Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How Heat led to Protocells formation on Earth?
Why in the News?
A new Nature Physics study suggests that warm volcanic rock surfaces may have concentrated organic molecules in watery cracks, triggering life-like chemistry—offering a clue to how protocells formed without membranes before life began.
What are Protocells?
- Overview: Protocells are primitive, cell-like bubbles believed to be early precursors of real biological cells. They were not fully alive but provided a space for early chemical interactions.
- Lack of Complexity: These structures lacked complex parts like organelles or DNA systems but could hold important molecules like RNA and amino acids together.
- Membrane Role: Protocells often formed simple membranes or boundaries, which allowed molecules to stay enclosed and interact more easily—helping early reactions like protein synthesis happen.
- Importance: Although not living, they offered a model of how basic chemistry could evolve into biology, bridging the gap between non-living and living systems.
History of Formation of Protocells:
- Early Earth Conditions: Over 3.5 billion years ago, Earth’s surface had warm water pools and volcanic cracks filled with organic molecules made by natural processes like lightning.
- Compartmentalization: The first step toward life was concentrating useful molecules in one place, so they could start reacting—this led to the idea of bubble-like protocells.
- Old Theories: In the 1920s, Oparin and Haldane proposed that life began in a “primordial soup” with spontaneous chemical reactions in early Earth’s oceans.
- Modern Insights: Newer research suggests cracks in volcanic rock or hydrothermal vents created temperature gradients and water flows that helped form protocells—no complex membranes were needed.
Key Findings in the 2025 Study:
- Lab Setup: Scientists created a 170-micrometre chamber with a warm top (40°C) and cool bottom (27°C), simulating early Earth rock cracks.
- DNA Test: They added DNA and a protein-making kit (PURExpress). Only in the warm-cool chamber did the DNA make green fluorescent protein (GFP), showing real protein synthesis.
- Molecule Gathering: Essential items like DNA, magnesium, and phosphate ions gathered more at the bottom—up to 70 times more concentrated than at the top.
- Cell-Like Behavior: Even without a membrane, the system kept useful molecules inside while letting waste escape, mimicking real cell selectivity.
- Big Implication: This experiment supports the idea that life could start in simple natural environments using just heat, flow, and basic chemicals—long before full cells appeared.
| [UPSC 2018] Consider the following statements:
1. The Earth’s magnetic field has reversed every few hundred thousand years. 2. When the Earth was created more than 4000 million years ago, there was 54% oxygen and no carbon dioxide. 3. When living organisms originated, they modified the early atmosphere of the Earth. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only * (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Endocrine Disruptors in Plastic Waste
Why in the News?
Microplastics and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are infiltrating the human body, affecting everything from reproduction to cancer risk, metabolism, and child development.
About Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals:
- What They Are: Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals interfere with the body’s hormone system, affecting growth, reproduction, mood, and metabolism.
- How They Work: They mimic or block natural hormones like estrogen, testosterone, thyroid hormones, and cortisol, leading to disrupted hormonal signals.
- Why They’re Dangerous: Even low-level exposure during pregnancy or puberty can cause lasting harm.
- How We’re Exposed: Through eating contaminated food, inhaling polluted air, or skin contact with certain plastics or cosmetics.
- Where They’re Found: In plastic bottles (Bisphenol A), toys and cosmetics (phthalates like Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate), food wrappers (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances), and pesticides (dioxins, Polychlorinated Biphenyls).
- Hidden Harm: They act silently, with long-term effects such as fertility loss, hormonal disruption, or cancer.
Impact on Human Health:
- Reproductive Harm: Reduced sperm quality disrupted menstrual cycles, and increased miscarriage risk. Found in semen, placenta, and breast milk.
- Hormonal Disruption: Chemicals like Bisphenol A trigger early puberty, thyroid issues, and hormonal imbalances.
- Cancer Risk: Linked to cancers of the breast, uterus, testicles, and prostate. Several are labeled probable carcinogens by global health agencies.
- Metabolic Effects: Interfere with insulin, promote obesity and type 2 diabetes. PFAS chemicals are linked to liver and heart disease.
- Brain and Behavior: Associated with ADHD, learning issues, and lower IQ in children, especially when exposure happens early in life.
- Across Generations: May cause gene expression changes that affect health in future generations—even without direct exposure.
| [UPSC 2020] Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment?
Options: (a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems * (b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children (c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields. (d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
India’s first Genomic Atlas reveals deep Ancestry and Health Risks
Why in the News?
A landmark study published in the ‘Cell’ journal has sequenced the genomes of 2,762 Indians from 23 states and union territories, creating the most comprehensive genomic map of India to date.
About the Genomic Atlas:
- Overview: The Genomic Atlas is the most comprehensive genetic mapping of Indian populations, covering caste, tribe, language, geography, and urban-rural distinctions.
- Collaboration: It was conducted by Indian and international institutions, aiming to understand how ancient migrations and social structures shaped Indian genomes.
- Use of Molecular Clocks: Researchers used genetic mutations as molecular clocks to trace human ancestry and map the evolutionary history of diverse groups in India.
- Focus on Disease and Ancestry: The study explores recessive disorders, disease-linked mutations, and interbreeding with archaic humans like Neanderthals and Denisovans.
- Scope: Plans include expanding coverage to more isolated communities and building tools to track disease origins within genetically distinct Indian groups.
- Impact on Precision Medicine: It aims to improve personalised healthcare by incorporating Indian genetic diversity into global medical research.
Key Highlights of the Study:
- Discovery of New Gene Variants: Over 2.6 crore previously undocumented genetic variants were discovered, many of which are absent from international gene databases.
- Single-origin migration: Indians descend primarily from a single out-of-Africa migration ~50,000 years ago, not earlier human groups.
- Three major ancestral components:
- Ancient Ancestral South Indians (AASI) – early hunter-gatherers.
- Iranian-related Neolithic farmers – from Sarazm (~4th millennium BCE).
- Eurasian Steppe pastoralists – arrived around 2000 BCE, tied to Indo-European languages.
- Additional East Asian ancestry: Found in East, Northeast, and some Central Indian populations (e.g., 5% in West Bengal), likely post-Gupta or rice cultivation-related (~520 CE).
- Caste endogamy impacts: Long-term inbreeding within castes has led to high homozygosity, raising the risk of recessive genetic diseases.
- Archaic DNA: Indian genomes show rich Neanderthal and Denisovan segments, especially in immune-related genes like MHC, TRIM, and BTNL2.
- Unique health risks: A BCHE variant linked to anaesthetic reaction is enriched in Telangana; 7% of discovered protein-altering variants relate to serious genetic disorders.
- Every individual had at least one genetic relative in the sample—revealing extreme interrelatedness and strong founder effects, particularly in South India.
- Unmatched Neanderthal diversity: India harbours the widest variety of Neanderthal-derived genetic fragments among global populations.
| [UPSC 2021] In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements:
1. Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of the egg. 2. A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from the mother and not from the father. Options: Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2* (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Botrytis Fungus and Wine-Making
Why in the News?
Scientists have found that Botrytis cinerea, the fungus used in high-end sweet wines, cannot be cloned because none of its nuclei carry a full set of chromosomes, a rare genetic trait among fungi.
About Botrytis Fungus:
- Overview: Botrytis cinerea, also called noble rot, is a fungus that infects ripe grapes and causes them to shrivel while concentrating sugar and flavour.
- Fungal Classification: It belongs to the ascomycetes group and produces spores in sac-like structures known as asci, each containing eight ascospores.
- Role in Winemaking: Under controlled vineyard conditions, Botrytis infection is desirable, as it enhances the sweetness and aroma of wine.
- How is Wine Made Using It?
-
- Effect on Grapes: The fungus dehydrates the grapes, which increases the sugar content and concentrates flavours naturally.
- Harvesting Method: Grapes affected by Botrytis are hand-harvested, making the process labour-intensive and expensive.
- Wine Varieties Produced: It is used to produce premium dessert wines such as Sauternes (France), Tokaji Aszú (Hungary), and Trockenbeerenauslese (Germany), known for their complex flavours and high value.
Significance of Recent Findings:
- Cloning Discovery: A recent study in Science found that Botrytis cannot be cloned, as no single nucleus contains a full set of chromosomes.
- Unique Genome Structure: The chromosomes are distributed across multiple nuclei, which is unprecedented in any known fungus, animal, or plant.
- Scientific Impact: This challenges conventional genetics and may lead to new insights in genome organisation and fungal evolution.
- Dual Importance: Botrytis is now seen not only as a key player in winemaking but also as a genetic curiosity in modern science.
| [UPSC 2009] In the context of alternative sources of energy, ethanol as a viable bio-fuel can be obtained from:
(a) Potato (b) Rice (c) Sugarcane* (d) Wheat |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Researchers validate Optical Properties of Teak Leaf Extracts
Why in the News?
In a breakthrough, scientists at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) have found that teak leaf extract (Tectona grandis) could offer a natural, sustainable solution for laser protection.
About Optical Properties of Teak Leaf:
- Natural Composition: Teak leaves (Tectona grandis) contain natural compounds that can interact with strong laser light.
- Laser Blocking Ability: These compounds can block harmful laser rays while allowing normal light to pass, making them suitable for selective light filtering.
- Nonlinear Optics: This unique behaviour is called a nonlinear optical property, where a material responds differently to high-intensity light.
- Linear vs Nonlinear: In linear optics, the material’s response is directly proportional to the light’s intensity. In nonlinear optics, the response becomes non-proportional, especially under laser exposure.
Back2Basics: Teak as Timber in India
|
Recent Breakthrough:
- New Discovery: Scientists discovered that teak leaf extract can function as a natural laser shield.
- Protection Potential: The extract can block high-intensity laser beams, offering protection to human eyes and sensitive optical devices.
- First of Its Kind: This marks the first known instance of a natural material exhibiting such laser-blocking properties.
Significance for Humans:
- Practical Applications: It can be used in laser safety goggles, optical sensors, and other light-sensitive technologies.
- Safe Alternative: It offers a non-toxic, eco-friendly substitute to chemical-based laser protection materials.
- Sustainability Impact: The use of plant-based materials supports cost reduction and promotes sustainable innovation in science and optics.
| [UPSC 2015] In India, in which one of the following types of forests is teak a dominant tree species?
Options: (a) Tropical moist deciduous forest* (b) Tropical rain forest (c) Tropical thorn scrub forest (d) Temperate Forest with grasslands |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
In-Body CAR T-Cell Therapy
Why in the News?
A new study published in Science journal shows that “In-Body CAR T-Cell Therapy” marks a breakthrough by enabling direct immune cell reprogramming for faster, safer treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases.
What is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
- Overview: CAR T-cell therapy is a treatment where a patient’s own T cells are genetically modified to detect and kill cancer cells.
- Science behind it: Scientists extract T cells and add a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) gene, which enables them to identify cancer cells.
- Working: These modified T cells are infused back into the patient, where they multiply and actively attack cancer.
- Effectiveness: The therapy has shown high success against certain blood cancers and is now being studied for autoimmune disorders like lupus.
- Issues: The traditional therapy is expensive (₹60–70 lakh), slow, and requires chemotherapy and specialised lab facilities.
Recent Breakthrough: In-Body CAR T-Cell Therapy
- Approach: A new technique uses mRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver instructions directly inside the body.
- Targeting Cells: These nanoparticles are programmed to locate and enter killer T cells, converting them into CAR T-cells internally.
- Benefits offered: This method eliminates the need for cell extraction, chemotherapy, or viral vectors, making it faster and safer.
Significance for India:
- Scalable Innovation: This platform may lower treatment costs and offer wider access in countries like India with high cancer and autoimmune burdens.
- Infrastructure Relief: Its in-body nature avoids dependence on advanced labs, making it suitable for resource-constrained settings.
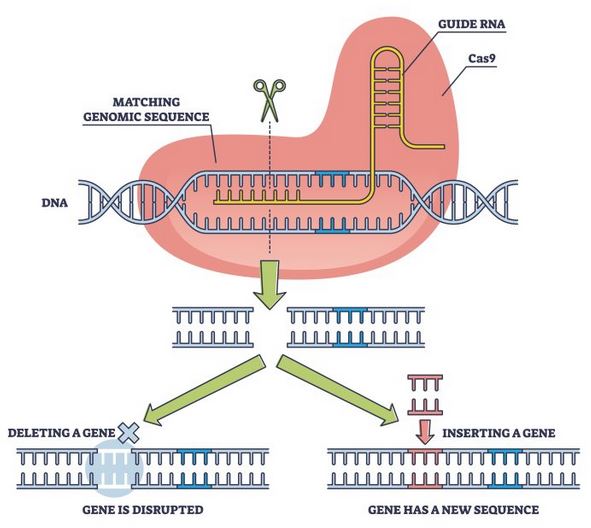
| [UPSC 2019] What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news?
Options: (a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing* (b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients (c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant (d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How DNA identification works?
Why in the News?
Following the tragic crash of the Air India Boeing 787 Dreamliner in Ahmedabad, authorities concluded the identities of the victims using DNA analysis.
What is DNA?
- Overview: DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the molecule that carries genetic instructions essential for the development, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms.
- Location in the Body: It is present in nearly every human cell and is unique to each person, except for identical twins.
- Structure: DNA is made up of four chemical bases—Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T)—arranged in sequences that encode genetic data.
- Biological Fingerprint: Due to its individual uniqueness, DNA acts like a biological fingerprint, useful in crime investigations and disaster victim identification.
How DNA Identification Works?
- Use in Forensics: DNA is extracted from human remains when visual identification is not possible due to burns, decomposition, or trauma.
- Reference Matching: Extracted DNA is compared with:
- Family reference samples (from parents, children, siblings)
- Personal belongings (like a toothbrush, razor, or hairbrush)
- Sample Reliability: Bones and teeth are preferred in degraded conditions, as they preserve DNA more effectively.
- Forensic Accuracy: Specialized forensic labs analyze and match DNA sequences, confirming identity with high levels of accuracy.
Common DNA Analysis Methods:
- Short Tandem Repeat (STR) Analysis:
-
- Focuses on short, repeating sequences of DNA that vary among individuals.
- Requires nuclear DNA, typically from well-preserved samples.
- Considered the gold standard for forensic identification.
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Analysis:
-
- Extracts DNA from mitochondria, not the nucleus, making it more resilient in degraded samples.
- Inherited only from the mother, allowing tracing through the maternal lineage.
- Y-Chromosome Analysis:
-
- Targets Y chromosomes, passed from father to son.
- Useful for identifying male victims when paternal relatives are available.
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis:
-
- Detects single-letter changes in the DNA sequence.
- Applied when DNA is highly degraded and other methods are less effective.
- Can be used with reference items like personal hygiene tools.
| [UPSC 2000] Assertion (A): DNA Finger-printing” has become a powerful tool to establish paternity and identity of criminals in rape and assault cases. Reason (R): Trace evidence such as hairs, saliva and dried semen are adequate for DNA analysis.
Options: (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not a correct explanation of A (c) A is true, but R is false (d) A is false, but R is true |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
BBX32 Protein in Plants
Why in the News?
A new study from researchers at IISER Bhopal has revealed how a single protein called BBX32 helps plants time the critical moment they emerge from darkness into light.
What is BBX32?
- Function: BBX32 is a plant protein that helps a seedling keep its protective hook closed as it pushes through the soil.
- Protection Mechanism: The hook shape shields the soft shoot tip in darkness; BBX32 extends this protection until it’s safe to open.
- Ethylene Activation: Underground, the plant hormone ethylene activates the BBX32 gene, signaling the seedling to stay protected.
How does it work?
- Light Stabilization: Once exposed to light, BBX32 is no longer broken down, allowing it to accumulate on one side of the hook.
- Protein Chain Reaction: BBX32 activates PIF3, which then activates HLS1, the protein that directly keeps the hook bent.
- Lab Testing: Plants were tested in different light types and sand to simulate real soil. Extra ethylene increased BBX32 activity.
- Mutant Comparison: Plants without BBX32 opened too early. Only 25% broke through sand, compared to 40% of normal and 80% with extra BBX32.
- Degradation Control: In darkness, COP1 breaks down BBX32. Ethylene slows this process. Light fully stabilizes BBX32.
- Coordinated Timing: The protein’s behavior is guided by light, hormone signals, and pressure, ensuring the hook opens at the right time.
Why is studying BBX32 important?
- Better Crop Survival: BBX32 can help develop crops that grow well in dense, wet, or compacted soils.
- Climate Adaptation: As climate change leads to tougher soil conditions, BBX32 can improve seedling emergence and survival.
- Boosting Yields: Supporting hook protection even slightly longer can lead to stronger early growth and higher productivity.
- Genetic Research: BBX32 is a potential target for gene editing in plants to improve resilience during germination.
- Broader Insight: Studying BBX32 helps us understand how plants balance internal signals with external cues for safe growth.
| [UPSC 2018] Which of the following leaf modifications occur(s) in the desert areas to inhabit water loss?
1. Hard and waxy leaves 2. Tiny leaves 3. Thorns instead of leaves Select the correct answer using the code given below: Options: (a) 2 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Magnetic Isolation and Concentration Cryo-electron Microscopy (MagIC)
Why in the news?
Researchers from Rockefeller University introduced MagIC, a new method that allows cryo-EM to work with samples up to 100 times more dilute, making it easier to study rare or hard-to-purify molecules.
About Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM):
|
What is MagIC (Magnetic Isolation and Concentration cryo-EM)?
- Overview: It is a new method developed by scientists in the U.S. to make it easier to study rare biological molecules under a special microscope called cryo-EM.
- Sampling involved: Normally, cryo-EM needs the molecules in a sample to be very concentrated, which is hard when the molecules are rare or hard to collect.
- MagIC solves this problem by using:
- Tiny magnetic beads (50 nanometers wide) that stick to the molecules researchers want to study.
- A magnet that pulls these beads together into one area.
- This way, even when the solution has less than 0.0005 milligrams per milliliter of the molecules, scientists can still get useful images.
Key Features of MagIC:
- Magnetic Pulling: After molecules stick to the tiny magnetic beads, a magnet pulls them into clusters, making them easier to see.
- Low Sample Requirement: Only 5 nanograms of sample per grid are needed. That’s a very tiny amount—much less than earlier methods.
- Faster Imaging: The magnetic beads are easy to see, so scientists can quickly find areas with useful particles in the microscope.
- Smart Software – DuSTER (Duplicated Selection to Exclude Rubbish):
- It helps remove bad or blurry images and keep only the clear ones.
- It picks each particle twice and only keeps it if the location matches both times.
- MagIC works with samples that are 100 times more dilute than what cryo-EM could handle before.
| [UPSC 2023] ‘Aerial metagenomics’ best refers to which one of the following situations?
Options: (a) Collecting DNA samples from air in a habitat at one go* (b) Understanding the genetic makeup of avian species of a habitat (c) Using air-borne devices to colect blood samples from moving animals (d) Sending drones to inaccessible areas to collect plant and animal samples from land surfaces and water bodies |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Kashmir Merino: India’s First Gene-Edited Sheep
Why in the News?
Researchers at Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology (SKUAST) have successfully created India’s first gene-edited sheep—a Kashmir Merino breed.

About Kashmir Merino Sheep:
- Overview: Kashmir Merino is a high-quality domestic sheep breed known for its fine wool and ability to thrive in cold climates.
- Genetics: It was developed by crossbreeding exotic Merino rams with local sheep breeds in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Characteristics: The breed produces soft, dense wool with high fibre quality, making it valuable for the textile industry.
- Resilience: It is well-adapted to high-altitude Himalayan conditions, including extreme cold and low oxygen levels.
- Significance: It plays a key role in regional livestock economies, contributing significantly to wool and mutton production in Jammu and Kashmir.
Gene-Editing Breakthrough in Kashmir Merino:
- Gene Targeted: Researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 technology to edit the myostatin gene, which normally inhibits muscle growth.
- Impact: Disabling this gene led to a 30% increase in muscle mass, resulting in higher meat yield and improved economic returns for farmers.
- Lab-to-Field Success: The edited embryo was developed in a laboratory and then successfully implanted into a surrogate mother, marking a full-cycle gene-editing achievement.
- Biotech Significance: This success represents a major advancement in India’s livestock biotechnology, opening new paths for research in disease resistance, wool quality enhancement, and production of transgenic proteins.
| [UPSC 2017] What is the application of somatic cell nuclear transfer technology?
Options: (a) Production of biolarvicides (b) Manufacture of biodegradable plastics (c) Reproductive cloning of animals* (d) Production of organisms free of diseases |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
IISc develops Nanozyme to prevent Abnormal Blood Clotting
Why in the News?
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have created an artificial metal-based nanozyme that can help prevent dangerous blood clotting, especially in conditions like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and COVID-19.

What is Blood Clotting?
- About: When we get a cut or injury, our body quickly stops the bleeding by forming a blood clot. This is done by special blood cells called platelets that stick together and seal the wound.
- Control mechanism: This natural process is called blood clotting or haemostasis and is controlled by certain chemicals in our body like collagen and thrombin.
- Post covid issues: But in some illnesses like pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) or COVID-19, the body sends too many signals to make clots, even when there is no injury.
- Oxidative Stress: This creates a problem called oxidative stress, where harmful molecules called Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) build up in the blood. These ROS molecules over-activate the platelets, causing them to make too many clots inside blood vessels.
- Hazards: This can block blood flow, leading to serious health issues like heart attacks, strokes, or lung problems. This condition is called thrombosis, and it can be life-threatening.
Vanadium-Based Nanozyme and Its Features:
- Purpose and Design: Scientists at IISc developed vanadium-based nanozymes to mimic natural antioxidant enzymes that reduce ROS levels.
- How they work: The nanozymes control oxidative stress by copying glutathione peroxidase, an enzyme that removes ROS and protects platelets.
- Optimal Structure: Spherical-shaped vanadium pentoxide (V₂O₅) nanozymes were found to be the most effective.
- Test Results in Mice: These nanozymes reduced blood clots and improved survival in PTE-affected mice with no toxicity signs over five days.
- Next Steps: Scientists plan to test the nanozyme in ischemic stroke and are optimistic about human clinical trials after promising lab results with human platelets.
| [UPSC 2015] With reference to the use of nano-technology in health sector, consider the following statements:
1. Targeted drug delivery is made possible by nanotechnology. 2. Nanotechnology can largely contribute to gene therapy. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2* (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Thermophilic Bacteria in Rajgir Hot Spring could help fight Deadly Infections
Why in the News?
Researchers from the Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT) have discovered antibiotic-producing bacteria in the Rajgir hot spring in Nalanda, Bihar.
What are Thermophilic Bacteria?
- About: Thermophilic bacteria, or thermophiles (meaning “heat lovers”), are microorganisms that thrive in high-temperature environments ranging from 45°C to 70°C.
- Adaptation: These temperatures can cause third-degree burns in humans, but thermophiles are biologically adapted to survive and grow in such conditions.
- Habitats: They are commonly found in hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and compost piles, which are mineral-rich and have low microbial competition.
- Advantages: Some thermophiles produce potent antibiotics to outcompete other microbes and dominate their niche.
- Global Example: Thermophiles from hot springs in Saudi Arabia have shown antibacterial activity against gram-positive pathogens.
Key Findings from India:
- Sampling Challenge: Samples were collected from water and soil at 43°C–45°C, making fieldwork difficult.
- Microbial Analysis: In the sample, Actinobacteria made up 40–43% of the microbial population, double the typical amount in hot springs.
- Significance: Actinobacteria are well known for producing key antibiotics like streptomycin and tetracycline.
- AMR Context: The findings are crucial in the fight against antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which could cost $1 trillion globally by 2050, according to the WHO.
- Antibiotic Potential:
- Lab Testing: Seven Actinobacteria strains were found to inhibit pathogens such as E. coli, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Compound Discovery: Scientists identified diethyl phthalate using GC-MS, which showed effectiveness against Listeria monocytogenes, a deadly foodborne pathogen.
- Future Scope: The compound has potential for antibiotic development, but not all thermophiles produce antibiotics, so screening is essential.
- Uses:
- Industrial Use: The enzyme Taq polymerase, used in PCR tests (including during COVID-19), is derived from a thermophile called Thermus aquaticus.
- Agricultural Use: A 2018 BHU study showed thermophiles from Chumathang hot springs (Leh) promote plant growth, revealing wider industrial and ecological value.
| [UPSC 2023] Consider the following statements:
1. Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperature above the boiling point of water. 2. Some microorganisms can grow in environments with temperature below the freezing point of water. 3. Some microorganisms can grow in highly acidic environment with a pH below 3. How many of the above statements are correct? Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) Only three* (d) All four |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
TR1 Cells: The Hidden Warriors in Malaria Immunity
Why in the News?
Scientists at Stanford University discovered that TR1 cells play a dominant role in fighting malaria reinfections.
Understanding the Body’s Immune Response:
- What is the Immune System? It’s the body’s defence system that protects us from infections like malaria.
- First Defence: The skin and body surfaces block germs from entering.
- Innate Immunity: If germs get in, the innate immune system reacts fast, like an emergency response team.
- Adaptive Immunity: Then, the adaptive immune system kicks in, targeting germs specifically and remembering them for future protection.
- B-Cells and T-Cells:
- B-cells make antibodies to fight germs.
- T-cells attack infected cells and guide other immune cells.
- Helper T-Cells: A type called CD4+ T-cells helps organise the defence. Earlier, scientists thought TH1 cells were key in malaria, but a new study shows TR1 cells are more important, especially in repeat infections.
What are TR1 Cells?
- Role of TR1 Cells: These are special T-cells that help control the immune system and prevent overreaction.
- Major Response in Malaria: Though small in number, during malaria, TR1 cells become the main helper cells.
- Study in Uganda: In young children with repeated malaria, TR1 cells grew in number and improved the body’s ability to fight malaria without severe illness.
- Memory and Immunity: TR1 cells remember the malaria parasite and return stronger with each infection.
- Types of TR1 Cells:
- Naïve TR1 – not yet active.
- Effector TR1 – fighting infection.
- Memory TR1 – remembering past infections.
- Epigenetic Role: TR1 cells may respond by switching genes on or off, not by changing the genes themselves.
Key Findings of the Study:
- Research Team: Scientists from Stanford University studied people in Uganda over many months and years.
- Tracking Infections: They followed individuals through multiple malaria infections to see how immune cells behaved.
- Gene Scanning: A special technique was used to read the genes of each immune cell — like scanning a barcode.
- Findings: TR1 cells were accurate, long-lasting, and clearly connected to malaria (not other infections).
- Why it matters: This discovery can help in making better malaria vaccines, boosting long-term protection, and even improving treatments for other serious diseases.
| [UPSC 2025] With reference to monoclonal antibodies, consider the following:
I. They are man-made proteins. II. They stimulate the patient’s immune system to fight the specific disease. III. They are produced using animal cells only. Which of the statements given above are correct? Options: (a) I and II only (b) II and III only (c) I and III only (d) All the three * |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Scientists verify Mendel’s Experiments on Inheritance
Why in the News?
Researchers have solved the genetic mysteries behind Mendel’s Experiments on Inheritance, using advanced DNA sequencing and genome analysis.
About Mendel’s Experiments on Inheritance:
- Who Was Mendel: Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied pea plants starting in 1856 to find out how traits like height or color are passed from parents to children.
- Years of Study: He worked for 8 years and tested over 10,000 plants. His results were shared in 1865 but ignored at the time.
- Rediscovered Later: In 1900, other scientists realised how important Mendel’s work was.
- What He Studied: He looked at 7 traits in peas – Seed shape, seed colour, flower colour, pod shape, pod colour, flower position, and plant height.
- What He Found: Some traits (like round seeds) are stronger than others (like wrinkled seeds). These stronger traits usually show up in the next generation.
- Why It Matters: Mendel showed that traits are passed through tiny units called genes, and each gene can have different versions called alleles. This became the foundation of genetics.

