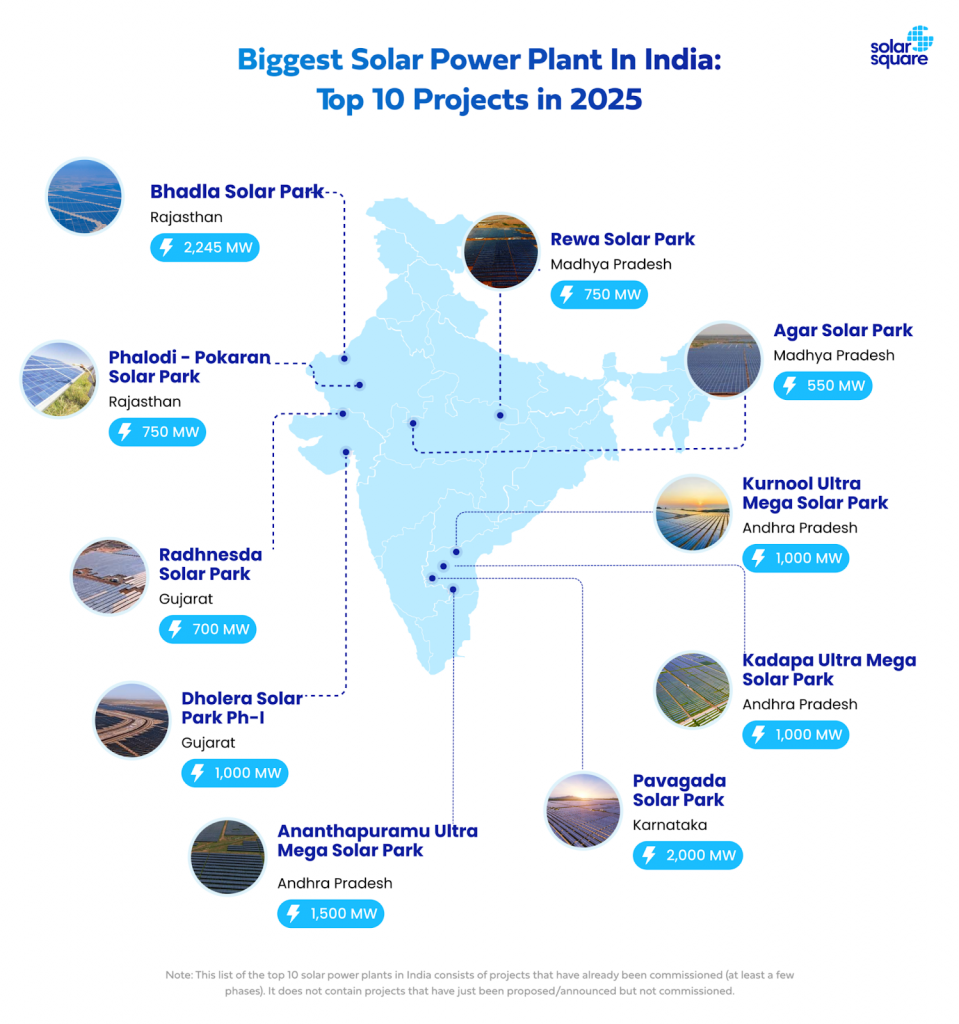
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions – Solar is carbon-neutral during operation. Eg– Bhadla Solar Park (Rajasthan) avoids ~4 million tonnes of CO₂ annually.
- Air Quality Improvement – Cuts SO₂, NOx, particulate emissions from coal. Eg– NTPC Dadri has integrated solar to offset coal-based generation.
- Water Conservation – Thermal plants need 3–5 m³/MWh water; solar PV is nearly waterless.
- Reduced Land Pressure through Innovative Deployment – Rooftop, floating solar, and canal-top solar save agricultural land. Eg– Gujarat’s Narmada canal-top solar.
- Synergy with Agriculture – Agrivoltaics allow crops beneath panels, reducing water loss. Eg– Maharashtra pilot projects under PM-KUSUM scheme.
- Contributes to Climate Commitments – Key to India’s pledge of 50% power capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030.
Economic Benefits
- Energy Security – Reduces fossil fuel imports.(2024–25: India imported 243 MMT coal)
- Cost Competitiveness – Tariffs now among the lowest globally (less than ₹3/unit ).
- Job Creation – Solar PV sector employed ~319,000 workers in 2023; total RE jobs ~1.02 million. Eg– CEEW projects 3.4 million clean energy jobs by 2030.
- Rural Empowerment – Solar pumps (PM-KUSUM) reduce diesel dependence and enhance farmer income. Eg– Over 2.3 lakh solar pumps installed by 2023.
- Boost to Domestic Manufacturing – Under PLI, India’s solar module manufacturing capacity crossed 74 GW in 2025, making it second globally.
- Foreign Exchange Savings – According to NITI Aayog, renewable energy expansion could reduce fossil fuel imports by up to $94 billion annually by 2030.
- Infrastructure Development & Local Growth – Large solar parks bring roads, transmission lines, and jobs to underdeveloped regions. Eg– Pavagada Solar Park (Karnataka)
- Energy Access & Decentralisation – Off-grid solar improves rural electrification.
| Challenges | Way Forward |
| High import dependence on modules & cells | Boost domestic manufacturing (PLI scheme) |
| Land acquisition issues for mega-parks | Promote rooftop, canal-top, floating solar |
| Intermittency & storage gap | Invest in battery storage, hybrid RE projects |
| Grid integration & transmission bottlenecks | Strengthen Green Energy Corridors |
Solar energy offers a dual dividend—ecological sustainability and economic resilience. It is the backbone of India’s path toward green growth and energy transition.