Why in the News?
ISRO Chairman V. Narayanan announced that the upcoming rocket launching site at Kulasekarapattinam (Tamil Nadu) will handle 20–25 satellite launches annually.
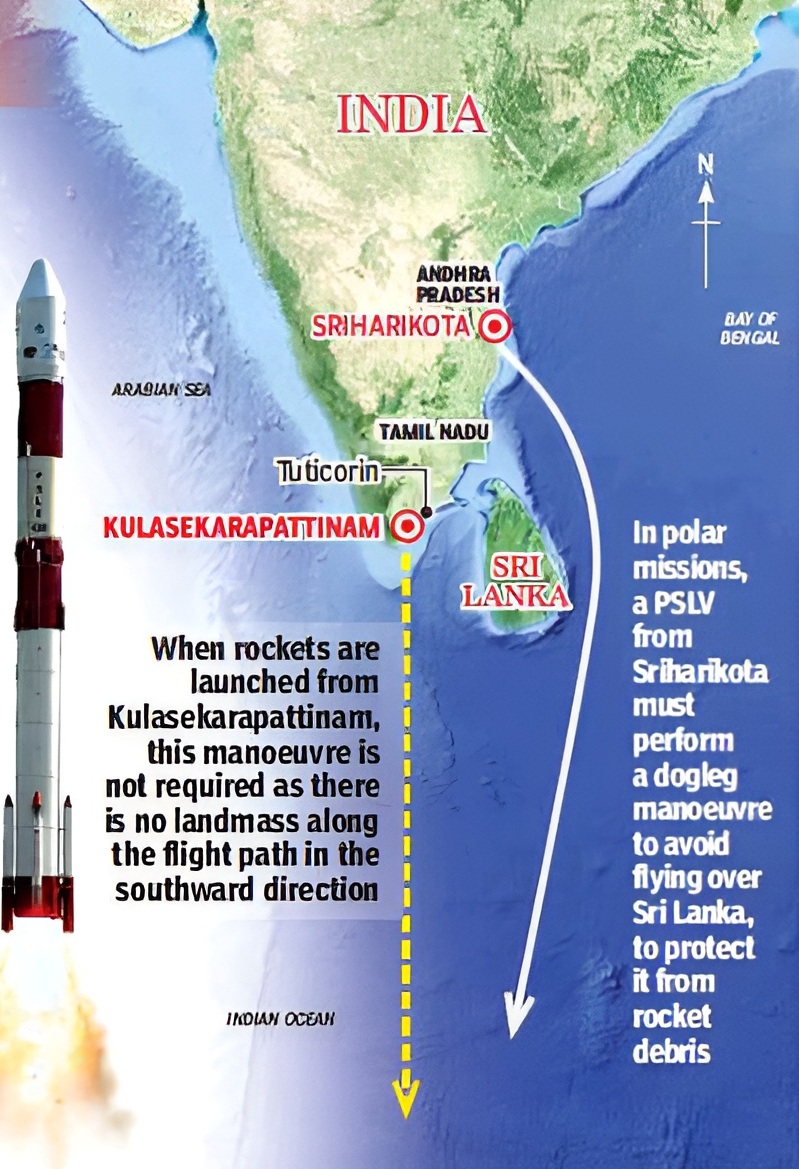
About Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- Location: Coastal hamlet near Tiruchendur, Thoothukudi district, Tamil Nadu; inaugurated by PM in February 2024.
- Second Spaceport: India’s second spaceport after Satish Dhawan Space Centre (Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, 1971).
- Capacity: Can handle 20–25 launches annually, including 24 launches using a Mobile Launch Structure.
- Focus: Dedicated to Small Satellite Launch Vehicles (SSLVs), with capacity to launch rockets up to 500 kg.
- Facilities: About 35 facilities including launch pad, rocket integration units, ground range, checkout systems, and Mobile Launch Structure with onboard checkout computers.
Advantages offered by Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport:
- Direct Southward Launches: Location allows launches into the Indian Ocean without crossing landmasses; ensures more safety from debris fall.
- No Dogleg Manoeuvre: Unlike Sriharikota, no detour is needed to avoid Sri Lanka, saving fuel.
- Efficient Trajectory: Improves efficiency for satellites in Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbits (SSPOs).
- Payload Advantage: SSLVs from Kulasekarapattinam can place ~300 kg into SSPO, higher than from Sriharikota.
- Decongestion: Reduces pressure on Sriharikota, which will focus on larger PSLV, GSLV, and Gaganyaan launches.
- Commercial Boost: Strengthens India’s role in the global small-satellite launch market, enhancing space economy.
- Strategic Advantage: Near-equator position provides benefits for certain orbital paths.
| [UPSC 2008] ISRO successfully conducted a rocket test using cryogenic engines in the year 2007. Where is the test-stand used for the purpose, located?
Options: (a) Balasore (b) Thiruvananthapuram (c) Mahendragiri* (d) Karwar |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

