- The question expects us to explain what do we mean by decentralised cotton textile industry in India. Next, we need to explain the reasons why the cotton textile industry in India is decentralised in India
- In the Introduction, mention that at present, the cotton textile industry is the largest organised modem industry of India. There has been a phenomenal growth in this industry during the last four decades. About 16 per cent of the industrial capital and over 20 per cent of the industrial labour of the country is engaged in this industry.
- In the main body, explain that initially, the textile industry developed in certain major centres such as Mumbai, Surat etc which had all the factors that are responsible for the location of textile industries. Mention factors such as easy transportation, cheap labour, closer to market etc.
- Next, discuss the reasons for decentralization of cotton textile industry such as – Dispersal of the industry from the old nuclei started after 1921 with railway lines penetrating into the peninsular region. New centres like Coimbatore, Madurai, Bangalore, Nagpur, Indore, Solapur and Vadodara were favourably located in respect to raw material, market and labour than places of original locations.
- This industry also reached some places with some additional advantages, such as nearness to coal (Nagpur), financial facilities (Kanpur) and wide market with port facilities (Kolkata); Dispersal of cotton textile industry was further boosted with the development of hydroelectricity. The growth of this industry in Coimbatore, Madurai and Tirunelveli is largely due to the availability of hydroelectricity from Pykara dam. The industry also tended to shift from areas of high labour cost to those with low labour cost. The labour cost factor played a crucial role in establishing this industry at Madurai, Tirunelveli, and Coimbatore etc.
Answer:
Cotton plays an important role in the Indian economy as the country’s textile industry is predominantly cotton based. India is one of the largest producers as well as exporters of cotton yarn. The textile industry is also expected to reach US$ 223 billion by the year 2021.
The states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Punjab are the major cotton producers in India. There has been a phenomenal growth in this industry during the last four decades. About 16 per cent of the industrial capital and over 20 per cent of the industrial labour of the country is engaged in this industry.
India has a glorious tradition of producing excellent quality cotton textiles. Before the British rule, Indian handspun and handwoven cloth already had a wide market. The Muslins of Dhaka, Chintzes of Masulipatnam, Calicos of Calicut and Gold-wrought cotton of Burhanpur, Surat and Vadodara were known worldwide for their quality and design. But the production of handwoven cotton textile was expensive and time-consuming. Hence, the traditional cotton textile industry could not face the competition from the new textile mills of the West, which produced cheap and good quality fabrics through mechanized industrial units.
A host of factors such as low labour costs, government subsidies, irrigation, proximity to ports led to the spread of the cotton textile industry.
Pre-1920’s:
- Traditionally, the cotton industry in India was largely concentrated in cotton-growing areas of the peninsula, Like Gujarat (Surat), Maharashtra(Mumbai).
- These areas had advantages of proximity to the market, capital facility, cheap labour, proximity to port facility and favourable humid climate.
- But cotton is lightweight, non-perishable material, humidity can be created artificially and there is hardly any weight loss during production.
- As a result, proximity to raw material becomes a non-critical factor in location.
- Production can be carried out anywhere with cheap labour, energy and water supply is available for dyeing.
Post-1920’s:
- Dispersal of industry from the old nuclei started after 1921 with railway lines penetrating into the peninsular region.
- Gradually industry shifted towards small towns and cities. Example: centres like Coimbatore, Madurai, Bangalore, Nagpur, Indore, Solapur, Vadodara, Jaipur, Jodhpur, Indore, Amritsar.
- These were favourably located in respect to raw material, market and labour than places of original locations.
- This industry also reached some places with some additional advantages, such as nearness to coal (Nagpur), financial facilities (Kanpur) and wide market with port facilities (Kolkata).
- Dispersal of the cotton textile industry was further boosted with the development of hydroelectricity. The growth of this industry in Coimbatore, Madurai and Tirunelveli is largely due to the availability of hydroelectricity from Pykara dam.
Post-Independence:
- The industry also tended to shift from areas of high labour cost to those with low labour cost. The labour cost factor played a crucial role in establishing this industry at Madurai, Tirunelveli, and Coimbatore.
- Government Incentives: Handloom industry considered highly labour-intensive, beneficial to the village economy and women empowerment. Therefore the government aids them with measures such as the Integrated Village Handloom Development scheme and National Silk Yarn Scheme.
- Handloom sector employs more than 65 lakh people and contributes to 15 % of total textile productions. They are widely distributed throughout the country, states of Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Assam and Manipur account for nearly 50 per cent of the production capacity.
