Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bats and thier natural role
Mains level: Illict wildlife trade and its prevention
The COVID pandemic has magnified our fear of bats, but their conservation is crucial to prevent such events from arising again.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2014:
Q.Consider the following:
- Bats
- Bears
- Rodents
The phenomenon of hibernation can be observed in which of the above kinds of animals?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) Hibernation cannot be observed in any of the above
Bats
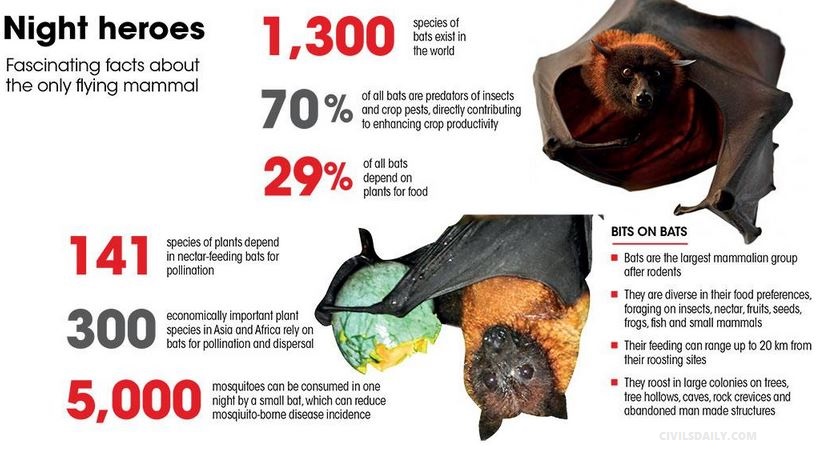
- Bats are the largest mammalian group after rodents, with over 1,300 species making up a quarter of all mammals.
- They occur on all continents except Antarctica and are particularly diverse in South Asia, with 114 species of insect-eating bats and 14 fruit bats, also known as “flying foxes”, occurring in India.
- They roost in large colonies on trees, tree hollows, caves, rock crevices and abandoned manmade structures.
- They play a unique role in maintaining ecosystem structure, making a singular contribution to our food production, economy and well-being.
- They are the only mammals capable of true flight and have a unique sonar-based echolocation mechanism to capture prey at night.
Their significance
1) Seed dispersal
- About 29 per cent of all bats depend upon plants for food.
- The diet of fruit-eating bats consists largely of flowers and fruits such as mangoes, bananas, guavas, custard apples, figs, tamarind and many species of forest trees.
- Therefore, bats play a vital role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. Studies have shown that seedlings raised from bat dispersed seeds show higher germination and vigorous growth.
2) Pollination
- Studies have found that bats play a vital role in pollination, mainly of large-flowered plants, and in crop protection.
- Fruit bats (Megachiroptera) being large, require big flowers with copious amounts of nectar.
- Bats are major pollinators for many species of mangroves which are important for coastal ecosystems and local livelihoods.
3) Production boost
- Insects are a major problem for agriculture, destroying up to 26 per cent of the annual production of crops worldwide every year, roughly amounting to $470 billion.
- Insectivorous bats, which make up 70 per cent of all bat species, are voracious predators of nocturnal insects and crop pests.
- Some large insectivorous bats are also reported to feed on small rodents. Thus they contribute directly to enhancing the crop productivity with tremendous economic impact.
4) Soil fertility
- Bats contribute significantly to soil fertility and nutrient distribution due to their large numbers, high mobility and varied habitats for roosting and foraging.
- Bat droppings provide organic input to soil and facilitate nutrient transfer, contributing to soil fertility and agricultural productivity. The practice is harmless vis-a-vis human health.
5) Health benefits
- Several species of bats, in fact, contribute to human health by reducing populations of mosquitoes and other insect vectors that spread malaria, dengue, chikungunya and other diseases.
- It is reported that a small bat may feed on almost 5,000 mosquitoes each and every feeding night far more than other measures adopted to eliminate them.
Their conservation
- According to the IUCN, about 5 per cent of bats are categorised as endangered and another 11 per cent are data deficient.
- Further, some species of fruit bats are categorised under Schedule 5 of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1973, along with other vermin species like rats, making it difficult to legally conserve them.
Conclusion
- The pandemic has demonstrated that conservation of biodiversity and natural habitats is absolutely essential to prevent such events from arising again.
- Understanding the role played by bats helps us appreciate how their absence can greatly affect all facets of our lives.
- Viruses don’t jump directly from bats or other animals to humans.
- Rather, illicit trade in wildlife, high levels of hunting for the consumption of wild meat, and destruction of natural habitats are responsible for this.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