What the Study Found (2024):
- What Scientists Did: In April 2024, scientists studied the DNA of 697 types of pea plants to understand the exact genes behind all 7 traits that Mendel studied.
- Big Data: They used powerful machines to look at a huge amount of data — as much as 14 billion pages of information!
- Surprising Results: They found that the pea plant family is more mixed than expected, with 8 different genetic groups due to crossbreeding.
- New Genetic Details:
- Pod color changes due to a missing piece of DNA.
- Pod shape is controlled by 2 specific genes.
- Flower position changes with a small DNA change.
- More Than Mendel: They also found 72 other traits related to seeds, pods, leaves, and roots.
- Why It’s Useful: These findings can help farmers grow better crops, protect plants from diseases, and prepare for climate change.
| [UPSC 2013] Mycorrhizal biotechnology has been used in rehabilitating degraded sites because mycorrhiza enables the plants to
(1). resist drought and increase absorptive area (2). tolerate extremes of pH (3). resist disease infestation Select the correct answer using the codes given below. Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 * |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is A-to-I mRNA Editing?
Why in the News?
Chinese researchers found that A-to-I mRNA editing, once considered random, plays a key role in development, especially in the wheat pathogen Fusarium graminearum.
About A-to-I mRNA Editing:
- mRNA: Our cells use DNA as a guide to make proteins. First, they copy DNA into messenger RNA (mRNA).
- A-to-I editing: This is a process where the letter adenosine (A) in mRNA is changed to inosine (I) by special enzymes called ADARs. The cell reads inosine as guanine (G), which can change the protein being made.
- Why it matters:
- It helps the cell make different versions of proteins without changing the DNA.
- It can remove early stop signals, allowing full proteins to be made.
- It helps the cell adapt to different conditions or stages of life.
What did scientists discover in the fungus?
- Fungal Discovery: Scientists found that the fungus edits over 26,000 mRNA sites during reproduction, not during normal growth.
- Development Role: This editing fixes early stop signals in key genes, helping the fungus develop and reproduce properly.
- Stress Adaptation: Some genes work better unedited under stress, showing the fungus edits only when needed for survival.
Does this happen in humans?
Yes, A-to-I editing is common in humans:
- In the brain: It helps with brain growth, memory, and learning.
- In the immune system: It helps fight infections and control inflammation.
Health Implications:
- Health Risks: Faulty editing is linked to epilepsy and certain cancers.
- Therapeutic Potential: Understanding this process can lead to new treatments and improve gene-editing technologies.
| [UPSC 2016] In the context of the developments in Bioinformatics, the term ‘transcriptome’, sometimes seen in the news, refers to:
Options: (a) a range of enzymes used in genome editing (b) the full range of mRNA molecules expressed by an organism * (c) the description of the mechanism of gene expression (d) a mechanism of genetic mutations taking place in cells |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
New RNA-Based Approach to Combat Plant Viruses
Why in the News?
Recently, a team of scientists from Germany reported a breakthrough in combating the cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) through an innovative RNA-based antiviral agent.
About Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV):
- CMV is one of the most widespread and destructive plant viruses, affecting over 1,200 plant species, including important food crops such as cucumbers, melons, and cereals.
- The virus is transmitted by aphids, tiny insects that spread the virus as they feed on plants, making outbreaks difficult to control.
- In India, CMV causes significant yield losses in crops like bananas, pumpkins, and cucumbers, leading to mosaic discoloration, stunted growth, and unviable fruits.
- The economic impact of CMV includes both direct financial losses from reduced crop yields and the indirect costs of pest management.
RNA Silencing Methods discussed (HIGS vs SIGS):
RNA silencing is a natural defense mechanism that plants use to protect themselves from viral infections.
Two RNA-based technologies, Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS) and Spray-Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS), have been developed to enhance plant immunity against diseases like CMV.
[1] Host-Induced Gene Silencing (HIGS):
- HIGS involves genetically modifying plants to produce dsRNA, which activates the plant’s immune system to fight off the virus.
- This method provides continuous protection and long-term immunity throughout the plant’s lifecycle.
- However, it faces challenges such as regulatory issues, high production costs, and the potential for viruses to evolve resistance over time.
[2] Spray-Induced Gene Silencing (SIGS):
- SIGS, unlike HIGS, does not require genetic modification. Instead, plants are treated with RNA sprays containing dsRNA that targets specific viruses.
- This method is cost-effective, non-GMO, and can be applied to a variety of crops.
- However, SIGS provides short-term protection, may be ineffective due to random RNA mixtures, and its effectiveness can be reduced by environmental factors such as sunlight, rain, and soil microbes.
| [UPSC 2019] RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why?
1. It is used in developing gene silencing therapies. 2. It can be used in developing therapies for-the treatment of cancer. 3. It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies. 4. It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens. Select the correct answer using the code given below: Options: (a) 1, 2 and 4* (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Role of Lipids in Protein Function and Co-Evolution
Why in the News?
New research by CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology, Hyderabad suggest that lipids (along with DNA), particularly in mitochondrial membranes, are not just structural elements but play an integral role in the function and evolution of proteins.

About Lipids and RC1 in Cells:
Lipids:
- Lipids, including fats, phospholipids, and sterols, make up to 30% of the dry weight of cells.
- They are crucial for membrane integrity and various biological processes.
- They vary in fatty acid composition and length, influenced by genetics, diet, and environmental factors.
- They form a bilayer in membranes, with hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails inward, providing stability and enabling protein function.
- Role of Lipids in Cells:
- Lipids form the bilayer, providing flexibility and stability for membrane proteins that perform functions like receptor binding and ion channelling.
- They like cardiolipin stabilize RC1 and other respiratory complexes, aiding energy production.
RC1 (Respiratory Complex 1):
- RC1 is a protein complex in the mitochondrial membrane, crucial for cellular respiration and energy production.
- It is composed of 44 proteins, some synthesized in the cytoplasm and others in mitochondria.
- Mutations in RC1 lead to diseases due to its vital role in respiration.
Lipid-Protein Co-evolution as per new Research:
- New research highlights the co-evolution of proteins and lipids, especially in mitochondrial membranes, where proteins interact with specific lipids from their own kingdom (plant or animal).
- Plant lipids, richer in polyunsaturated fatty acids, are more flexible, aiding stress resistance, while animal lipids evolve differently to meet their needs.
- Lipid-protein co-evolution adds complexity to cellular evolution, with implications for human health and disease treatment.
| [UPSC 2001] Which of the following cell organelles play the most significant role in protein synthesis?
Options: (a) Lysosome and Centrosome (b) Endoplasmic reticulum and Ribosome* (c) Golgi apparatus and Mitochondria (d) Lysosome and Mitochondria |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Science behind Uterine Transplants
Why in the News?
Uterine transplant surgery offers a groundbreaking solution for women with absolute uterine infertility, as seen in the recent birth of the first child in the U.K. born to a mother who received a donated uterus.
About Uterine Transplants:
- Uterine transplantation is a surgical procedure where a woman who lacks a functional uterus receives a donor uterus, enabling her to carry and give birth to a child.
- The transplant is typically temporary, allowing for one or two pregnancies, after which the uterus is usually removed to avoid complications.
- Donor Criteria:
- Age: Between 30 to 50 years.
- Health: Must be in good overall health, with a BMI under 30, and no history of diabetes, cancer (within 5 years), or STIs.
- Exclusions: Women with HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, or other complications.
- The procedure requires gynecological transplant surgeons with specific training. A 6-month recovery period is needed before attempting pregnancy.
Indian Scenario:
- India’s first transplant was performed on May 18, 2017, at Galaxy Care Hospital in Pune. The recipient was a 26-year-old woman who received her mother’s uterus.
- In October 2018, India’s first baby was born via Caesarean section, weighing 1.45 kg and healthy.
- This success story reflects India’s growing capabilities in reproductive medicine, providing hope to women with uterine infertility, offering them an opportunity for biological motherhood.
| [UPSC 2020] In the context of recent advances in human reproductive technology, “Pronuclear Transfer” is used for:
Options: (a) fertilization of egg in vitro by the donor sperm (b) genetic modification of sperm producing cells (c) development of stem cells into functional embryos (d) prevention of mitochondrial diseases in offspring |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Coenzyme Q: A Vital Molecule for Energy Production
Why in the News?
A recent paper published in Nature by a team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences explored the genetic modification of rice plants to increase Coenzyme CoQ10 production.
What are Coenzymes and CoQ?
- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed in the process.
- Coenzymes are organic molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions, making cellular metabolism more efficient.
- Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is a lipid-soluble antioxidant that helps stabilize cells under stress. It is crucial for cellular energy production.
- CoQ exists in 10 forms (CoQ1 to CoQ10), all present in the respiratory chain within cells.
Importance of CoQ9 and CoQ10
- CoQ9: It is found in cereal crops (wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc.), bamboo, and flowering plants like cinnamon, avocado, and pepper. It is rich in daily foods, making it an accessible nutrient.
- CoQ10: It is vital for mitochondrial energy production. Concentrated in high-energy organs like the heart. CoQ10 is crucial for health, especially in those with neurological issues or age-related deficiencies.
- Health Benefits of CoQ10:
- 2008: CoQ10 supplementation helped patients with neurological disorders, improving their health (Montini et al., Milan).
- 2012: Infants with CoQ10 deficiency benefitted from ubiquinone analogues (Shamima Ahmed, London).
- CoQ10-based supplements are now commonly prescribed by healthcare professionals.
| [UPSC 2007] Question: Which one of the following is not a digestive enzyme in the human system?
Options: (a) Trypsin (b) Gastrin* (c) Pepsin (d) Amylase |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
India’s first-ever Seed Germination Database
Why in the News?
On April 16, 2025, the Ecological Restoration Alliance-India (ERA-I) has released a first-of-its-kind seed germination database aimed at enhancing the success of growing native plants for ecological restoration.
About the Seed Germination Database:
- It was launched by the Ecological Restoration Alliance-India (ERA-I). ERA was formed in July 2021, as an informal collective between practitioners, ecologists and individuals.
- ERA-I collaborated with organizations like Auroville Botanical Gardens, NCF, and Wildlife Trust of India.
- It features over 1,000 germination techniques for 465 native plant species found across India.
- It aims to help restoration practitioners, nursery managers, and native plant enthusiasts improve success rates in growing plants for ecological restoration.
- It is a free-access database and offers valuable information on germinating native plants crucial for restoration projects.
- Native Plants Included:
- The database features a diverse array of native plant species. These species are key to restoring balance in degraded ecosystems.
- They are – Aegle marmelos (Wood apple), Bauhinia racemosa (Beedi leaf tree), Ficus benghalensis (Banyan), Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Ziziphus mauritiana (Indian jujube), Knema attenuata (Wild nutmeg), Lawsonia inermis (Henna), Madhuca longifolia (Mahua), Vachellia nilotica (Babool).
Significance:
- Native plants are essential for creating climate-resilient ecosystems.
- Such database plays a vital role in ecological restoration.
- It provides 1,000+ techniques for growing native plants, enhancing the success of restoration projects.
- The database supports India’s Bonn Challenge commitment to restore 26 million hectares of degraded land by 2030.
| [UPSC 2016] In the context of food and nutritional security of India, enhancing the ‘Seed Replacement Rates’ of various crops helps in achieving the food production targets of the future. But what is/are the constraint/constraints in its wider/greater implementation?
1. There is no National Seeds Policy in place. 2. There is no participation of private sector seed companies in the supply of quality seeds of vegetables and planting materials of horticultural crops. 3. There is a demand-supply gap regarding quality seeds in case of low value and high volume crops. Select the correct answer using the code given below: Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only * (c) 2 and 3 only (d) None of the above |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The conservation argument for resurrecting dire wolf is not credible
Why in the news?
Colossal Biosciences is an American company that combines genetics and conservation in a unique way by bringing back species that have been extinct for thousands of years.
What is the primary goal of Colossal Biosciences’ de-extinction project?Colossal Biosciences is a biotechnology company specializing in de-extinction projects, aiming to revive extinct species through advanced genetic engineering.
|
Why do critics question the credibility of reviving extinct species for conservation purposes?
- Lack of Scientific Proof: The actual success of reviving extinct species like the woolly mammoth has not yet been proven through rigorous peer review or established results.
- Limited Genetic Editing: The extent of genetic editing in revived species often involves only a small number of genes, leading to incomplete or flawed replicas of the original species. Eg: In the case of the dire wolf, only 20 genes were edited, resulting in what critics describe as just a “strange-looking gray wolf” rather than a true de-extinct species.
- Ethical Concerns: There are ethical debates over the potential consequences of creating species that may not thrive in the modern environment or might cause unforeseen ecological imbalances. Eg: The introduction of revived species like the woolly mammoth could disrupt current ecosystems in ways that may not be beneficial.
How can bringing back the woolly mammoth help stop global warming?
- Restoring Grasslands: The woolly mammoth can help restore Arctic grasslands by grazing on shrubs and plants, which would create open grasslands where permafrost can remain intact. Eg: By grazing, mammoths would prevent the growth of shrubs that trap heat, promoting the return of grasslands that are cooler and better at reflecting sunlight.
- Slowing Permafrost Melt: Grasslands absorb less heat than shrub forests, helping to keep the permafrost cool. The return of woolly mammoths could help prevent the thawing of permafrost, which releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Eg: Mammoth grazing can keep the ground cooler and slow the thawing of permafrost, thus reducing the release of methane into the atmosphere.
- Preventing Methane Emissions: As the permafrost melts, it releases large amounts of methane into the atmosphere. Woolly mammoths could help mitigate this by maintaining ecosystems that slow down the permafrost’s thaw. Eg: With mammoths grazing, the tundra could remain cooler and less prone to releasing methane.
- Enhancing Carbon Sequestration: Grasslands are more effective at absorbing carbon than shrubbery or forested areas. By converting tundra back into grasslands, woolly mammoths could enhance carbon sequestration and help store more carbon in the soil. Eg: Woolly mammoths could help re-establish healthy grasslands, which would act as carbon sinks, absorbing more CO2 from the atmosphere.
What is India’s situation in advanced genetic engineering?
|
Way forward:
- Strengthen Ethical and Regulatory Frameworks: India should establish robust regulations and ethical guidelines for genetic engineering, particularly for gene-editing technologies like CRISPR, to ensure safety and sustainability in areas such as agriculture and medicine.
- Promote Collaborative Research and Innovation: Encouraging partnerships between academic institutions, the private sector, and the government will help accelerate research and application of advanced genetic technologies, positioning India as a global leader in biotechnology innovation.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2024] What strategies have been developed to prevent such a catastrophe [mass extinction of life]?
Linkage: The article says we should focus more on saving the species that are alive today, rather than trying to bring back extinct ones. The debate about de-extinction raises the question of whether it’s better to spend resources on protecting current species instead.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Miller-Urey Hypothesis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Miller-Urey Hypothesis
Why in the News?
A recent study led by Stanford University chemist Richard Zare has introduced a novel perspective on the origins of life on Earth, providing an alternative to the well-known Miller-Urey hypothesis.

About the Miller-Urey Hypothesis
- The Miller-Urey hypothesis emerged from an experiment conducted in 1952 by chemists Stanley Miller and Harold Urey.
- It sought to simulate the conditions of early Earth to understand how life could have originated.
- They used a mixture of water, methane, ammonia, and hydrogen, gases believed to be present in the early Earth’s atmosphere.
- The setup also included an electric spark to simulate lightning, which they hypothesized could have played a role in the formation of organic compounds.
- Results: The experiment successfully demonstrated that organic molecules, like amino acids, essential for life, could form when an electrical spark (simulating lightning) was applied to the gas mixture.
- Impact and Debate:
- The experiment was a landmark in understanding life’s chemical origins.
- However, over time, critics argued that real lightning would have been rare and mostly occurred over open ocean, where organic compounds would have been quickly dispersed.
- This led to the questioning of lightning as the primary trigger for life’s origins.
Life on Earth and the Role of ‘Microlightning’ in Water Droplets
- The Stanford study shows that when water droplets divide, they develop opposing electrical charges—larger droplets become positively charged, and smaller droplets become negatively charged.
- When these oppositely charged droplets come close together, tiny sparks (termed micro-lightning) can leap between them, mimicking the electrical phenomena that occur in thunderstorms.
- Experimental Evidence:
- In the experiment, when water sprays were mixed with nitrogen, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia, they produced organic compounds like glycine and uracil, similar to those in the Miller-Urey experiment.
- Microlightning from water sprays can therefore generate organic compounds, providing a plausible and common natural process for the origin of life.
- These microlightning events could have been far more common and accessible than lightning strikes, offering an alternative mechanism for the generation of life-building organic molecules.
PYQ:
(a) Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sodium (b) Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen (c) Oxygen, Calcium, Phosphorus (d) Carbon, Sodium, Phosphorus |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
World’s first ‘Supersolid’ created from Light
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Supersolid
Why in the News?
In a groundbreaking achievement, Italian researchers have successfully transformed light into a supersolid for the first time in history.
About Supersolid
- A supersolid is a rare state of matter that behaves like both a solid and a liquid at the same time.
- While it maintains a rigid structure, similar to a solid, it can also flow like a liquid without any internal friction.
- How was a supersolid created?
- Researchers made a supersolid by combining light and matter.
- They used polaritons (a mix of light and particle pairs called excitons) to create this new state of matter.
- When these polaritons reach their lowest energy, they form the supersolid that behaves like both a solid and a liquid.
- Features of a Supersolid:
- Dual Nature: A supersolid is solid in structure but can also flow like a liquid.
- Quantum Coherence: The particles inside a supersolid work together in a special way because of quantum mechanics, creating unique behaviors.
- Zero Viscosity: It moves without any resistance, just like a superfluid, meaning it can flow freely even though it’s solid.
- Temperature Dependency: Supersolids only form at extremely low temperatures (close to absolute zero, or -273.15°C).
Applications of Supersolids
- Quantum Computing: Supersolids could help improve the performance of quantum computers, making them more stable.
- Superconductors: They might be used to create materials that allow zero-resistance electricity, improving energy transmission.
- Frictionless Lubricants: Supersolids could lead to frictionless lubricants, making machinery work more efficiently and last longer.
- Fundamental Physics: Studying supersolids helps us understand quantum physics and how particles behave under extreme conditions.
- Material Science: Supersolids could help create new materials for advanced technology, including computers, sensors, and energy storage.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Neurobiological basis of Substance Abuse Addiction
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Three-Stage Cycle of Addiction
Why in the News?
A groundbreaking study at the University of British Columbia, published in Nature Mental Health, reveals that addiction involves a complex neural circuit regulating cravings, emotions, and decision-making, shifting approaches to treatment and recovery.
Key Findings of the Research:
|
The Three-Stage Cycle of Addiction
- Binge/Intoxication Stage (Basal Ganglia – Reward Processing)
-
- Substance use triggers dopamine release, reinforcing pleasurable behaviors.
- Over time, the brain associates substance use with intense rewards, increasing dependence.
- Users experience cravings, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
- Withdrawal/Negative Affect Stage (Extended Amygdala – Emotional Distress)
-
- When substance use stops, individuals experience withdrawal symptoms like stress, anxiety, and depression.
- The brain craves relief, pushing individuals toward continued substance use to avoid discomfort.
- This stage makes quitting extremely difficult, reinforcing addiction.
- Preoccupation/Anticipation Stage (Prefrontal Cortex – Impulse Control & Cravings)
-
- The prefrontal cortex weakens, impairing decision-making and self-control.
- Cravings dominate thoughts, leading to obsessive focus on substance use.
- Despite knowing the negative consequences, individuals struggle to quit due to impaired cognitive function.
This cycle continuously repeats, making addiction a self-reinforcing loop.
PYQ:[2007] Which one of the following parts of the human brain is the regulating center for swallowing and vomiting? Options: (a) Cerebellum (b) Cerebrum (c) Medulla oblongata (d) Pons |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Genetically-Engineered Bananas to Reduce Food Waste
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RNA interference (RNAi)
Why in the News?
Scientists at Tropic, a UK-based biotech company, disabled the PPO gene in bananas slowing down the browning process while allowing normal ripening.
About the Genetically Engineered Bananas
- Genetically engineered bananas are modified using biotechnology to extend shelf life, resist browning, and enhance durability.
- These bananas stay yellow for 12 hours after peeling and are less prone to bruising.
- The modification prevents enzymatic browning, making bananas look fresh for longer without altering their ripening process.
- The modification targets polyphenol oxidase (PPO), the enzyme responsible for browning.
- By disabling PPO activity, oxidation of pigments is slowed, delaying the formation of brown spots.
Gene-Silencing Method Used:
- RNA interference (RNAi) is used to silence the PPO gene, reducing its activity without affecting overall banana development.
- RNAi introduces small RNA molecules that block PPO gene expression, preventing the synthesis of the browning enzyme.
- This method is precise and does not introduce foreign DNA, making it different from traditional genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Gene-editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 are also being explored for future crop modifications.
PYQ:[2019] ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why? 1. It is used in developing gene silencing therapies. 2. It can be used in developing therapies for-the treatment of cancer. 3. It can be used to develop hormone replacement therapies. 4. It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Wolly Mammoth Traits in Mice using Gene Editing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Wolly Mammoth
Why in the News?
Recently, Colossal Biosciences has created a “Woolly Mouse” by editing seven genes in mice embryos to mimic the cold-adaptive traits of woolly mammoths.
What are Woolly Mammoths?
|

About Woolly Mice
- The Woolly Mouse is a genetically modified laboratory mouse developed by Colossal Biosciences to test their de-extinction research.
- Scientists successfully edited seven genes, resulting in mice with thick, woolly fur, mimicking the coat of a woolly mammoth.
- Key Features of Woolly Mice:
-
- Genetically engineered for cold-resistant traits using DNA modifications.
- Long, thick, wavy fur and curled whiskers, resembling mammoth adaptations.
- Created by combining multiple genetic variants into a single organism.
- Serves as a model organism to test gene-editing techniques before applying them to Asian elephants, the closest living relatives of woolly mammoths.
Technology Used in Woolly Mouse Development:
- The CRISPR-Cas9 system was used to precisely modify DNA.
- Scientists identified genes responsible for fur texture, length, and body fat metabolism, allowing them to engineer cold-resistant traits.
- Scientists edited seven genes simultaneously, an unprecedented feat in genetic engineering.
- Key genes modified included:
- FGF5: regulates hair growth, making it longer and thicker.
- MC1R: controls hair color, giving the mice a golden hue similar to mammoth fur.
- Hair follicle structure genes: induced woolly hair texture, wavy coats, and curled whiskers.
PYQ:[2013] Recombinant DNA technology (Genetic Engineering) allows genes to be transferred: 1. across different species of plants 2. from animals to plants 3. from microorganisms to higher organisms Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) in DNA
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) in DNA
Why in the News?
Researchers have discovered a reason why certain segments of the human and mouse genomes (Tra2b gene) have remained unchanged for 80 million years. These segments, known as ultra-conserved elements (UCEs), play a vital role in regulating protein production
What are Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) in DNA?
- Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) are long, highly conserved DNA sequences (200+ base pairs) that have remained unchanged for millions of years across multiple species, including humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish.
- Key Characteristics:
- Found in both coding (gene) and non-coding (regulatory) regions of the genome.
- Do not tolerate mutations, meaning they remain identical across species for tens of millions of years.
- Many UCEs do not code for proteins but play crucial roles in gene regulation and cellular function.
- Their importance:
-
- Evolutionary Significance: Their extreme conservation suggests they are essential for survival, as any mutation would likely be harmful.
- Gene Regulation: UCEs may function as enhancers or silencers, controlling when and where genes are activated.
- Developmental Roles: They are often linked to brain development, fertility, and immune response.
- Disease Prevention: UCEs may protect against genetic disorders and cancers by stabilizing gene expression.
Why do Human and Mouse Genomes overlap?
- Humans and mice share a common mammalian ancestor that lived around 80 million years ago.
- Genomic Similarity:
- Around 85% of mouse genes have direct counterparts in humans.
- Nearly 500 UCEs are identical between humans and mice, despite millions of years of evolution.
- Many fundamental processes like cell division, metabolism, and brain function are similar between species, necessitating high conservation of crucial DNA regions.
- Medical Research:
- Because of these similarities, mice serve as a model organism for studying human genetics, diseases, and drug responses.
- UCEs help scientists understand gene function across species, leading to insights into evolution and biomedical advancements.
PYQ:[2013] Recombinant DNA technology (Genetic Engineering) allows genes to be transferred 1. across different species of plants 2. from animals to plants 3. from microorganisms to higher organisms Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is the Cancer Vaccine Russia is offering?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: mRNA (Messenger RNA)
Why in the News?
In December 2024, Russia announced the development of a new mRNA-based personalized cancer vaccine, with plans to make it available for free to patients by early 2025.
What is mRNA (Messenger RNA)?
|
What is an mRNA Cancer Vaccine?
- Unlike traditional vaccines, mRNA vaccines provide genetic instructions to train the immune system to detect and attack cancer cells.
- This technology gained prominence with the COVID-19 vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna) and is now being adapted for cancer treatment.
- These vaccines are therapeutic, designed for patients who already have cancer, not for prevention.
How do mRNA Cancer Vaccines Work?
- Cancer cells evade the immune system by suppressing immune responses.
- Immunotherapy works by enhancing the body’s natural ability to detect and destroy these cancerous cells.
- Unlike chemotherapy, which kills both healthy and cancerous cells, immunotherapy selectively targets only cancer cells, reducing harmful side effects.
- mRNA cancer vaccines are customized for each patient, targeting specific tumor antigens, making them highly personalized and potentially more effective.
- While traditional infectious disease vaccines prevent illness, mRNA cancer vaccines are therapeutic, meaning they are administered to patients who already have cancer to help their immune system fight the disease.
PYQ:[2019] RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment (BioE3) Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BioE3 Policy
Why in the News?
After the BioE3 Policy approval in August 2024, the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) held consultations with State governments on setting up biomanufacturing facilities across India.
What is the BioE3 Policy?
- It is a national initiative by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology to promote biomanufacturing and a circular bioeconomy in India.
- Biomanufacturing involves the industrial production of bio-products such as biopolymers, enzymes, smart proteins, functional foods, precision biotherapeutics, and climate-resilient agricultural products.
- It focuses on scaling up biotechnology-based industries, enhancing research and innovation, and creating employment opportunities in sustainable bio-based sectors.
- It aligns with India’s Net Zero carbon commitment and aims to make biomanufacturing a key driver of economic growth.
Objectives and Features of the BioE3 Policy
- Promoting Biomanufacturing: Establishing biomanufacturing hubs and biofoundries to produce bio-based chemicals, polymers, and enzymes.
- Strengthening R&D and Innovation: Encouraging state-driven biotechnology policies, bio-AI hubs, and technology-driven bioindustries.
- State-Centric Implementation: States will adopt at least two thematic areas under BioE3, focusing on local bio-based industries and sustainable agriculture.
- Workforce Development: Expanding biotechnology training programs in Tier-II and Tier-III cities to build a skilled workforce.
- Biosafety and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to global biosafety standards and responsible biotechnology innovation.
- Carbon Capture and Sustainability: Supporting carbon sequestration technologies and climate-resilient agriculture to mitigate climate change impacts.
- Encouraging Private Sector Investment: Creating a business-friendly environment for biotech startups, public-private partnerships, and global collaborations.
Programs Implemented Under the BioE3 Policy:
- State-Centric BioE3 Cells: Dedicated cells will be established in State departments to coordinate investments, research, and policy execution.
- Precision Biotherapeutics and Functional Foods Initiative: Research into next-generation bio-based medicines, smart proteins, and functional foods.
- Carbon Capture and Bioeconomy Models: Development of technologies for carbon sequestration and sustainable bio-based industrial processes.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between government, industry, and research institutions to drive biomanufacturing investments and commercialization.
PYQ:[2015] With reference to bio-toilets used by the Indian Railways, consider the following statements: 1. The decomposition of human waste in the bio-toilets is initiated by a fungal inoculum. 2. Ammonia and water vapour are the only end products in this decomposition which are released into the atmosphere. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Second National Gene Bank
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: First National Gene Bank
Why in the News?
As part of the Union Budget 2025-26, Finance Minister announced the establishment of a second National Gene Bank in India.
About the First National Gene Bank
|
About the Second National Gene Bank
- It aims to store over 10 lakh germplasm lines to strengthen food and nutritional security.
- It will complement the first National Gene Bank and expand genetic conservation capacity.
- It is designed to support both public and private sectors in conserving genetic diversity.
- Features and Significance:
- Largest conservation facility in India, expanding germplasm storage capacity beyond the existing 0.47 million accessions in the first gene bank.
- Ensures germplasm accessibility for future generations, preventing genetic erosion due to habitat loss or overexploitation.
- Protects India’s agricultural heritage by preserving native, traditional, and rare plant varieties.
- Aligns with global conservation efforts, including India’s Seed Vault in Chang La (Ladakh) and the Svalbard Global Seed Vault (Norway).
- Promotes ex-situ conservation, ensuring crop diversity for future breeding, research, and sustainable farming.
PYQ:[2021] What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Labrys portucalensis F11
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Labrys portucalensis F11
Why in the News?
A research team has discovered that Labrys portucalensis F11, a strain of aerobic bacteria from the Xanthobacteraceae family, can break down and transform multiple types of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), a group of persistent environmental pollutants.
About Labrys portucalensis F11
- It is a type of bacteria that can break down harmful chemicals known as PFAS (Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances).
- It was first found in contaminated soil at an industrial site in Portugal.
- Scientists have discovered that it can remove fluorine from certain chemical pollutants, making them less toxic.
- PFAS are known as “forever chemicals” because they do not break down easily in nature.
- Labrys portucalensis F11 can digest PFAS, helping to clean up polluted soil and water.
How does it work?
- It attacks the strong chemical bonds in PFAS, removing fluorine atoms.
- It uses carbon from PFAS as food, helping it grow while reducing pollution.
- It survives in oxygen-rich environments, making it ideal for cleaning up industrial waste sites.
- In 100 days, it broke down 90% of PFOS, one of the most harmful PFAS chemicals.
- Unlike most bacteria, it can also break down PFAS leftovers, making them even safer.
Back2Basics: Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)
|
PYQ:[2013] Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 and 3 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Stargardt Disease?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Stargardt Disease
Why in the News?
Researchers have created a gene-editing tool to fix ABCA4 gene mutations, offering hope for treating Stargardt disease, a rare condition that causes progressive vision loss.
What is Stargardt Disease?
- Stargardt Disease is a rare inherited eye disorder that causes progressive vision loss, primarily affecting the central part of the retina, called the macula.
- It is typically caused by mutations in the ABCA4 gene, which disrupts the body’s ability to use Vitamin A, leading to an excessive buildup of lipofuscin (yellowish-brown pigment) in retinal cells.
- The disease commonly begins in childhood or early adulthood and is usually bilateral, involving both eyes.
- Currently, there is no cure for Stargardt Disease.
Symptoms of Stargardt Disease
- Progressive vision loss, particularly affecting central vision.
- Difficulty seeing in low light (night blindness).
- Blurred or distorted vision, with colors appearing less vivid.
- Appearance of dark spots or areas of vision loss in the central visual field.
- Gradual deterioration of visual acuity, leading to potential legal blindness.
Present Scenario in India
- According to a 2023 study by L.V. Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad:
- The disease predominantly affects males and typically manifests during the second decade of life.
- Estimated prevalence: 1 in 8,000 to 10,000 individuals.
- 10.79% of patients had a family history of Stargardt disease, while 10.69% were from consanguineous marriages.
- In India, Stargardt disease is a not uncommon hereditary condition, with limited treatment options available.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Selective Gene Silencing?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Selective Gene Silencing
Why in the News?
Researchers at Columbia University found that cells can selectively switch off one parent’s copy of a gene. This may explain why some people with harmful mutations remain symptom-free, and it could lead to new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for genetic disorders.