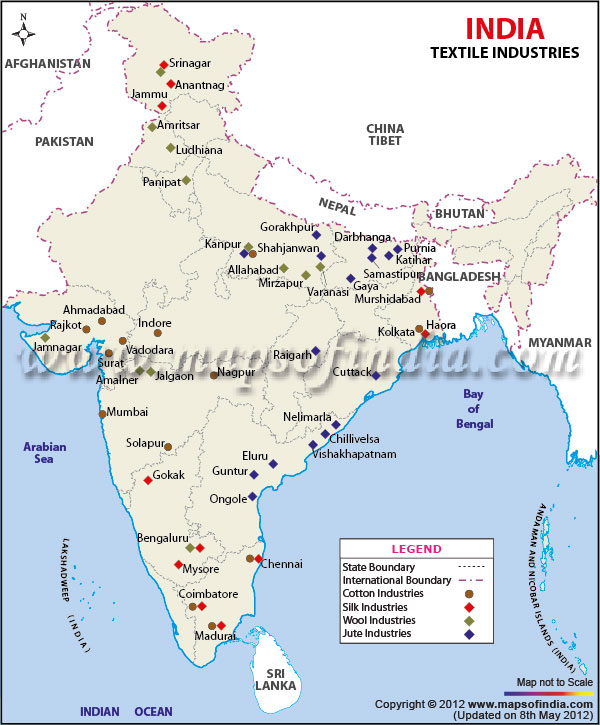
A huge population is dependent on the growth of cotton as well as textile industry. The labour-intensiveness, low-capital and high export incentives, urbanization and demand changing fashion has led to setting up of many decentralised textile centers.

Payment Id- MOJO0101D00A20979010
Very good attempt.
Right from intro till conclusion, the structure is decent.
Points are comprehensive and well placed.
Language crisp and explanation apt.
All in all nice answer.
But avoid cutting that is done in the end.
Also before mentioning post 1920s, discuss a few points regarding pre 1920s because that was the time when the textile industry got established. That will give a perfect base to your answer
plz review
Not reviewed.
Very good use of the map.
Half baked answer.
Your content is not up to the mark.
The discussions on the reason for the decentralization of the textile industry is not done properly.
It is passed on with a couple of remarks.
The flowchart is confusing and is not done with proper execution.
Read the model answer
MOJO9c31Y00D50827870
Not reviewed #parthverma
Quite a good intro.
Perfect way forwards.
There is nothing wrong with your attempt.
Good content and presentation.
Structure and flow of the answer is smooth.
Your presentation is quite clear and demarcation between various subsects is near perfect.
keep writing.
MOJO9c26500A04493668
Work on your grammar. Poor grammar makes the meaning of the sentence wrong.
Whenever changing the topic, please subheading, be it a paragraph styled discussion or the bullet points one.
The overall direction is fine but content needs more points.
This is a 15 marks question and UPSC expects some more data on it.
You have just skimmed the topic and the main discussion.
read the model answer.
When making diagrams and maps, give some information. What is the map trying to show? Industry? Cotton growing area? What?
MOJO0108C00A53108865
Highlight your subheadings properly.
And try to keep the length of your subheadings small. This will save you space as well as time in the real examination.
Underline imp points in your answer.
The discussion in the main body is well attempted.
You have enough points and dimensions there.
Good conclusion.
Avoid lengthy statements.
MOJO0102A00A52642901
Points are comprehensive and well placed.
Language crisp and explanation apt.
Right from intro till conclusion, the structure is decent.
All in all nice answer.
You have improved a lot in your answer writing.
Now is the time to take the next step.
You have to start discussing these points with little more explanations. That means that your reliance on short statements should now gradually be decreased and use proper statements.
Write as many points as you know but write 1-2 statements about that point. It’s always better to cover more points and write a couple of statements.
MOJO9c30X00D35455509
Missing subheadings in the answer.
Whenever changing the topic, please subheading, be it a paragraph styled discussion or the bullet points one.
The overall answer is good.
You have placed all the necessary arguments in the answer with proper structure.
Presentation can be improved.
Points are deep in explanation but you could discuss a couple of more points in the 2nd part. Read the model answer.
PAYMENT ID MOJO0108200A53118559,
Except intro and conclusion, try to give subheadings in each part of your answers.
Try to frame your bullet points in a non-paragraph style presentation.
Right now they look like small paragraphs.
The content is decent in all the parts of your answer.
The depth needed in the answer is present and it is well explained.
Good hand writing