Why in the News?
India has rejected Nepal’s objection to resumption of India–China border trade through the Lipulekh Pass in Uttarakhand.
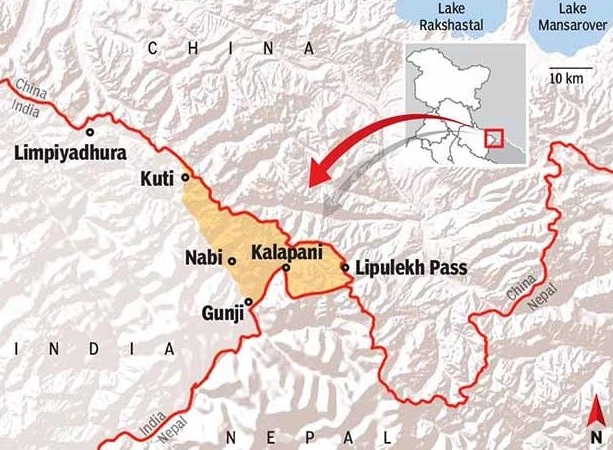
About Lipulekh Pass:
- Location: High-altitude Himalayan pass (~17,000 ft) near the trijunction of India, Nepal, and China (Tibet).
- Connectivity: Links Uttarakhand’s Kumaon region with Taklakot in Tibet.
- Cultural Role: Serves as the shortest route for the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra.
- Trade Importance: Historic India–China trade route since 1954; disrupted during COVID-19 but later resumed.
- Strategic Significance: Crucial for India due to its proximity to the India–China–Nepal border.
What is Limpiyadhura–Lipulekh–Kalapani Dispute?
- Origin: Rooted in the 1815 Treaty of Sugauli (Nepal–British East India Company), fixing Nepal’s western boundary at the Kali (Mahakali) River.
- India’s Position: Claims Kali River originates near Lipulekh, placing Lipulekh and Kalapani within India.
- Nepal’s Position: Claims Kali River originates at Limpiyadhura, extending Nepal’s boundary east to include Lipulekh and Kalapani.
- Disputed Area: About 370 sq. km., under Indian administration since the 19th century.
- Recent Development: In 2020, Nepal issued a new map showing Limpiyadhura, Lipulekh, and Kalapani as its territory; India rejected the claim citing lack of historical basis.
Back2Basics: India–Nepal Border Disputes
|
| [UPSC 2007] Which one of the following Himalayan passes was reopened around in the middle of the year 2006 to facilitate trade between India and China?
Options : (a) Chang La (b) Jara La (c) Nathu La* (d) Shipki La |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

