Why in the News?
The Union Ministry of Power has inaugurated India’s largest and first MWh-scale Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB) of 3 MWh capacity at NETRA, NTPC’s R&D Centre in Greater Noida.
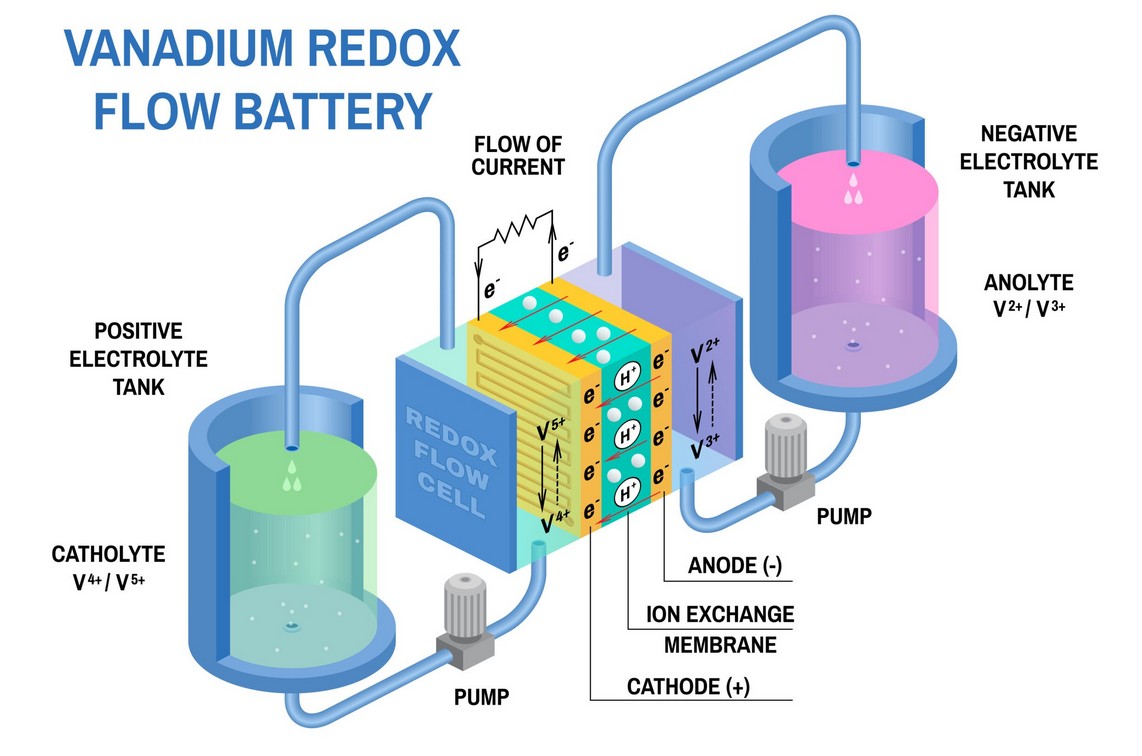
About the Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB):
- Overview: A rechargeable flow battery that stores energy in liquid electrolytes containing vanadium ions in different oxidation states.
- Core Principle: Uses the same element vanadium for both electrolytes, preventing cross-contamination and extending operational life.
- Working Mechanism: Energy is stored through oxidation and reduction reactions of vanadium ions, where electrons are exchanged between two electrolyte tanks.
- Cell Design: Electrolytes circulate through a cell stack separated by an ion-selective membrane that enables ion movement while stopping mixing.
- Scalability: Energy capacity depends on electrolyte volume, while power output depends on cell stack size, allowing flexible scaling.
- Application Focus: Ideal for stationary, grid-scale energy storage, renewable energy integration, and backup power systems.
Benefits over Conventional Batteries:
- Independent Scalability: Energy and power can be scaled separately, perfect for large utility storage and renewable grids.
- Extended Lifespan: Can endure thousands of cycles since vanadium electrolytes don’t degrade or mix.
- Full Discharge Safety: Can be fully discharged (100%) without damaging capacity, unlike lithium-ion batteries.
- High Safety Level: Uses non-flammable, water-based electrolytes, eliminating risk of fire or explosion.
- Eco-Friendly: Recyclable and non-toxic electrolytes reduce environmental impact and support circular use.
- Long-Duration Storage: Provides 6–10+ hours of continuous energy, ideal for stabilizing solar and wind supply.
- Low Maintenance: Fewer mechanical parts and no thermal runaway risk ensure long-term durability.
- Fast Response: Reacts quickly to grid fluctuations, improving power quality and reliability.
Limitations:
- High Initial Cost: Requires expensive vanadium electrolyte and specialized components, leading to higher upfront installation costs than lithium-ion systems.
- Low Energy Density: Stores less energy per unit volume, making it unsuitable for mobile or space-constrained applications like electric vehicles.
- Complex Infrastructure: Needs large storage tanks, pumps, and control systems, which increase operational complexity and land requirements.
| [UPSC 2025] In the context of electric vehicle batteries, consider the following elements:
I. Cobalt II. Graphite III. Lithium IV. Nickel How many of the above usually make up battery cathodes? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three* (d) All the four |

