Since the advent of Industrial revolution humankind has been exploiting the nature like never before. Forests and trees are cut to make way for agriculture land, large factories, transport vehicles etc emit lots of CO2 and other gases and pollutants. But it was all forgotten as it came with immense prosperity.
But since the 2nd half of 20th century, citizens world over started getting conscious of this unbridled exploitation of nature. There were also signs suggesting this exploitation was unsustainable and harming us. That even the climate was changing.
Climate is the weather conditions prevailing in an area in general or over a long period. Climate of any region is generally stable. Climate change is changes in that stable climate due to anthropocentric or natural factors.
In 1966, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) proposed the term climatic change to encompass all forms of climatic variability on time-scales longer than 10 years, whether the cause was natural or anthropogenic. But soon it was realized that major factor was human intervention and since then we are concerned about anthropogenic climate change.
International Conferences on Environment
UN conference on Human Environment (UNCHE):-
- An international conference under the UN aegis in 1972- UN conference at Stockholm to discuss issues realted to environment and development
- came out with a declaration containing 26 principles concerning environment and development
- led to creation of UN Environment Programme (UNEP)- an agency of United Nations with HQ in Nairobi, Kenya, which coordinates its environmental activities and assist developing countries in implementing environmentally sound policies
World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED)-
- As things did not change much after UNCHE and its Declaration remained on paper, UN set up a commission in 1984 to give a report on environment and development, World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) – Brundtland Commission <after its chairperson Norwegian PM’s name>
- Came out with the report Our Common Future in 1987 and enunciated the concept of sustainable development
- Gave the most iconic definition of that concept to this date
Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Note that the definition contains two key concepts-
- the concept of needs, in particular the essential needs of the world’s poor, to which overriding priority should be given; and
- the idea of limitations imposed by the state of technology and social organization on the environment’s ability to meet present and future needs <so called carrying capacity>
In 1988, UNEP <set up after UNCHE) and WMO set up an organization called IPCC – Intergovernmental Panel on Climate change which analyses and synthesizes scientific literature available on climate change and produces assessment reports (1st in 1990, 2nd 1995, 3rd- 2001, 4th- 2207, 5th -2014)
UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED)-
Brundtland commission report resulted in landmark 1992 summit, UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) at Rio De janeiro <What is Brazil’s capital?>, also k/a Earth Summit
It resulted in 3 legally binding documents –
- UN framework convention on Climate Change (UNFCC) <entered into force in June 1994> <1st assessment report of IPCC had already come out in 1990>
- UN Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD) <entered into force in DEC 1993>
- UN convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) <entered into force in Dec 1996>
The summit also resulted in 3 non-binding documents
- Rio Declaration on Environment and Development
- Agenda 21 <21 is agenda for 21st century, UNCCD was the result of direct recommendation of Agenda 21>
- Forest Principles
World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD)-
- 10 years after 1st earth summit, another Summit took place, this time in Johannesburg , known as World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD).
- US boycotted the summit and I don’t need to tell you the fallout of that
UN conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) –
- Another earth summit was convened 10 years later, this time again in Rio, UN conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD). <Are you following that they are changing the name of summits and if you don’t pay close attention, you can mark an MCQ incorrect.>
- Primary Outcome of the summit was the non binding document <documents of every summit were non binding> The Future We Want
- Summit also Proposed Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to replace Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) in 2015. <MDG were agreed upon at the UN’s millennium summit in 2000>
Meeting of parties to UNFCC
Meanwhile after coming into force of UNFCC in 1994, various parties (nations) to the conference started meeting every year to come to a legally binding document to reduce GHG to a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
Kyoto Protocol –
- In 3rd such meeting in 1997, called CoP 3 (3rd Conference of Parties) at Kyoto, Japan, Parties came to a conclusion and Kyoto Protocol was signed <entered into force in 2002> <there are frameworks/conventions and under them there are protocols which contain detailed legally binding provisions>
- Basic objective was to reduce emission of anthropogenic GHG to limit global warming. It followed the principles of UNFCC such as Common But Differential Responsibility and Respective Capabilities (CBDR-RC)
- USA never ratified the KP, Canada walked out in 2011. But anyway 1st commitment period followed from 2008-2012.
