From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Food Security Act (NFSA)
Mains level: demands of farmers for a legal guarantee of Minimum Support Prices (MSP) in India
![]()
Central Idea:
The article discusses the ongoing demands of farmers for a legal guarantee of Minimum Support Prices (MSP) in India, highlighting the necessity of such a mechanism to stabilize agricultural commodity prices and support farmers’ incomes. It addresses misconceptions surrounding MSP, emphasizing its importance in insulating farmers from market price volatility and rectifying imbalances in agricultural productivity and regional procurement.
Key Highlights:
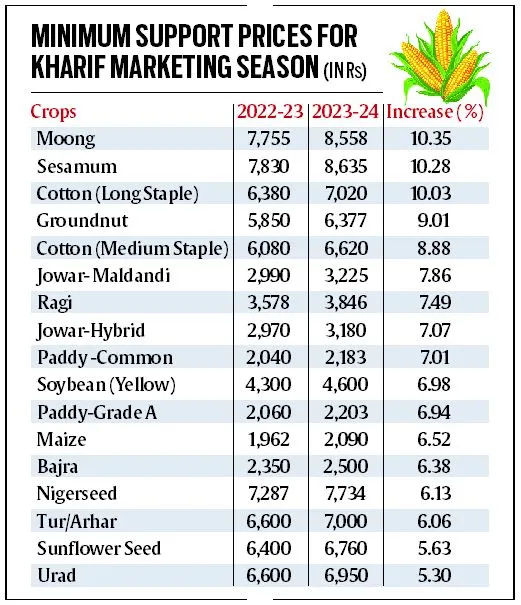
- Farmers are demanding a legal guarantee for MSP to ensure price stability and protect their incomes.
- MSP has been a longstanding mechanism in India to stabilize agricultural commodity prices, but its implementation has been limited.
- Misconceptions about the fiscal costs and operational aspects of MSP have led to hesitancy in legalizing it, despite political consensus.
- Government procurement under MSP primarily benefits consumers, not farmers, as it fulfills obligations under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- Expansion of MSP to cover a wider range of crops and regions is necessary to address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity and support crop diversification.
Key Challenges:
- Misunderstanding of MSP’s fiscal implications and operational requirements.
- Limited government intervention beyond rice and wheat procurement, leading to neglect of other crops and regions.
- Concerns over excessive government expenditure and market distortions.
- Ensuring effective implementation and monitoring of MSP across diverse agricultural sectors and regions.
Main Terms or keywords for answer writing:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- National Food Security Act (NFSA)
- Market Price Volatility
- Agricultural Commodity Procurement
- Price Stability
- Geographical Imbalances
- Crop Diversification
Important Phrases for answer quality enrichment:
- Legal Guarantee for MSP
- Price Stability Mechanism
- Market Price Volatility
- Government Intervention in Agricultural Markets
- Regional Imbalances in Agricultural Productivity
- Income Protection for Farmers
Quotes:
- “A guaranteed MSP may not solve the farmers’ problems. But it offers a good opportunity to rectify the imbalances in the MSP and procurement system.”
- “Price stability will protect the average consumer from the vagaries of inflation.”
- “Protecting the income of farmers will help revive the rural economy.”
Anecdotes:
- Instances of government procurement primarily benefiting consumers rather than farmers, highlighting the need for MSP reform.
- Farmers’ struggles with declining real incomes and wages, reflecting long-standing neglect of the agrarian economy.
Useful Statements:
- “Misconceptions surrounding the fiscal costs of MSP overlook its role in stabilizing prices and supporting farmers’ incomes.”
- “Expansion of MSP to cover a wider range of crops and regions is necessary to address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity.”
Examples and References:
- Government procurement data for rice and wheat compared to other crops, illustrating limited intervention beyond major staples.
- Comparative analysis of MSP implementation in India and other countries with similar price stabilization mechanisms.
Facts and Data:
- Government procurement figures for rice and wheat in recent years.
- Estimates of the potential fiscal costs of implementing a legal guarantee for MSP.
- Statistics on declining real incomes and wages in the agrarian sector.
Critical Analysis:
- Emphasizes the importance of MSP in stabilizing agricultural prices and supporting farmer livelihoods.
- Addresses misconceptions and challenges surrounding MSP implementation.
- Advocates for reforms to expand MSP coverage and address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity.
Way Forward:
- Implement legal guarantee for MSP to ensure price stability and support farmer incomes.
- Expand MSP coverage to include a wider range of crops and regions.
- Enhance monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to ensure effective implementation of MSP.
- Address misconceptions and concerns regarding fiscal costs and market distortions associated with MSP.
Overall, the article underscores the necessity of legalizing MSP to support farmers’ incomes, stabilize agricultural prices, and address long-standing neglect in the agrarian sector. It advocates for comprehensive reforms to expand MSP coverage and ensure its effective implementation across diverse agricultural sectors and regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