About the Selective Silencing Mechanism:
- Selective gene silencing refers to the process where cells inactivate one parent’s copy of a gene (either maternal or paternal), resulting in an unequal contribution of the two gene copies to cellular function.
- Previously thought to be rare, recent research reveals that this phenomenon is relatively common and plays a significant role in genetic variability, disease progression, and individual health outcomes.
- Key Features:
- Inactivation can vary between different cell types (e.g., immune cells and kidney cells).
- The process is dynamic and may change over time, adding complexity to how genes function in the body.
- Approximately 1 in 20 active genes in some immune cells exhibit this selective bias.
- Implications for Health:
- This mechanism helps explain why individuals carrying the same disease-causing mutation can have vastly different symptom severities.
- It shifts the understanding of genetic diseases, emphasizing the importance of dynamic gene activity patterns alongside static genetic codes.
- The discovery opens up opportunities for novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches by focusing on gene expression rather than genetic sequences.
What are its significant applications?
- Selective Gene Manipulation: Therapies could be developed to activate healthy gene copies while suppressing diseased ones, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional genetic editing.
- Improved Understanding of Diseases: Selective gene silencing explains variability in conditions like lupus and cancer, revealing why some individuals remain symptom-free.
- Precision Medicine: By identifying individual patterns of gene expression, personalized treatment options become possible, reducing the need for one-size-fits-all approaches.
- Early Interventions: Recognizing at-risk but asymptomatic individuals allows healthcare providers to implement preventive measures and potentially delay disease onset.
- Protein-Based Therapies: Focusing on selective gene activity aids in detecting and differentiating disease-related proteins from healthy ones, paving the way for targeted, protein-specific drugs.
PYQ:[2014] Consider the following techniques/phenomena:
Which of the above is/are used to create transgenic crops? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Nanopore Technology
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nanopore-Based Tool
Why in the News?
Researchers at the University of California, have developed a nanopore-based diagnostic tool capable of detecting illnesses more quickly and accurately by analyzing signals from individual molecules.
What is the Nanopore-Based Tool?
- The Nanopore-Based Tool is a groundbreaking innovation developed by UC Riverside scientists for disease diagnostics.
- It leverages nanopores, which are tiny openings capable of detecting individual molecules like DNA and proteins.
- By measuring electrical signals generated as molecules pass through the nanopore, the tool enables ultra-sensitive and precise detection of illnesses.
How does it Work?
- Biological samples mixed with salts are introduced into the system.
- Salts dissociate into ions, creating a flow through the nanopore.
- As a DNA or protein molecule passes through the nanopore, it blocks the flow of ions.
- This blockage reduces the flow, creating electrical signals.
- The system measures the reduction in ion flow to identify the molecule.
- Advanced circuitry accounts for missed signals, ensuring precise detection.
- Nanopores filter out background noise, unlike traditional systems that require external filters, preserving critical data for accurate diagnostics.
Significance and Features of Nanopore Technology
- It helps detect infections within 24 to 48 hours, much faster than traditional methods.
- It is crucial for fast-spreading diseases, enabling timely intervention.
- It captures signals from single molecules, eliminating the need for large biological samples.
- It could revolutionize home testing and clinic-based diagnostics.
- It helps Identify subtle differences in proteins, aiding in personalized treatment plans.
- It promotes deeper understanding of how proteins impact health and disease.
- It paves the way for single-molecule protein sequencing, offering insights beyond DNA sequencing.
PYQ:[2015] With reference to the use of nanotechnology in health sector, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. Targeted drug delivery is made possible by nanotechnology. 2. Nanotechnology can largely contribute to gene therapy. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Mitochondrial Genome (mtDNA)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mitochondria, mtDNA
Why in the News?
Recent research indicates that age-related losses in our cell’s mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)—specifically, deletion mutations—could be a major driver of aging. These mutations, once they accumulate, reduce the mitochondrion’s ability to produce energy (ATP), causing cell and tissue dysfunction.

What are Mitochondria?
- Mitochondria generate most of the cell’s energy (hence called the Powerhouse) in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
- They originated from free-living bacteria absorbed by ancient single-celled organisms, retaining a fraction of their own DNA (mtDNA).
- Unlike nuclear DNA, mitochondria have their own circular DNA, though limited in size.
- Humans inherit mitochondria exclusively from the mother’s egg; sperm-contributed mitochondria are generally not passed on.
- They have a double membrane: a relatively permeable outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane (cristae) that maximizes surface area for energy production.
- Their inner compartment, the mitochondrial matrix, houses mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), ribosomes, and enzymes for the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) and fatty acid β-oxidation.
- Mitochondria help regulate intracellular calcium levels, which is crucial for various signalling pathways.
- They play a role in apoptosis (programmed cell death) by releasing factors such as cytochrome c when the cell is under severe stress.
Functions of DNA, mRNA, and the gene:
|
Functions of the Mitochondrial Genome (mtDNA):
- Encodes Key Mitochondrial Proteins:
- The mtDNA has 13 protein-coding genes crucial for mitochondrial energy production (ATP synthesis).
- It also encodes 24 non-coding genes (like rRNAs and tRNAs), essential for mitochondrial protein synthesis.
- Energy Production:
- mtDNA-encoded proteins form part of the electron transport chain, where most ATP is produced.
- Distinct Inheritance Pattern:
- Inherited exclusively from the mother.
- Each cell contains multiple mitochondria, each with multiple copies of mtDNA.
- Implication in Aging and Disease:
- Age-related mutations (deletions, chimeric genes) in mtDNA can lead to functional decline in tissues like muscle and brain.
- Loss of intact mtDNA reduces ATP generation, contributing to cellular and tissue ageing.
PYQ:[2021] In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] CAR T-Cell Therapy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAR-T Cell Therapy
Why in the News?
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has been a key supporter of research projects focusing on CAR T-cell therapies for cancers.

About CAR T-Cell Therapy:
| What is it? |
|
| Objective of the Therapy |
|
| Implementation and Structural Mandate |
|
| Future Scope for Phase II |
Future Scope: Holds the potential for expanding to other cancers, such as Multiple Myeloma, Glioblastoma, and Hepatocellular Carcinomas, based on continued research and results from Phase II trials. |
PYQ:[2022] Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (a) They protect the environmental allergens body. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
ecDNA Challenges Law of Genetics
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA)
Why in the News?
A recent study published in the ‘Nature’ has shown that Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) is present in approximately 50% of cancer types, playing a significant role in tumor evolution and genetic heterogeneity.
What is ecDNA?
| Details | • ecDNA stands for extrachromosomal DNA, which is small, circular DNA found in the nucleus of cells, separate from regular chromosomes. • Forms when DNA breaks off from chromosomes, often due to damage or errors in cell division. • Can carry extra copies of oncogenes, which promote cancer growth. • Initially thought to be unimportant, recent studies show it plays a major role in cancer. |
| How ecDNA Contributes to Cancer and Drug Resistance | • Helps Tumors Grow: ecDNA contains extra copies of oncogenes that help cancer cells grow faster and become more aggressive. • Drug Resistance: The extra oncogenes make the cancer harder to treat with standard drugs by producing more harmful proteins. • Faster Tumor Evolution: ecDNA allows cancer cells to evolve rapidly, making them more resistant to treatments like chemotherapy and enabling the tumor to grow even when drugs are used. |
How ecDNA Challenges Genetics Laws?
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] India’s First Indigenous Antibiotic: Nafithromycin
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nafithromycin
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Science & Technology has launched Nafithromycin, India’s first indigenous antibiotic to combat drug-resistant infections.
About Nafithromycin:
| Details | |
| About | • It was developed with the support of the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), a unit under the Department of Biotechnology, to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR). • It aims to treat Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia (CABP) caused by drug-resistant bacteria. ( Awaiting final approval from CDSCO for manufacturing and public use.) |
| Features | • Developed over 14 years of clinical trials in the U.S., Europe, and India. • 10 times more effective than azithromycin. (3 doses to combat Drug-Resistant Pneumonia) • Minimal side effects, no significant drug interactions, and food-independent. |
| Significance | • It targets both typical and atypical pathogens. • It addresses a global health issue, especially CABP, contributing to over 2 million deaths annually. • Offers a more effective, faster, and safer treatment for drug-resistant pneumonia. • Demonstrates successful public-private collaboration between the government and Wockhardt Pharmaceuticals. • A cost-effective solution for treating resistant infections in low-resource settings. |
PYQ:[2019] Which of the following are the reasons for the occurrence of multi-drug resistance in microbial pathogens in India?
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Caterpillar fungus
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Caterpillar fungus
Why in the News?
Recent research by scientists at the University of Nottingham’s has found that a chemical produced by a fungus growing on caterpillars may slow cancer cell growth.
What is Caterpillar fungus?
- Cordyceps militaris, also known as caterpillar fungus, is a parasitic fungus that primarily infects caterpillars and other insects.
- Found in the Himalayan region and parts of Asia, it is valued in traditional Asian medicine for its health benefits, including immune support, anti-inflammatory properties, and energy enhancement.
- It is considered a delicacy in some Asian cultures and has long been used for its purported wellness effects.
How it can slow down growth of cancer cells?
- Researchers from the University of Nottingham’s School of Pharmacy have identified cordycepin, a compound produced by Cordyceps militaris, as potentially effective in slowing cancer cell growth.
- Cordycepin works by interrupting overactive cell growth signals in cancer cells, which prevents rapid multiplication and allows for more targeted treatment.
- This approach may be less harmful to healthy tissues compared to conventional cancer treatments, offering a promising direction for targeted cancer therapies.
Other observations and significance of the species
- In addition to its traditional uses, Cordyceps militaris is significant for its role in ecological balance, helping control insect populations in forest ecosystems.
- Advances in research have enabled large-scale studies on cordycepin’s effects, with future studies focusing on derivatives of cordycepin for potentially enhanced anti-cancer properties.
- The fungus illustrates how natural compounds can contribute to sustainable medical practices, offering less toxic alternatives for disease treatment, especially in oncology.
PYQ:[2019] Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of: (a) Anti-malarial drug (b) Biodiesel (c) Pulp for paper industry (d) Textile fibre |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How Vitamin D deficiency can trigger autoimmune conditions?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Autoimmune Conditions, Vitamin D
Why in the News?
Recent research conducted by scientists at McGill University has shed light on the critical role of vitamin D in maintaining thymus health and its implications for immune function.
About Autoimmune Conditions:
|
What is Vitamin D?
- Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin crucial for the body’s ability to absorb calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, which are essential for bone health.
- It supports muscle movement, nerve function, and immune system responses. Due to its synthesis in the skin upon exposure to sunlight, it is often called the ‘sunshine vitamin’.
- The body naturally produces Vitamin D when skin is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from sunlight.
- Sources of Vitamin D:
- Fish: Salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines are rich in Vitamin D.
- Cod liver oil: A concentrated source, providing 400–1,000 IU per teaspoon.
- Mushrooms: Varieties like portobello contain Vitamin D if exposed to UV light.
- Fortified Foods: Milk, yogurt, orange juice, and cereals often have added Vitamin D.
- Egg yolks: Contain a small amount of Vitamin D.
- Common forms include Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), especially useful in autumn and winter when sunlight exposure is limited.
Significance of Vitamin D
- Bone Health: Essential for calcium absorption, which strengthens bones and prevents osteoporosis.
- Muscle and Nerve Function: Supports muscle contractions and nerve signaling between the brain and body.
- Immune System: Enhances immune defenses, helping to fight off infections by viruses and bacteria.
- Brain Health: May play a role in maintaining cognitive health, especially with aging.
- Inflammation and Pain: Helps regulate the body’s response to inflammation and pain.
- Blood Pressure: Linked to regulating blood pressure; deficiency is associated with hypertension.
Impacts of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Increases the risk of rickets in children (softening of bones) and osteoporosis in adults.
- Low levels of Vitamin D are linked to autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
- Recent studies indicate that Vitamin D deficiency can accelerate thymus aging, leading to immune dysfunction and a higher risk of autoimmune diseases.
- Deficiency has been associated with cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, depression, and chronic pain.
- Can include fatigue, muscle weakness, bone pain, and depression.
- In severe cases, deficiency may cause impaired bone growth and fracture susceptibility.
PYQ:[2011] Regular intake of fresh fruits and vegetables is recommended in the diet since they are a good source of antioxidants. How do antioxidants help a person maintain health and promote longevity? (a) They activate the enzymes necessary for vitamin synthesis in the body and help prevent vitamin deficiency. (b) They prevent excessive oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and help avoid unnecessary wastage of energy. (c) They neutralize the free radicals produced in the body during metabolism. (d) They activate certain genes in the cells of the body and help delay the ageing process. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The Gompertz Model
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gompertz Model
Why in the News?
Indian researchers have developed a predictive model based on the Gompertz Model to estimate a newborn’s birth weight using routine pregnancy scans.
What is the Gompertz Model?
- It is a mathematical model developed by English mathematician Benjamin Gompertz in the early 19th century.
-
- It was originally designed to model population growth in a constrained environment, such as a specific geographic region.
- The model uses an S-shaped (sigmoid) curve to represent growth patterns that start slowly, accelerate, and then slow again as they approach a plateau.
- Applications:
-
- Biology: The Gompertz Model is used to study tumor growth and cell population dynamics, reflecting constrained growth in biological systems.
- Epidemiology: Applied in predicting the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19, capturing how transmission rates slow with interventions.
- Ecology: Useful for modelling species population growth in habitats with limited resources, aiding conservation and ecosystem management.
- Healthcare: Recently adapted to predict foetal birth weight, helping identify potential risks associated with low or high birth weight.
- Aging Research: Employed to analyze mortality rates and lifespan patterns, contributing to studies on aging and longevity.
Recent Research and Significance
- Recent research has applied the Gompertz Model in predicting foetal birth weight using routine scans, as shown by researchers from IISER Pune and IMSc Chennai, offering a non-invasive alternative for maternal health.
- The model is used in tumor growth studies, allowing researchers to understand and predict cancer progression.
- Its predictive accuracy under constrained conditions makes it useful for biological systems, including population growth and cell dynamics.
- In healthcare, it supports early detection and intervention for conditions impacted by growth patterns, such as low or high birth weight risks.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How Tardigrades are able to resist high levels of radiation?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tardigrades