- 2nd Commitment period is from 2012 to 2020 in which only 37 countries have binding targets. <Japan, NZ and Russia participated in 1st commitment period but not in 2nd>
As KP clearly seemed to be failing, negotiation started for separate treaty under UNFCC for measures to be taken after 2020 resulting in Paris Agreement of Dec. 2015.
Meeting of Parties to CBD
Similarly Parties to CBD started meeting since 1994 <they meet every 2 years while UNFCC parties meet every year>. Convention has 3 main goals <UNFCCC only 1 – Climate change>
- conservation of biological diversity
- sustainable use of its components; and
- fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources
Cartagena Protocol – At COP 5 in 2000, they adopted Cartagena protocol on Biosafety – to protect biological diversity from the potential risks posed by living modified organisms resulting from modern biotechnology..
Nagoya Protocol– In 2010 they adopted -Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization
UN declared the decade 2010-2020 as decade of biodiversity
UN convention to Combat Desertification–
- UNCCD is the only internationally legally binding framework set up to address the problem of desertification
- The Convention is based on the principles of participation, partnership and decentralization
- in 1994 treaty signed to prevent and reverse land degradation
- in 2009, agreed on 11 indicators to measure progress towards the goal of reducing land degradation
- In 2013 Canada withdrew from this convention as well
Montreal Protocol – A similar environmental issue which came into prominence in 1980s was ozone hole or ozone depletion. To recover lost ozone, in 1987 Montreal Protocol(to Vienna convention) on substances that deplete ozone was signed and it was a remarkable success.
Many other international organization sprang up in 80s and 90s to protect environment and biodiversity. Many other conventions were also signed. Some of them are –
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs)
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
- Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal
- Rotterdam Convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in International Trade
- Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands <where is Ramsar?>
- Bonn convention on Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals<Capital of East and West Germany?>
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, Washington Convention
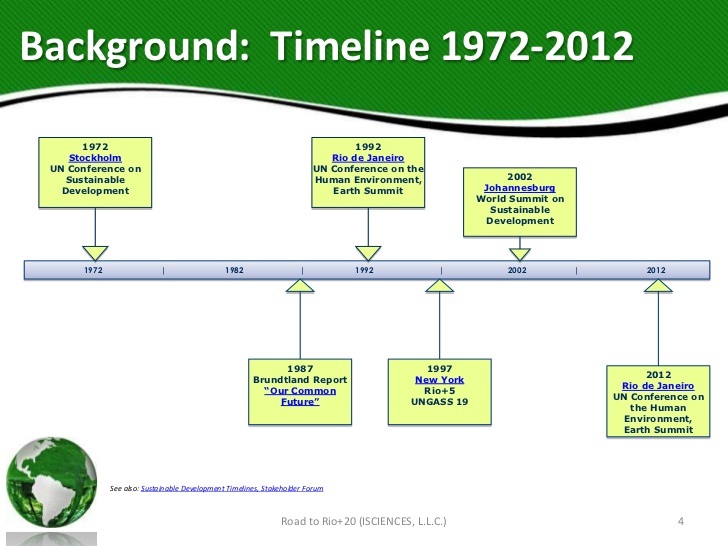
Before we end this chapter, a brief summary
- 1972 – UN conference on Human Environment at Stockholm, Formation of UNEP
- 1987- World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED)-Brundtland commission, report- Our Common Future, Defined Sustainable Development
- 1987 – Montreal Protocol to Vienna Convention
- 1988 – WMO and UNEP together formed IPCC
- 1992 – UN conference on Environment and Development / earth summit at Rio, led to UNFCC, UNNCCD, CBD
- 1997 – Kyoto Protocol
- 2002 – World Summit on Sustainable Development /Rio + 10 at Johannesburg
- 2012 – UN conference on sustainable development/ Rio + 20, report – future we want, SDGs
Plz note that in the pic above, conference of 1972 and 1992 are interchanged. Learn what is written in text.
In the subsequent articles we would now discuss these issues (climate change, ozone depletion, acid rain, air pollution. biodiversity etc) in detail.