Why in the News?
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded to Richard Robson, Susumu Kitagawa, and Omar Yaghi for pioneering the creation of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs).
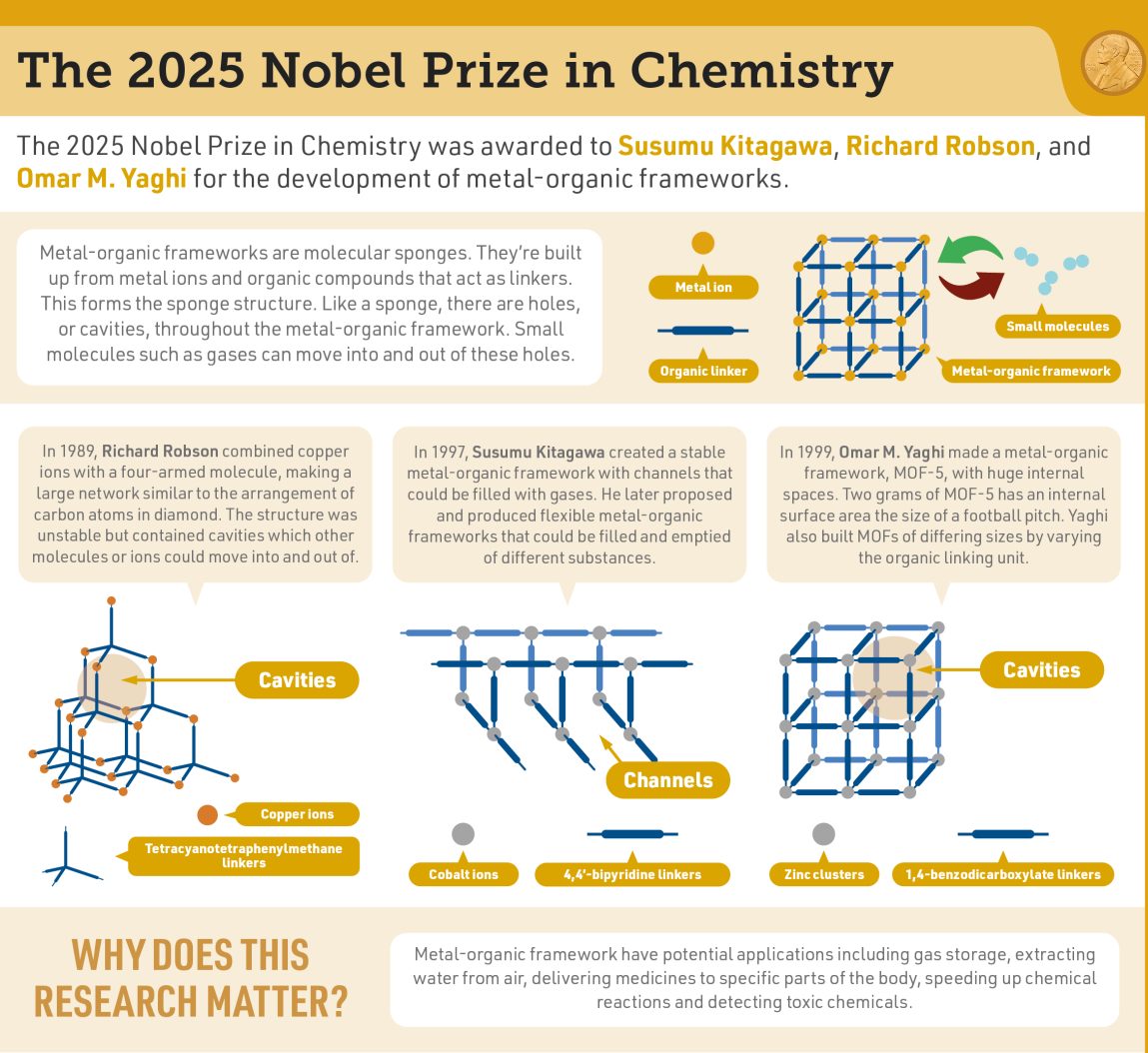
What are Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)?
- Overview: They are crystalline materials composed of metal ions linked by organic molecules, forming a three-dimensional porous network capable of selectively trapping and storing gases, vapours, or liquids.
- Structure: Metal ions serve as nodes or connectors, while organic ligands (carbon-based linkers) create scaffold-like frameworks with very high surface area and controllable pore size.
- Porosity: MOFs possess some of the highest porosity among solids, often exceeding 7,000 square metres per gram, enabling the storage of large volumes of gases within minimal material.
- Flexibility: Organic linkers can be chemically modified, allowing custom design for specific interactions, such as selective gas capture or catalysis.
- Thermal and Chemical Stability: Advanced MOFs remain stable up to 300–400°C and can withstand diverse chemical environments, suitable for industrial and environmental use.
- Bonding Principle: Based on coordination chemistry, MOFs combine metal rigidity with organic flexibility, enabling precise control over molecular architecture.
- Functionality: Their open channels permit easy adsorption and desorption, making MOFs reusable, durable, and efficient for a range of scientific and industrial applications.
Applications of MOFs:
- Water Harvesting: Capture moisture from arid air and release it upon heating — enabling portable water generation in desert regions.
- Carbon Capture: Their selective pores allow efficient CO₂ capture and storage, aiding climate change mitigation.
- Hydrogen and Methane Storage: Act as solid sponges essential for fuel cells and clean energy systems.
- Pollutant Filtration: Remove PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances), heavy metals, and organic contaminants from water sources.
- Food Preservation: Absorb ethylene gas emitted by fruits, slowing ripening and extending shelf life.
- Catalysis and Sensing: Serve as heterogeneous catalysts and chemical sensors for trace-level detection in industrial settings.
- Clean Energy Systems: Integrated into batteries, fuel cells, and supercapacitors for energy storage due to high conductivity and surface area.
Scientific Development:
- Richard Robson (University of Melbourne, 1970s): He pioneered the idea of linking metal atoms and ligands into extended frameworks, though early models were fragile.
- Susumu Kitagawa (Kyoto University): Built porous coordination polymers, the first to demonstrate that gases could diffuse through molecular cavities—a defining MOF feature.
- Omar Yaghi (University of California, Berkeley, 1990s): Created robust, heat-resistant MOFs, standardised synthesis techniques, and coined the term “Metal–Organic Framework” in a 1995 Nature paper.
- Breakthrough Achievement: Yaghi’s team designed copper- and cobalt-based MOFs stable up to 350°C, capable of hosting guest molecules without collapse.
| [UPSC 2024] With reference to Direct Air Capture, an emerging technology, which of the following statements is/are correct?
I. It can be used as a way of carbon sequestration. II. It can be a valuable approach for plastic production and in food processing. III. In aviation, it can be a source of carbon for combining with hydrogen to create synthetic low-carbon fuel. Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) I and II only (b) II only (c) I, II, and III* (d) None of the above statements is correct |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

