Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Thermokarsts, Thawing of permafrost
Mains level: Impact of climate change on polar permafrost
A recent study makes a disturbing connection between the loss of Arctic sea ice and thawing (melting) of permafrost in the region, with global implications.
What is Permafrost?
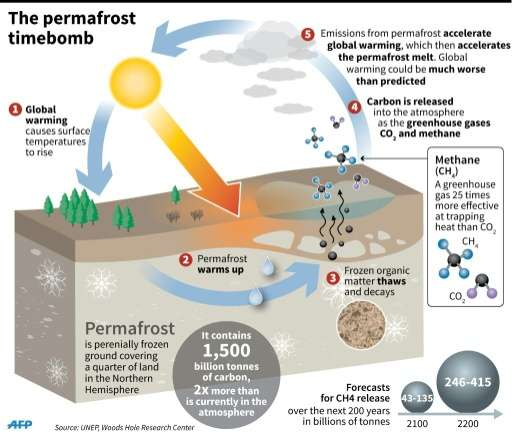
- ‘Permafrost’ or permanently frozen ground is land that has been frozen at or below 0 degrees Celsius for two or more consecutive years.
- A staggering 17 per cent of Earth’s entire exposed land surface is comprised of permafrost.
- Composed of rock, sediments, dead plant and animal matter, soil, and varying degrees of ice, permafrost is mainly found near the poles, covering parts of Greenland, Alaska, Northern Canada, Siberia and Scandinavia.
- The Arctic region is a vast ocean, covered by thick ice on the surface (called sea ice), surrounded by land masses that are also covered with snow and ice.
Permafrost thawing
- When permafrost thaws, water from the melted ice makes its way to the caves along with ground sediments, and deposits on the rocks.
- In other words, when permafrost thaws, the rocks grow and when permafrost is stable and frozen, they do not grow.
Why thawing?
- The link between the Siberian permafrost and Arctic sea ice can be explained by two factors:
- One is heat transport from the open Arctic Ocean into Siberia, making the Siberian climate warmer.
- The second is moisture transport from open seawater into Siberia, leading to thicker snow cover that insulates the ground from cold winter air, contributing to its warming.
- This is drastically different from the situation just a couple of decades ago when the sea ice acted as a protective layer, maintaining cold temperatures in the region and shielding the permafrost from the moisture from the ocean.
- If sea ice (in the summer) is gone, permafrost start thawing.
Impact on Climate Change
- Due to relentlessly rising temperatures in the region, since the late-twentieth century, the Arctic sea ice and surrounding land ice are melting at accelerating rates.
- When permafrost thaws due to rising temperatures, the microbes in the soil decompose the dead organic matter (plants and animals) to produce methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), both potent greenhouse gases.
- CH4 is at least 80 times more powerful than CO2 on a decadal timescale and around 25 times more powerful on a century timescale.
- The greenhouse gases produced from thawing permafrost will further increase temperatures which will, in turn, lead to more permafrost thawing, forming an unstoppable and irreversible self-reinforcing feedback loop.
- Experts believe this process may have already begun. Giant craters and ponds of water (called ‘thermokarst lakes’) formed due to thawing have been recorded in the Arctic region. Some are so big that they can be seen from space.
Why a matter of concern?
- An estimated 1,700 billion tonnes — twice the amount currently present in the atmosphere — of carbon is locked in all of the world’s permafrost.
- Even if half of that were to be released to the atmosphere, it would be game over for the climate.
- Scientific estimates suggest that the Arctic Ocean could be largely sea ice-free in the summer months by as early as 2030, based on observational trends, or as late as 2050, based on climate model projections.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

shouldn’t be this under GS-III?
it leans more on P1