Why in the News?
- A team of researchers has discovered the genetic mechanisms that allow a newly identified tardigrades species—Hypsibius henanensis—to withstand high levels of radiation.
About Tardigrades
- Tardigrades, often called “water bears” or “moss piglets,” are tiny, water-dwelling microorganisms known for their remarkable ability to survive extreme conditions.
- They can withstand environments that would be lethal for most life forms, including:
- Extremely high and low temperatures (from near absolute zero to over 150°C),
- High levels of radiation and vacuum conditions found in space,
- Extreme dehydration (losing nearly all water in their bodies),
- High pressures (up to six times that of the ocean’s deepest trenches).
- This adaptability makes them a subject of interest for scientists, especially in understanding survival mechanisms in extreme conditions.
How Tardigrades resist High Radiations?
The researchers identified 2,801 genes involved in DNA repair. Three key factors contributing to radiation tolerance include:
- DNA Repair Protein (TRID1): Enabled the species to repair double-strand DNA breaks due to radiation.
- Gene Activation for Mitochondrial Proteins: Radiation exposure activated a gene that produced two proteins vital for mitochondrial synthesis and DNA repair.
- Antioxidant Pigments (Betalains): These pigments neutralize harmful chemicals generated by radiation within cells.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Why precision medicine in India can’t advance without biobank laws?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Significance of biobanks;
Why in the News?
Precision medicine is ushering in a new era of personalized healthcare, with its foundations taking shape during the completion of the Human Genome Project by scientists.
What is the current legal framework governing biobanks in India?
- Lack of Comprehensive Legislation: India lacks specific, comprehensive laws governing biobanks. The current framework consists of guidelines rather than enforceable laws, creating gaps in the regulation of biobanking practices.
- National Ethical Guidelines by ICMR: The Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) has issued guidelines on ethical practices in biomedical research involving human participants. However, these guidelines are not legally binding and do not address all aspects of biobanking, such as long-term storage and data sharing.
- Department of Biotechnology (DBT) Standards: The DBT has certain practices in place for data storage and analysis, but these also lack enforceability and do not fully cover issues such as informed consent and privacy.
- Absence of a Single Regulatory Authority: India currently does not have a dedicated regulatory authority to oversee biobanks, which leads to inconsistencies and limited oversight in biobanking activities.
How do privacy concerns impact biobank operations and precision medicine?
- Informed Consent Issues: Participants often give consent without detailed information about how their biological samples and associated data will be used, who will have access, and for how long. This lack of transparency raises privacy concerns.
- Genetic Data Privacy Risks: Genetic information can reveal intimate details about an individual’s health and predisposition to diseases, potentially affecting their family members. If data privacy is not robustly protected, it may lead to genetic discrimination in insurance or employment.
- Data Sharing Without Proper Regulation: In the absence of clear legal provisions, data or samples could be shared without proper consent, risking misuse by pharmaceutical companies or research organizations, including foreign entities.
- Impact on Public Trust: Weak data and privacy protections may reduce public willingness to participate in biobank projects, thus limiting the scale and diversity necessary for effective precision medicine research.
What are the ethical implications of biobanking practices in India?
- Ownership and Benefit Sharing: Without legal protections, there is ambiguity regarding the ownership of biological samples. Individuals contributing samples may not receive benefits from commercial applications resulting from their data, raising ethical concerns about fair compensation.
- Consent Transparency: Participants may not fully understand the scope of their consent, especially regarding future uses of their samples and data. This lack of clarity can be considered ethically problematic, as it may involve the exploitation of participants’ contributions.
- Risk of Misuse or Mismanagement: Inconsistent regulations and the absence of penalties for ethical violations create a risk of mishandling samples, unauthorized data access, and exploitation, which may compromise research integrity.
- Discrimination Risks: Genetic information obtained from biobanks could be used to discriminate against individuals based on their health risks or genetic traits, which raises concerns about ethical and legal safeguards.
Way forward:
- Establish Comprehensive Legislation: Develop and implement a comprehensive legal framework specifically governing biobanks, including clear guidelines on informed consent, data protection, ownership rights, and benefit sharing.
- Create a Regulatory Authority: Establish a dedicated regulatory authority to oversee biobank operations, ensuring compliance with ethical standards and legal requirements.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Combination Therapeutic Clotting Implant
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Combination Therapeutic Clotting Implant
Why in the News?
Scientists at the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, in collaboration with other researchers have developed the Combination Therapeutic Clotting Implant.
What is the Combination Therapeutic Clotting Implant?
|
How does It Work?
- The implant is created using Nano-Micro-Sera (NMS), which consists of drug and metal-based nanomedicine stabilized by the patient’s own serum protein corona.
- The hybrid implant is reinforced into autologous fibrin, which quickly bonds with damaged tissue in the tumor bed after surgery.
- Once the surgical site is closed, the implant delivers localized chemo-phototherapy, triggering immunogenic cell death (ICD).
- This process activates dendritic cells and T-cells, which boosts the body’s immune response and prevents the recurrence of tumors.
Significance of the Implant
- The implant offers an affordable and effective solution for localized post-surgical cancer management, especially for marginalized patients.
- By using the patient’s own serum proteins and fibrin, the implant ensures personalized treatment, reducing the risk of systemic toxicity.
- The implant’s design is resource-efficient, making it accessible for bedside fabrication with simple equipment, ensuring wider availability.
- It has demonstrated superior outcomes in suppressing recurrent breast tumors, and its use could prevent tumor recurrence and reducing the chances of metastasis.
PYQ:[2015] With reference to the use of nanotechnology in health sector, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. Targeted drug delivery is made possible by nanotechnology. 2. Nanotechnology can largely contribute to gene therapy. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Why you should care about Mapping of the Fruit Fly’s Brain?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brain mapping of fruit flies and its applications
Why in the News?
Researcher have successfully mapped the entire brain of an adult fruit fly, marking the first time researchers have created such a detailed map of an adult animal’s brain.
How Was the Fruit Fly Brain Mapped?
|
Key findings
- Scientists identified more than 50 million connections between 139,000 neurons (brain nerve cells).
- They classified the cells into 8,453 distinct types, making it the largest catalogue of cell types in any brain.
- The research gave insights into how different types of cells function and how the fruit fly’s eyes process motion and color.
- A group of “hub neurons” was discovered, which may help speed up information flow.
Significance of the Work
- Although the human brain is more complex, the logic of how neurons communicate is similar between fruit flies and humans.
- Fruit flies are a valuable model system for neuroscience. Their brains solve many of the same problems that human brains do.
- It could help in understanding and treat mental health conditions like Parkinson’s and depression.
- The mapping of the fruit fly’s brain raises hopes that scientists will eventually be able to map the entire human brain.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
BRCA Testing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: BRCA1Testing
Why in the News?
Angelina Jolie’s case highlighted hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) after she underwent preventive surgeries due to a BRCA1 gene mutation.
What is BRCA Testing?
- BRCA testing is a genetic test that looks for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
- These genes normally help repair DNA, but when they are mutated, they increase a person’s risk of developing certain cancers, particularly breast and ovarian cancers.
- BRCA testing identifies whether a person has inherited these mutations, which can lead to Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) and other cancers.
- The test is done using a blood or saliva sample, which is collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- In the lab, next-generation DNA sequencing or other genetic analysis methods are used to examine the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes for harmful mutations.
- The test results can show whether a person has inherited a harmful mutation in these genes.
- If the result is positive, it means they are at a higher risk for developing certain cancers.
Issues with BRCA Testing
- BRCA testing in India is expensive, costing between ₹15,000 to ₹30,000, which makes it unaffordable for many, particularly in lower-income populations.
- Testing is often only offered to individuals with a family history of cancer, which misses about 50% of people who may have the mutations but no known family history.
Significance for India
- Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in India, accounting for 27% of all cancer cases.
- Women with BRCA mutations have up to a 72% risk of developing breast cancer.
- Early identification allows for preventive measures, such as regular screenings or surgeries, which can reduce cancer incidence by up to 100%.
- By increasing access to population-wide BRCA testing, India can improve early detection and reduce the burden of cancer on its healthcare system.
- Early identification can also lower treatment costs and improve outcomes.
PYQ:[2019] ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MRSA, Vancomycin
Why in the News?
In 2019, MRSA caused over 100,000 deaths, and although vancomycin has been the main treatment for 40 years, a new study shows it may not stay effective for long.
About Vancomycin
|
How Vancomycin is losing its effectiveness against MRSA?
MRSA rarely develops resistance to vancomycin, but when it does, it leads to the emergence of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (VRSA).
- Resistance Mechanism: When S. aureus acquires the vanA operon, a gene cluster responsible for vancomycin resistance, it can resist the antibiotic. However, this resistance usually comes with a fitness cost—the bacteria tend to grow slower, making them less virulent.
- Fitness Compensation: Recent research shows that S. aureus can evolve to overcome this fitness cost, allowing VRSA to grow faster and remain resistant even in the absence of vancomycin. This adaptation means the bacteria are less likely to lose their resistance and can spread more easily.
- Mutations: The study found that additional mutations in the VRSA strains exposed to vancomycin helped the bacteria adapt and maintain resistance. These mutations made the bacteria more fit, ensuring they could thrive even in the presence of vancomycin.
- Diminishing Options: As VRSA continues to adapt, vancomycin may no longer be reliable for treating MRSA infections. This raises concerns about the long-term viability of the antibiotic, prompting the need for new treatment strategies.
PYQ:[2014] Can overuse and free availability of antibiotics without Doctor’s prescription, be contributors to the emergence of drug-resistant diseases in India? What are the available mechanisms for monitoring and control? Critically discuss the various issues involved. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
PresVu: India’s First Eye Drop for Presbyopia
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PresVu
Why in the News?
Mumbai-based Entod Pharmaceuticals has announced that the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has approved its new eye drop, PresVu, aimed at reducing the dependency on reading glasses for individuals with presbyopia.
What is Presbyopia?
|
How does PresVu work?
- The active ingredient in PresVu is pilocarpine, a compound that contracts the iris muscles, controlling the size of the pupil and helping individuals focus better on nearby objects.
- PresVu also uses an advanced dynamic buffer technology to adapt to the pH levels of tears, ensuring consistent efficacy and safety for extended use over the years.
- However, PresVu’s effects are temporary, typically lasting between four to six hours, and it is prescription-only.
- PresVu should not be used by individuals with iris inflammation.
- Regular use may lead to side effects such as:
- Itching and redness
- Eyebrow pain
- Muscle spasms in the eyes
Is this a Novel Therapy?
- Although Entod claims PresVu is novel, the main compound, pilocarpine, has been available in India for decades and is commonly used as a first-line therapy for cataracts.
- Pilocarpine’s ability to temporarily improve the depth of focus has been explored in other countries, including the United States, where the FDA approved a pilocarpine eye drop for presbyopia in 2021.
- In India, the government regulates the ceiling price of pilocarpine in 4% and 2% concentrations, whereas PresVu contains 1.25%.
PYQ:[2018] Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Yellow Food Dye can improve Cancer Treatment
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yellow Food Dye
Why in the News?
Recent research reveals that FD&C Yellow 5, a common food dye, can temporarily make tissue transparent, with potential implications for cancer treatment and medical procedures.
About Yellow Food Dye
- FD&C Yellow 5, also known as Tartrazine, is a widely used synthetic food dye found in various snacks, drinks, and processed foods.
- Approved by the FDA, it is commonly used to give products a vibrant yellow color.
How does it work?
- The dye has the ability to make tissue transparent is based on its interaction with light, specifically through the Kramers-Kronig relations, a principle in physics.
- It absorbs blue light, leaving only the red-orange spectrum visible.
- This alters the refractive index of water, causing it to match the refractive index of fats and proteins in tissue.
- When the refractive indices match, light can pass through tissue with less scattering, creating the appearance of transparency.
Potential Medical Applications of Yellow Food Dye
- Cancer Treatment: By making tissues transparent, FD&C Yellow 5 could enhance photodynamic and photothermal therapies, allowing laser light to reach deeper tissues and target cancerous cells more effectively.
- Vein Visibility: Transparent tissues could help make veins more visible, aiding in procedures like venepuncture for blood draws or injections, particularly in patients with hard-to-see veins.
- Non-invasive Diagnostics: The dye could allow doctors to visualize internal organs and structures without the need for invasive procedures like biopsies or expensive imaging technologies like CT scans or MRIs.
PYQ:[2018] Consider the following statements: 1. The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 replaced the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954. 2. The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is under the charge of Director General of Health Services in the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Gut molecule in C. Elegans Worms slows fat burning
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: C. Elegans Worm
Why in the News?
Researchers have discovered a mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) worms that explains why fat loss slows down during fasting.
Fasting and Fat Metabolism
|
About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans):
| Details | |
| Overview | A small, free-living nematode (roundworm) used as a model organism in biological research. |
| Size | Approximately 1 millimeter in length. |
| Habitat | Found in soil environments worldwide. |
| Reproduction | Primarily self-fertilizing hermaphrodites; males make up a small percentage and can mate with hermaphrodites. |
| Genome | First multicellular organism to have its genome fully sequenced; about 20,000 genes. |
| Chromosomes | Six chromosomes (five autosomes, one sex chromosome). |
| Body Plan | Approximately 1,000 cells in an adult hermaphrodite; transparent body allows for easy microscopic observation. |
| Lifespan | Around 2 to 3 weeks under laboratory conditions. |
| Research Contributions | Instrumental in discoveries related to apoptosis, RNA interference, gene regulation, and human diseases. |
PYQ:[2013] Improper handling and storage of cereal grains and oilseeds result in the production of toxins known as aflatoxins which are not generally destroyed by normal cooking process. Aflatoxins are produced by: (a) Bacteria (b) Protozoa (c) Moulds (d) Viruses |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Simple Medical Tools of an OPD Visit
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Medical devices mentioned and their working
Why in the News?
- These medical tools—thermometers, stethoscopes, weighing scales, and sphygmomanometers—are essential for diagnosing and monitoring basic health parameters.
- Each tool has its own function and specific way of operation, which helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about patient care.
Here is the list of tools used in a Doctor’s Diagnosis:
| Function | Description and Working Principle | |
| Thermometer | Measures body temperature. |
|
| Stethoscope | Listens to internal body sounds. |
|
| Weighing Scale | Measures body weight. |
|
| Sphygmomanometer | Measures blood pressure. |
|
PYQ:[2019] In the context of wearable technology, which of the following tasks is/are accomplished by wearable devices?
Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Can blood tests for cancer save more lives?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Status of Cancer in India;
Mains level: Limitation of Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED) Test;
Why in the News?
A multi-cancer early detection test can identify circulating tumour DNA or circulating tumour cells at an early stage, allowing for more effective treatment.
Status of Cancer:
- Cancer’s Impact in India: Cancer accounts for 18% of deaths from noncommunicable diseases in India, making it the second leading cause of mortality. In 2022, there were approximately 1.46 million new cancer cases, with projections indicating a 12% increase by 2025.
- Common Cancers as per GLOBOCAN: Among women, the most prevalent cancers are breast, cervical, ovarian, and colorectal.
- For men, lung, esophageal, colorectal, and stomach cancers are the most common.
- Survival Rates and Detection: Late detection of cancer significantly reduces survival rates and increases treatment costs. In contrast, early detection through screening improves treatment outcomes and quality of life.
- Countries are aligning with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals 3 to enhance early cancer detection.
- Limited screening: As per NHFS, screening is limited in India which is primarily to cervical, breast, and oral cancers, with only 0.2-2% of the population having undergone any form of screening.
What is a Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED) Test?
- A multi-cancer early detection (MCED) test is a new type of blood test that can screen for multiple types of cancer simultaneously. These tests look for cancer signals, such as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and circulating tumor cells (CTCs), released by cancerous cells into the bloodstream at early stages.
Role of Blood-based tests in the detection of cancer:
- Early Detection of Multiple Cancer Types: Blood tests, particularly multi-cancer early detection (MCED) tests, can identify cancer signals from over 50 different types of cancer, including those that currently lack effective screening methods.
- For example, a recent study demonstrated that a new blood test could detect 93% of stage 1 cancers in men and 84% in women by analyzing protein biomarkers.
- Non-Invasive and Accessible Screening: Blood tests are non-invasive and can be performed with a simple blood draw, making them more accessible compared to traditional screening methods like colonoscopies or imaging tests. This ease of use encourages more individuals to participate in screening.
Limitation of blood test in the detection of Cancer:
- Lack of Proven Mortality Benefit: It is still unclear whether detecting cancers earlier with MCED tests will actually reduce cancer deaths. More research is needed to determine if earlier treatment based on MCED results improves outcomes compared to waiting for symptoms to develop.
- Regulatory Challenges: MCED tests are not yet approved by regulatory bodies like the U.S. FDA or India’s CDSCO because of not undergone rigorous premarket review to prove they benefit patients.
- False Positives: One significant risk is false positive results, where the test indicates cancer when none is present. When multiple tests are used for screening, the false positive rate can be as high as 50%.
Way forward:
- Strengthening Screening Infrastructure and Research: India should invest in expanding its cancer screening infrastructure, ensuring that more types of cancer are included beyond cervical, breast, and oral cancers.
- Public Awareness and Regulatory Preparedness: Increasing public awareness about the importance of early cancer detection is crucial. At the same time, regulatory bodies like CDSCO should establish clear guidelines and frameworks for the evaluation, approval, and monitoring of MCED tests.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is the Hayflick Limit?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hayflick Limit
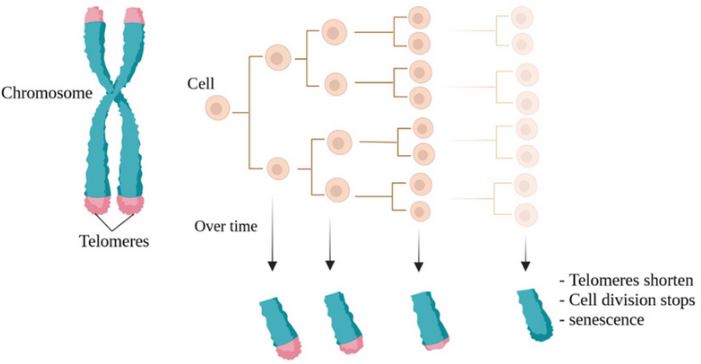
Why in the News?
Leonard Hayflick, the renowned biomedical researcher who made a discovery about the limits of cell division in somatic cells (Hayflick Limit) has passed away at 98.
What is the Hayflick Limit?
- In the early 1960s, Hayflick discovered that somatic (non-reproductive) cells have a finite number of divisions, typically between 40-60 times.
- This phenomenon, the ‘Hayflick limit’ suggests that aging occurs because cells eventually stop dividing.
- This leads to the accumulation of senescent cells that contribute to the aging process.
- The “ultimate Hayflick limit” for humans is estimated to be around 125 years.
- Beyond this, no amount of lifestyle changes or medical interventions can extend the human lifespan.
- Hayflick’s discovery has been applied to cells from various animals, revealing different Hayflick limits based on species’ lifespans.
- Ex. Galapagos turtles, have cells that can divide approximately 110 times, whereas laboratory mice have a much lower limit of around 15 divisions.
Broader Implications and Research
- Hayflick’s discovery led to the discovery of telomeres in the 1970s.
- Telomeres are protective DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes, which shorten with each cell division.
- When telomeres reach a critical length, cell division stops, which correlates with the Hayflick limit.
- In the 1980s, scientists discovered telomerase, a protein capable of replenishing telomeres, which is naturally active in cancer cells, allowing them to bypass the Hayflick limit.
PYQ:[2011] Regular intake of fresh fruits and vegetables is recommended in the diet since they are a good source of antioxidants. How do antioxidants help a person maintain health and promote longevity? (a) They activate the enzymes necessary for vitamin synthesis in the body and help prevent vitamin deficiency (b) They prevent excessive oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and help avoid unnecessary wastage of energy (c) They neutralize the free radicals produced in the body during metabolism (d) They activate certain genes in the cells of the body and help delay the ageing process |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Waggle Dance of Bees
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Waggle Dance of Bees
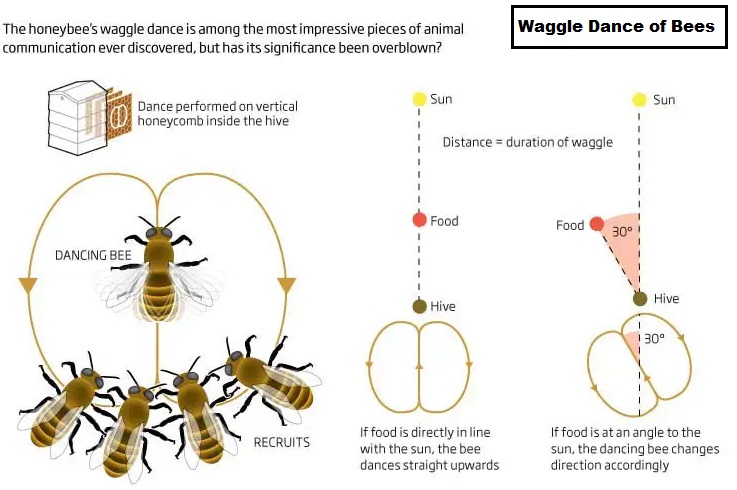
Why in the News?
Two scientists have raised concerns about “problematic behaviour” in papers on honeybee communication co-authored by Dr. Mandyam Srinivasan, a highly honoured neuroscientist.
About Waggle Dance of Bees
| Details | |
| Purpose | Communicates location of food sources to other bees. |
| Dance Pattern | Figure-eight (8) movement with a waggle run in the middle. |
| Direction Indication | Angle of waggle run shows direction relative to the sun. |
| Distance Indication | Duration of waggle run indicates distance to the food source. |
| Efficiency | Enhances foraging efficiency by guiding bees directly to food sources. |
| Environmental Impact | Accuracy affected by Sun position, wind, and landscape. |
| Scientific Importance | Decoded by Nobel laureate Karl von Frisch; an example of advanced insect communication. |
PYQ:[2023] Which of the following organisms perform waggle dance for others of their kin to indicate the direction and the distance to a source of their food? (a) Butterflies (b) Dragonflies (c) Honey Bees (d) Wasps |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Extremophile bacteria have learnt to survive microwaves
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Extremophile bacteria
Why in the News?
Researchers have isolated extremophile bacteria from harsh environments like volcanic vents, permafrost, acid mines, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and lakes beneath polar ice caps.
What are Extremophiles?
- Extremophiles are microorganisms that thrive in extreme environmental conditions where other life forms typically cannot survive.
- For example: Volcanic vents, Permafrost, Acid mines, Deep-sea hydrothermal vents, dark lakes buried beneath polar ice caps, on the exteriors of spacecraft, around nuclear waste storage sites.
Adaptation and Evolution:
- Extremophiles have developed unique biological and biochemical processes over millions of years to adapt to diverse habitats.
- Unlike more complex life forms, which have one set of proteins, extremophiles have multiple sets of proteins, each adapted to specific environmental conditions.
- These proteins are ‘activated’ based on the surrounding environment, enabling survival during extreme conditions like high temperatures, lack of water, or high acidity.
- Significance: Some scientists believe that life on Earth may have begun as an extremophile in extreme environmental niches before spreading and adapting to more temperate ecosystems.
About the ‘Earth Microbiome Project’
|
PYQ:[2017] With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? 1. Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants. 2. This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants. 3. It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The hormone Oestrogen
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Oestrogen, KISS1 neurons, CCN3 hormones
Why in the News?
- “Osteoporosis” is a condition where bones become weak and brittle, with over 10 million cases annually in India.
- It predominantly affects ageing women due to decreased oestrogen levels post-menopause.
| A recent study in Nature by researchers at the Universities of California uncovered a brain-derived hormone, CCN3, which increases bone mass in postpartum lactating mothers. |
What is Oestrogen?
|
Role of Oestrogen in Bone Growth
- Oestrogen is crucial for bone growth and formation, acting as a manager signaling the bone construction crew.
- During breastfeeding, oestrogen production drops to focus on milk production, which should weaken bones.
- Contrary to expectations, mothers’ bones become stronger to meet their babies’ high calcium demands.
How does the ‘Hidden’ Hormone Keep Mice Mothers’ Bones Healthy?
- During breastfeeding, the body suppresses oestrogen production to focus on milk production, which should weaken bones.
- Despite low oestrogen, mothers’ bones strengthen.
| Researchers found that KISS1 neurons in the hypothalamus (a part of the brain) release the CCN3 hormone, which helps maintain and even increase bone mineralisation. |
Experimental Findings:
- In experiments with genetically modified mice, those lacking the oestrogen receptor alpha still maintained healthy bones due to CCN3.
- When CCN3 was introduced to skeletal stem cells, it significantly increased bone formation, showing its potential to strengthen bones independently of oestrogen.
PYQ:[2019] ‘RNA interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. Why?
Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The Physics of Pressure
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pressure and its impacts
Why in the News?
- Pressure is an indispensable part of life, often unnoticed but always present.
- It’s the interaction of microscopic particles with the macroscopic world, creating phenomena like air pressure.
What is Pressure?
|
Everyday Examples of Pressure
(1) Measuring Blood Pressure:
- Blood pressure, measured in mm of mercury (mmHg), is an example of pressure in a different context.
- Blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomanometer, which balances the pressure in an arm cuff with the pressure of the blood in the arteries.
- The readings, such as 120/80 mmHg, represent the pressure during heartbeats (systolic) and between beats (diastolic).
- Mercury, being 15 times heavier than water, allows for portable blood-pressure machines.
(2) Pressure Cookers:
- The whistle of a pressure cooker is a direct result of the increased pressure cooking the food efficiently.
- The pressure cooker exemplifies the practical application of pressure in cooking, making it an indispensable kitchen tool.
PYQ:[2021] In a pressure cooker, the temperature at which the food is cooked depends mainly upon which of the following? 1. Area of the hole in the lid 2. Temperature of the flame 3. Weight of the lid Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
‘Zombies’ in our Genes helped us evolve
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Endogenous Retroviruses and their significance in human evolution
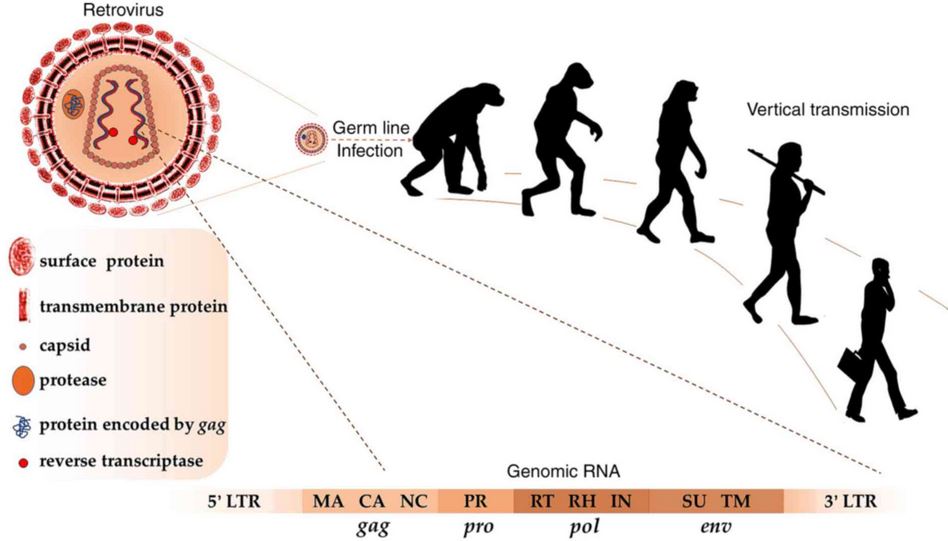
Why in the News?
Research suggests that around 8% of the human genome is composed of Endogenous Retroviruses (ERVs) often referred to as ‘zombie’ regions.
Retroviruses and Human Genome Integration
|
What are Endogenous Retroviruses (ERVs)?
- ERVs are remnants of ancient viral infections that have integrated into the genome of the host species.
- When these retroviruses infect germ cells (sperm or egg cells), their genetic material can be passed down to the next generation, becoming a permanent part of the host’s DNA.
- Zombie Regions:
- They refer to inactive viral sequences within the genome that no longer produce functional viruses but remain as embedded genetic fossils.
- These regions are a result of retrovirus integration that has lost its ability to replicate and produce proteins, yet they persist in the host’s DNA.
Evolutionary Significance of ERVs:
- In the life cycle of a retrovirus, reverse-transcribed DNA is integrated into the host’s DNA with the help of integrase.
- The viral DNA, called a provirus, hijacks human cells, turning them into virus-making factories.
- Over tens of thousands of years, many retroviruses have left genomic elements in human genome, contributing to evolutionary processes.
- Example:
- Syncytins are genes thought to have descended from ERVs and are crucial for placental development. These genes originally came from viruses and were acquired during mammalian evolution.
Their Contribution to Human Biology
- ERVs are highly expressed in the placenta and may influence conditions like preeclampsia.
- Researchers found that a particular RNA derived from an ERV is dysregulated in early-onset preeclampsia, suggesting it could be used as a biomarker for the condition.
- ERVs play a role in cell-type differentiation during embryo development.
- A protein called MERVL-gag is derived from an ERV. This transition is crucial for producing pluripotent stem cells capable of forming different cell types.
- Researchers also found that a human ERV element LTR10 affects tumour formation in colorectal cancer.
PYQ:[2021] Consider the following statements : 1. Adenoviruses have single-stranded DNA genomes whereas retroviruses have double-stranded DNA genomes. 2. Common cold is sometime caused by an adenovirus whereas AIDS is caused by a retrovirus. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Surprising ‘Dark Oxygen’ discovery could ensnarl deep-sea mining
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About Dark Oxygen
Mains level: Impact of Deep-Sea Mining
Why in the News?
Scientists reported on July 22 in Nature Geoscience that an unknown process is generating oxygen in the deep oceans, where photosynthesis is not possible due to the lack of light.
About the recent study:
- Discovery of Oxygen: Scientists reported an unknown process producing oxygen in the deep ocean, specifically in the abyssal zone, where photosynthesis is not feasible due to insufficient sunlight.
- Location of Study: The study was conducted in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, located off Mexico’s west coast, which is known for having the highest concentration of polymetallic nodules.
- Oxygen Measurement: At a depth of 4 km, researchers observed unexpected increases in oxygen levels, sometimes tripling within two days, contrary to expectations of decreasing levels due to consumption by marine life.
- Source of Oxygen: The researchers hypothesized that the oxygen could be generated by polymetallic nodules, which may create electric charges that split water molecules, releasing oxygen. The nodules exhibited voltages up to 0.95 V, suggesting they could function like battery cells.
What is Deep-Sea Mining?
- Deep-Sea Mining: It involves extracting minerals from the ocean floor at great depths, targeting resources such as polymetallic nodules, polymetallic sulphides, and cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts.
Economic and Strategic Importance of Deep-sea Mining:
- Resource Potential: The Clarion-Clipperton Zone holds substantial reserves, including 6 billion tonnes of manganese, and over 200 million tonnes each of copper and nickel, making it a significant target for future mining operations.
- International Contracts: The International Seabed Authority has granted exploration contracts to various contractors, including the Government of India, for deep-sea mining activities.
What is Dark Oxygen?
- “Dark oxygen” refers to the oxygen found in the deep ocean, specifically in regions where photosynthesis cannot occur due to the absence of sunlight. In such areas, known as the abyssal zone, oxygen levels are typically low and depend on global ocean circulation for replenishment.
Impact of Deep-Sea Mining
- Ecological Concerns:
- Potential Damage: The recent findings highlight the potential risks of deep-sea mining to unique marine ecosystems that depend on ‘dark oxygen’. There is concern that mining could disrupt these ecosystems, leading to significant and possibly irreversible environmental impacts.
- Historical Evidence: Previous experiments, such as the DISCOL Experiment, have shown long-term ecological damage from simulated mining activities, including reduced biodiversity and altered sedimentological profiles.
- Industry Response and Challenges:
- Insurance Withdrawal: In response to growing concerns, major European insurance companies announced they would exclude deep-sea mining from their underwriting portfolios.
- Sustainability Issues: The new discovery of ‘dark oxygen’ adds complexity to the debate on deep-sea mining. If sustainable practices are not implemented, such mining could become unfeasible due to its potential negative impacts on marine ecosystems.
Way forward:
- Develop Comprehensive Environmental Regulations: The Government should establish and enforce robust environmental regulations and impact assessment protocols for deep-sea mining.
- Promote Sustainable Mining Practices: Need to invest in research and innovation to develop and implement technologies and methods that minimize environmental impact.
Mains PYQ:
Q Coastal sand mining, whether legal or illegal, poses one of the biggest threats to our environment. Analyse the impact of sand mining along the Indian coasts, citing specific examples. (2019)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Could Pythons be a Protein alternative?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Python Farming
Why in the News?
- In the farmlands of central Thailand, thousands of pythons are raised in a warehouse for their diamond-patterned skins, which are sold to high-end European fashion houses.
- Some scientists and industry insiders believe the true value of these snakes lies in their meat.
Python Farming in Asia
- Researchers estimate that China and Vietnam alone have at least 4,000 python farms, producing several million snakes primarily for the fashion industry.
- A study published in Nature highlighted python farming as a flexible and efficient response to global food insecurity.
Benefits of Python Farming
- Pythons can survive for months without food or water and maintain their condition.
- They were fed waste chicken and wild-caught rodents, offering a more efficient feed-to-meat ratio than poultry, beef, and even crickets.
- Female pythons can lay between 50 and 100 eggs annually, leading to rapid reproduction.
Advantages of Python Meat
- Pythons offer a more efficient feed-to-meat ratio than poultry, beef, and even crickets.
- They can survive without food and water for months without losing condition.
- Python meat has a chicken-like texture and is low in saturated fats.
- It could provide a sustainable protein source with a lower environmental impact compared to traditional meat.
Challenges and Market Acceptance
- Despite the advantages, the market is limited for python meat.
- Python farmers struggle to convince people to consume snake meat, resulting in most of it being discarded or sold to fish farms.
Environmental Impact of Traditional Meat
Python Meat as an Alternative
|
PYQ:[2018] How far do you agree with the view that the focus on lack of availability of food as the main cause of hunger takes the attention away from ineffective human development policies in India? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
100 years of Electroencephalography (EEG)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: EEG and its working
Why in the News?
This year marks the 100th anniversary of the first human electroencephalography (EEG) by German physiologist Hans Berger.
Historical Development of EEG
|
What is EEG?
- EEG stands for electroencephalography. “Electro” means electricity, “encephalo” refers to the brain, and “graphy” means recording.
- It tracks the electrical activity in the brain that happens when neurons, the brain’s cells, move tiny charged particles.
- This helps doctors tell if the brain is working normally or not.
- Doctors use EEG to diagnose epilepsy, check how deep a person is under anesthesia, study sleep patterns, and even confirm if a person has passed away.
Understanding Volume Conduction
- Volume conduction explains how the brain’s electrical signals move through different layers like skin and bone to reach the electrodes on the scalp.
- The signals that electrodes pick up need to be cleaned up from any distortions caused by these layers or other noises before doctors can read them accurately.
How does an EEG Test Works?
- Neurons interact with their surroundings and sometimes push ions around.
- This movement creates waves of electrical activity.
- Electrodes on the head detect these waves and measure how strong they are, which is then recorded as an EEG.
- Setting up an EEG involves putting gel on the head and placing electrodes accurately, which can be affected by things like having thick hair.
What EEG Can and Can’t Show?
- Strengths: EEG is very good at catching fast changes in the brain’s electrical activity, which is helpful for immediate observations.
- Limitations: It mainly detects signals from the surface of the brain and is better at picking up signals from certain types of cell parts than others.
- Pinpointing exactly where the brain an activity started can be difficult.
Cost and Accessibility
- EEG is simple and affordable compared to other methods like MRI.
- It’s portable, doesn’t use large equipment, and is safe.
PYQ:[2015] With reference to ‘Near Field Communication (NFC) Technology’, which of the following statements is/are correct? 1. It is a contactless communication technology that uses electromagnetic radio fields. 2. NFC is designed for use by devices which can be at a distance of even a metre from each other. 3. NFC can use encryption when sending sensitive information. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) Cases in Kerala
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM); Naegleria fowleri.
Why in the News?
There have been four cases, including three deaths, of the rare, but fatal brain-eating primary amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) in Kerala in the last two months.
What is Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM)?
- PAM is a rare brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba found in warm freshwater and soil worldwide.
- An amoeba is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods.
- Higher temperatures of up to 115°F (46°C) are conducive to its growth and it can survive for short periods in warm environments.
- The amoeba enters the body through the nose, typically during activities like swimming, and travels to the brain, causing severe damage.
- PAM is also non-communicable.
- Symptoms: Headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, confusion, seizures, hallucinations, and coma.
- According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), most people with PAM die within 1 to 18 days after symptoms begin. It usually leads to coma and death after 5 days.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Currently, there are no established effective treatments for PAM.
- Diagnosis involves PCR tests of cerebrospinal fluid, though detection can be challenging due to the rarity of PAM.
- Treatment follows CDC guidelines, including miltefosine, Azithromycin, and Amphotericin B, with miltefosine recently procured by the State Health Department from Germany.
- Medical interventions typically involve a combination of drugs, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What makes mosquitoes suck blood?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diseases spread by Mosquitoes; Factors driving mosquito evolution.
Why in the News?
A study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) 1 has suggested that a pair of hormones work together to activate or suppress mosquitoes’ blood cravings.
Mosquito Species and Behavior
- There are around 3500 mosquito species globally, found on every continent except Antarctica.
- Female mosquitoes consume blood to aid in egg development.
- After feeding, female mosquitoes lose their appetite for blood until they lay their eggs.
Research by Michael Strand and Team
- Strand observed that levels of the mosquito gut hormone F (NPF) spiked when mosquitoes were seeking a host and dropped after feeding.
- Their study analyzed mosquito enteroendocrine cells responsible for gut hormone production.
- Hormonal Mechanisms:
-
- NPF levels increased before blood meals and decreased six hours after feeding.
- Another gut hormone, RYamide, was found to influence mosquitoes’ blood lust. As NPF levels decreased after a blood meal, RYamide levels increased, and vice versa.
- The researchers concluded that NPF and RYamide work together to regulate mosquitoes’ attraction to humans and other hosts.
Implications of the Study
- Controlling the Deadliest Animal: Mosquitoes are the deadliest animal on the planet, acting as vectors for diseases such as malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, yellow fever, Zika, chikungunya, and lymphatic filariasis, which collectively kill more people than any other creature.
- Pesticide Development: The discovery could lead to new pesticide targets for preventing mosquito reproduction and disease transmission.
Note: Mosquitoes are responsible for over 1 million human deaths per year worldwide. They transmit deadly diseases like malaria, yellow fever, dengue, and Zika virus
PYQ:[2023] ‘Wolbachia method’ is sometimes talked about with reference to which one of the following? (a) Controlling the viral diseases spread by mosquitoes |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Metal Oxide Nano-composite developed for Environmental Clean-up
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NiTF Nanocomposite; Nanotechnology.
Why in the News?
A new metal oxide nanocomposite has been developed by The Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) that can help photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants like dyes and pharmaceuticals and hence can be used as sustainable technologies for cleaning up the environment.
Understanding Photocatalysis and Metal Oxides
- Photocatalysis is a process that uses light to accelerate chemical reactions, particularly useful for degrading harmful substances in water and air.
- They facilitate this reaction without being consumed.
- Examples: Titanium Dioxide (TiO2), Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and Tungsten Trioxide (WO3)
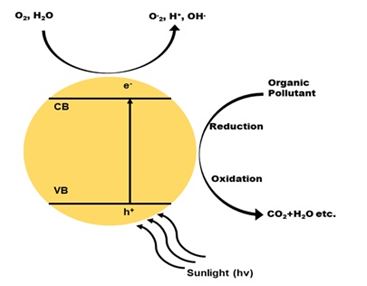
How do they work?
- When exposed to light, these metal oxides generate electron-hole pairs.
- These pairs are highly reactive and can break down pollutants into harmless by-products.
- Work Efficiency: The overall efficiency of this process depends on several factors, including the choice of metal oxide, its crystal structure, light intensity, pollutant concentration, pH level, and the amount of catalyst used.
- Optimisation: Optimizing these factors is crucial for maximising the degradation rates of pollutants. Adjustments in the type of metal oxide, light parameters, and other conditions can significantly enhance the photocatalytic efficiency.
Breakthrough by IASST: NiTF Composite
- The team developed a nanocomposite called NiTF, which stands for Nickel-doped Titanium Dioxide on Fuller’s Earth.
- This innovative material combines the photocatalytic properties of titanium dioxide with the adsorption capabilities of Fuller’s earth, a type of natural clay.
What is Fuller Earth?
|
Testing and Results
- The NiTF nanocomposite was tested for its ability to decolorize methylene blue, a common dye.
- Methylene blue is a persistent pollutant toxic to aquatic life, harmful to human health, and causes colour pollution in water bodies.
- The results were impressive, with the composite achieving a 96.15% decolorization of the dye solution at a pH of 9.0 under visible light within 90 minutes.
- Fuller’s earth enhanced the TiO2’s ability to adsorb pollutants, even in the absence of light.
- This suggests that the NiTF nanocomposite could be a cost-effective solution for environmental photocatalysis, providing benefits even in low-light conditions.
Potential Applications
- Catalysis: The nanocomposite can enhance the efficiency of various chemical reactions.
- Energy Storage: It has the potential to improve systems for storing energy.
- Sensors: The material can be used to develop highly sensitive detection devices.
- Optoelectronics: The nanocomposite can advance technologies that use light for electronic devices.
- Biomedical Fields: It can be applied in medical treatments and diagnostics.
- Coatings: The material can be used to create protective and functional surfaces.
- Renewable Energy: It can facilitate water splitting to produce renewable energy.
PYQ:[2015] With reference to the use of nanotechnology in the health sector, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Motor Neuron Disease (MND)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MND and its causes; NIMHANS.
Why in the News?
The annual conference on Motor Neuron Disease (MND) ‘Awareness, Care and Management’ was held at NIMHANS.
What is Motor Neuron Disease (MND)?
- MND is a condition that affects the nerves in the brain and spinal cord, which are responsible for controlling your muscles.
- Over time, these nerves (called motor neurons) stop working properly, leading to muscle weakness and wasting away.
Types of MND:
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): The most common type. It affects both upper and lower motor neurons, leading to weakness in various body parts.
- Progressive Bulbar Palsy (PBP): Affects the nerves in the brainstem, leading to problems with speaking and swallowing.
- Progressive Muscular Atrophy (PMA): Affects only the lower motor neurons, causing muscle weakness and wasting.
- Primary Lateral Sclerosis (PLS): Affects only the upper motor neurons, causing stiffness and movement difficulties.
Causes of MND:
- Genetic Factors: In some families, MND can be inherited due to specific gene mutations.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins, viruses, or physical injuries might contribute, but this is less clear.
- Age and Gender: It usually affects people between the ages of 50 and 70 and is slightly more common in men.
Symptoms:
- Muscle Weakness: Starts in one part of the body, like an arm or leg, and gradually spreads.
- Muscle Cramps and Twitching: Small, involuntary muscle movements.
- Difficulty Speaking and Swallowing: Due to weakness in the muscles used for these functions.
- Breathing Problems: In advanced stages, muscles that control breathing can be affected.
- Emotional Changes: Some people might experience changes in behavior or thinking.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: A doctor examines your symptoms and medical history.
- Electromyography (EMG): Tests the electrical activity of your muscles.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Checks how well your nerves send signals.
- MRI: Scans to rule out other conditions.
- Genetic Testing: To check for inherited forms of MND.
Treatment:
There is no cure for MND, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Medications:
- Riluzole: Can slow down the progression of ALS.
- Edaravone: Another drug that may slow down the decline in daily activities.
- Symptomatic Treatments: For muscle cramps, excess saliva, and emotional symptoms.
- Therapies:
- Physical Therapy: Helps maintain muscle strength and mobility.
- Occupational Therapy: Aids in performing daily activities.
- Speech Therapy: Assists with speech and swallowing difficulties.
- Respiratory Therapy: Supports breathing issues.
Back2Basics: National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro-Sciences (NIMHANS)
| Details | |
| Location | Bangalore, India |
| Affiliation | Autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India |
| Ranking | Ranked 4th best medical institute in India by the “National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF)” |
| History |
|
| Governance |
|
| Funding | Receives resources for academic and research activities from national and international funding organisations. |
| Outreach |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
AMRSense Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMRSense Project, AMR, National Programme on AMR Containment
Why in the News?
- The AMRSense Project of the IIIT-Delhi has won the joint second prize in Trinity Challenge’s competition focused on combating Antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- The project shares the £600,000 joint second prize with ‘OASIS: OneHealth Antimicrobial Stewardship for Informal Health Systems,’ also from India.
The Trinity Challenge
|
What is the AMRSense Project?
- The AMRSense is aimed at addressing the critical issue of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) through a comprehensive and proactive approach.
- The project focuses on empowering communities, particularly Community Health Workers (CHWs), with tools and strategies to enhance AMR surveillance and management.
- It seeks to bridge the gap in data collection and evidence-based interventions at the community level in India.
- Collaborators: The project involves collaboration with CHRI-PATH, 1mg.com, and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
Four Components of AMRSense:
- Community Engagement: AMRSense empowers CHWs with AI-assisted tools for accurate and simplified data collection related to AMR. This helps in improving the quality and reliability of AMR data gathered from local communities.
- Data Integration: The project integrates various sources of AMR-related data, including antibiotic sales, consumption patterns, and WHONet-compliant surveillance data. This integration is facilitated through open-source tools and APIs, aiming to create a unified AMR data ecosystem.
- Predictive Analytics: AMRSense employs federated analytics across the OneHealth ecosystem. This approach provides integrated insights into AMR trends, facilitating proactive decision-making and interventions to manage and mitigate AMR risks.
- AMRaura Scorecard: This tool is designed to monitor and evaluate AMR trends over time. It helps in assessing the effectiveness of interventions and guiding targeted strategies to combat AMR effectively.
Impact and Future Prospects
- AMRSense aims to fill gaps in CHW awareness, training, and motivation, enhancing community-level AMR data collection and management in India.
- The project’s comprehensive approach seeks to foster proactive AMR surveillance and management practices.
National Programme on AMR Containment
|
PYQ:[2020] What is the importance of using Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines in India? 1. These vaccines are effective against pneumonia as well as meningitis and sepsis. 2. Dependence on antibiotics that are not effective against drug-resistant bacteria can be reduced. 3. These vaccines have no side effects and cause no allergic reactions. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CRISPR Cas9 Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/india-getting-close-to-developing-gene-therapy-for-sickle-cell-disease-say-officials/article68308487.ece
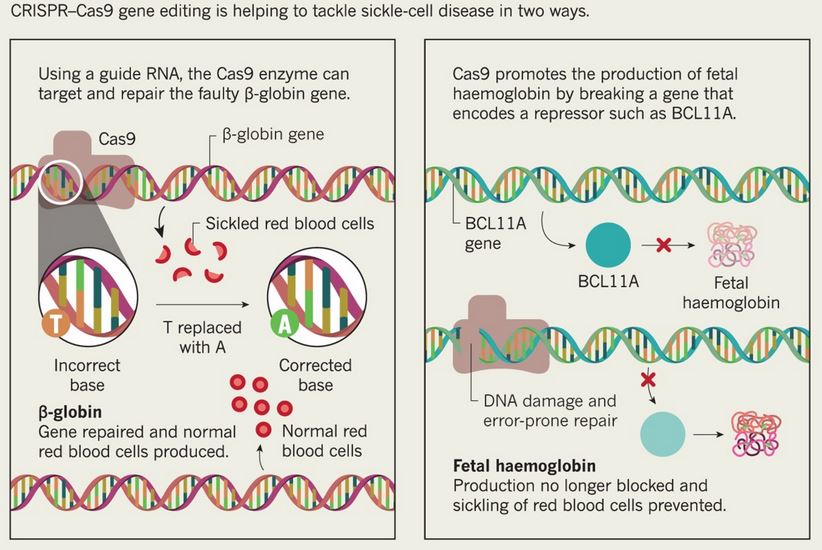
Why in the News?
- India is close to developing a gene therapy using CRISPR-Cas9, a gene-editing tool for sickle cell disease (SCD).
- SCD is a genetic blood disorder prevalent among the Scheduled Tribes.
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
- Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited blood disorders caused by a genetic mutation in the hemoglobin-β gene located on chromosome 11.
- This mutation results in defective hemoglobin, which forms rod-like structures after releasing oxygen.
- As a result, red blood cells become rigid and assume a sickle shape.
- The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the abnormal gene for a child to inherit it.
- Symptoms may not manifest immediately in newborns but can include extreme tiredness, fussiness, swollen hands and feet, and jaundice.
- Implications:
-
-
- The mis-shapen RBCs can block small blood vessels, leading to impaired blood flow and causing chronic anaemia.
- Individuals with SCD often experience acute pain episodes, severe bacterial infections, and tissue damage due to inadequate blood supply.
-
- Treatment:
-
- Presently treatment includes medications for pain relief, regular blood transfusions to replace damaged red blood cells.
- In rare cases, a bone marrow or stem cell transplant, which carries significant risks, is recommended.
Eliminating Sickle Cell Disease: Global and National Context
- This progress follows the approval of CRISPR-Cas9 technology by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for a cell-based gene therapy to treat sickle cell disease in December 2023.
- One of the main challenges for India is to develop a cost-effective therapy, as part of its mission to eradicate sickle cell disease by 2047, launched by Prime Minister in July 2023.
- The mission aims to conduct over 7 crore screenings among vulnerable tribal populations across 17 States and Union Territories, with three crore screenings completed so far.
Back2Basics: CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
|
PYQ:[2023] Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anaemin Mukt Bharat Strategy :
How many of the statements given above are correct? (a) Only one |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Scientists back new Alzheimer’s drug: Benefits vs Risks
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: How Does Donanemab Work?
Why in the News?
Donanemab, a new Alzheimer’s disease therapy developed by Eli Lilly, has gained unanimous support from independent scientists advising the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), moving it closer to clinical use.
What is Donanemab?
How Does Donanemab Work?
|
How do the benefits of the drug stack up against its risks?
- Target Population: The drug is intended for those in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease (mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia).
- Benefits: Significant clinically meaningful slowing of the disease, allowing patients to retain their functions for a longer time. Phase 3 study shows a 35.1% slowdown in cognitive decline in early Alzheimer’s patients over 76 weeks.
- Risks: Main adverse effects include brain swelling (24%) and brain bleeds (19.7%), with most cases being asymptomatic.Three treatment-related deaths reported.Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) like brain bleeds and seizures were mostly non-serious and resolved after discontinuation of therapy.
- Risk Management: The key risks can be mitigated through appropriate labeling and clinical monitoring. Further risks will be characterized through post-authorization studies.
Why is a breakthrough of this kind important?
- Rising Burden of Alzheimer’s: The global population is ageing, leading to an increased burden of diseases like Alzheimer’s. In India, 5.3 million people are currently living with dementia, expected to rise to 14 million by 2050.
- Lack of Effective Treatments: There are limited options for disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s. Innovations like donanemab are crucial for providing new hope and potential therapies.
- Economic Considerations: While the drug is expensive, it offers the potential for several more years of quality life for patients.
Why was the approval for the drug delayed?
- Additional Data Requirements: The USFDA wanted to understand further the data relating to the therapy, especially regarding the limited dosing protocol used during trials.
- Limited Dosing Protocol: During the trial, therapy was stopped in patients who achieved a certain level of amyloid beta plaque clearance, which is a distinguishing feature of donanemab compared to other therapies.
- Previous Drug Approval Irregularities: Scrutiny increased after irregularities were found in the approval process of the first drug, aducanumab, which involved close collaboration between the regulator and the drugmaker and approval despite negative trial outcomes. The second drug, lecanemab, also had cautious optimism from doctors due to its demonstrated efficacy with fewer side effects.
Conclusion: Ensure rigorous and transparent review processes for new Alzheimer’s treatments, incorporating comprehensive data analysis and post-authorization studies to monitor long-term safety and efficacy.
Mains PYQ:
Q Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? (UPSC IAS/2017)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
N332-GT5 and eOD-GT8: Advancements in HIV Vaccine Development
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: N332-GT5, eOD-GT8, HIV-AIDS
Why in the News?
Researchers at the Duke Human Vaccine Institute have successfully induced broadly neutralising antibodies (bNAbs) against HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) through vaccination for the first time.
About HIV/AIDS:
Causes:
Symptoms:
Vaccines Development:
|
How B cells and mRNA play distinct roles in the context of HIV infection?1. B cells (B lymphocytes):
2. mRNA (messenger RNA):
|
N332-GT5 and eOD-GT8: The New Vaccines in Making
- N332-GT5: This vaccine candidate targets a specific region on the surface of the HIV virus known as the N332 glycan site. By engaging B-cells that have the potential to produce bNAbs against this site, N332-GT5 aims to stimulate the immune system to generate a protective response against a wide range of HIV strains.
- eOD-GT8: Similarly, eOD-GT8 is designed to target another region on the HIV virus, known as the eOD protein. By leveraging nanoparticles as carriers, eOD-GT8 aims to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and neutralize HIV, ultimately leading to the production of bNAbs.
What are Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies (bNAbs)?
- In the 1990s, scientists discovered that some HIV-infected individuals produced bNAbs, which neutralize many viral strains.
- bNAbs target viral protein areas crucial for infectivity, making them less likely to change.
- Despite their effectiveness, bNAbs take years to develop, by which time HIV has often evolved to escape them.
Developing bNAb-Based Vaccines
- The goal is to make the immune system produce bNAbs quickly in response to a vaccine.
- Germline targeting involves three steps:
- Identify and engage B-cells capable of producing bNAbs.
- Use a booster to guide these cells to produce stronger bNAbs.
- Refine bNAbs to neutralize a wide range of HIV strains.
PYQ:[2013] Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? 1. Chikungunya 2. Hepatitis B 3. HIV-AIDS Select the correct answer using the codes given below. (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Will understanding Cancer become a data problem?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Use of Data Analytical Tools in Diagnosis
Why in the news?
WHO reports 33,000 new brain cancer cases yearly in India, highlighting widespread suffering.
What is brain cancer?
- Brain cancer, also known as primary brain cancer, is an overgrowth of cells in the brain that form masses called brain tumours.
- It is different from secondary brain cancer, which occurs when cancer that began in another part of the body spreads to the brain
The World Health Organization (WHO) Report:
- Incidence of Brain Cancer: WHO reports approximately 33,000 new incidences of brain cancer annually in India.
- Global Cancer Observatory 2020: Brain cancer ranks as the 19th most common type of cancer worldwide.
Use of Data Analytical Tools in Diagnosis:
- Potential of Data Analytics: Utilization of data analytical tools like Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) can simplify the diagnosis process.
- Advantages: Data analysis can provide real-time results with precision, reducing the need for invasive procedures like surgeries.
- Liquid Biopsy: The introduction of techniques like liquid biopsy offers a less invasive alternative to surgery, enhancing patient comfort.
Impact on Risks, Discomfort, and Pain:
- Reduction of Risks: Adoption of data analytics in diagnosis can lower the risks associated with invasive procedures, ranging from short-term paralysis to death.
- Enhanced Patient Experience: By offering less invasive alternatives, such as liquid biopsy, patients and their families can experience reduced discomfort and pain during the diagnostic process.
- Improved Precision: Data analytics enable clinicians to detect genetic patterns indicative of cancer cells, facilitating early detection and treatment planning, ultimately leading to better outcomes for patients.
Way forward:
- Emphasize the transformative potential of data analytics in oncology research, particularly in simplifying diagnosis and reducing risks and discomfort for patients.
- Highlight the importance of leveraging innovative technologies like NGS to unlock new possibilities in cancer research and treatment.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Neo: A Novel Protein in Bacterial Defense
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Neo Protein, Reverse Transcriptase
Why in the News?
“Klebsiella pneumoniae” bacteria might employ a newly discovered protein called “Neo” to halt bacteriophage infections.
About Neo Protein
- Discovery Details: Researchers, led by Stephen Tang and Samuel Sternberg, reported the discovery of Neo in a 2023 preprint paper on bioRxiv, while investigating Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Neo’s Defense Strategy: Bacteria employ diverse immune systems to fend off viral infections, including defense-associated reverse transcriptase (DRT) systems, which Neo is a part of.
- DRT-2 System: This system involves de novo gene synthesis via rolling-circle reverse transcription (RT) of a non-coding RNA (ncRNA).
- Operational Process: In uninfected cells, the ncRNA and RT enzyme catalyze the synthesis of a repetitive single-stranded cDNA.
- Activation by Phage: Phage presence triggers the synthesis of the second-strand cDNA, resulting in long double-stranded DNA.
- Role of Neo Protein: The translation of this double-strand cDNA produces the Neo protein, which induces potent growth arrest (cell dormancy), thereby protecting the bacterial population from phage proliferation.
Biotechnological and Medical Implications
- Potential Applications: Neo represents a promising tool for controlling viral infections, holding significance in both biotechnology and medicine.
- Evolutionary Connections: Neo’s discovery sheds light on the shared evolutionary history and functional mechanisms of retroelements in the human genome and bacterial reverse transcriptases.
- Technological Influence: Bacterial reverse transcriptases, predecessors of their eukaryotic counterparts, share analogous mechanisms and have revolutionized molecular biology research methods.
What is Reverse Transcriptase?
|
PYQ:[2019] What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in the news? (a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing. (b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients. (c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant. (d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and its Health Impacts
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fatty Acids and their health implications
Why in the News?
- Fish oil supplements, highly regarded for their high omega-3 fatty acid content, have long been associated with heart health benefits.
- A recent study has caused controversy by raising the possibility that these supplements may be as harmful as previously thought.
What are Fatty Acids?
Types of Fatty AcidsFatty acids are classified based on the presence and number of double bonds in their hydrocarbon chain:
|
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
- Omega-3 fatty acids (omega-3s) are polyunsaturated fats that perform important functions in the human body.
- There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
- EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). EPA is a “marine omega-3” because it’s found in fish.
- DHA (docosahexaenoic acid). DHA is also a marine omega-3 found in fish.
- ALA (alpha-linolenic acid). ALA is the form of omega-3 found in plants.
-
- When we get ALA from food, the human body can turn some of the ALA into EPA and subsequently to DHA. However, this process provides just a small amount of EPA and DHA. So, dietary sources of EPA and DHA (like fish) are essential.
Functions of Omega-s fatty acids:
-
- They help to provide structure and supporting interactions between cells.
- Omega-3s are concentrated in high levels in cells in human eyes and brain.
- They provide the human body with energy (calories) and support the health of many body systems. These include the human cardiovascular system and endocrine system.
Significance of Omega-3 fatty acids:
- Omega-3 fatty acids have many potential benefits for human cardiovascular health.
- One key benefit is that they help lower human triglyceride levels.
- Too many triglycerides in human blood (hypertriglyceridemia) raise human risk of atherosclerosis, and through this, can increase human risk of heart disease and stroke. So, it’s important to keep triglyceride levels under control.
- Omega-3s may help us by raising human HDL (good) cholesterol and lowering human blood pressure.
- Some studies show omega-3s may lower human risk for Cardiovascular disease (CVD), and hence lowering the sudden death caused by an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia), and blood clots.
- Beyond heart health, omega-3s may help lower the human risk of developing some forms of cancer, including breast cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), research continues to investigate these and other possible benefits.
PYQ:[2011] A company marketing food products advertises that its items do not contain trans-fats. What does this campaign signify to the customers?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Xenotransplantation: Prospects and Challenges
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Xenotransplantation, Crispr-Cas9
Mains level: NA
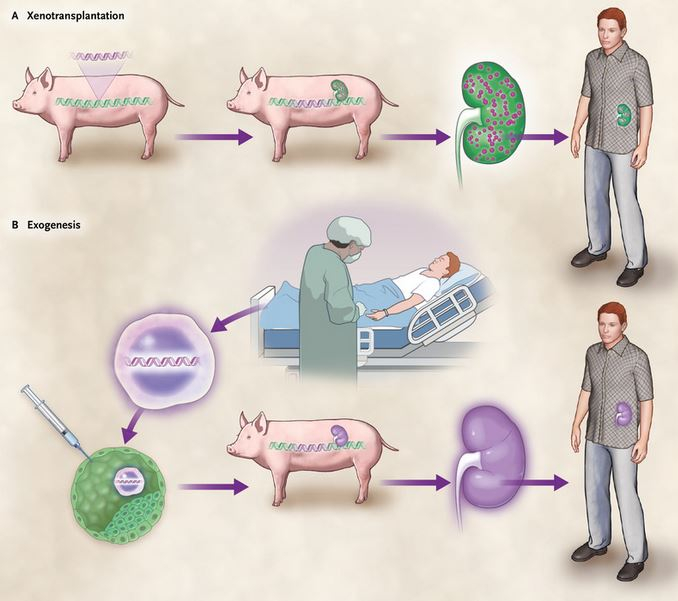
Why in the News?
The recent passing away of Richard Slayman, the first recipient of a modified pig kidney transplant, has drawn attention to xenotransplantation—an innovative medical procedure with the potential to revolutionise organ transplantation.
What is Xenotransplantation?
- It involves transplanting live cells, tissues, or organs from nonhuman animal sources into human recipients.
- It seeks to address the critical gap between organ demand and supply.
- Xenotransplantation, pioneered in the 1980s with heart transplants, has emerged as a promising solution to alleviate the organ shortage crisis, particularly prevalent in kidney transplantation.
Examples:
- Chimpanzee-to-Human Transplants: In the 1960s, there were attempts at chimpanzee-to-human kidney transplants, heart transplants, and liver transplants.
- Pig-to-Human Heart Transplant: In 2022, a groundbreaking milestone was achieved with the first successful transplantation of a pig heart into a human with end-stage heart disease
Procedural Details
- Xenotransplantation involves genetic modifications to animal organs, like 69 CRISPR-Cas9 edits to a pig kidney, removing pig genes and adding human genes for compatibility.
Why is the Pig a Preferred Source?
- Anatomical Resemblance: Pigs are favoured for xenotransplantation due to their physiological similarities to humans, facilitating successful integration. Pig organs, like heart valves, have been used in human medicine for over 50 years.
- Breeding Advantages: Extensive pig farming ensures a readily available and cost-effective supply of organs, with diverse breeds offering size-matching opportunities.
Challenges associated
- The main challenge is preventing organ rejection. Innovative methods, such as embedding the pig’s thymus gland under the kidney’s outer layer, help manage immune responses.
- There are also significant concerns regarding potential infections from both recognised and unrecognised infectious agents that could affect not only the recipient but also the wider population.
- Retroviruses present in the animal organs pose a risk of cross-species infection, which could remain latent and cause diseases years after the transplantation.
PYQ:[2017] With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
X chromosome revival in older Women increases Autoimmune Disease risk
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Autoimmune Diseases, X Chromosome
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
The X chromosome influences biological functions and disease susceptibilities, affecting genetic disorders, autoimmune diseases, and Alzheimer’s, with research offering potential new treatments and therapies.
Back2Basics: Chromosomes
Types of Chromosomes:
Functions of Chromosomes
|
Genetic Landscape of the X chromosome:
- The human X chromosome encodes around 800 genes, producing proteins.
- Loss of function in these genes can lead to various genetic diseases.
- Diseases influenced by the X chromosome fall into three categories:
- X-linked genetic diseases
- Diseases influenced by XCI (X chromosome inactivation) escape
- Diseases linked to X-chromosome aneuploidy
What is the X chromosome?
- It is one of the two sex chromosomes in humans, the other being the Y chromosome.
- Females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
- Significance:
- Encodes around 800 genes that are crucial for various biological processes.
- Plays a significant role in determining sex and influencing many physiological functions.
- Loss of function or mutations in X chromosome genes can lead to several genetic disorders.
What are Autoimmune Diseases?
- Diseases where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells and tissues.
- Normally, the immune system defends against infections by targeting harmful pathogens.
- Common Autoimmune Diseases:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Chronic inflammation affecting various body parts.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Inflammation of joints and surrounding tissues.
- Sjogren’s Syndrome: Affects glands that produce moisture, leading to dry mouth and eyes.
How does the X chromosome cause Autoimmune Diseases?
- X Chromosome Inactivation (XCI):
- In females, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated during early embryonic development to balance gene expression between males and females.
- This process is crucial to prevent overexpression of X-linked genes.
- XCI Escape:
- Not all genes on the inactive X chromosome are completely silenced.
- Up to a fourth of these genes may escape inactivation and continue to be expressed.
- Link to Autoimmune Diseases:
- Skewed XCI: Uneven inactivation of X chromosomes may lead to an imbalance in gene expression, contributing to autoimmune disorders.
- Incomplete XCI: Reactivation of genes that should be silenced can result in abnormal immune responses.
Studies, such as one published in Science Advances (May 3, 2023), have shown that reactivation of X-linked genes in immune cells can lead to lupus-like symptoms in mice.
Linkage between X chromosome and Alzheimer’s disease
- Sex Bias in Alzheimer’s:
- Women are almost twice as likely as men to develop Alzheimer’s disease.
- Role of X-Linked Genes:
- Researchers have identified a gene called ubiquitin-specific peptidase 11 (USP11) on the X chromosome.
- USP11 Gene: Involved in protein modification processes and thought to influence the accumulation of tau proteins in the brain.
- XCI Escape: USP11 may escape XCI in females, leading to higher expression levels and contributing to Alzheimer’s pathology.
- A study from Case Western Reserve University (Cell, October 2022) highlighted this mechanism, suggesting it as a target for new treatments.
PYQ:[2011] At present, scientists can determine the arrangement or relative positions of genes or DNA sequences on a chromosome. How does this knowledge benefit us?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Decoding C. Elegans Worm: A Remarkable Discovery
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: C. Elegans Worm
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
Researchers at Princeton University found that Caenorhabditis elegans can inherit the ‘knowledge’ to avoid a disease-causing bacterium, Pseudomonas vranovensis, across several generations after initially consuming it.
C. Elegans: Breakthrough made in Scientific Research
|
About C. Elegans Worm
- C. elegans, or Caenorhabditis elegans, is a small, transparent nematode (roundworm) widely used in scientific research.
- It is about 1 mm in length, making it easy to study under a microscope.
- It has a simple body plan, which simplifies many types of biological research.
- C. elegans was the first multicellular organism to have its entire genome sequenced in 1998.
Key Features of C. Elegans Worm
- Short lifespan and quick regeneration: It has a short lifespan of about 2-3 weeks and develops from an egg to an adult in just 3-5 days. This allows for quick generation turnover and facilitates studies on genetics and developmental biology.
- Transparency: It allows researchers to easily observe its internal structures and developmental processes in real time.
- Genetic information: This has provided a wealth of genetic information and made it a powerful tool for genetic studies.
- Consistent Somatic Cell Count: Adult C. elegans have exactly 959 somatic cells, and their lineage has been fully mapped, providing a consistent model for studying cell development and death.
PYQ:[2021] Consider the following: 1. Bacteria 2. Fungi 3. Virus Which of the above can be cultured in artificial/synthetic medium? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CRISPR’s Breakthrough in Treating Blindness
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LCA, CRISPR Cas9;
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
Scientists have successfully used CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to restore vision in individuals with a rare form of inherited or congenital blindness.
- The groundbreaking clinical trial, named “BRILLIANCE,” demonstrated promising results in improving vision and quality of life for participants with Leber congenital amaurosis (LCA), a severe vision disorder.
What is Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA)?
- LCA is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the retina the ‘light-sensitive’ tissue at the back of the eye. It leads to severe visual impairment or blindness at birth or within the first few months of life.
- It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning a child needs to inherit one defective gene from each parent to develop the condition.
- There are several genes associated with LCA, with mutations in at least 14 different genes known to cause the disorder.
- These genes generally affect the development and function of photoreceptors or the retinal pigment.
Key highlights of the BRILLIANCE trial:
- The BRILLIANCE trial involved 12 adults and two children diagnosed with LCA, a condition characterized by early-onset vision loss.
- Participants received a single dose of a CRISPR gene therapy called EDIT-101, designed to correct mutations in the CEP290 gene responsible for LCA.
- In this case, CRISPR-Cas9 cuts out the faulty DNA segment in the CEP290 gene and replaces it with a healthy DNA sequence, restoring the function of the CEP290 protein crucial for vision.
- Out of 14 participants, 11 experienced improved vision without serious side effects.
Back2Basics: CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing
|
PYQ:[2019] What is Cas9 Protein that is often mentioned in news? (a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing (b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients (c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant (d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and the Science behind
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MRI and its working principle
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) revolutionized medical diagnostics, offering non-invasive insights into soft tissues.
- The pioneering efforts of Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield led to its commercialization, earning them the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 2003.
What is MRI?
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic procedure used to obtain detailed images of soft tissues within the body.
- It is particularly valuable for imaging sophisticated structures like the brain, cardiovascular system, spinal cord, joints, muscles, liver, and arteries.
- MRI is instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, including cancer, neurological disorders (such as Alzheimer’s and stroke), and cardiovascular diseases.
- Functional MRI (fMRI) can also assess brain activity by monitoring changes in blood flow.
Working Principle:
- MRI utilizes the magnetic properties of hydrogen atoms (one proton with one electron around it), which are abundant in water and fat molecules found throughout the body.
- The MRI machine generates a powerful magnetic field, aligning hydrogen atoms within the body.
- Radiofrequency pulses are then applied, causing hydrogen atoms to absorb energy and emit signals.
- These emitted signals are detected by sensors and processed by a computer to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures.
Components of an MRI Machine:
The MRI machine consists:
- Superconducting Magnet: Large magnet (superconducting magnet) that produces a powerful and stable magnetic field.
- Gradient Coils: Gradient magnets produce smaller magnetic fields with varying strengths and directions, allowing for precise imaging of specific body areas.
- Radiofrequency Coils: This emit radiofrequency pulses to excite hydrogen atoms in the body. The frequency of pulse the ‘excess’ atoms have to absorb is called the Larmor frequency.
- Detectors: It capture emitted signals from hydrogen atoms and convert them into image data for analysis.
Advantages of MRI:
- High-Resolution Imaging: MRI offers high-resolution imaging with excellent tissue contrast, allowing for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Versatile Viewing Angles: It can visualize structures from various angles without the need for repositioning, providing comprehensive information.
- Safety and Non-Invasiveness: MRI scans are non-invasive and do not involve ionizing radiation, making them safe for repeated use.
- Enhanced Image Quality: Contrast agents can enhance image quality by highlighting specific tissues or abnormalities.
Limitations of MRI:
- High Costs: MRI machines are expensive to purchase and maintain, resulting in high healthcare costs for patients.
- Requirement for Patient Stillness: Patients undergoing MRI scans must remain still for extended periods to prevent image distortion, which can be challenging for some individuals.
- Discomfort or Anxiety: The strong magnetic fields and loud noises produced during MRI scans may cause discomfort or anxiety for patients.
- Limitations with Metallic Implants: Certain metallic implants or objects can interfere with MRI scans, limiting their use in individuals with such implants.
PYQ:[2020] With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only (c) 2, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Role of Fusobacterium in Colorectal Cancer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis (Fna)
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- Researchers at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in the US have identified specific subtypes of Fusobacterium nucleatum associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors.
- These subtypes, particularly Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis (Fna), have been found in relatively higher quantities in CRC tumors.
About Fusobacterium nucleatum
- Fusobacterium nucleatum is a species of bacteria commonly found in the human mouth.
- It is a gram-negative anaerobic bacterium, meaning it does not require oxygen for growth.
- While typically residing in the oral cavity, it has been associated with various diseases and conditions, including periodontal diseases and colorectal cancer.
Association with Colorectal Cancer (CRC):
- In cases of colorectal cancer (CRC), Fusobacterium nucleatum has been found within tumors in the gut.
- Studies have shown that this bacterium can aid cancer cells in evading the immune system and promoting metastasis, or the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
- Its presence in CRC tumors has led to investigations into its potential role in the development and progression of colorectal cancer.
Impact:
- Assisting cancer cells in evading the immune system.
- Promoting inflammation and creating an environment conducive to tumor growth.
- Facilitating metastasis by interacting with cancer cells and promoting their spread to other tissues.
PYQ:[2013] Improper handling and storage of cereal grains and oilseeds result in the production of toxins known as Aflatoxins which are not generally destroyed by normal cooking process. Aflatoxins are produced by: (a) Bacteria (b) Protozoa (c) Moulds (d) Viruses |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
West Nile Fever Outbreak in Kerala
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: West Nile Virus, Its host, Transmission;
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- The Kerala government disclosed the re-emergence of West Nile fever cases in Thrissur, Malappuram, and Kozhikode districts.
- West Nile fever was first detected in Kerala in 2011, with a fatal case recorded in 2019 involving a six-year-old from Malappuram.
What is West Nile Fever?
- West Nile fever is caused by a West Nile Virus (WNV) transmitted through bites from infected Culex mosquitoes.
- The WNV is a mosquito-borne, single-stranded RNA virus.
- According to the WHO, it is a member of the flavi-virus genus and belongs to the Japanese Encephalitis antigenic complex of the family Flaviviridae.
How does it spread?
- It is transmitted by infected mosquitoes between and among humans and animals, including birds, which are the reservoir host of the virus.
- Mosquitoes become infected when they feed on infected birds, which circulate the virus in their blood for a few days.
- The virus eventually gets into the mosquito’s salivary glands.
- During later blood meals (when mosquitoes bite), the virus may be injected into humans and animals, where it can multiply and possibly cause illness.
- WNV can also spread through blood transfusion, from an infected mother to her child, or through exposure to the virus in laboratories.
- It is not known to spread by contact with infected humans or animals.
Symptoms of WNV infection:
- The disease is asymptomatic in 80% of the infected people.
- The rest develop what is called the West Nile fever or severe West Nile disease.
- In these 20% cases, the symptoms include fever, headache, fatigue, body aches, nausea, rash, and swollen glands.
PYQ:[2017] Consider the following statements: 1. In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue. 2. Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Back2Basics: Type of Viruses
| Subtypes | Description | Examples | |
| DNA Viruses | Herpesviruses | DNA viruses with a complex structure causing various diseases including cold sores, chickenpox, and mononucleosis. | HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, EBV |
| Papillomaviruses | DNA viruses associated with warts and certain cancers. | HPV | |
| Adenoviruses | DNA viruses causing a wide range of infections in humans. | Adenovirus types causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, and ocular infections | |
| Poxviruses | Large, complex DNA viruses responsible for diseases like smallpox. | Variola virus (smallpox), Vaccinia virus | |
| RNA Viruses | Positive-Sense RNA Viruses | RNA viruses with genomes that can directly serve as mRNA, causing diseases like the common cold, Zika, and COVID-19. | Picornaviruses, Flaviviruses, Coronaviruses |
| Negative-Sense RNA Viruses | RNA viruses requiring transcription into positive-sense RNA before translation, causing diseases like influenza and rabies. | Orthomyxoviruses, Paramyxoviruses, Rhabdoviruses | |
| Retroviruses | RNA viruses that use reverse transcriptase to integrate their genome into the host cell’s DNA. | HIV, HTLV | |
| Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA) Viruses | RNA viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes causing gastroenteritis and other infections. | Reoviruses | |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Ambisense Genome | RNA viruses with genomes containing both positive-sense and negative-sense RNA regions. | Arenaviruses, Bunyaviruses | |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Segmented Genome | RNA viruses with genomes consisting of multiple segments, causing diseases like influenza and hemorrhagic fevers. | Orthomyxoviruses, Bunyaviruses | |
| Single-Stranded RNA (ssRNA) Viruses with Circular Genome | Satellite viruses with a circular RNA genome requiring helper viruses for replication. | Hepatitis Delta Virus (HDV) | |
| Enveloped Viruses | Influenza Viruses | RNA viruses surrounded by a lipid envelope causing seasonal flu outbreaks. | Influenza A, B, C viruses |
| Herpesviruses | Enveloped DNA viruses causing diseases like cold sores, chickenpox, and mononucleosis. | HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, CMV | |
| Coronaviruses | Enveloped RNA viruses causing diseases like severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and COVID-19. | SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2 | |
| HIV | Enveloped retroviruses responsible for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). | Human immunodeficiency virus | |
| Ebola Virus | Enveloped RNA virus causing severe hemorrhagic fever in humans. | Ebola virus | |
| Non-enveloped Viruses | Adenoviruses | DNA viruses lacking a lipid envelope, causing various infections in humans. | Adenovirus types causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, and ocular infections |
| Papillomaviruses | DNA viruses associated with warts and certain cancers, lacking an envelope. | HPV | |
| Noroviruses | RNA viruses causing gastroenteritis, lacking an envelope. | Norovirus | |
| Rotaviruses | RNA viruses causing severe gastroenteritis in infants and young children, lacking an envelope. | Rotavirus | |
| Bacteriophages | T4 Bacteriophage | Viruses that infect bacteria, with a complex structure and lifecycle. | T4 bacteriophage |
| Lambda Phage | Temperate bacteriophage capable of lysogenic and lytic cycles in E. coli. | Lambda phage |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Endosymbiotic Theory and Symbiogenesis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Endosymbiotic Theory, Nitrogen Cycle
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- The endosymbiotic theory suggests that tiny structures in cells called mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent bacteria.
- A biologist named Lynn Margulis came up with the idea that cells merged with bacteria, challenging the usual belief that evolution happens mainly through genetic changes.
What is the Endosymbiotic Theory?
- The endosymbiotic theory proposes that organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free-living bacteria engulfed by recipient cells.
- American biologist Lynn Margulis introduced Symbiogenesis, challenging the Neo-Darwinist consensus on genetic mutations driving evolution.
- Margulis’s Struggle:
- Margulis’s manuscript on symbiogenesis faced rejection by academic journals before finally being published in The Journal of Theoretical Biology in 1967.
- It took years for mitochondria and chloroplasts to be acknowledged as former free-living bacteria turned endosymbionts.
Recent Discoveries and Endosymbiotic Theory
- Recent papers published in Science and Cell have reignited interest in the endosymbiotic theory.
- The focus is on nitrogen fixation, crucial for proteins and DNA in living organisms.
- Despite abundant atmospheric nitrogen, plants lack the means to utilize it efficiently.
- Legumes host nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules, aiding in ammonia production for plant use.
Evolution of Nitroplast
- Cyanobacterium UCYN-A was found in marine algae, establishing a symbiotic relationship.
- Nitroplast, a new organelle, co-evolved with its host cell, satisfying criteria for organelle classification.
- Nitroplast integrates into host cell function and architecture, imports host cell proteins, synchronizes growth, and is inherited during cell division.
- Nearly half of nitroplast proteins are derived from the host cell.
Nitrogen Cycle:
|
Significance of the Nitroplasts
- Agriculture: Nitroplasts offer potential solutions for reducing the harmful effects of industrial ammonia production.
- Biotechnology: Biotechnological applications may include engineering host cells and nitroplasts for efficient nitrogen fixation in plants.
PYQ:[2021] In case of which one of the following biogeochemical cycles, the weathering of rocks is the main source of release of nutrient to enter the cycle? (a) Carbon cycle (b) Nitrogen cycle (c) Phosphorus cycle (d) Sulphur cycle |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Unveiling the Link between Fairness Creams and Nephrotic Syndrome
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mercury Poisoning, Membranous Nephropathy, Minamata Convention.
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- Researchers from Kerala reported 15 cases of Membranous Nephropathy (MN) linked to the regular application of fairness creams.
- These creams contained high levels of mercury, sometimes exceeding the safe limit by 10,000 times.
Mercury Contamination in Hair Cream
- Blood and urine screenings of affected individuals unveiled alarmingly high levels of mercury, a well-known toxic element.
- The fairness creams contained mercury levels up to 10,000 times above the permissible limit of 1 ppm under Minamata Convention (2013).
- Most cases were PLA2R (phospholipase A2 receptor) negative, indicating a different cause.
- Cases of MN linked to Neural epidermal growth factor-like protein 1 (NELL-1) have been identified.
- NELL-1 has been associated with MN caused by traditional medicines containing high mercury levels.
Understanding Membranous Nephropathy
- Membranous Nephropathy (MN) is a nephrotic syndrome, characterized by excessive protein leakage into urine, eventually leading to kidney failure. Symptoms such as fatigue, edema, and proteinuria were found to have a history of regular fairness cream usage.

