Why in the News?
The World Health Organization’s Global TB Report 2025 says India’s TB incidence dropped 21% from 237 to 187 per lakh between 2015 and 2024, almost twice the global decline rate of 12%.
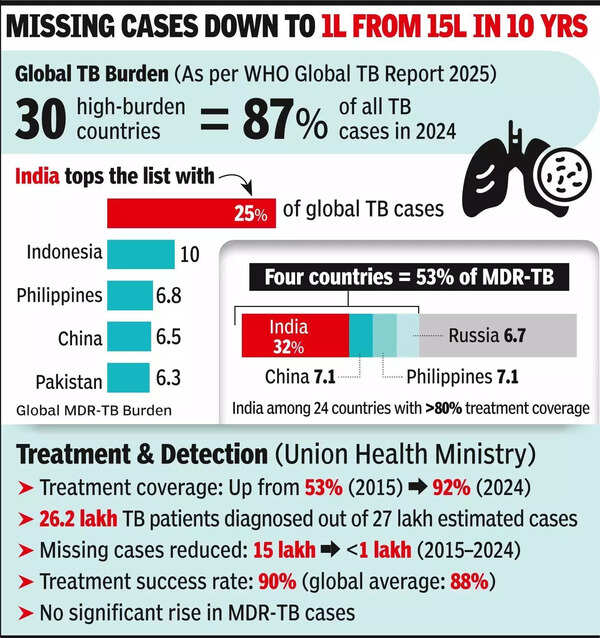
About Global TB Report 2025:
- Publisher: Released by the World Health Organization (WHO) in November 2025.
- India’s TB Incidence Decline: Fell 21 percent from 237 to 187 cases per lakh (2015–2024), nearly double the global decline of 12 percent.
- Treatment Coverage: Reached 92 percent, with 26 lakh cases diagnosed in 2024.
- Mortality Reduction: Dropped from 28 to 21 deaths per lakh between 2015–2024.
- Key Drivers: Community-based screening, molecular diagnostics (CBNAAT / Truenat), Ni-kshay digital tracking, and TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan.
About Tuberculosis (TB):
- What is it: Bacterial disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis mainly affecting the lungs; spreads through air via coughing/sneezing.
- Types of TB:
- Pulmonary TB: Affects lungs, highly contagious.
- Extrapulmonary TB: Affects organs like spine, kidneys, brain, or lymph nodes.
- Latent TB: Dormant infection, asymptomatic but may reactivate.
- Active TB: Symptomatic and infectious stage.
- Drug-resistant TB (DR-TB): Resistant to standard drugs due to incomplete or improper treatment.
- Medicine Regimens:
- Drug-sensitive TB: 6-month course- 2 months of HRZE (Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol) + 4 months of HR.
- MDR-TB: Resistant to Isoniazid and Rifampicin; treated with 18–24-month regimen using Bedaquiline, Linezolid, Levofloxacin, Clofazimine, and Cycloserine.
- Preventive Therapy: Isoniazid Preventive Therapy (IPT) for HIV-positive persons and close contacts of TB patients.
Various Government Interventions for TB Prevention:
- National TB Programme (NTP), 1962: India’s first structured TB-control effort; introduced BCG vaccination and district-level treatment services.
- Revised National TB Control Programme (RNTCP), 1993: Adopted the DOTS strategy; achieved nationwide coverage by 2006, improving standardized treatment and cure rates.
- Ni-kshay Portal, 2012: Launched as a national digital platform for TB case notification, tracking, and treatment monitoring across public and private sectors.
- Ni-kshay Poshan Yojana, 2018: Introduced nutritional support of ₹500 per month to all notified TB patients through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT).
- National Strategic Plan for TB Elimination (2017–2025): Implemented in phased manner; structured around Detect, Treat, Prevent, Build, promoting CBNAAT/Truenat and decentralised care.
- National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP), 2020: Renamed and upgraded from RNTCP; targets TB elimination by 2025 with universal free diagnostics, treatment, and surveillance.
- Ni-kshay Sampark Helpline, 2023: Launched as a nationwide toll-free platform for patient counselling, treatment support, and follow-up.
- Ni-kshay Mitra Initiative, 2022: Enabled individuals, NGOs, corporates to adopt TB patients for nutritional and diagnostic support under the Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan framework.
- TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan, 2024: Large-scale screening campaign covering 19 crore individuals; detected 24.5 lakh TB cases, including asymptomatic infections.

