Why in the News?
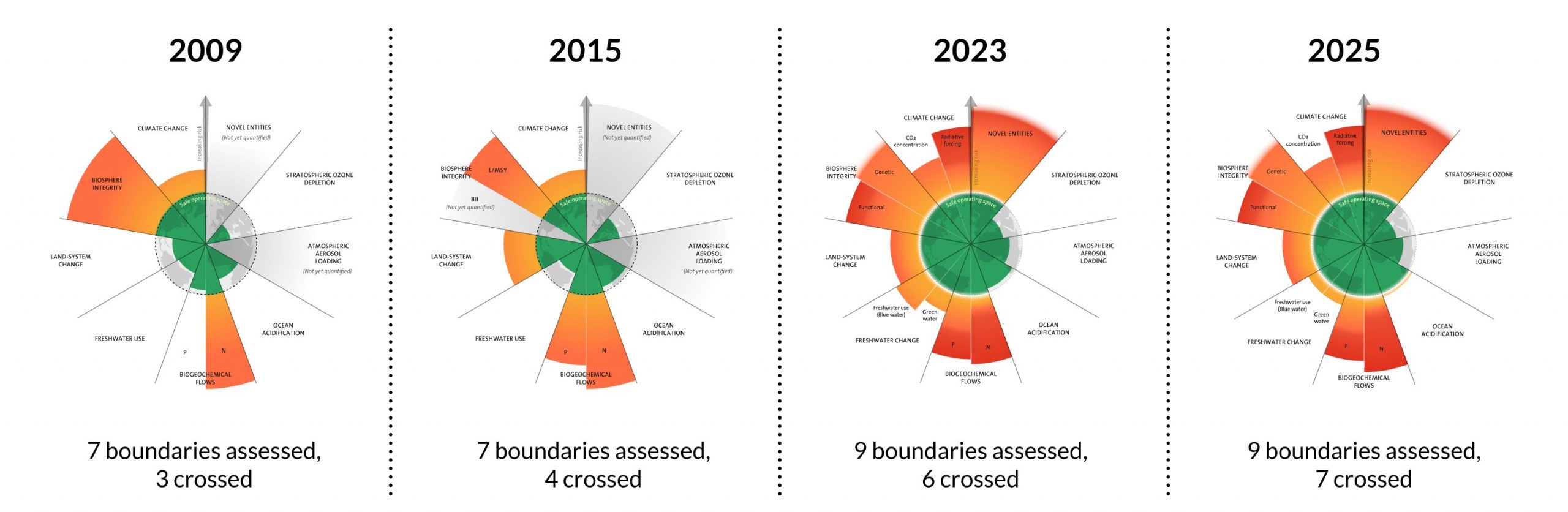
The Planetary Health Check (PHC) 2025 has warned that 7 of 9 planetary boundaries have now been breached.
About Planetary Health Check (PHC):
|
What are Planetary Boundaries?
- Proposition: Coined in 2009 by scientists led by Johan Rockstrom.
- What are they: Defines safe operating space for humanity by setting ecological thresholds that regulate Earth system stability and resilience.
- Basis: Based on Holocene conditions (last ~11,000 years) that enabled human civilisation to thrive.
- Significance: Crossing boundaries risks irreversible environmental collapse.
-
Nine Planetary Boundaries (PBs):
-
- Climate Change (CO₂ Concentration & Radiative Forcing): Safe atmospheric Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) level: 350 parts per million (ppm). Current: 423 ppm (2025); radiative forcing at +2.97 Watts per square meter (W/m²) (safe: +1.5 W/m²).
- Biosphere Integrity (Biodiversity Loss / Extinction Rate): Extinction rate at 100 extinctions per million species years (E/MSY) vs safe 10 E/MSY; severe biodiversity decline continues.
- Land System Change (Deforestation / Ecosystem Conversion): Global forest cover reduced to 59% (safe: 75%). All major terrestrial biomes breached.
- Freshwater Change (Streamflow & Soil Moisture Deviations): Over 20% of global land shows significant streamflow (22.6%) and soil moisture (22%) deviations beyond thresholds. Indo-Gangetic Plain & North China basins most at risk.
- Biogeochemical Flows (Nitrogen & Phosphorus Cycles): Excessive use of Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) in agriculture, worsening dead zones and eutrophication in water bodies.
- Novel Entities (Synthetic Pollutants & Plastics): Release of plastics, synthetic chemicals, and untested compounds exceeds the safe zero-threshold for environmental introduction.
- Ocean Acidification (Aragonite Saturation State): Surface ocean acidity has increased by 30–40% since the industrial era. Aragonite saturation state (Aragonite) at 2.84 (safe: 2.86). Threatens corals, molluscs, and plankton.
- Atmospheric Aerosol Loading (Aerosol Optical Depth – AOD) [Currently Safe]: Interhemispheric Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) difference: 0.063, below safe threshold 0.10. Still harmful for health despite planetary stability.
- Stratospheric Ozone Depletion (Ozone Concentration in Dobson Units – DU) [Currently Safe]: Global ozone concentration stable at 285–286 Dobson Units (DU) (safe: 277 DU). Ozone hole recovery continues, though new threats flagged from rocket launches and satellite debris.
| [UPSC 2018] The term “sixth mass extinction/sixth extinction” is often mentioned in the news in the context of the discussion of:
(a) Widespread monoculture practices in agriculture and large-scale commercial farming with indiscriminate use of chemicals. (b) Fears of a possible collision of a meteorite with the Earth. (c) Large scale cultivation of genetically modified crops. (d) Mankind’s over-exploitation/misuse of natural resources, fragmentation/loss of natural habitats, destruction of ecosystems, pollution and global climate change. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