Impact of Mercury:
- Mercury in fairness creams inhibits melanin formation, resulting in lighter skin. Consumers perceive higher mercury levels as more effective for skin whitening.
- Mercury, a potent heavy metal found in these creams, penetrates the body through various channels, including sweat glands and hair follicles, causing systemic toxicity.
- Chronic exposure to mercury can result in kidney damage, neurological disorders, and a myriad of other health complications.
Back2Basics: Minamata Convention on Mercury
Activities covered by the Convention:
|
PYQ:[2010] Indiscriminate disposal of used fluorescent electric lamps causes mercury pollution in the environment. Why is mercury used in the manufacture of these lamps? (a) A mercury coating on the inside of the lamp makes the light bright white (b) When the lamp is switched on, the mercury in the lamp causes the emission of ultra-violet radiations (c) When the lamp is switched on, it is the mercury which converts the ultra-violet energy into visible light (d) None of the statement given above is correct about the use of mercury in the manufacture of fluorescent lamps |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
95Mat5 Antibody: Revolutionizing Snakebite Treatment
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 95Mat5 Antibody
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
After multiple rounds of screening, researchers have identified an antibody, 95Mat5 that showed promising results in making a potent antidote against various snake venoms.
What is 95Mat5?
- 95Mat5 is a universal antivenom developed to neutralize the toxins present in snake venoms.
- Development Process:
- The scientists first synthesized variants of a toxin called long-chain 3FTxs (3FTx-L), which are found in the venoms of various snakes, including cobras, kraits, mambas, and monocled cobras.
- They then screened billions of human antibodies expressed on the surface of yeast cells to find antibodies that bound best to the synthesized toxins.
- After multiple rounds of screening, they identified a shortlist of antibodies that broadly reacted with most of the 3FTx variants used in the study.
- The selected antibodies were further tested in vitro in human cells to determine which ones could best neutralize the toxins.
Mechanism of Action
- 95Mat5 specifically targets α-neurotoxins, which are a specific class of 3FTxs that prevent nerve and muscle cells from responding to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in carrying messages from neurons to muscles.
- By binding to the toxins, 95Mat5 prevents toxins from interacting with the receptors in human nerve and muscle cells, thereby blocking their ability to induce paralysis and other deadly effects.
- In animal experiments, 95Mat5 demonstrated efficacy in neutralizing the toxins present in the venoms of various snake species, protecting the animals from death.
Global Impact of Snakebites
|
PYQ:[2020] With reference to carbon nanotubes, consider the following statements:
Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2, 3 and 4 only (c) 1, 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Plasma Therapy to Treat Rodenticide Poisoning
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plasma Therapy; Plasmapheresis, Components of Human Blood;
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- A significant health concern in Tamil Nadu is found through ingestion of Rat poison containing Yellow Phosphorus, leading to liver toxicity.
- Since December 2017, the team at CMC Vellore introduced Plasma Exchange, (a cost-effective treatment) for acute liver failure caused by rat poison ingestion.
What is Plasma Therapy (Plasmapheresis)?
- Plasma exchange, also known as plasmapheresis, is a medical procedure used to treat various conditions by removing and replacing plasma from the blood.
- During Plasma Exchange, the patient’s blood is circulated through a machine that separates plasma from other blood components, such as red and white blood cells and platelets.

