Why in the News?
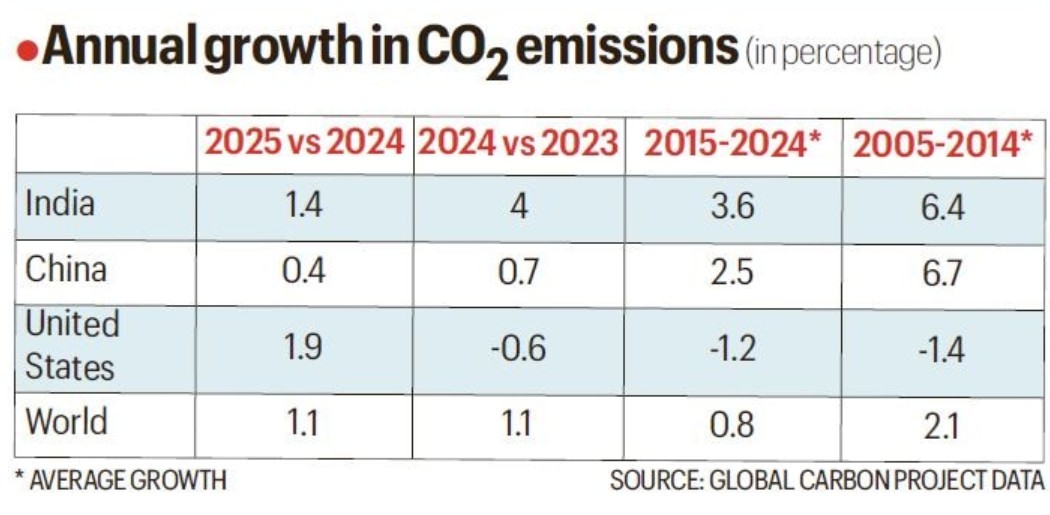
The Global Carbon Budget 2025 shows India’s fossil fuel emissions barely rising (3.19 to 3.22 billion tonnes) with growth slowing to 1.4 per cent, hinting at early stabilisation.
India’s CO₂ Emission Trends:
- Annual Growth: Fossil fuel CO₂ emissions rose from 3.19 billion tonnes (2024) to 3.22 billion tonnes (2025) a 1.4% increase, significantly slower than the 4% rise seen in 2024.
- Decadal Trend: Average annual growth fell to 3.6% (2015–2024) from 6.4% (2005–2014), indicating efficiency gains and rapid renewable energy deployment.
- Sectoral Profile: Roughly 90% of emissions originate from power generation, transport, industry, and buildings; 10% from land-use factors like deforestation.
- Drivers of 2025 Slowdown: An early monsoon in 2024 reduced electricity demand for cooling; renewable energy growth reduced reliance on coal.
- Electricity Sector Shift: CREA reported that India’s power-sector CO₂ emissions declined in early 2025 for the first time, due to strong solar and wind generation.
- Global Context: India is the third-largest CO₂ emitter, yet its per capita emissions (~2.3 tonnes) remain far below the global average and major emitters like the U.S. (14.4 t) and China (8.7 t).
- Outlook: Global fossil CO₂ emissions expected to rise 1.1% to 38.1 Gt, with total emissions (including land use) stabilising near 42 Gt.
What is the Global Carbon Budget?
- Overview: It is an annual scientific assessment by Global Carbon Project (GCP) that quantifies global CO₂ sources and sinks across fossil fuels, land use, and oceans, forming the most authoritative dataset on global carbon trends.
- GCP Origins: Established in 2001 under Future Earth and the World Climate Research Programme as a global consortium of climate scientists.
- Mandate: To measure, monitor, and explain the global carbon cycle and its influence on the climate system.
- Purpose of the Global Carbon Budget:
- Quantifies CO₂ sources and sinks globally.
- Tracks emission trends, carbon sequestration, and atmospheric CO₂ levels.
- Provides authoritative data for COP negotiations and national climate assessments.
- Scope and Methodology
- Covers CO₂, methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) using global datasets.
- Combines national inventories, satellite data, and earth system models.
- Uses the Global Carbon Atlas to visualise national and sector-wise emissions.
- Significance:
-
- Produces transparent, peer-reviewed carbon accounting.
- Helps evaluate national performance under Paris Agreement targets.
- Supports policy design on energy transition, carbon removal, and land use.
- Key Collaborations: Works with major climate bodies including: IPCC, UNFCCC, WMO.
| [UPSC 2024] Consider the following statements:
I. Carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions in India are less than 0.5 t CO2/capita. II. In terms of CO2 emissions from fuel combustion, India ranks second in Asia-Pacific region. III. Electricity and heat producers are the largest sources of CO2 emissions in India. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) I and III only (b) II only (c) II and III only * (d) I, II and III |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

