Why in the News?
The SAIME Initiative, developed by the Nature Environment and Wildlife Society (NEWS) in the Sundarbans of West Bengal, has been conferred Global Technical Recognition by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
What is SAIME Initiative?
- Concept: A multi-stakeholder partnership model integrating shrimp aquaculture with mangrove restoration in the Sundarbans.
- Implementing Agencies: Developed by the Nature Environment and Wildlife Society (NEWS) with support from the Global Nature Fund (Germany), Naturland, and Bangladesh Environment & Development Society (BEDS).
- Purpose: Promotes climate-adaptive, conservation-linked livelihoods balancing ecological health with local economic growth.
- Implementation: Covers 29.84 hectares with 42 fish farmers, achieving 100% rise in net profits through low-input, eco-friendly methods.
- Target Group: Focuses on climate-vulnerable coastal communities, encouraging chemical-free shrimp farming to build coastal resilience.
Core Features and Approach:
- Ecosystem Integration: Maintains 5–30% mangrove cover within aquaculture ponds, directly linking productivity with ecosystem restoration.
- Community Participation: Adopts a bottom-up co-management model, involving local farmers in planning, monitoring, and benefit-sharing.
- Sustainable Practices: Utilises mangrove litter as shrimp feed, cutting chemical dependence and improving natural nutrient cycles.
- Climate Resilience: Mitigates cyclones, salinity intrusion, and erosion, functioning as a nature-based adaptation system.
- Economic Efficiency: Promotes low-input, high-yield aquaculture, enhancing smallholder profitability and resource efficiency.
- Environmental Benefits: Supports carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and blue carbon economy objectives.
- Global Alignment: Advances SDG-13 (Climate Action), SDG-14 (Life Below Water), and SDG-15 (Life on Land) through integrated coastal sustainability.
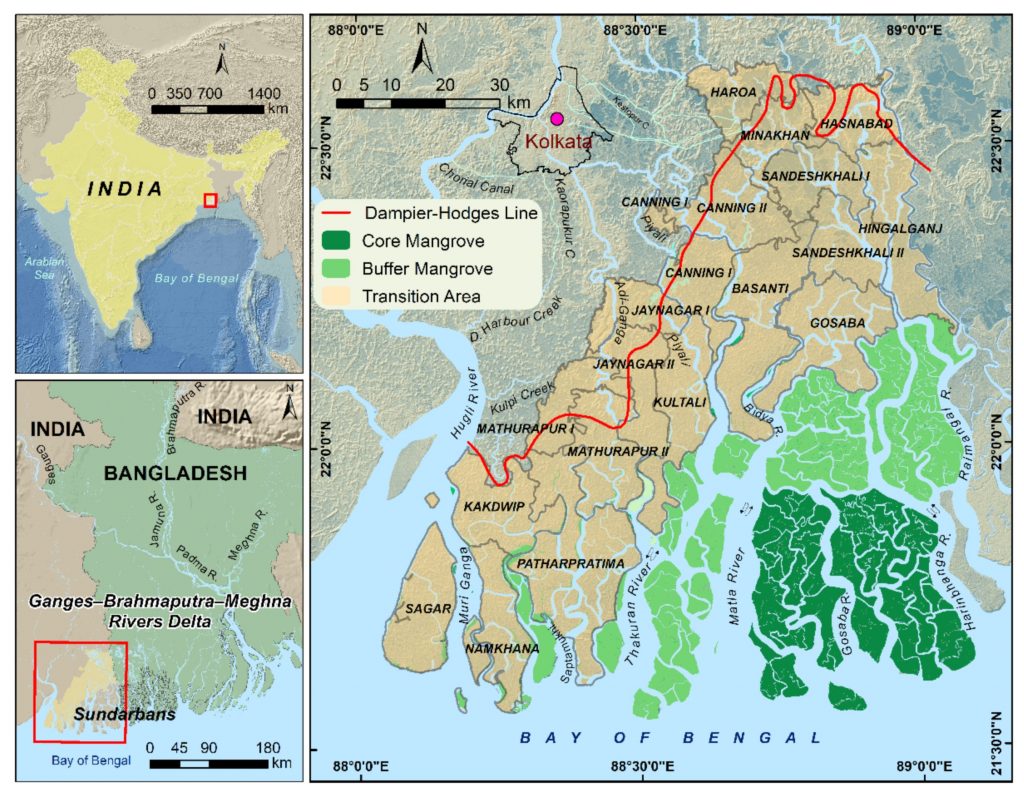
About the Sundarbans:
|
| [UPSC 2023] Which one of the following is the best example of repeated falls in sea level, giving rise to present-day extensive marshland?
Options: (a) Bhitarkanika Mangroves (b) Marakkanam Salt Pans (c) Naupada Swamp (d) Rann of Kutch* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024