Why in the News?
SpaceX’s Starship has completed its first fully successful test flight after a series of failures.
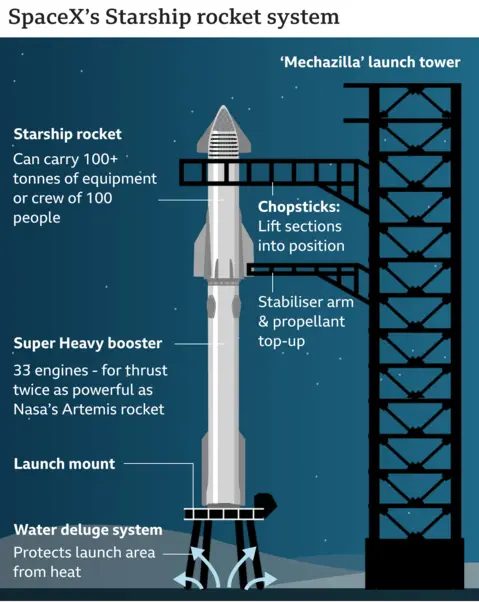
About SpaceX Starship:
- Design: A two-stage heavy-lift launch vehicle built to carry crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- Developer: SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, with the vision of enabling interplanetary travel and colonisation.
- Size: Nearly 120 metres tall with booster, making it the largest rocket ever built and flown. Taller than Saturn V (111 m) and India’s Qutub Minar (72.5 m).
- Historic Test Flight: On 27 August 2025, achieved its first fully successful flight. Booster splashed down in the Gulf of Mexico, spacecraft reached the Indian Ocean.
- Role in NASA Missions: Critical to Artemis Program for returning humans to the Moon and later missions to Mars.
- Long-term Goal: Make Starship fully and rapidly reusable, cutting costs and redefining space travel.
Key Features of Starship:
- Two-Stage Rocket System:
- Super Heavy booster powered by 33 Raptor engines generating 74 meganewtons of thrust, nearly double NASA’s SLS and twice Saturn V.
- Engines burn liquid oxygen and methane, enabling deep-space use and Mars resource utilisation.
- Booster fully reusable, capable of atmospheric re-entry and recovery.
- Six Raptor engines and four landing fins, designed for full reusability on long-duration missions.
- Payload Capacity: Can carry up to 150 tonnes to Low-Earth Orbit and over 100 tonnes to the Moon and Mars, more than all soft-landed lunar payloads combined.
- Cost Reduction Potential: Estimated to deliver 100 tonnes of cargo to Mars for ~$50 million, compared to NASA Shuttle’s $1.5 billion per launch with far less payload.
| [UPSC 2025] Consider the following space missions:
I. Axiom-4 II. SpaDeX III. Gaganyaan How many of the space missions given above encourage and support microgravity research? Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All the three* (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

