UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)

Context
The RBI has repeatedly reiterated its strong views against cryptocurrencies since it gained popularity in India following a sudden boom in Bitcoin prices. The central bank’s argument is that cryptocurrencies pose serious threats to the macroeconomic and financial stability of the country.
The development of Bitcoin and thousands of other cryptocurrencies in a little over a decade has changed the definition of money — and spawned a parallel universe of alternative financial services, allowing crypto businesses to move into traditional banking territory.
In recent times, new services and platforms have been introduced to help people manage bitcoin and other such digital coins in day-to-day finances. Let us learn about the topic in detail.
Cryptocurrencies
(1) Rise of Cryptocurrencies: After the growth and response received to bitcoin, many newer coins have also been introduced and their cumulative market value touched $2.5 trillion by May 2021.
(2) Significance of Cryptocurrencies
- Corruption Check: As blocks run on a peer-to-peer network, it helps keep corruption in check by tracking the flow of funds and transactions.
- Time Effective: Cryptocurrencies can help save money and substantial time, as it is conducted entirely on the Internet, involves very less transaction fees and is almost instantaneous.
- Cost Effective: Intermediaries such as banks, credit card and payment gateways draw almost 3% from the total global economic output of over $100 trillion, as fees for their services.
- Integrating blockchain into these sectors could result in hundreds of billions of dollars in savings.
(3) Cryptocurrencies in India
- RBI’s apprehension: In 2018, The RBI issued a circular preventing all banks from dealing in cryptocurrencies. This circular was declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in May 2020.
- Govt’s stand: Recently, the government has announced to introduce a bill; Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 2021, to create a sovereign digital currency.
- Boosting startups ecosystem: In India, the funds that have gone into the Indian blockchain start-ups account for less than 0.2% of the amount raised by the sector globally.
- The current approach towards cryptocurrencies makes it near-impossible for blockchain entrepreneurs and investors to acquire much economic benefit.

What do crypto businesses offer?
- Lending and borrowing services: Generally, crypto businesses offer lending and borrowing services. One can earn interest on holdings of digital currencies, often a lot more than on cash deposits in a bank.
- Collateral to bank: Borrow with crypto as collateral to back a loan. Crypto loans generally involve no credit checks as transactions are backed by digital assets.
Benefits
- Fosters financial inclusion
- Unusually high return on their holdings for consumers
- Provide financial stability for customers in countries with volatile government-issued currencies.
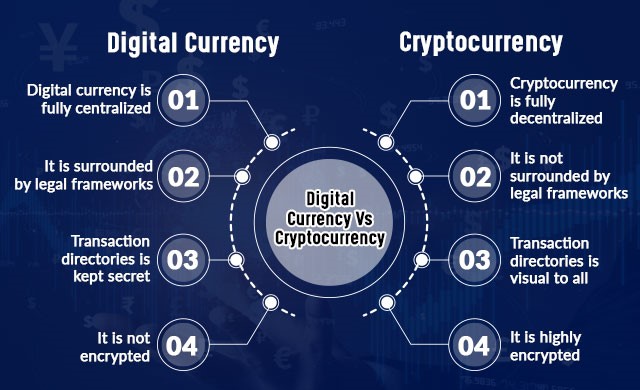
What is cryptocurrency banking?
- The virtual currency is not held in physical form. Digital currency is decentralized by a ledger system called blockchain, which means that it is not controlled by a bank or central authority.
- Cryptocurrency banking mostly just allows people to hold their funds in a digital wallet or spend it like they would spend traditional money.
- People can manage their cryptocurrency balances on exchange platforms.
- These banking services can include simply holding a balance, making payments with a crypto debit card and even earning interest involving one or more cryptocurrencies.
Why such high yields?
- Similar to traditional banking: Crypto outfits pool deposits to offer loans and give interest to depositors, just as traditional banks.
- No reserve requirements: But by law, banks are required to have minimum reserves as a safety backup. Unlike this, crypto banks do not have the reserve requirements; the institutions they lend to can take risky bets.
- Other risks: Cyber attacks, extreme market conditions, or other operational or technical difficulties that could lead to a temporary or permanent halt on withdrawals or transfers.
What is a stablecoin?
Crypto is very volatile, making it less practical for transactions like payments or loans. That’s where stablecoins come in.
- Pegged to stable assets: stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets, commonly the dollar.
- They are meant to provide the steady value of government-issued money in digital form for blockchain transactions, but they are issued by private entities.
- Popular dollar-tied tokens include Tether and USD Coin.
- High global appeal: The number of stablecoins in circulation globally has jumped from $29 billion in January to $117 billion as of early September.
- Keep the value of digital currency stable: It aims to do in digital form what government money does.
- But issued by private entities: They provide the steady value of government-issued money in digital form for blockchain transactions, but they are issued by private entities.
Risks involved
- Stablecoin issuers hold and monitor reserves, just as central bankers manage supply and demand.
- But there is no guarantee they actually hold the one-to-one dollar backing they claim.
- So, a sudden surge in withdrawals could lead to a collapse in one of those assets, putting clients and the broader economy at risk.
- Also, a central bank digital currency would render stablecoins irrelevant.

