From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fatty Acids and their health implications
Why in the News?
- Fish oil supplements, highly regarded for their high omega-3 fatty acid content, have long been associated with heart health benefits.
- A recent study has caused controversy by raising the possibility that these supplements may be as harmful as previously thought.
What are Fatty Acids?
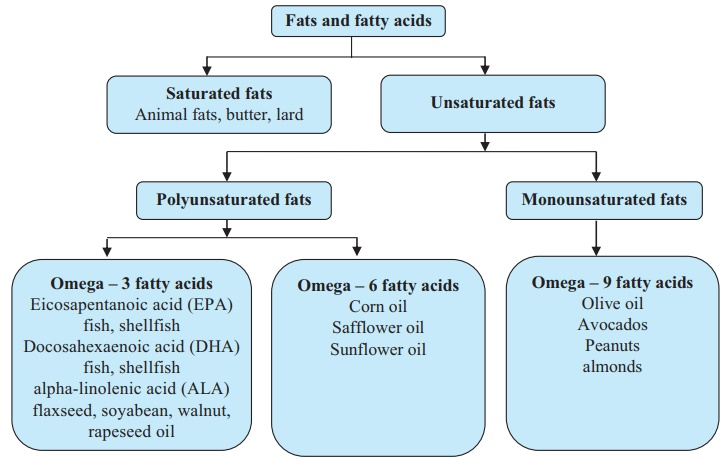
Types of Fatty AcidsFatty acids are classified based on the presence and number of double bonds in their hydrocarbon chain:
|
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
- Omega-3 fatty acids (omega-3s) are polyunsaturated fats that perform important functions in the human body.
- There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). EPA is a “marine omega-3” because it’s found in fish.
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). DHA is also a marine omega-3 found in fish.
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). ALA is the form of omega-3 found in plants.
-
- When we get ALA from food, the human body can turn some of the ALA into EPA and subsequently to DHA. However, this process provides just a small amount of EPA and DHA. So, dietary sources of EPA and DHA (like fish) are essential.
Functions of Omega-s fatty acids:
-
- They help to provide structure and supporting interactions between cells.
- Omega-3s are concentrated in high levels in cells in human eyes and brain.
- They provide the human body with energy (calories) and support the health of many body systems. These include the human cardiovascular system and endocrine system.
Significance of Omega-3 fatty acids:
- Omega-3 fatty acids have many potential benefits for human cardiovascular health.
- One key benefit is that they help lower human triglyceride levels.
- Too many triglycerides in human blood (hypertriglyceridemia) raise human risk of atherosclerosis, and through this, can increase human risk of heart disease and stroke. So, it’s important to keep triglyceride levels under control.
- Omega-3s may help us by raising human HDL (good) cholesterol and lowering human blood pressure.
- Some studies show omega-3s may lower human risk for Cardiovascular disease (CVD), and hence lowering the sudden death caused by an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia), and blood clots.
- Beyond heart health, omega-3s may help lower the human risk of developing some forms of cancer, including breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), research continues to investigate these and other possible benefits.
PYQ:[2011] A company marketing food products advertises that its items do not contain trans-fats. What does this campaign signify to the customers?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024