Why in the News?
The Union Environment Ministry has approved the capture and translocation of eight tigers from Tadoba-Andhari and Pench reserves to the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR) in western Maharashtra.
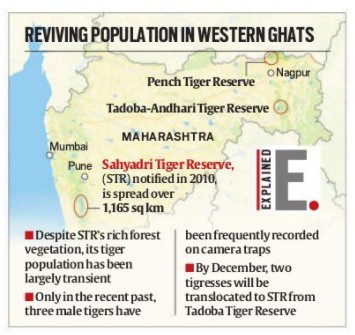
About Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR):
- Overview: Situated in the Sahyadri Range, Western Ghats (Maharashtra), spanning districts of Satara, Sangli, Kolhapur, Ratnagiri.
- Status: Declared Tiger Reserve (2010); part of UNESCO Western Ghats World Heritage Site (2012).
- Geography: Dominated by Shivsagar (Koyna) and Vasant Sagar (Warana) reservoirs.
- Vegetation: Moist evergreen, semi-evergreen, moist & dry deciduous forests; endemic trees like karvi, bamboo, Terminalia, Emblica.
- Fauna: Bengal tiger, leopard, dhole, gaur, antelopes, mouse deer, giant squirrel. Birds include hornbills, vultures, river tern.
- Tiger Status: Tigers absent for years; 5–9 present since 2018 (as per camera trap evidence).
- Corridor Linkages: Connected to Radhanagari WLS (north) and Anshi–Dandeli TR (south, Karnataka), forming a key Western Ghats corridor.
- Ecological Role: Secures catchments of Koyna & Warna rivers, crucial for farming and livelihoods.
Need for Tiger translocation:
- Prey base: Reserve has prey-rich habitat but lacks a stable breeding tiger population.
- Other benefits: Prevents local extinction, strengthens corridor connectivity, supports Project Tiger, conserves biodiversity, and secures river watersheds.
| [UPSC 2017] From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats?
Options: (a) Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve* (b) Nallamala Forest (c) Nagarhole National Park (d) Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