What is a central bank’s digital currency?
- Offer reliability: Central bankers are examining the potential for issuance of a government-issued cryptocurrency which would offer the convenience of crypto with the reliability of money controlled by a central bank.
- Growing innovation is a challenge: But governments catching up to the innovations in the market for years will be a challenge.
- Introducing India’s own cryptocurrency: The government is considering the possibility of introducing India’s own cryptocurrency, code-named “Lakshmi”.
What is the need?
- Crypto-currency is a digital currency that allows transacting parties to remain anonymous while confirming the transaction is valid.
- The provision of anonymity is widely misused especially in making cross-border transactions.
- They are widely used as a means for money-laundering, terror funding and drug trafficking, and other illegal activities.
- The increasing share and presence of bitcoins due to speculative trading for return on investments is getting to be a cause of concern.
How can legalizing help address this?
- Status of fiat currency: India’s attempt to legalize and introduce its own cryptocurrency would give it the status of a fiat currency.
- Good alternative: This formal government authorization could prove to be an alternative to popular non-fiat cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ethereum.
- Syncing with the technology: “Lakshmi” would adopt a variation of the blockchain technology employed by bitcoin.
- Avoid dual transaction: The technology would help verify every trade and rule out the possibility of dual transactions employing the same coin.
- Also, the new currency would be subject to the same capital account controls as the rupee, in terms of cross-border transactions.
- No manipulation in money supply: The money supply at every instant is known and cannot be manipulated, unlike with normal fiat currencies.
- Besides, users would have to submit to the usual know-your-customer norms.
What are the challenges?
- The introduction of such a new cryptocurrency, would make it a legal tender alongside the rupee.
- This requires legislative action of making amendments to the Currency Act.
- Pegging it to rupee would have an impact on the rupee exchange rate along with the risk of fluctuations.

What is Decentralized finance (DeFi)?
- Alternative finance ecosystem: DeFi, refers to an alternative finance ecosystem where consumers transfer, trade, borrow and lend cryptocurrency.
- Financial products become available on a public decentralized blockchain network, independently of traditional financial institutions and the regulatory structures.
- Eliminating middleman: DeFi aims to “disintermediate” finance, using computer code to eliminate the need for trust and middlemen from transactions.
- It’s a computer-controlled market that automatically executes transactions.
- User governed: DeFi platforms are structured to become independent from their developers and backers over time and to ultimately be governed by a community of users.

What are the benefits of Crypto Finance?
- Financial Inclusion: Innovators argue that crypto fosters financial inclusion. Consumers can earn unusually high returns on their holdings, unlike at banks.
- Quick and Cheap Transactions: Crypto finance gives people long excluded by traditional institutions the opportunity to engage in transactions quickly, cheaply and without judgment.
- Low checks and hassles: As crypto backs their loans, the services generally require no credit checks, although some take customer identity information for tax reporting and anti-fraud purposes.
- Privacy: On a DeFi protocol, users’ personal identities are generally not shared, since they are judged solely by the value of their crypto.
What are some risks associated with DeFi?
- DeFi cuts out the third parties that financial regulators rely on to ensure market integrity.
- Licensed operators like banks and brokers play a quasi-governmental role in traditional finance, collecting and reporting data to the authorities, including information on capital gains, to ensure taxes are paid.
- By contrast, DeFi programs are unregulated apps created by coders interested in capital markets.
- Users’ assets can and have been hacked, and not all of the operations are built in good faith. Possibility of developers abandoning programs after investors contribute significant assets cannot be refused.
Way Forward
- Require new approach: New technology demands a new approach; novel risks can be addressed without necessarily restricting innovation.
- E.g., Requirements like code audits and risk parameters, instead of mandating that DeFi protocols maintain the reserves of a bank and collect customer information.
- Controlling financial frauds: Using artificial intelligence and data analysis to monitor suspicious activity and tracking identity to fight financial fraud.
- Monitor suspicious activity: Using artificial intelligence and data analysis to monitor suspicious activity and working back to track identity.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)

why there is no option to download this burning issue ?