Working procedure:
- The plasma, which may contain harmful substances or antibodies, is discarded.
- The remaining blood components are mixed with replacement plasma or a plasma substitute and returned to the patient’s bloodstream.
Usage of Plasmapheresis:
- In Autoimmune diseases: Conditions such as Guillain-Barre syndrome, myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and certain forms of vasculitis.
- In Neurological disorders: Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, and certain types of encephalitis.
- In Toxicological emergencies: Poisoning or overdose with substances such as drugs, chemicals, or toxins that can be removed from the bloodstream through plasma exchange.
Benefits observed in TN’s Case
- The treatment significantly improved survival rates, with 63.9% of patients treated in 2022-2023 successfully discharged.
- Retrospective studies at CMC Vellore demonstrated promising outcomes, with survival rates of 75% among children and 80.2% among adults treated with plasma exchange.
What is Plasma in Human Blood?
Composition:
Functions:
|
PYQ:[2011] A married couple adopted a male child. A few years later, twin boys were born to them. The blood group of the couple is AB positive and 0 negative. The blood group of the three sons is A positive, B positive, and O positive. The blood group of the adopted son is- (a) O positive (b) A positive (c) B positive (d) Cannot be determined based on the given data |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Geroscience: the Science related to Ageing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Geroscience, DNA Methylation
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- Dr. Daniel Belsky from Columbia University introduced the concept of “Geroscience” and develops a blood test, termed “gerozyme,” to measure aging pace by studying DNA methylation.
- Various research groups explore drugs like Metformin and Rapamycin to target aging and enhance immunity in the elderly.
What is Geroscience?
- Geroscience refers to the interdisciplinary field focused on understanding the biological mechanisms of ageing and age-related diseases.
- It involves studying various factors, including DNA methylation, enzyme activity (such as the gerozyme), socio-economic influences, and lifestyle interventions like nutrition, exercise, and music therapy.
- It aims to develop strategies, such as drug interventions targeting specific ageing-related processes, to promote healthy ageing and combat age-related conditions like dementia.
What is DNA Methylation?
|
Drug Interventions in Geroscience
- Metformin and TORC1 inhibitors show promise in targeting aging and improving immune response in seniors.
- Research proposes rapamycin’s potential in extending longevity and combating age-related diseases.
Impact of Socio-Economic Factors in Ageing
- Dr. Belsky’s research reveals the influence of socioeconomic status on DNA methylation levels, highlighting the role of disadvantage in ageing.
- Columbia Aging Centre emphasizes the role of a balanced diet in supporting brain health and reducing inflammation.
- Healthline.com advocates for proteins, healthy fats, and antioxidant-rich foods to promote healthy ageing, crucial for India’s ageing population.
PYQ:[2011] At present, scientists can determine the arrangement or relative positions of genes or DNA sequences on a chromosome. How does this knowledge benefit us?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Crafted in Indian labs, NexCAR19 takes India to next level in Cancer Care
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Science and Technology; Biotechnology; NexCAR19;
Mains level: Process and Significance of CAR T thearpy;
Why in the News?
- President Droupadi Murmu launched India’s first indigenously-developed CAR T-cell therapy, hailing it as a major breakthrough against cancer.
- This therapy was developed by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay and the Tata Memorial Centre, and it is known as ‘NexCAR19 CAR T-cell therapy’.
BACK2BASICS:What is CAR T cell thearpy?CAR T-cell therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves modifying a patient’s T cells, a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system, to recognize and attack cancer cells. This therapy is designed to target specific proteins found on the surface of cancer cells, such as CD19, which is commonly found on B cells. |
How are CAR-T cells made?

Significance of CAR T Thearpy:
- Promising results: This therapy has shown promising results in treating some types of blood cancers, including certain kinds of lymphoma, pediatric leukemia, and adult leukemia. It has shown with approximately 70% of patients responding to the treatment.
- Less time for treatment: CAR T-cell therapies are generally a single infusion with less than 2 weeks of inpatient care, while stem cell transplants and chemotherapy treatment regimens can take months to complete
Limitiations of CAR-T Therapy:
- Risks of CAR-T Therapy: The efficacy of CAR-T therapy varies from person to person, and it is too early to declare it a complete cure. While it has shown remarkable progress in challenging cases, its effectiveness is not universal.
- High Cost Therapy: NexCAR19 is priced at a fraction of its US counterpart, it remains relatively high for many Indians, ranging from ₹40 to 45 lakh.
- It’s Side Effects includes:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS): CRS is the most common side effect of CAR-T therapy, triggering an ‘Inflammatory Response’ that leads to immune system hyperactivity.
- Neurotoxicity: Although not observed in early-stage clinical trials, neurotoxicity is a common side effect of CAR-T therapy that can manifest as confusion, seizures, or difficulty speaking or walking.
- Infections and Blood Cell Counts: Patients undergoing CAR-T therapy may experience infections and low blood cell counts as anticipated side effects.
Conclusion: India’s is moving towards heralding a breakthrough in Cancer Care Therapy. Despite cost challenges, Government efforts are aimed to enhance accessibility and better outputs in Healthcare Sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Microbial Formulations for Enhanced Agricultural Productivity
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bactolime, Bactogypsum, and Trichogypsum; Soil Microbes
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
The Indian Institute of Spices Research (IISR), located in Kozhikode, has introduced and validated three new microbial formulations (Bactolime, Bactogypsum, and Trichogypsum) aimed at improving agricultural productivity.
IISR Microbial Formulations
- It leverages granular lime and gypsum to address soil pH issues while simultaneously delivering beneficial microorganisms.
- These are developed using IISR’s proprietary patent-applied technology.
- The formulations are:
- Bactolime:
- Bactolime, the flagship product, combines beneficial bacteria, specifically plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria, with liming material in a single formulation.
- This integration ensures not only the correction of soil acidity but also the provision of essential nutrients to plants.
- Bactogypsum and Trichogypsum:
- The other two formulations, Bactogypsum and Trichogypsum, utilize gypsum as a base material to buffer soil pH to a near-neutral level.
- By creating an optimal environment for beneficial microbes, these formulations improve soil structure, enhance the availability of secondary nutrients, and boost overall microbial activity.
Back2Basics: Soil Microbes
Soil microbes refer to microorganisms that inhabit the soil environment and play vital roles in soil health, nutrient cycling, and plant growth. These microorganisms are diverse and include bacteria, fungi, archaea, protozoa, and algae.
| Function | Benefits | |
| Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria | Convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, making it available to plants | Enhance soil fertility, improve plant growth and yield |
| Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria | Solubilize insoluble phosphorus, making it available to plants | Increase phosphorus availability, promote root development and flowering |
| Mycorrhizal Fungi | Form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, facilitate nutrient uptake | Improve soil structure, enhance nutrient absorption, increase plant resilience |
| Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) | Stimulate plant growth, enhance nutrient uptake, suppress pathogens | Promote root development, improve nutrient efficiency, increase stress tolerance |
| Actinomycetes | Decompose organic matter, produce antibiotics | Enhance soil fertility, control soil-borne diseases and pests |
| Azotobacter | Fix atmospheric nitrogen, produce growth-promoting substances | Increase nitrogen availability, stimulate root growth and nutrient uptake |
| Azospirillum | Fix atmospheric nitrogen, produce phytohormones | Enhance nitrogen availability, promote root growth and stress tolerance |
| Bacillus spp. | Produce antimicrobial compounds, enzymes | Control plant diseases and pests, improve soil health and fertility |
PYQ:[2016] Why does the Government of India promote the use of ‘Neem-coated Urea’ in agriculture? (a) Release of Neem oil in the soil increases nitrogen fixation by the soil microorganisms (b) Neem coating slows down the rate of dissolution of urea in the soil (c) Nitrous oxide, which is a greenhouse gas, is not at all released into atmosphere by crop fields (d) It is a combination of a weedicide and a fertilizer for particular crops |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
NexCAR19: India’s First Indigenous CAR T- Cell Therapy for Cancer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAR-T Cell Therapy, NexCAR19
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
- President Droupadi Murmu has unveiled ‘NexCAR19’ India’s first indigenously-developed CAR T-cell therapy for cancer treatment.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
| What is it? |
|
| How does it work? |
|
| Therapy Process | The process involves several steps, including:
1. Collecting T Cells: Blood is drawn from the patient’s arm, and T cells are separated from the blood using an apheresis machine. 2. Engineering T Cells: In a laboratory, the T cells are modified by adding a manufactured CAR, and they are allowed to multiply and grow. 3. Infusing CAR-T Cells: Once enough CAR-T cells are prepared, they are injected back into the patient’s arm.
|
| Cancers Treated |
|
NexCAR19: India’s Indigenously Developed CAR-T Therapy
- NexCAR19 is designed to target cancer cells carrying the CD19 protein, a marker on cancer cells, enhancing precision in treatment.
- It has been developed jointly by IIT Bombay and the Tata Memorial Centre.
- Initially approved for patients aged 15 and above with B-cell lymphomas who did not respond to standard treatments, leading to relapse or recurrence.
Effectiveness and Unique Features
- Approximately 70% of patients respond to NexCAR19 treatment, with some achieving complete remission.
- Lab and animal studies indicate lower drug-related toxicities, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
- Trials for paediatric patients are underway at Tata Memorial Hospital, ensuring broader applicability.
Availability and Affordability
- ImmunoACT is in the process of securing licenses and partnering with hospitals, including Tata Memorial, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, across multiple cities.
- Initially priced at Rs 30-40 lakh, ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
PYQ:2017: Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments?
Practice MCQ:With reference to the CAR-T Cell Therapy, consider the following statements: 1. T cells are Red Blood Cells responsible for identifying and fighting illness and infection. 2. Each T cell has a receptor that can recognize antigens (proteins or molecules recognized by the immune system). Which of the given statements is/are correct? (a) Only 1 (b) Only 2 (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
OptiDrop platform for studying Single Cells
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: OptiDrop, C-MAP, Cytometry
Mains level: NA

Why in the news?
The Centre for Cellular and Molecular Platforms (C-CAMP) in Bengaluru has unveiled OptiDrop platform designed to simplify and significantly reduce the cost of studying single cells.
About C-CAMP
|
What is OptiDrop?
- OptiDrop presents a cost-effective alternative to traditional flow cytometry methods, making single-cell analysis more accessible to a broader range of researchers and institutions.
- OptiDrop simplifies single-cell analysis by encapsulating individual cells within droplets, facilitating easier manipulation and analysis compared to traditional methods.
- Key features such as affordability, live data visualization, compact design, and closed-system architecture enhance its suitability for diverse clinical applications.
| Cytometry is the measurement of number and characteristics of cells. Variables that can be measured by cytometric methods include cell size, cell count, cell morphology (shape and structure), cell cycle phase, DNA content, and the existence or absence of specific proteins on the cell surface or in the cytoplasm. |
Applications of OptiDrop
- Expansive Utility: OptiDrop unlocks various downstream applications, including drug screening, environmental monitoring, immunotherapy, and single-cell genomics, revolutionizing research across multiple domains.
- Advanced Research Capabilities: Researchers can leverage OptiDrop to study individual cell behavior during drug screenings, identify and monitor environmental contaminants, sort specialized cell populations, and explore genetic heterogeneity within cell populations.
Benefits offered by OptiDrop
- Accessible Technology: Unlike conventional cytometers, which can cost up to Rs 40 lakh or more, OptiDrop offers a cost-efficient solution likely priced around Rs 10 lakh, making it accessible to a broader range of research labs and institutions.
- Affordable Scalability: OptiDrop’s affordable pricing and scalable design allow institutions of varying sizes to adopt the technology, democratizing access to cutting-edge single-cell analysis capabilities.
- Long-Term Sustainability: By reducing the barrier to entry for single-cell analysis, OptiDrop paves the way for sustainable and impactful research initiatives, driving innovation and discovery in the life sciences.
PYQ:2020: Which of the following statements are correct regarding the general difference between plant and animal-calls? 1. Plant cells have cellulose cell walls whilst animal cells do not. 2. Plant cells do not have plasma membrane unlike animal cells which do. 3. Mature plant cell has one large vacuole whilst animal cell has many small vacuoles. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3
Practice MCQ:The OptiDrop equipment recently seen in news finds application in: (a) Cytometry (b) Astronomy (c) Geology (d) Radiometry |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Discovery of Amino Acid unveils How Light makes Stomata Open in Plants

Why in the news?
Scientists from Nagoya University have made a discovery about the regulation of Stomatal opening in plants, a process vital for efficient photosynthesis by a type of amino acid threonine (Thr881).
What are Stomatal Openings?
- Stomata are microscopic pores on plant leaves crucial for gas exchange.
- They particularly uptake carbon dioxide necessary for photosynthesis.
How does Light make Stomata Open?
- Research unveiled a novel regulatory mechanism involving the phosphorylation of the 881st threonine residue (Thr881) of the plasma membrane proton pump in response to red and blue light.
- Phosphorylation, a process involving the addition or removal of a phosphate group from amino acids, acts as a regulatory switch, influencing protein structure and function.
- The researchers focused on the phosphorylation of Thr881 and its role in stomatal opening.
- They observed phosphorylation in response to both red and blue light conditions, highlighting the interplay between photosynthesis and light signaling.
Significance of Thr881 Phosphorylation
- Mutant studies confirmed the critical role of Thr881 phosphorylation in stomatal opening.
- Plants expressing a mutant proton pump lacking Thr881 phosphorylation exhibited reduced stomatal aperture and transpiration rates, emphasizing the regulatory significance of this amino acid residue.
- The study identified Thr881, along with Thr948, as crucial phosphorylation sites for the activation of the enzyme H+-ATPase, essential for stomatal opening.
- Manipulating Thr881 could offer avenues for promoting plant growth, enhancing carbon dioxide absorption, and reducing fertilizer usage.
PYQ:2014: Which one of the following is the process involved in photosynthesis? a) Potential energy is released to form free energy b) Free energy is converted into potential energy and stored c) Food is oxidized to release carbon dioxide and water d) Oxygen is taken, and carbon dioxide and water vapour are given out
Practice MCQ:What is the significance of phosphorylation of the threonine residue (Thr881) in the context of plants? a) It helps in reducing carbon dioxide uptake and photosynthesis efficiency. b) It enhances photosynthesis in dark conditions. c) It reduces transpiration leading to enhanced water conservation. d) It is essential for regulating stomatal aperture and facilitating gas exchange in plants. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Project ANAGRANINF
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project ANAGRANINF, AMR
Mains level: NA
What is the news?
- The Technology Development Board (TDB) has allocated a grant of ₹75 Lakhs for the project “ANAGRANINF – Development of a Novel Class of Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Bacterial-Infections,” totalling ₹1.5 crores.
What is Project ANAGRANINF?
- Project ANAGRANINF is titled “Development of a Novel Class of Antibiotics Against Gram-Negative Bacterial-Infections.”
- It is a collaborative initiative involving M/s Peptris Technologies Pvt. Ltd. and the Foundation for Neglected Disease Research (FNDR) in India, along with ABAC THERAPEUTICS SL from Spain.
- The primary objective of the project is-
- To develop a novel antibiotic capable of inhibiting the FabI enzyme and
- Combating critical gram-negative pathogens.
- Project ANAGRANINF aims to produce a series of compounds with enhanced efficacy against gram-negative bacterial infections.
- The project aims to identify a candidate molecule that meets WHO’s innovation criteria, ensuring a new chemical structure, no cross-resistance with existing antibiotic classes, and a novel mechanism of action.
About the Candidate Molecule ‘MMV1578564’
The selected hit molecule from the project, MMV1578564, has exhibited promising activity against gram-negative pathogens, providing a foundation for further research and development efforts.
Back2Basics:
- Gram-Negative Bacteria:
- Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, which is located between the outer and inner membranes.
- They stain pink or red when subjected to the Gram staining technique.
- Gram-negative bacteria are generally more resistant to antibiotics due to the presence of an outer membrane that acts as a barrier against certain antibiotics.
- Examples of gram-negative bacteria include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
- They are known to cause infections like pneumonia, bloodstream infections, wound infections, and meningitis in healthcare settings
- Gram-Positive Bacteria:
- Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, which retains the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining technique.
- They appear purple or blue under a microscope after staining.
- Gram-positive bacteria are generally more susceptible to antibiotics because their thick peptidoglycan layer allows antibiotics to penetrate more easily.
- Examples of gram-positive bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Bacillus subtilis, and Clostridium difficile.
- Some examples of diseases caused by Gram-positive bacteria include anthrax, diphtheria, enterococcal infections, erysipelothricosis, and listeriosis.These bacteria can cause a range of infections from food poisoning to serious respiratory diseases and may require specific antibiotics for treatment.
PYQ:
2021: Consider the following:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Virus
Which of the above can be cultured in artificial/synthetic medium?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Practice MCQ:
The recently launched Project ‘ANAGRANINF’ deals with:
- Agricultural Grant
- Artificial Intelligence
- Antibiotics Development
- None of these
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Indigenous Drug for Sickle Cell Disease developed
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sickle Cell Disease (SCD), Anemia
Mains level: NA

What is the news-
- Based in Delhi, Akmus Drugs and Pharmaceutical Limited unveiled a groundbreaking drug for sickle cell disease on March 16.
- This drug marks India’s first indigenous, room-temperature stable solution for sickle cell disease, available at a mere 1% of the global price.
What is Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)?
|
About Akmus Sickle Cell Drug
- The oral suspension of Hydroxyurea is the basic component of the drug.
- Priced at less than ₹600, the drug is poised to revolutionize access to treatment for sickle cell disease patients nationwide.
- It is tailored for patients across all age groups.
- It offers convenience and precision in dosage administration through provided oral syringes.
What makes it a revolutionary drug?
- Room Temperature Stability: Unlike imported hydroxyurea solutions requiring storage at 2-8 degrees Celsius, Akmus Pharmaceuticals’ formulation ensures accessibility without stringent storage conditions.
- Cost-Efficiency: With the global brand priced at approximately ₹77,000, Akmus’ solution underscores a paradigm shift towards affordable medication.
Sickle Cell Disease Menace in India
|
PYQ:
Q. Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Practice MCQ:
Q. Regarding the prevalence of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) in India, consider the following statements:
- Sickle cell disease is a hereditary disorder affecting affects haemoglobin in red blood cells.
- About one in 86 births among STs have sickle cell disease.
- India has identified it among the top 10 issues disproportionately affecting tribal communities.
- The National Sickle Cell Anemia Elimination Mission, aims to eliminate sickle cell anemia from India by 2030.
How many of the given statements is/are correct?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
GE Marvel: Parthenogenesis in Drosophila Fruit Flies
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Drosophila, Parthenogenesis
Mains level: NA

In the news
- In a recent milestone, researchers from Cambridge University and the California Institute of Technology achieved a remarkable feat: transforming a sexually reproducing fruit-fly species into one capable of asexual reproduction through minor genetic modifications.
About Drosophila
- Drosophila is a genus of two-winged flies commonly known as fruit flies that are used in evolutionary and developmental studies.
- It is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called “small fruit flies” or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit.
- The Drosophila melanogaster genome has 200,000,000 base pairs distributed across four DNA molecules, encoding about 13,600 genes.
- Hence it is one of the most widely-used and preferred model organisms in biological research across the world for the last 100 years.
Parthenogenesis (Asexual Reproduction) in Drosophila Family
- Parthenogenesis Discovery: Parthenogenesis, or fatherless reproduction, was observed in Drosophila mangebeirai, a species consisting solely of females.
- Facultatively Parthenogenetic Species: Approximately 76% of sexually reproducing species, including Drosophila mercatorum, were found to exhibit facultative parthenogenesis, wherein isolated virgin females hatch eggs that develop into offspring without fertilization by males.
- Canonical Species: Drosophila melanogaster, the standard species for research, strictly reproduces sexually.
Genetic Basis of Parthenogenesis
- Identifying Relevant Genes: Researchers aimed to identify genes facilitating parthenogenetic development in Drosophila mercatorum eggs and modify the Drosophila melanogaster genome accordingly.
- RNA Sequencing: Utilizing RNA sequencing, researchers identified 44 genes in parthenogenetic D. mercatorum eggs that exhibited differential expression compared to sexually reproducing eggs.
Engineering Asexual Reproduction
- Genetic Modifications: Researchers manipulated the expression levels of specific genes in the Drosophila melanogaster genome to mimic those observed in parthenogenetic D. mercatorum eggs.
- Outcome: Genetic alterations, including overexpression of the pologene and Myc gene and reduced expression of the Desat2 gene, resulted in approximately 1.4% of D. melanogaster eggs exhibiting parthenogenesis, with viable offspring reaching adulthood.
- Reproductive Potential: Parthenogenetically produced adult flies were capable of mating with males and producing progeny, demonstrating facultative parthenogenesis in a strictly sexually reproducing species.
Mechanism Involving Polar Bodies
- Role of Polar Bodies: Polar bodies, by-products of chromosome transmission mechanisms during fertilization, were implicated in initiating embryonic development in unfertilized eggs.
- Efficiency Alterations: Genetic modifications likely impaired the sequestration and disposal of polar bodies, enabling them to substitute for the missing male pronucleus and initiate embryonic development.
Implications for Pest Control
- Pest Management: Raises concerns about unintended consequences in pest control strategies reliant on sterilization or genome editing.
- Genetic Engineering: Opens avenues for genetic manipulation in model organisms, aiding research in gene drive technology and population control.
- Conservation Biology: Offers insights into species adaptability and potential impacts of genetic interventions on natural populations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Connectome: the Map of the Brain
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Connectome, Synapse, Neurons
Mains level: NA

In the news
- The human brain, composed of billions of neurons, orchestrates intricate processes that sustain life and enable complex cognitive functions.
- Understanding these neural interactions is paramount, and scientists have achieved this through the concept of the connectome.
What is Connectome?
- Definition: The Connectome serves as a comprehensive map of neuronal connections, akin to a cartogram illustrating the intricate network of synapses transmitting electrical and chemical signals within the brain.
- Neural Communication: Neurons communicate through synapses, where dendrites receive chemical signals converted into electrical impulses transmitted along the axon. Subsequently, the cell releases chemicals into synapses based on electrical inputs, facilitating communication with neighbouring neurons.
Applications in Neuroscience
- Functional Insights: Mapping the connectome provides invaluable insights into brain function, shedding light on processes underlying cognitive functions and elucidating the impact of neurological disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Drug Development: By unravelling cellular connections, researchers gain crucial knowledge about cognitive processes and associated disorders, informing the development of novel therapeutic interventions for conditions affecting neurological health.
Challenges and Progress
- Complexity of the Brain: The intricate nature of the brain and the vast amount of data it processes present significant challenges in mapping the connectome.
- Simplified Understanding: Despite these challenges, the connectome has revolutionized scientists’ comprehension of the brain, offering a clearer understanding of neurological health and paving the way for advancements in neuroscience research.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Cannabis Use: Implications for Psychiatry
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cannabis , THCBD, NDPS Act, Exception for 'Bhang'
Mains level: Therapeutic uses of narcotic substances

