PYQ Relevance:[UPSC 2013] ‘The expansion and strengthening of NATO and a stronger US-Europe strategic partnership works well in India.’ What is your opinion about this statement? Give reasons and examples to support your answer. Linkage: Turkiye is a NATO member, and its foreign policy decisions (like supporting Pakistan or Azerbaijan) are influenced by its position within such alliances, which in turn affects India’s relationships and interests in the region. |
Mentor’s Comment: India, Turkey, and Azerbaijan entered into diplomatic tensions after Turkey and Azerbaijan openly supported Pakistan following the Pahalgam massacre. This support sparked a sharp rise in regional political conflicts and strong public reactions. Social media anger quickly escalated, prompting top Indian institutions to pause agreements and causing many travelers to cancel trips to Turkey and Azerbaijan, as reported by travel websites.
Today’s editorial explains the diplomatic tensions between India, Turkey, and Azerbaijan and their implications. This topic will be included in GS Paper I (Unity in Society) and GS Paper II (International Relations).
_
Let’s learn!
Why in the News?
Data shows that even if India officially bans trade with Azerbaijan and Turkey, it is likely to experience minimal losses due to limited economic dependence on these countries.
What triggered the boycott of Turkiye and Azerbaijan in India?
- Support for Pakistan: Turkiye and Azerbaijan backed Pakistan following India’s military confrontation after the Pahalgam massacre, which angered many Indians.
- Social media-driven calls for boycott: The support sparked calls on social media to boycott both countries, leading to a surge in travel cancellations. Eg: Sharp spike in cancellations of tour bookings to Turkiye and Azerbaijan reported by travel platforms.
- Institutional actions: Indian institutions suspended ties, and trader associations resolved to boycott trade and commercial ties with these countries. Eg: IIT Bombay and IIT Roorkee suspended MoUs with Turkish universities.
Why do Azerbaijan and Turkey oppose India?
|
How have arms trade relations evolved between Turkiye and Pakistan?

- Long-term arms exports since the 1990s: Turkiye has been supplying arms to Pakistan continuously for over three decades. Eg: SIPRI data shows arms exports from Turkiye to Pakistan starting in the 1990s.
- Major focus on artillery systems: A significant part of the trade involves artillery like naval guns, howitzers, self-propelled guns, and multiple rocket launchers. Eg: Pakistan has received multiple rocket launchers and howitzers from Turkiye.
- Supply of armored vehicles: Turkiye exports tanks, armored cars, and personnel carriers to Pakistan’s military. Eg: Delivery of armored vehicles strengthens Pakistan’s ground forces.
- Mutual strategic and political support: Arms trade is supported by reciprocal backing in geopolitical issues such as Kashmir and Cyprus. Eg: Turkiye supports Pakistan on Kashmir; Pakistan supports Turkiye on Cyprus disputes.
- Strengthened ties during regional conflicts: The relationship deepened as Turkiye provided diplomatic and military backing to Pakistan in various geopolitical standoffs. Eg: Turkiye’s vocal support for Pakistan during Kashmir-related tensions.
Who stands to lose more economically if trade is banned?
- India’s low dependency on crude oil: The combined share of crude oil imports from these two countries is less than 1% of India’s total crude imports. Eg: Charts show less than 1% crude import share over the past six years.
- Azerbaijan’s significant reliance on India: India was Azerbaijan’s third largest destination for crude oil exports in 2023. Eg: Azerbaijan could face a bigger impact if India bans trade.
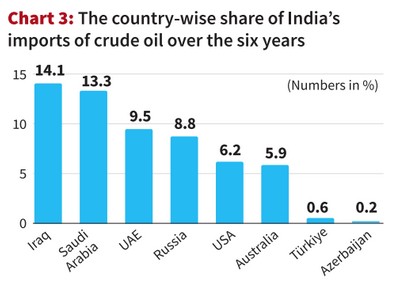
- Limited trade volume in machinery: Turkiye accounts for only about 1% of India’s total imports in machinery, including nuclear reactors and boilers. Eg: India relies more on countries like China and Germany for such equipment.

- India’s diversified import sources: India’s major imports come from several other countries, making it less vulnerable to a ban on trade with Turkiye and Azerbaijan. Eg: China and Germany are larger suppliers of machinery than Turkiye.
- Greater economic impact likely on Azerbaijan: Azerbaijan stands to lose more from India’s trade ban because India is a major crude oil buyer for them. Eg: India being the third largest market for Azerbaijan’s crude oil exports highlights this dependence.
Where has there been a notable rise in Indian tourism and student migration recently?Indian tourism
Student migration
Note: This 2024 data is from before Operation Sindoor. The real effects on tourism and student migration will be seen later because it takes time for such events to show their impact. |
Way forward:
- Promote diplomatic dialogue: India should engage in sustained diplomatic efforts with Turkiye and Azerbaijan to address mutual concerns and reduce geopolitical tensions.
- Expand people-to-people and economic ties: Enhancing cultural exchanges, trade, and educational cooperation can build trust and diversify relations beyond political differences.


