Why in the News?
NASA has recently launched the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy Space Centre, Florida.
About IMAP Mission:
- Context: Operates under NASA’s Solar Terrestrial Probes Program, following missions like STEREO and IBEX.
- Objective: To map the heliosphere boundary, study energetic particle acceleration, and understand how the solar wind interacts with the interstellar medium.
- Location: Positioned at Sun–Earth Lagrange Point 1 (L1), ~1.5 million km from Earth, ensuring continuous solar observation.
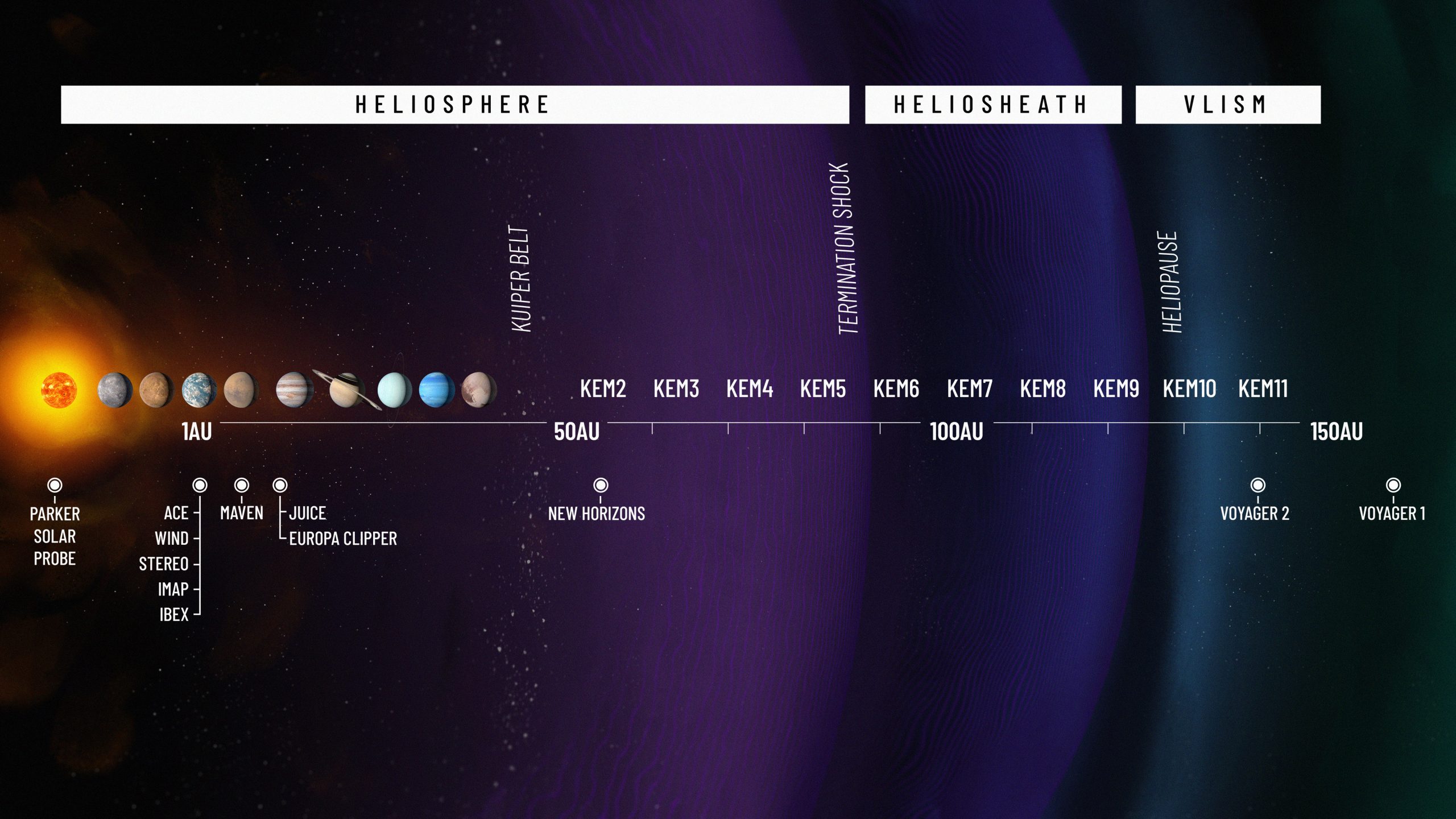
Back2Basics: Heliosphere
|
Key Features:
- Scientific Payload: 10 instruments including- Energetic Neutral Atom Detectors; Charged Particle Detectors and Magnetic & Dust Sensors.
- Real-Time Alerts: Equipped with I-ALiRT (Active Link for Real-Time) to broadcast space weather data and provide ~30 minutes’ warning of harmful solar radiation.
- Spacecraft Design: Spin-stabilized, in a Lissajous orbit around L1, ensuring Sun-facing stability.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: Higher resolution compared to ACE and IBEX, enabling detection of faint cosmic signals.
Significance:
- Scientific: Creates the most detailed maps of the heliosphere boundary, improves understanding of solar wind, cosmic rays, and space weather.
- Technological: Strengthens space weather forecasting, safeguarding satellites, GPS systems, and power grids.
- Human Spaceflight: Critical for Artemis and future deep-space missions, informing radiation shielding and safe travel routes.
- Global Collaboration: Complements missions like NASA–ESA’s Solar Orbiter and the upcoming LISA mission, boosting multi-messenger space science.
- Habitability Research: Provides insights into how heliospheres shield planets, vital for studying Earth’s resilience and exoplanet habitability.
| [UPSC 2016] What is ‘Greased Lightning-10 (GL-10)’, recently in the news?
Options: (a) Electric plane tested by NASA * (b) Solar-powered two-seater aircraft designed by Japan (c) Space observatory launched by China (d) Reusable rocket designed by ISRO |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