In the news
- Cannabis (Cannabis sativa) has long intrigued psychiatrists due to its impact on mood and cognition, prompting research into its potential therapeutic applications for conditions like schizophrenia and mood disorders.
Do you know?
|
What is Cannabis?
- Cannabis, also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or ganja, is a genus of flowering plants that belongs to the Cannabaceae family.
- It is primarily known for its psychoactive properties due to the presence of compounds such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
- This THC interacts with the brain’s cannabinoid receptors, resulting in various effects including relaxation, euphoria, altered perception of time, and increased appetite.
- The plant contains over 100 different cannabinoids, with THC and cannabidiol (CBD) being the most well-known and studied.
Why discuss this?
- Researchers at the University of British Columbia initiated a clinical trial to explore the efficacy of cannabidiol (CBD) in treating bipolar depression, offering promise for addressing depressive episodes in bipolar disorder.
- While delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, CBD has garnered attention for its potential antipsychotic and neuroprotective effects.
Understanding the Cannabinoid System
- Receptor Mechanisms: The human cannabinoid system, comprising CB1 and CB2 receptors, plays a crucial role in modulating various bodily functions, including pain, memory, and appetite, with THC exerting acute effects on motor control and memory.
- Endo-cannabinoid System (ECS): The ECS, governed by endogenous molecules, regulates neurotransmitter activity, influencing mood and cognitive processes.
Therapeutic Applications
- Medical Uses: THC and synthetic cannabinoids are utilized to stimulate appetite, alleviate nausea, and manage pain associated with conditions like HIV-AIDS and cancer.
- Addiction and Withdrawal: Debate surrounds the addictive potential of THC, with animal studies suggesting addictive responses and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation of heavy use.
Psychiatric Implications
- Mood Effects: Cannabis’ impact on mood is multifaceted, with reports suggesting associations with depression and bipolar disorder, although rigorous scientific scrutiny is lacking.
- Psychotic Risks: Individuals with psychotic illnesses, including schizophrenia, exhibit heightened susceptibility to cannabis-induced psychotic symptoms, with youth cannabis use potentially advancing the onset of schizophrenia in genetically vulnerable individuals.
Policy Considerations
- Global Trends: The global trend toward legalizing medical and recreational cannabis underscores the need for informed policymaking to mitigate risks, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children and individuals with mental illnesses.
- Decriminalization Debate: Broader debates on decriminalization necessitate measures to prevent commercialization and ensure safeguards against misuse, emphasizing protection for vulnerable segments of society.
Conclusion
- Navigating the complexities of cannabis necessitates a balanced approach, leveraging its therapeutic potential while addressing associated risks through evidence-based policymaking and clinical interventions.
Back2Basics: Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985
- The NDPS Act is a comprehensive law that consolidates and amends the existing laws relating to narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances in India.
- The Act prohibits the manufacture, cultivation, possession, sale, purchase, transport, storage, or consumption of drugs without permission from appropriate authorities.
- Violations are punishable with rigorous imprisonment for a minimum of 10 years and a fine.
- Lesser punishments are mandated for illegal possession in small quantities for personal consumption.
- The Act also provides for the forfeiture of property derived from, or used in, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
- Drugs covered include:
- Narcotic Drugs: Coca leaf, cannabis (hemp), opium, poppy straw, and their manufactured goods.
- Psychotropic Substances: Any substance that modifies the mind, including amphetamine, methaqualone, diazepam, alprazolam, ketamine, etc.
- Other substances: Cocaine, morphine, diacetylmorphine, or any other narcotic drug or any psychotropic substance as may be specified on this behalf by the Central Government.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Newfound ‘Obelisks’ join Viruses, Viroids as third unusual life form
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Obelisks, Viroids
Mains level: NA

In the news
- Recently identified by scientists at Stanford University, obelisks represent a distinct class of virus-like entities residing within the human body.
What are Obelisks?
- Novel Discoveries: Recently identified, obelisks represent a distinct class of virus-like entities residing within the human body.
- Genetic Diversity: Comprising diverse RNA molecules, obelisks have pervaded both human and global microbiomes, yet remained unnoticed until now.
- Distinctive Characteristics:
-
- Structural Symmetry: Named after the rod-like, highly symmetrical structures formed by their twisted RNA strands.
- Genetic Makeup: Obelisks boast compact genetic sequences of approximately 1,000 nucleotides, devoid of known similarities to other biological agents.
- Size Disparity: Significantly larger than conventional genetic molecules like plasmids, which are primarily composed of DNA.
- Taxonomic Position: Positioned between viruses and viroids, obelisks constitute a unique class of organisms with intriguing properties.
- Host Interaction: While the hosts of certain obelisks remain unidentified, bacterial associations are speculated, hinting at a broader ecological significance.
- Spatial Distribution: Various types of obelisks inhabit diverse regions within the human body, highlighting their pervasive presence and potential physiological roles.
Understanding Viroids: Nature’s Tiny RNA Loops
- Genetic Cousins: Viroids are compact loops of RNA, closely related to DNA, primarily infecting plant organisms.
- Discovery: In 1971, Theodor Diener identified viroids during research on potato spindle tuber disease, revealing naked RNA entities devoid of protein coats or lipid layers.
- Unique Features:
- Lack of Encapsulation: Unlike larger RNA viruses, viroids lack protective shells, relying solely on their RNA structure for stability.
- Genetic Composition: Viroid RNA does not encode protein-building instructions, contrasting with viruses that carry genetic blueprints for their replication machinery.
- Host Interactions: Viroids exploit host enzymes for replication, highlighting their parasitic nature within plant cells.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
IISc develops Synthetic Antibody that Neutralizes Deadly Snake Venom
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Three-finger toxin (3FTx)
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc.) in Bengaluru have successfully created a synthetic human antibody capable of neutralizing potent neurotoxins found in the venom of highly toxic snakes.
Synthetic Antibody against Snake Venom
- Approach: The team utilized a method previously employed to screen antibodies against HIV and COVID-19 to synthesize the new venom-neutralizing antibody.
- Targeted Region: The developed antibody targets a conserved region within the core of a major toxin called the three-finger toxin (3FTx) present in elapid venom.
- Library of Antibodies: The team designed a library of artificial antibodies from humans displayed on yeast cell surfaces and screened them for binding to 3FTxs from different elapid snakes worldwide.
- Effective Binding: After rigorous screening, one antibody emerged capable of binding strongly to various 3FTxs, displaying effectiveness across different elapid species.
Challenges with Current Anti-venom
- Animal-Based Production: Existing anti-venom production involves injecting snake venom into equines and collecting antibodies from their blood, leading to therapeutically redundant antibodies due to exposure to various microorganisms.
- Efficacy Concerns: Research indicates that less than 10% of anti-venom contains antibodies specifically targeting snake venom toxins, raising concerns about efficacy.
Animal Model Testing
- Efficacy in Mice: Mice injected with a toxic 3FTx along with the antibody survived past the 24-hour observation window, while those given only the toxin succumbed within four hours.
- Versatility: The antibody showed effectiveness against the venom of different elapid species, including the monocled cobra and black mamba, with nearly 15 times the potency of conventional products.
- Delayed Administration: Crucially, administering the antibody after a time delay still successfully saved the mice, highlighting its potential for delayed treatment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Understanding Ultradian Rhythms: The Cycle of Life
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ultradian vs. Circadian Rhythms and key difference between them
Mains level: NA
Introduction
- Life on Earth is characterized by cyclical processes that sustain and enhance survival, with one such fundamental process being ultradian rhythms.
- Ultradian rhythms are distinct from circadian rhythms and refer to biological cycles that occur more frequently than once every 24 hours, governing essential physiological functions.
Ultradian vs. Circadian Rhythms
| Ultradian Rhythms | Circadian Rhythms | |
| Definition | Repeat at intervals of less than 24 hours. | Repeat approximately every 24 hours. |
| Duration | Shorter cycles, typically minutes to a few hours. | Longer cycles, around 24 hours. |
| Examples | Sleep cycles, heart rate variability, hormone release. | Sleep-wake cycle, body temperature regulation. |
| Influence | Impact physiological processes within a single day. | Regulate sleep-wake patterns, hormone release, etc. |
| Importance | Essential for various bodily functions and processes. | Crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. |
| Disruption Effects | Interruption can lead to fatigue or mood swings. | Disruption can cause sleep disorders or mood disorders. |
Key Characteristics of Ultradian Rhythms
- Frequency: Ultradian rhythms recur more frequently than circadian rhythms, impacting various biological processes.
- Physiological Patterns: These rhythms regulate heartbeat, breathing, hormonal release, and brain-wave activity, ensuring proper functioning of living organisms.
Significance
- Sleep Cycle: A well-known example of ultradian rhythm is the sleep cycle, which comprises alternating periods of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) and non-REM sleep, typically lasting around 90 minutes each.
- REM and Non-REM Sleep: REM sleep involves dreaming, while non-REM sleep is essential for physical restoration and memory consolidation.
Role in Hormonal Regulation
- Pulsatile Hormone Secretion: Ultradian rhythms influence the pulsatile secretion of hormones like growth hormone, cortisol, and insulin throughout the day.
- Metabolism and Stress Response: These hormonal fluctuations are crucial for regulating metabolism, energy levels, and responses to stress, ensuring overall well-being.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Untapped Potential of Stem Cells in Menstrual Blood
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Endometrial Stem Cells
Mains level: Not Much

Introduction
- Approximately 20 years ago, biologist Caroline Gargett embarked on a quest to uncover remarkable cells within hysterectomy tissue.
- Dr. Gargett discovered two types of cells in the endometrium through rigorous microscopy examination, suspected to be adult stem cells due to their regenerative capabilities.
- The discovery of these cells, known as endometrial stromal mesenchymal stem cells, opened new avenues for research in tissue repair and disease treatment.
What are Endometrial Stem Cells?
- Potential for Regeneration: Endometrial stem cells possess the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including neurons, cartilage, fat, bone, heart, liver, and skin cells.
- Collection Methods: These stem cells can be obtained through a biopsy procedure or harvested from menstrual blood, offering a less invasive and more accessible means of procurement.
Application in Women’s Health
- Understanding Endometriosis: Endometrial stem cells have been linked to endometriosis, a condition affecting millions of women worldwide, providing insights into its etiology and potential therapeutic targets.
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Potential: Differences in menstrual stem cells between healthy individuals and those with endometriosis offer promising avenues for diagnostic tests and targeted treatments.
- Treatment Innovations: Clinical trials exploring the transplantation of menstrual stem cells have shown potential for treating pelvic organ prolapse and other gynecological conditions.
Beyond Gynecological Diseases
- Wider Therapeutic Applications: Research indicates the potential of menstrual stem cells in treating diseases beyond gynecological disorders, including diabetes and wound healing.
- Clinical Trials and Future Prospects: Small-scale trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of stem cell transplantation in humans, paving the way for further exploration and application in diverse medical fields.
Challenges and Biases
- Underrepresentation in Research: Despite their therapeutic potential, menstrual stem cells constitute a minuscule fraction of stem cell research, attributed to cultural taboos and biases surrounding menstruation.
- Funding and Investment: Limited funding and gender bias in research funding pose significant challenges to advancing research on menstrual stem cells, necessitating greater advocacy and support.
Way Forward
- Addressing Bias: Tackling sex and gender bias in research funding is crucial for fostering equitable investments in women’s health research.
- Recognition and Validation: By overcoming cultural taboos and biases, menstrual stem cells can be recognized as a valuable resource in regenerative medicine, transforming perceptions of menstruation from inconvenience to scientific opportunity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Understanding Brumation in Reptiles
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brumation, Hibernation, Estivation (Inactivity in response to high temperatures)
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- Imagine seeing an alligator resting quietly underwater, with only its snout visible. Is it alive or dead? There’s another possibility: brumation.
What is Brumation?
- Definition: Brumation is a period of dormancy or slowed activity in reptiles, similar to hibernation in mammals. It occurs during colder months when temperatures drop and food becomes scarce.
- Purpose: Reptiles enter brumation to conserve energy and survive adverse environmental conditions.
- Habitat: They may retreat to underground burrows, rock crevices, or other sheltered areas where temperatures are stable.
- Metabolic Slowdown: During brumation, their metabolism significantly slows, allowing them to go weeks or months without eating.
- Reduced Activity: Reptiles minimize their resource requirements and conserve energy during this period of reduced activity.
Observations
- Species Affected: Researchers have observed brumation in various reptilian species across habitats.
- Examples: Box turtles and painted turtles burrow into the mud at the bottom of ponds or lakes. Snakes seek refuge in underground dens or caves, while lizards hide under rocks or within vegetation.
Significance of Brumation
- Survival Strategy: Brumation is crucial for reptiles to survive cold climates and endure challenging environmental conditions.
- Re-emergence: It allows reptiles to conserve energy until they can re-emerge to feed and reproduce in more favorable conditions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Celebrating Darwin Day: Understanding Evolution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Darwin Day, Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Mains level: Not Much

Introduction
- February 12 is celebrated globally as Darwin Day to honor the birth of naturalist Charles Darwin and his contributions to evolutionary theory.
- Darwin’s seminal work, ‘On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection,’ published in 1859, revolutionized our understanding of evolution.
Who was Charles Darwin (1809–1882)?
| Description | |
| Early Life | Shrewsbury, Shropshire, England |
| Education | Studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh but later shifted focus to natural history at the University of Cambridge |
| Famous Work | “On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection,” published in 1859, outlining his theory of evolution by natural selection |
| Scientific Contributions |
|
| Research Expeditions | Voyage of the HMS Beagle (1831-1836), a significant expedition during which Darwin collected specimens and made observations that influenced his theories |
| Death | April 19, 1882, at Down House, Downe, Kent, England |
| Legacy | Considered one of the most influential figures in scientific history, his work laid the foundation for modern evolutionary biology |
Evolutionary Insights
- Contributions of Darwin and Wallace: Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace independently proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection, sparking a paradigm shift in biology.
- Scientific Advancements: Darwin Day serves as an occasion to highlight recent scientific advancements in evolutionary biology and promote public engagement with science.
- Impact on Modern Biology: Darwin’s ideas continue to shape modern biology, providing a framework for understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
Key Propositions by Darwin
[A] Understanding Genetic Variations
- Role in Adaptation: Genetic diversity within populations facilitates adaptation to changing environments, as observed in the process of natural selection.
- Example: Genetic variants conferring heat tolerance in a population become advantageous in warmer climates, leading to their increased prevalence through natural selection.
- Mechanisms of Variation: Mutation, recombination, and gene flow contribute to the generation and maintenance of genetic diversity within populations.
[B] Mechanisms of Evolution
- Natural Selection: Darwin and Wallace’s theory of natural selection explains how advantageous traits become more common in populations over successive generations.
- Genetic Drift: Random fluctuations in allele frequencies, known as genetic drift, can lead to significant changes in small populations.
- Gene Flow: Migration and gene flow between populations can introduce new genetic variations and prevent genetic divergence.
Universal Principles of Evolution
- Biodiversity and Evolution: Evolutionary processes have shaped the rich biodiversity observed on Earth, spanning billions of years.
- Conservation Implications: Understanding evolution informs conservation efforts aimed at preserving species and ecosystems.
- Ecological Interactions: Evolutionary dynamics influence ecological interactions, including predator-prey relationships, competition, and mutualism.
Human Evolution and Genetic Diversity
- Human Origins: Humans share a common ancestry with other great apes and have undergone genetic divergence over millennia.
- Genetic Variation: Every individual carries unique genetic variations, contributing to the diversity within human populations.
- Cultural Evolution: Human societies have evolved culturally and genetically, contributing to the global pool of knowledge and skills.
Promoting Equality and Diversity
- Inclusive Society: Recognizing genetic diversity underscores the importance of equality and inclusion across all aspects of society.
- Cultural Diversity: Embracing cultural diversity enriches human experience and promotes mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Addressing Biases: Understanding the genetic basis of traits can help address biases and stereotypes related to race, ethnicity, and identity.
Challenges and Conservation
- Habitat Degradation: Human activities pose threats to biodiversity, necessitating conservation efforts to preserve genetic diversity.
- Climate Change: Rapid environmental changes, such as climate change, can impact the adaptive potential of species, highlighting the importance of evolutionary resilience.
- Community Engagement: Collaborative conservation efforts involving local communities and stakeholders are essential for biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
Conclusion
- Continued Learning: Advancements in evolutionary biology deepen our understanding of life’s complexities and guide efforts towards a sustainable future.
- Celebrating Diversity: Embracing genetic, cultural, and ecological diversity enriches human experience and promotes harmony in a rapidly changing world.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Deep Learning and Antibiotics Discovery
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Deep Learning in Antibiotic Discovery
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- The year 1944 witnessed the simultaneous emergence of artificial neural networks, laying the foundation for deep learning, and the discovery of streptomycin, the first aminoglycoside antibiotic.
- This historical synchrony ultimately connects deep learning and antibiotics.
Why in news?
- In December 2023, scientists introduced a groundbreaking alliance between deep learning and antibiotics by leveraging deep learning techniques to discover a new class of antibiotics, addressing a multi-decade gap in antibiotic development.
Deep Learning in Antibiotic Discovery
- Different Approach: Unlike previous applications of deep learning in drug discovery, this study focused on identifying chemical motifs or substructures used by the deep learning model to evaluate compounds for antibiotic potential, rendering the model “explainable”.
- Proven Efficacy: The research successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of two compounds from the newfound antibiotic class against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections, a major cause of human fatalities in 2019.
- Recognition and Expansion: Experts praised the study for its contributions to antibiotic research and its potential to enhance drug development strategies.
Understanding Deep Learning and Explainability
- Neural Networks: Deep learning relies on artificial neural networks, comprising layers of artificial “neurons” that process inputs and yield outputs through training and testing phases.
- Training and Testing: Deep learning networks are trained on large datasets with annotated inputs to learn specific tasks. During testing, they classify novel inputs based on their learned knowledge.
- The Black Box Issue: Most deep learning models lack transparency in explaining how they arrive at their conclusions, remaining “black boxes.”
- Explainable Deep Learning: In contrast, the study’s model was designed to be explainable, allowing it to not only predict antibiotic potential but also elucidate the substructures contributing to this property.
Journey to Novel Antibiotics
- Experimental Screening: The research began by screening over 39,000 compounds to inhibit S. aureus growth, shortlisting 512 active compounds.
- Graph Neural Network (GNN): A GNN was trained on the dataset, representing atoms as nodes and bonds as edges on a mathematical graph.
- Selecting Non-Toxic Compounds: To ensure safety, 306 compounds were identified that didn’t harm human cells, and other GNNs were trained to identify cytotoxic compounds.
- Identifying Potential Antibiotics: The GNNs evaluated a database of over 1.2 crore compounds, identifying 3,646 potential antibiotics based on substructures.
- Substructure Rationales: The study introduced “rationales” to explain the substructures that conferred antibiotic properties to molecules.
- Efficacy Against MRSA and VRE: Certain compounds, including N-[2-(2-chlorophenoxy)ethyl]aniline, exhibited inhibition of MRSA and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE).
- Mouse Models: One compound effectively reduced MRSA-related skin and thigh infections in mouse models.
Significance and Ongoing Challenges
- Transparency in Drug Discovery: The study’s significance lies in rendering deep learning approaches to drug discovery more transparent and reproducible across drug categories.
- Future Exploration: Researchers are applying substructure rationales to design new antibiotics and explore applications in drugs targeting age-related disorders.
- Addressing a Lacuna: An identified shortcoming is that explainability analysis occurred after predicting antibiotic properties. Implicitly incorporating explainability in deep learning models is proposed as a more robust approach.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Cannabis and Antibiotic Resistance: A Promising Solution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cannabis , THCBD
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- To combat the menace of growing antibiotic resistance, scientists at CSIR-Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM), Jammu, have made a groundbreaking discovery.
- They found that phytocannabinoids, compounds found in the cannabis plant, possess previously untapped antibiotic properties.
Understanding India’s AMR Challenge
- Escalating AMR Threat: AMR occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites no longer respond to antibiotics, leading to increased disease risk and treatment complications.
- Alarming Statistics: In 2019, India reported 2.97 lakh deaths attributed to AMR and 10.42 lakh linked to AMR-related factors.
- Contributing Factors: Overuse of antibiotics, misuse in animal husbandry, and inadequate waste disposal practices are exacerbating AMR, potentially making India the “AMR capital of the world.”
Cannabis Unveils Antibiotic Potential
- Phytocannabinoid Research: IIIM researchers explored the antibiotic properties of tetrahydrocannabidiol (THCBD), a semisynthetic phytocannabinoid derived from cannabis.
- Fighting MRSA: THCBD exhibited remarkable efficacy against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a highly resistant strain of bacteria responsible for numerous deaths worldwide.
- Synergy with Existing Antibiotics: THCBD complemented or showed indifference to common antibiotics like mupirocin, penicillin G, and ciprofloxacin, suggesting potential combinatory treatments.
Overcoming Cannabis Research Challenges
- Legal Constraints: Cannabis research faces legal constraints due to its intoxicating properties, making collaboration with other institutes challenging.
- Policy Advocacy: The research project aims to advocate for a unified national policy for cannabis research, highlighting its antibacterial potential and transforming it into a valuable resource.
Future Prospects for THCBD
- Collaborative Efforts: IIIM researchers seek collaborations to expedite their progress in developing THCBD as a potential drug.
- Addressing Solubility Challenge: Ensuring THCBD’s solubility is a critical step. The molecule leans slightly towards lipophilicity, requiring optimization for proper absorption in biological systems.
- Healthcare Impact: This research not only promises significant contributions to the healthcare system but also offers economic benefits by establishing related industries and creating sustainable job opportunities.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Unveiling the Human Microbiomes: A Genetic Exploration
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Human Microbiome
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The human microbiome, consisting of trillions of microorganisms residing primarily in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in regulating health and disease.
- This intricate microbial community impacts various facets of human well-being, encompassing digestion, nutrient absorption, metabolite processing, immune function, and mental health.
What are Human Microbiomes?
- The human microbiome refers to the vast and diverse community of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes, that inhabit various parts of the human body, such as the skin, mouth, gut, and reproductive organs.
- These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining health by aiding digestion, supporting the immune system, and influencing metabolic processes.
- Imbalances in the microbiome have been linked to various health conditions, including digestive disorders and autoimmune diseases.
- Research on the human microbiome has grown significantly in recent years, leading to a better understanding of its impact on overall well-being.
Genomic Advancements in Microbiome Research
- Challenges in Study: Many microbiome microorganisms defy conventional laboratory culturing, necessitating innovative approaches.
- The Human Microbiome Project: Launched in 2012, this international consortium initiated genomic exploration of the human microbiome through DNA sequencing.
- Technological Progress: Advancements in genomic technology over the last decade have empowered scientists to achieve greater revelations.
Impact on Human Health
- Vital Physiological Functions: The human gut microbiome significantly contributes to essential processes like digestion, nutrient absorption, and the production of necessary enzymes.
- Health Conditions: Imbalances in microbial populations can lead to various health conditions, emphasizing the importance of a balanced microbiome.
- Response to Antibiotics: The gut microbiome can undergo significant changes when individuals take antibiotics, eventually reverting to its original state.
Manipulating Microbiome for Clinical Outcomes
- Microbiota Transplants: Researchers have employed treatments like fecal microbiota transplants to manage infections and metabolic syndromes, demonstrating the potential to artificially alter the human microbiome.
From Genetics to Gut Microbes
- Genetic Influence on Microbes: Recent studies suggest that genetic variations in individuals may affect the diversity and abundance of gut microbes.
- A Link to ABO Blood Group: Researchers identified a link between genetic variants in the ABO blood group and microbial genes involved in metabolizing N-acetylgalactosamine, revealing potential links to cardiometabolic traits and even COVID-19 susceptibility.
Implications for Cancer and Neurons
- Cancer Link: Gut microbes have been associated with the development of colorectal cancer, offering new prospects for cancer therapy.
- Neuronal Signaling: Microbiome-produced vitamin B12 may influence neuronal signaling through its impact on choline availability.
Role in Urobilinogen Metabolism
- Yellow Urine Pigment: Researchers uncovered the role of the human microbiome in metabolizing urobilinogen, impacting bilirubin levels and jaundice.
- Personalized Healthcare: These genetic insights are shaping future healthcare by enabling personalized interventions.
Conclusion
- The study of the human microbiome, guided by genomic research, continues to unravel its profound impact on human health and well-being.
- From its vital role in physiological functions to potential links with diseases and even neurological processes, the microbiome is an essential component of our overall health.
- Understanding the genetic intricacies of this microbial community holds great promise for personalized healthcare and innovative therapies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Private: Ancient European DNA reveals origin of Multiple Sclerosis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Multiple Sclerosis
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The study of ancient DNA from early European populations, dating back up to 34,000 years, offers valuable insights into the origins of multiple sclerosis (MS) and sheds light on various genetic traits among modern Europeans.
- By comparing ancient and modern DNA, researchers have unravelled a complex interplay between genetic variants that once provided protection against animal-borne diseases and the increased risk of MS in contemporary populations.
What is Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
- MS is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system.
- It leads to various symptoms, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness, and vision problems.
- MS comes in different forms, with relapsing-remitting MS being the most common.
- While there is no cure, treatments are available to manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Role of Ancient DNA
- Genomic Exploration: Ancient DNA from 1,664 individuals across Western Europe and Asia was sequenced, enabling a deep exploration of genetic changes over time.
- Modern Comparisons: These ancient genomes were compared with DNA from the UK Biobank, comprising over 410,000 “white-British” individuals, to identify evolutionary shifts.
Multiple Sclerosis Insights
- Protective Variants: The study revealed that genetic variants, now associated with an increased risk of MS, initially served as protective mechanisms against infections transmitted by livestock herders called the Yamnaya people.
- Bronze Age Migration: A pivotal migration event approximately 5,000 years ago during the Bronze Age brought the Yamnaya people to Western Europe from regions including modern Ukraine and southern Russia.
Regional Disparities in MS
- Northern Europeans: MS prevalence is highest in Northern Europeans, particularly in countries like Ireland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, where Yamnaya-related genetic ancestry is more prominent.
- Southern Europeans: In contrast, Southern Europeans have a lower prevalence of MS due to differing genetic ancestry from Neolithic farmers.
Implications for Disease and Evolution
- Changing Genetic Traits: The findings illustrate how genetic traits that were once advantageous can become detrimental as environments and living conditions evolve.
- Rise of Pathogenic Infections: The Bronze Age saw an increase in pathogenic infections due to closer proximity between humans and domestic animals, leading to the development of protective genetic variants.
Recalibrating Immune Systems
- Reinterpretation of MS: This research offers a new perspective on MS, emphasizing the need to recalibrate the immune system rather than suppress it, considering the shifts from past to modern sanitary environments.
- Broader Health Implications: The study’s insights extend to other health conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and type 2 diabetes risks among Eastern Europeans.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Could Sisal Leaves make Sanitary Napkins more Sustainable in India?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sisal Leaves
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Scientists at Stanford University have developed a method to produce highly absorbent material from sisal leaves for use in menstrual hygiene products.
Using Sisal for Sanitary Napkins
- Historical Use of Sisal: Originating from ancient Aztec and Mayan civilizations, sisal leaves have been used for various purposes, including making paper, twine, cloth, carpets, and mezcal.
- Superior Absorption: The material created from sisal leaves has a higher absorption capacity than commercial menstrual pads.
- Environmentally Sustainable Method: The production process is free from polluting or toxic chemicals and can be conducted locally on a small scale.
Global Menstrual Hygiene Challenges
- Rising Use of Hygienic Methods: Despite an increase in the use of sanitary napkins, tampons, and menstrual cups in India, access to menstrual hygiene products remains limited globally.
- Environmental Concerns: The widespread use of sanitary napkins poses environmental challenges due to the non-biodegradable waste they generate.
Sisal as an Eco-Friendly Alternative
- Comparison with Other Plant Fibers: Unlike banana plants, sisal is drought-resistant, making it a more sustainable option for producing absorbent material in arid regions.
- Innovative Delignification Process: The team uses peroxyformic acid for delignification, a more environmentally friendly method than traditional processes.
Life-Cycle Analysis and Environmental Footprint
- Cradle-to-Gate Carbon Footprint Analysis: The environmental footprint of the sisal-based process is comparable to commercial processes for timber and cotton.
- Water Consumption: Water usage in sisal cultivation is significantly lower than in cotton industries, enhancing its sustainability.
Local Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Pilot Production in Nepal: The team is testing the scalability of their method for mass-producing sanitary napkins in Nepal.
- Global Student Engagement Program: High school students worldwide are encouraged to test local plants using this process and contribute to a public database.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Quality Standards Compliance: Ensuring that plant fiber-based menstrual hygiene products meet existing quality standards is crucial.
- Distributed Manufacturing Approach: This model focuses on smaller-scale production catering to local populations, reducing carbon emissions from transportation.
- Research Consortium and Collaboration: The team aims to build a research consortium for open-source collaboration in addressing menstrual health and period poverty.
Conclusion
- Innovative Solution to Period Poverty: The use of sisal in menstrual hygiene products represents a significant advancement in addressing period poverty and environmental sustainability.
- Collaborative Efforts for Global Impact: The initiative’s success hinges on global collaboration, quality control, and adapting the technology to diverse environmental conditions.
- Potential for Widespread Adoption: If successful, this innovation could transform menstrual hygiene practices, making them more sustainable and accessible worldwide.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Private: Mysteries of Plant Root Oscillation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plant root oscillation
Mains level: NA
Introduction
- Plant roots, hidden beneath the soil, are more influential in shaping our environment than we often realize.
- Recent scientific discoveries have revealed that the growth of plant roots involves complex genetic processes.
Discoveries in Root Growth
- Gene Oscillation Discovery: Scientists found that certain genes in the root tip pulsate in their activity, a discovery made about 15 years ago.
- Ongoing Research: This pulsation is still not fully understood, but ongoing research is shedding more light on it.
- Importance for Agriculture: Understanding this process is crucial for selecting and designing plants that can thrive in various soils and climates, especially with the increasing occurrence of extreme weather.
Inside Plant Cells
- Chemical Reactions and Gene Activity: Plant cells are constantly undergoing a variety of chemical reactions and changes in gene activity.
- External Influences: These processes can be influenced by external factors like light, temperature, and nutrient availability.
- Genetic Programming: Many of these cellular activities are predetermined by the plant’s genetic makeup.
- Common Misconception: Plants are often seen as simple organisms primarily beneficial for producing oxygen.
Oscillations in Plant Cells
- Molecular Rhythms: Certain molecules in plant cells show rhythmic patterns, appearing and disappearing at regular intervals.
- Circadian Rhythms: An example of such a rhythm is the circadian clock, which is present in both plants and animals.
- Variety in Nature: Oscillations occur in various forms in nature, from quick cycles like heartbeats to slower ones like the menstrual cycle.
- Root Chemical Processes: Similar oscillatory processes are happening in plant roots, contributing to their growth.
Understanding Root Growth Oscillation
- Feedback Loops: The oscillation in root growth is thought to be caused by negative feedback loops, a common mechanism in natural processes.
- Microscopic Markers: Scientists have used fluorescent markers to observe how this oscillation influences the direction of root growth.
Mystery of Root Tip Oscillation
- Unknown Causes: The exact reason for this oscillation at the root tip is still unknown, and it’s not related to circadian rhythms.
- Auxin’s Role: The plant hormone auxin, which promotes growth, appears to play a crucial role in this process.
- Gene and Hormone Interaction: The interaction between auxin and certain genes, which involves complex feedback loops, might be key to understanding these oscillations.
Mathematical Models in Plant Growth
- Historical Use of Geometry: Geometry has been used to study the visible parts of plants.
- Dynamical Systems Theory (DST): This mathematical approach helps explain the oscillatory patterns in plant roots, particularly how auxin distribution is affected by cell division.
Challenges in Understanding Auxin Patterns
- Cell Division Synchronization Theory: There was a hypothesis that synchronized cell division could lead to regular auxin pulses.
- Irregular Auxin Patterns: However, observations show that auxin distribution is not as regular as expected, indicating a more complex process.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Private: Study Reveals Oldest Evidence of Photosynthesis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Evidence of Photosynthesis
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- Researchers have identified the oldest known photosynthetic structures in microfossils dating back 1.75 billion years, as reported in Nature.
- This finding provides crucial insights into the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis, a process unique to cyanobacteria and certain eukaryotic organelles.
What is Photosynthesis?
- Process: Photosynthesis is a process used by plants, algae, and certain bacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Chlorophyll Role: Chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants, is crucial for absorbing light, primarily sunlight.
- Location in Plants: Takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, with the main action occurring in leaf cells.
- Light Reaction: Involves the absorption of light by chlorophyll, resulting in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
- Water’s Role: Water molecules are split into oxygen, protons, and electrons in the light reactions. Oxygen is released as a byproduct.
- Carbon Dioxide Fixation: In the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic molecules, a process known as carbon fixation.
- Production of Glucose: The end product of photosynthesis is glucose, which plants use as food for energy and growth.
- Oxygen Release: Oxygen is released into the atmosphere as a byproduct, which is vital for the respiration of most living organisms.
Oxygenic Photosynthesis and Its Origins
- Process: Oxygenic photosynthesis is a process where sunlight catalyses the conversion of water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, primarily performed by cyanobacteria and certain eukaryotes.
- Historical Impact: Cyanobacteria played a crucial role during the Great Oxidation Event around 2.4 billion years ago, but the exact timeline of oxygenic photosynthesis evolution remains debated.
Discovery of Ancient Photosynthetic Structures
- Fossil Evidence: Researchers identified fossilized thylakoids, photosynthetic structures, in Navifusa majensis microfossils from the McDermott Formation in Australia.
- Age and Significance: At 1.75 billion years old, these are the oldest known photosynthetic structures, indicating that photosynthesis may have evolved before this time.
Thylakoids: Key to Photosynthesis
- Description: Thylakoids are membrane-bound structures within chloroplasts of plants and some modern cyanobacteria, crucial for photosynthesis.
- Evidence of Photosynthesis: The presence of thylakoids in N. majensis suggests active oxygenic photosynthesis and confirms the cyanobacterial nature of these ancient organisms.
Implications and Future Research
- Evolutionary Timeline: While the discovery doesn’t pinpoint whether photosynthesis evolved before or after the Great Oxidation Event, it suggests an earlier origin for oxygenic photosynthesis than previously known.
- Further Investigations: Researchers propose that examining older microfossils with similar ultrastructural analyses could expand our understanding of early photosynthesizers and the development of early ecosystems.
Conclusion
- Historical Context: This discovery pushes back the fossil record of thylakoid-bearing cyanobacteria by at least 1.2 billion years, providing a minimum age for their divergence at roughly 1.75 billion years ago.
- Future Predictions: The team anticipates that further ultrastructural analyses of well-preserved microfossils might reveal more about the geological record of oxygenic photosynthesizers and the early, weakly oxygenated ecosystems where complex cells evolved.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Zosurabalpin: Antibiotic against Drug-Resistant Bacteria
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zosurabalpin
Mains level: Read the attached story
Introduction
- New Antibiotic Class: Researchers have identified zosurabalpin, a new class of antibiotics showing potential against the drug-resistant bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii.
- Effective against CRAB: Zosurabalpin has been found effective against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)-induced pneumonia and sepsis in mouse models.
About Zosurabalpin
- Development Process: The antibiotic originated from a tethered macrocyclic peptide (MCP) selectively targeting A. baumannii and was optimized for efficacy and tolerability.
- Novel Mode of Action: Zosurabalpin operates through a previously unknown mechanism, inhibiting the transport of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in bacteria.
- Inhibition of LPS Transport: By blocking a protein complex essential for LPS transport to the bacterial surface, zosurabalpin disrupts the outer membrane structure of Gram-negative bacteria, leading to bacterial death.
Effectiveness and Clinical Trials
- Laboratory and Animal Studies: Zosurabalpin demonstrated effectiveness against over 100 CRAB clinical samples in the lab and significantly reduced bacterial levels in mice with CRAB-induced pneumonia and sepsis.
- Phase I Clinical Trials: The antibiotic has undergone evaluation in two phase I clinical trials, marking the initial steps towards potential human use.
Implications and Future Prospects
- Addressing Antibiotic Resistance: The discovery of zosurabalpin offers hope in the fight against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a growing global health concern.
- Potential Clinical Application: If further trials are successful, zosurabalpin could become a vital tool in treating infections caused by drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
- Continued Research: Ongoing and future studies will be crucial to fully understand the antibiotic’s safety, efficacy, and potential resistance mechanisms.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Evolution of Genomic Medicine: Research to Mainstream Healthcare
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Genomic Medicine
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Over the past two decades, genomics and the use of genetic information in healthcare have undergone significant transformations.
- Once limited to major research centers, personal genome sequencing has become widely accessible, empowering individuals with detailed knowledge of their genetic makeup.
What is genome sequencing?
- Genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome.
- The genome is the entire set of genetic material (DNA in the case of most organisms) that provides the instructions for building, maintaining, and functioning of the organism.
- Genome sequencing involves identifying the order of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) in an organism’s DNA.
Applications of Personal Genome Sequencing
- Disease Risk Assessment: Personal genome sequencing can identify genetic variants associated with an increased risk of certain diseases, such as cardiovascular conditions, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Pharmacogenomics: Personal genome sequencing helps predict how an individual will respond to specific medications, allowing for the customization of drug prescriptions based on genetic factors.
- Cancer Genomics: Personal genome sequencing of cancer cells helps identify specific mutations driving tumor growth.
- Rare Genetic Disorders: Personal genome sequencing is a powerful tool for diagnosing rare genetic disorders, particularly in cases where traditional diagnostic methods may be inconclusive.
- Reproductive Health: Couples planning to have children can undergo personal genome sequencing to assess the risk of passing on genetic conditions to their offspring.
- Forensic Identification: Personal genome sequencing can be used in forensics for human identification and the resolution of criminal investigations.
- Research and Scientific Discovery: Aggregated personal genomic data from large populations contribute to ongoing research, advancing our understanding of the genetic basis of diseases and human biology.
Case Study: Iceland’s Genetics Research
- Iceland’s Unique Demographics: Iceland’s historical demographic isolation and early initiation of population-level genome sequencing have made it a focal point in genetics research.
- Research on Lifespan and Genetic Variants: A study in Iceland suggested that actionable incidental genetic variants could potentially improve lifespan, with significant findings related to cancer-related genotypes.
Future of Genome Sequencing and Healthcare
- Increasing Accessibility: As genome sequencing becomes more accessible and affordable, regular population-scale sequencing and newborn sequencing initiatives are becoming more feasible.
- Benefits for Population Health: Widespread implementation of these programs could provide medically actionable insights, enabling proactive and effective disease treatment and prevention.
- Advancements in Technology: Current genome sequencing technologies, often referred to as second-generation sequencing, have limitations in handling repetitive sequences and resolving structural variations. Third-generation sequencing technologies, such as single-molecule sequencing, are expected to overcome these challenges and provide longer read lengths, improving the accuracy and completeness of genome sequences.
Conclusion
- The advancements in genomics are paving the way for a more proactive and personalized approach to healthcare, with significant potential for disease prevention and management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Huntington’s Disease: Insights from Medical Genetics and Fruit Fly Research
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Huntington's Disease
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Nizam’s Institute of Medical Sciences in Hyderabad reports three to four cases of Huntington’s disease monthly, with each case impacting entire families.
Understanding Huntington’s Disease
| Details | |
| Nature of Disorder | Genetic, progressive brain disorder |
| Genetic Cause | Mutation in the huntingtin gene on chromosome 4 |
| Inheritance Pattern | Autosomal dominant disorder (only one copy of the defective gene, from either parent, is enough for disease onset) |
| Symptoms | Movement Disorders: Involuntary movements (chorea), muscle problems (dystonia), abnormal eye movements.
Cognitive Disorders: Difficulty in organizing and focusing, lack of flexibility, impulse control issues. Psychiatric Disorders: Depression, mood swings, changes in personality |
| Age of Onset | Typically between 30 and 50 years of age, but can vary widely
Gradual onset, worsening over 10-25 years, leading to severe disabilities |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing to detect the presence of the defective gene |
| Treatment | No cure; treatment focuses on managing symptoms, including medication for movement and psychiatric disorders, and therapy |
| Impact on Life Expectancy | Can shorten life expectancy, particularly if onset is at a younger age |
Role of the HTT Gene and Glutamine Repeats
- Genetic Mutation: Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene, leading to abnormal huntingtin (Htt) proteins that damage neurons.
- Polyglutamine Tracts: The severity of the disease correlates with the length of glutamine repeats in the Htt protein; longer repeats result in earlier and more severe symptoms.
- Inheritance Pattern: The disease manifests even if only one copy of the HTT gene is mutated, demonstrating its dominant nature.
- Similar Proteins and Diseases: Other proteins with polyglutamine tracts, when mutated, can also cause neuronal degeneration, leading to disorders like spinocerebellar ataxia.
Fruit Fly Study: A Model for Understanding Huntington’s
- Genetic Engineering in Flies: Researchers engineered fruit flies to express the human HTT gene with extended polyglutamine tracts in their neurons.
- Gal4/UAS System: Utilizing the Gal4 gene from baker’s yeast, the study induced expression of mutated HTT in fly neurons.
- Symptoms in Flies: Flies with longer glutamine tracts exhibited symptoms similar to Huntington’s disease, unlike those with shorter, normal tracts.
Yod1 Gene Discovery
- Gene Expression Experiment: The study explored the effects of altering the expression of 32 genes on disease-like symptoms in fruit flies.
- Yod1’s Protective Role: Overexpression of the Yod1 gene eliminated neurodegeneration and other disease-like effects in flies with longer glutamine tracts.
Broader Implications and Future Research
- Potential in Human Treatment: If overexpression of the human version of Yod1 shows similar benefits in fruit flies, it could be a promising avenue for treating Huntington’s in humans.
- Value of Model Organisms: Studies in fruit flies and yeasts are pivotal for understanding molecular mechanisms of diseases like Huntington’s.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Nematocysts in Aquatic Ecosystems
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nematocysts
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Evolution has crafted unique defense mechanisms in the animal kingdom, one of which is the nematocyst.
Understanding Nematocysts
- Structural Composition: A nematocyst comprises a capsule with a coiled tubule and a toxin-filled bulbous structure.
- Rapid Deployment: Upon stimulation, the nematocyst ejects its tubule at an incredibly high acceleration, comparable to a bullet’s speed.
- Fastest Biological Mechanisms: This ejection process is among the quickest in the animal kingdom.
- Found in: Nematocysts are particularly prevalent in jellyfish, corals, sea anemones, and hydras, serving as effective tools for hunting and protection.
Role in Cnidarians’ Survival
- Cnidarians and Cnidocytes: Cnidarians, a group of animals characterized by cnidocytes (specialized cells), heavily rely on nematocysts for feeding and defense.
- Activation Process: Contact with potential prey triggers sensory structures on cnidocytes, leading to the nematocyst’s release and subsequent prey immobilization or toxin injection.
Diversity of Toxins in Nematocysts
- Variety of Effects: Nematocyst toxins can be paralytic, halting prey movement, or cytolytic, breaking down cells.
- Strategic Use: Cnidarians often employ a mix of toxins to enhance the effectiveness of their predatory and defensive actions.
- Contribution to Cnidarians’ Success: The complexity and efficiency of nematocysts play a vital role in the survival and dominance of cnidarians in aquatic habitats.
- Formidable Aquatic Predators: The presence of nematocysts makes cnidarians formidable entities in their ecosystems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CRISPR-Based Therapies: A New Era in Genetic Disease Treatment
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CRISPR Technology
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Revolutionary Development: The medical world is witnessing a significant breakthrough with the approval of CRISPR-based therapies for sickle-cell disease and β-thalassemia in the U.K. and the U.S.
- Global Impact: These advancements hold the potential to transform the lives of millions suffering from these inherited blood disorders.
CRISPR Technology: From Discovery to Application
- Origins of CRISPR: Discovered in archaea in 1993, CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) elements were later found to form an antiviral defense system in bacteria with Cas (CRISPR-associated) proteins.
- Nobel Prize-Winning Innovation: Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna’s work on CRISPR-Cas9 as a ‘molecular scissor’ earned them the 2020 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
- Eukaryotic Genome Editing: Subsequent research demonstrated CRISPR-Cas9’s ability to edit eukaryotic genomes, paving the way for various applications in genetic therapies and agriculture.
CRISPR in Medicine: Recent Approvals and Applications
- CRISPR-Based Treatment for Blood Disorders: The MHRA in the U.K. and the FDA in the U.S. approved ‘Casgevy’ for treating sickle-cell disease and transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia.
- Treatment Mechanism: Casgevy involves modifying a patient’s blood stem cells to correct the genetic defect causing sickling, then regrafting them to produce normal red blood cells.
- Historical Context: This approval marks a full circle from Linus Carl Pauling’s description of sickle-cell disease as a molecular disorder 74 years ago.
Emerging CRISPR Technologies and Approaches
- Base-Editing: This technique allows genome editing at the single nucleotide level.
- Prime Editing: A newer method that uses a search-and-replace strategy for precise genome modifications.
- Epigenetic Modifications: CRISPR systems are also being developed to target epigenetic effects.
Challenges and Future Prospects
- Safety and Accuracy Concerns: Issues like off-target events, where CRISPR-Cas9 edits unintended parts of the genome, pose significant challenges.
- Balancing Risks and Benefits: While the potential of these technologies is enormous, their risks must be weighed against both short- and long-term benefits.
- Ongoing Research and Surveillance: Continuous scrutiny is essential to uncover potential side effects that are currently unknown.
Conclusion
- Celebrating Advances: The approval of therapies like Casgevy heralds a new era for millions suffering from genetic diseases.
- Optimistic Outlook: The advancements in CRISPR technology signal a promising future in the field of genetic medicine and disease treatment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The future of healthcare is in our genes
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: gene and cell therapy
Mains level: gene and cell therapy

