Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SDG's target and associated developments
Mains level: India's progress on SDG's and challenges
Central Idea
- India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi, while addressing the first meeting of Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors under India’s G20 Presidency, expressed concern about the slowing down of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Given India’s large population, the success of achieving these goals is crucial for global progress. While India has made progress towards achieving some SDG targets, there are concerns regarding others.
India’s progress on SDG’s
- Neonatal and under-five mortality: India is on target to meet the SDG indicators for neonatal and under-five mortality. Both indicators have substantially improved in the last five years.
- Full vaccination: India is on target to meet the SDG indicator for full vaccination.
- Improved sanitation: India is on target to meet the SDG indicator for improved sanitation. The country has made significant progress in this area in the last five years.
- Electricity access: India is on target to meet the SDG indicator for electricity access.
- Access to banking: The number of women having bank accounts has improved across a vast majority of the districts between the years 2016 and 2021.
- Adolescent pregnancy: The SDG indicator for eliminating adolescent pregnancy has improved across a vast majority of the districts between the years 2016 and 2021.
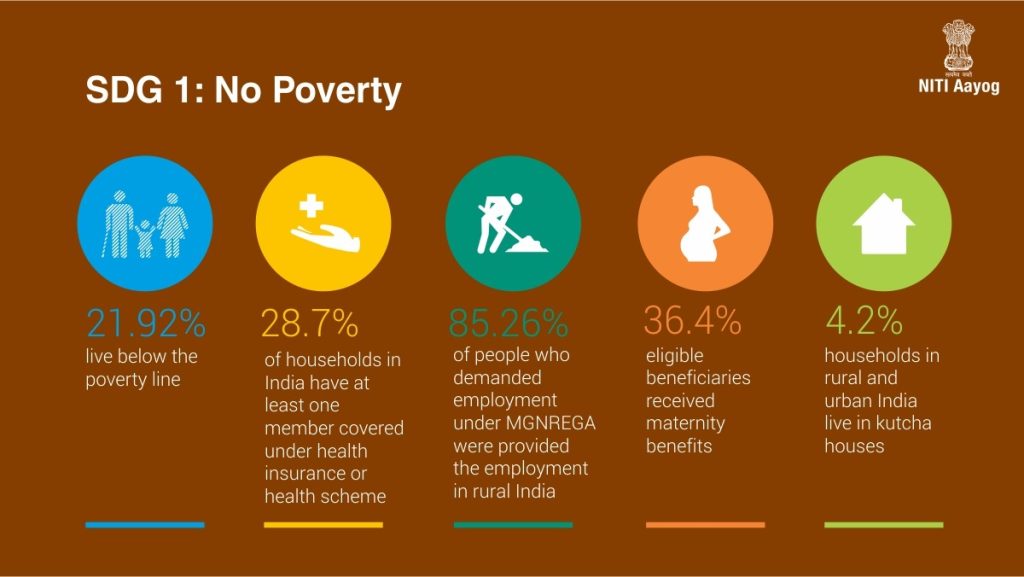
- Multidimensional poverty: The SDG indicator for reducing multidimensional poverty has improved across a vast majority of the districts between the years 2016 and 2021.
- Women’s well-being and gender equality: India has made progress in increasing mobile phone access, with 93% of households having access to mobile phones. However, only 56% of women report owning a mobile phone.
Facts for prelims
Recent findings by National Family Health Survey
|
Lessons from COVID-19 Approach
- Leadership: Strong political leadership and responsive administrative structure are critical to success, and India’s COVID-19 response demonstrated that a mission-oriented ethos that provides adequate support for accomplishing district-level SDGs is urgently needed.
- Infrastructure and Coordination: India’s success with COVID-19 was largely possible both because of the existing digital infrastructure, as well as new, indigenous initiatives such as the Co-WIN data platform and the Aarogya Setu application. Following these examples, India must put in place a coordinated, public data platform for population health management.
- Targeted delivery: A targeted SDG strategy delivered at scale must be executed with the same timeliness of India’s COVID-19 relief package. Key to this relief programme was a mix of spending to provide direct in-kind and economic support, as well as measures aimed at revitalising the economy, small businesses, and agriculture.
Concerns regarding India’s progress towards achieving SDGs
- Unequal progress across districts: While India is on target to meet 14 out of 33 SDG indicators, the progress is not uniform across all districts.
- For example: neonatal and under-five mortality rates are on target for the country as a whole, but many districts are not on track to meet these indicators.
- Pace of improvement: The current pace of improvement is not sufficient to meet the SDG targets for 19 out of 33 indicators.
- For instance: despite a national policy push for clean fuel for cooking, more than two-thirds of districts remain off-target for this indicator.
- Gender inequality: India is facing significant challenges in achieving gender-related SDG targets.
- For example: no district in India has yet succeeded in eliminating the practice of girl child marriage before the legal age of 18 years. Also, despite the overall expansion of mobile phone access in India, only 56% of women report owning a mobile phone, with many districts remaining off-target for this indicator.
- Multidimensional poverty: Although India has made progress in reducing multidimensional poverty, many districts are still off-track to meet this SDG indicator.
- Environmental sustainability: India has made progress in some areas related to environmental sustainability, such as improved sanitation and access to electricity. However, the country is still off-target for indicators related to clean cooking fuel, water and handwashing facilities, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Way ahead
- Implement targeted policies and programs that are aligned with the SDG goals, particularly for areas where progress has been slow or lacking.
- Improve the digital infrastructure, and create a coordinated public data platform for population health management.
- Ensure strong and sustained political leadership that is supported by a responsive administrative structure at all levels.
- Prioritize and accelerate efforts to address gender inequality and women’s well-being.
- Strengthen implementation and monitoring mechanisms to ensure timely and effective delivery of SDG policies and programs.
- Foster partnerships between government, civil society, and the private sector to mobilize resources and expertise to achieve SDG targets.
- Develop a decadal plan that outlines concrete steps and targets for achieving SDG goals in the next ten years.
Conclusion
- India needs to innovate a new policy path to achieve its SDG targets, especially those related to population health and well-being, basic quality infrastructure, and gender equality. India’s successful COVID-19 response has shown that it is possible to deliver at scale in such an ambitious and comprehensive manner. To achieve SDG targets, India needs a similar concerted, pioneering, and nationwide effort.
Mains Question
Q. India’s progress towards SDGs id often described as mixed progress. While there have been positive improvements, there are still concerns that needs to be addressed. Discuss along with a way ahead.
Also read:
| A recent analysis published in The Lancet has concluded that India is not on-target to achieve 19 of the 33 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) indicators. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024