Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jan Vishwas Act
Mains level: potential challenges and consequences of shortcut methods in law enforcement
Central Idea:
- The article explores challenges to the credibility of the rule of law, emphasizing the delicate balance between traditional norms and modern adaptations.
- Recent legal reforms in India, particularly the Jan Vishwas Act, are discussed, along with concerns about potential abuses of power through shortcuts in law enforcement.
Key Highlights:
- The article underscores the significance of faith in the inherent goodness of legal norms for trust in the rule of law.
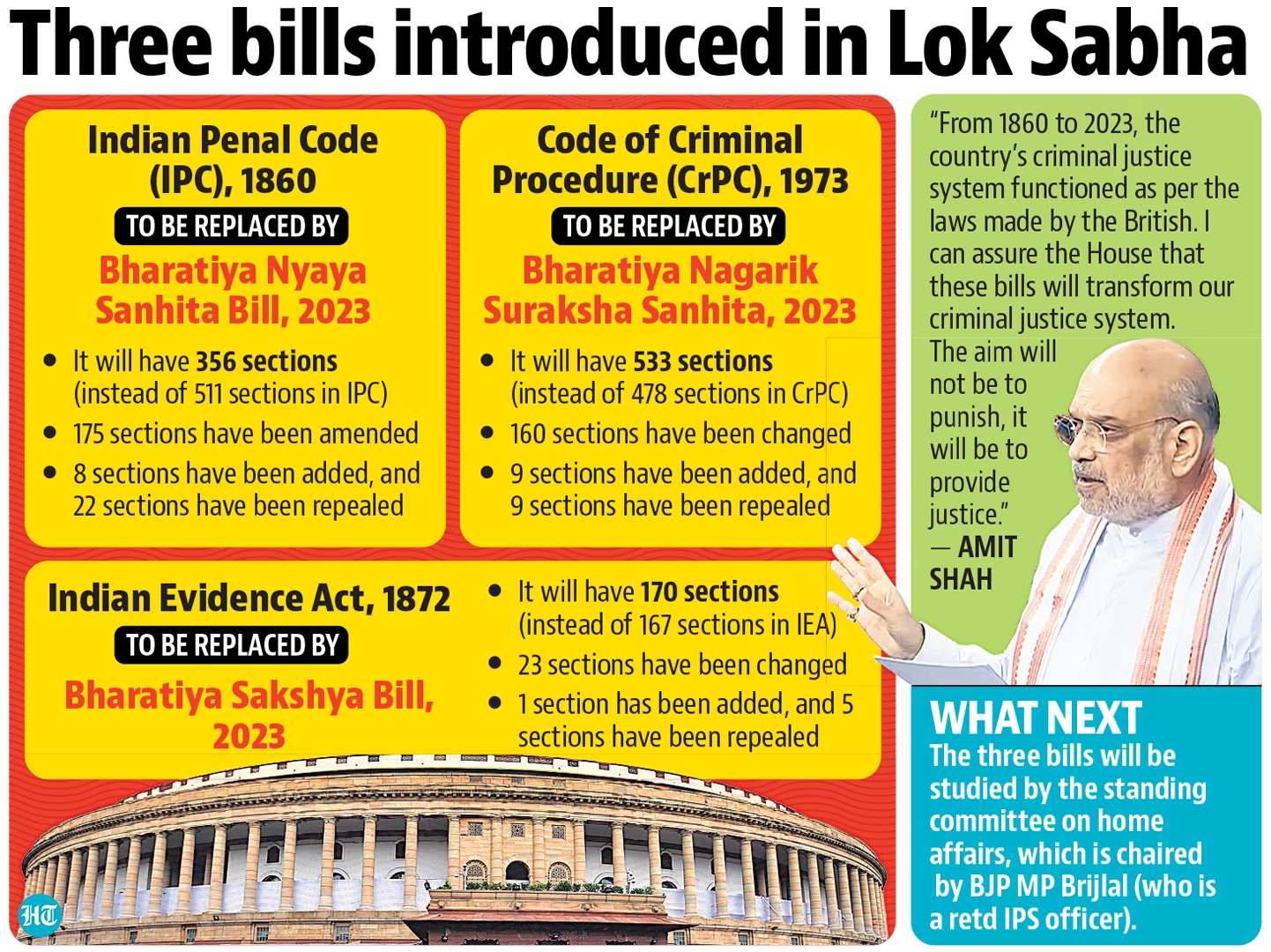
- Discussion on the Jan Vishwas Act addressing outdated laws to facilitate business activities and reduce compliance burdens.
- Replacement of colonial-era laws with the Bharatiya Nyaya (Second) Sanhita to modernize legal thinking and rebuild credibility.
- The credibility crisis is attributed to shifts in perceptions of law as a power resource and the adoption of shortcut methods in law enforcement.
Key Challenges:
- Potential misuse of power through encounters and ‘bulldozer’ methods without democratic checks and balances.
- Concerns about the crude nature of an abridged rule of law, leading to arbitrary justice and unpredictability.
Key Terms:
- Jan Vishwas Act
- Bharatiya Nyaya (Second) Sanhita
- Credibility crisis
- Shortcut or abridged rule of law model
Key Phrases:
- “Normative raison d’etre” – referring to the fundamental basis or justification of norms.
- “Smart governance” – addressing infirmities and outdatedness in laws through effective governance.
- “Encounter killings” and “bulldozer action” – methods of law enforcement discussed in the article.
Key Quotes:
- “Fear of imprisonment for minor offences is a major factor hampering the growth of the business ecosystem.”
- “The real credibility crisis of the rule of law is located not so much at the normative level but at the level of the rule of law reality.”
Key Statements:
- Acknowledgment of the government’s faith in the traditional rule of law as a positive aspect.
- Highlighting the dangers of growing reliance on shortcut or abridged rule of law models.
Key Examples and References:
- The Dandi March as an example of civil disobedience against an unjust law.
- Instances of police encounters and ‘bulldozer’ actions leading to potential abuses of power.
Key Facts:
- The Jan Vishwas Act addressed changes in numerous central Acts, including the Indian Post Office Act, and the Cinematograph Act.
- Replacement of colonial-era Indian Penal Code, Code of Criminal Procedure, and Indian Evidence Act in the second phase.
Critical Analysis:
- The article critically examines the evolving landscape of the rule of law, highlighting potential challenges and consequences of shortcut methods in law enforcement. It questions the credibility crisis and emphasizes the importance of maintaining faith in traditional norms.
Way Forward:
- The article suggests staying alert to the dangers of shortcut or abridged rule of law models.
- Encouragement to continue faith in the traditional rule of law while acknowledging the need for necessary reforms.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