Central idea
The article underscores the transformative potential of gene and cell therapy in addressing India’s healthcare challenges, particularly genetic disorders, cancer, and infectious diseases. It emphasizes the imperative for a paradigm shift, highlighting the need for collaborative efforts, regulatory frameworks, and increased awareness to integrate these therapies into mainstream healthcare.
Key Highlights:
- Genetic Disorders in India: Over 40 million individuals in India suffer from genetic disorders, emphasizing the urgent need for advanced treatments like gene therapy.
- Haemoglobinopathies: Conditions like Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anaemia affect millions, and gene therapy offers a potential cure by addressing the root genetic mutations.
- Cancer Treatment: With 1.16 million new cancer cases annually, gene and cell therapy, especially CAR-T therapy, present precision medicine solutions tailored to individual genetic profiles.
- Infectious Diseases: Gene therapy shows promise in treating infectious diseases, including potential applications against viral threats like dengue, HIV/AIDS, and others.
- Future Vision: Gene and cell therapies anticipate a future of precise and personalized treatments, reducing economic burdens associated with chronic conditions.
Key Challenges:
- Infrastructure Limitations: Integrating gene and cell therapy into mainstream healthcare faces challenges related to infrastructure readiness.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of gene therapy, including issues of consent and long-term consequences, pose challenges to widespread adoption.
- Awareness Gap: Limited awareness among healthcare professionals and the public about gene and cell therapy hinders successful integration.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Precision Medicine: Tailored medical approaches considering the unique genetic makeup of each patient.
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy (CAR-T): Modifying a patient’s immune cells to target cancer cells, exemplifying precision medicine.
- mRNA Vaccines: Groundbreaking gene-therapy products, as seen in Covid-19 vaccines like Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna.
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID): A genetic disorder potentially treatable with gene therapy to restore normal immune function.
Key Quotes:
- “Gene therapy is not just about managing symptoms — it is about rewriting the genetic code that underlies these conditions.”
- “The imperative lies in investing in research and infrastructure to make these transformative therapies accessible to those who need them.”
- “Gene and cell therapy are not just treatments; they are the future of healthcare.”
Key Examples and References:
- Haemoglobinopathies Impact: Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Anaemia affecting 40 million individuals in India.
- Cancer Cases: Over 1.16 million new cancer cases annually, highlighting the demand for advanced treatments.
- mRNA Vaccines: Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Covid-19 vaccines as groundbreaking gene-therapy products.
Key Facts and Data:
- Demographic Impact: Genetic disorders affect millions in India, necessitating advanced treatments.
- Cancer Statistics: Over 1.16 million new cancer cases reported annually in India.
- Economic Burden: Gene therapy’s potential to reduce long-term healthcare costs for chronic genetic conditions.
Critical Analysis:
- Integration Challenges: Infrastructural and ethical challenges pose hurdles to the mainstream integration of gene and cell therapy.
- Opportunities for Collaboration: Challenges present opportunities for collaborative efforts among scientific communities, industries, policymakers, and healthcare providers.
- Need for Awareness: Limited awareness emphasizes the importance of enhancing awareness among healthcare professionals and the public for successful integration.
Way Forward:
- Collaborative Efforts: Encourage collaboration between scientific communities, industries, policymakers, and healthcare providers to overcome challenges.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Develop regulatory frameworks balancing innovation with ethical considerations to guide gene therapy integration.
- Research and Development: Invest in research and development to advance gene and cell therapy, addressing infrastructure limitations and ethical concerns.
- Public Awareness: Foster awareness among healthcare professionals and the public to ensure successful integration into the broader healthcare landscape.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Population-Level Genome Sequencing and Its Impact
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: deCODE Initiative
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- The UK recently completed sequencing half a million whole genomes, nearly 0.7% of its population, under ‘deCODE’ Initiative.
- Various countries have launched large-scale genome projects, with some focusing on specific populations like African ancestry.
About ‘deCODE’ Initiative
- Inception: Launched in Iceland in 1996, deCODE genomics enrolled most of the Icelandic population for genetic studies.
- Contributions: The initiative enhanced disease genetics understanding and set standards for handling genomic data, integrating medical records with genealogies.
Merit of Large-Scale Sequencing
- Disease Research and Understanding: Large-scale genome sequencing allows researchers to identify genetic variations associated with various diseases. This information is crucial for understanding the genetic basis of diseases, including rare genetic disorders and complex conditions like cancer.
- Personalized Therapies: With a better understanding of an individual’s genetic makeup, it becomes possible to develop personalized and targeted therapies.
- Genetic Counseling: Large-scale genome sequencing provides valuable information for genetic counseling, helping individuals and families understand their risk for certain genetic conditions.
- Identification of Rare Variants: Large-scale sequencing efforts contribute to the identification of rare genetic variants that might be responsible for certain diseases. These discoveries are essential for expanding our knowledge of the genetic landscape and improving diagnostic capabilities.
- Population Genetics and Evolution: Genome sequencing on a large scale allows researchers to study the genetic diversity within populations. This information is valuable for understanding human evolution, migration patterns, and population-specific genetic traits.
Ethical and Regulatory Challenges
- Privacy Concerns: Genome sequencing generates highly sensitive and personal information. There is a risk that genetic data could be misused or lead to privacy breaches.
- Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent for genome sequencing is complex due to the vast amount of information generated and the potential for incidental findings.
- Data Ownership and Control: Balancing individual rights with the need for research and medical advancements requires careful consideration of data sharing, ownership, and access policies.
- Genetic Discrimination: Concerns about genetic discrimination in areas such as employment, insurance, and education may discourage individuals from undergoing genome sequencing. L
- Access to Genetic Services: Disparities in access to genetic services and genomic technologies may exacerbate existing healthcare inequalities.
- Ethical Use of Genetic Data in Research: Researchers must adhere to ethical standards when using genetic data in research. This includes obtaining proper consent, ensuring data security, and transparently communicating the purpose and potential risks of the research.
Long-Term Impact and Future Prospects
- Beyond Individual Health: Population-scale genomics will enhance our understanding of human evolution, migration, and adaptation.
- Personalized Medicine: It paves the way for personalized healthcare based on individual genetic profiles.
- Billion Genome Project: The possibility of sequencing a billion genomes in a single project is on the horizon, alongside individuals’ rights to access and understand their own genomic data.
Conclusion
- Population-scale genomics is at the forefront of a genomic revolution, with the potential to transform healthcare, deepen our understanding of human biology, and shape our approach to medicine and biology.
- This evolving field promises to bring personalized, precise treatments and a richer comprehension of our genetic heritage.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Embryonic Development: Unraveling the Mysteries of HERVH and ‘Jumping Genes’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HERVH and 'Jumping Genes'
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Recent breakthroughs in genetic research have shed light on the complexities of early embryonic development, particularly focusing on the inner cell mass, a key component in forming the human body.
Embryonic Development Explained
- Life’s Commencement: Life begins with the fusion of sperm and egg, creating a zygote, the first cell of a new individual.
- Cellular Multiplication: The zygote undergoes rapid cell division, marking the onset of embryonic development.
- Diverse Cell Differentiation: As the embryo develops, cells differentiate into various types, leading to the formation of organs and tissues.
- Journey to Birth: This intricate process culminates in the birth of a newborn after nine months of gestation.
Early Stages of Development
- Inner Cell Mass Formation: Early embryonic cells cluster around the inner cell mass, vital for the embryo’s development.
- Pluripotency of Cells: These cells are pluripotent, meaning they can develop into any cell type in the body.
- Scientific Focus: The inner cell mass is a primary subject of study due to its critical role in human development.
Gene Expression in Embryonic Cells
- Analyzing Gene Activity: Researchers study the proteins produced by genes to understand cell-specific gene expression.
- Deciphering Cell Development: This research provides insights into the active genes in each cell, revealing the mechanisms of cell development.
Discoveries in the Inner Cell Mass
- 2016 Research Insights: Manvendra Singh’s reanalysis of gene expression data identified a new group of non-committed cells in the inner cell mass.
- Enigma of Cell Death: These cells, unlike others, do not progress to later developmental stages and are eliminated early on.
HERVH Gene and Cell Survival
- HERVH’s Crucial Function: A 2014 study revealed that HERVH, a gene with virus-like properties, is essential for maintaining pluripotency in embryonic stem cells.
- Gene Expression Variations: Singh’s research showed that while most inner cell mass cells express HERVH, the non-committed cells that eventually die do not.
- Independent Confirmation: This discovery was corroborated by researchers at the University of Spain in lab-fertilized embryos.
Understanding ‘Jumping Genes’
- Transposons in Non-Committed Cells: The non-committed cells express transposons, or ‘jumping genes’, which can cause DNA damage and lead to cell death.
- HERVH’s Protective Role: HERVH protects most cells from the harmful effects of transposons, but cells lacking HERVH expression are vulnerable.
- Natural Selection in Embryos: The early human embryo acts as a selection ground, favoring cells with HERVH expression.
- HERVH’s Unique Nature: Interestingly, HERVH itself is a transposon but functions protectively rather than destructively.
Implications for Placenta and Beyond
- Placental Development: Cells that form the placenta also exhibit transposon activity but manage to survive without HERVH expression.
- Impact on Regenerative Medicine: Understanding HERVH’s role in cell pluripotency has profound implications for regenerative medicine and could influence embryo viability in fertility treatments.Top of Form
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Plant Eavesdropping: Role of Green Leaf Volatiles (GLVs)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plant Eavesdropping
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- The scent of freshly cut grass, more than just a pleasant aroma, is a part of a complex plant communication system involving Green Leaf Volatiles (GLVs).
- For plants, these GLVs are not just fragrances but crucial signals that alert them to imminent threats, such as herbivore attacks.
Concept of Plant Eavesdropping
- Inter-Plant Communication: Plants have the remarkable ability to ‘eavesdrop’ on the distress signals of their neighbors, preparing themselves for similar threats.
- Agricultural Implications: Understanding this natural warning system could revolutionize pest control in agriculture, potentially reducing the need for harmful pesticides.
Understanding Plant Defense Mechanisms
- Research involving mustard plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) has shown that calcium plays a crucial role in plant defense, with calcium levels spiking in response to damage.
- Using genetically modified plants that fluoresce in response to calcium surges, researchers have been able to visually track plant reactions to physical damage and GLV exposure.
- Experiments have demonstrated that plants can detect and respond to GLVs emitted by neighboring plants, as evidenced by fluorescence in modified mustard plants.
- Among the GLVs, specific compounds like E-2-HAL and Z-3-HAL were found to trigger significant responses in plants.
Gene-Level Defense Response
- Activation of Defense Genes: Exposure to GLVs leads to the activation of certain defence-related genes in plants, suggesting that they perceive these volatiles as danger signals.
- Implications for Plant Protection: This gene activation could be a crucial step in natural plant defense mechanisms against herbivores.
Implications and Future Directions
- Natural Pest Control: The study opens up possibilities for using GLVs in agricultural pest control, potentially reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
- Alternative Strategies: While promising, researchers also consider other substances like jasmonic acid, balancing pest control with the plant’s growth and fruit production.
- Expanding Plant Sensory Research: The findings encourage further exploration into plant perception and response to external stimuli, particularly in natural environments where signaling dynamics are more complex.
- Challenges in Field Studies: One of the main challenges in studying plant volatile signaling in natural settings is the dilution of these compounds in the open air.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Casgevy: Gene Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease and Thalassaemia
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Casgevy, Crispr-Cas9 technology
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- The recent approval of Casgevy, a groundbreaking gene therapy utilizing Crispr-Cas9 technology, by the UK health authorities represents a monumental achievement in medicine.
- This therapy holds the potential to provide a lifelong cure for individuals grappling with sickle cell disease and thalassaemia, offering newfound hope and possibilities in the field of genetic medicine.
Casgevy: A Gene-Editing Marvel
- World’s First Licensed Gene Therapy: Casgevy stands as the world’s inaugural licensed gene therapy employing Crispr-Cas9 technology, an innovation that garnered the Nobel Prize in 2020.
- Targeting Faulty Genes: This revolutionary therapy specifically targets the flawed genes responsible for sickle cell disease and thalassaemia, offering the tantalizing prospect of a lifelong cure.
- A Paradigm Shift: In the past, the only permanent treatment option was a bone marrow transplant, contingent on discovering a closely matched donor.
Mechanism of Action
- Genetic Errors: Sickle cell disease and thalassaemia both stem from genetic abnormalities within the haemoglobin gene, impairing the structure and functionality of red blood cells.
- Precision Gene Editing: Casgevy harnesses the patient’s blood stem cells, meticulously edited using Crispr-Cas9, with a specific focus on the BCL11A gene.
- Boosting Foetal Haemoglobin: By stimulating the production of foetal haemoglobin, which lacks the irregularities found in adult haemoglobin, the therapy mitigates the symptoms of these debilitating conditions.
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease and Thalassaemia
Sickle Cell Disease: Characterized by crescent-shaped red blood cells, this condition disrupts smooth blood flow, resulting in excruciating pain, infections, anaemia, and even strokes. India bears witness to an annual influx of 30,000-40,000 children born with sickle cell disease. Thalassaemia: This disorder leads to diminished haemoglobin levels, causing fatigue, breathlessness, and irregular heartbeats, necessitating lifelong blood transfusions and chelation therapy. India is home to the world’s largest population of children with thalassaemia major, numbering approximately 1-1.5 lakh. |
Clinical Trial Results
- Clinical trials of Casgevy showcased remarkable results, with participants afflicted by sickle cell disease reporting a substantial reduction in severe pain crises.
- Those with thalassaemia witnessed a remarkable 70% reduction in the need for blood transfusions.
Administration and Challenges
- One-Time Treatment: Casgevy involves a one-time treatment process, encompassing the collection of bone marrow blood stem cells through apheresis, followed by editing and testing over a span of approximately six months.
- Conditioning Medicine: Prior to the transplant with edited cells, conditioning medicine is administered to clear the bone marrow of existing cells.
- Challenges: Challenges include the expected high cost of the therapy, potentially around $2 million per patient, and the absence of local manufacturing facilities, necessitating the international transport of blood stem cells.
Future Prospects
- Price Reduction: Despite pricing challenges, experts hold the belief that ongoing research will lead to price reductions, making the therapy more accessible. Local manufacturing facilities are also anticipated to emerge.
- Indian Research: Researchers in India are actively pursuing gene therapies for sickle cell disease, with clinical trials on the horizon in the coming years.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
FDA Approves World’s First Chikungunya Vaccine: Ixchiq
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chikungunya , Ixchiq
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the US granted approval for the world’s inaugural vaccine against chikungunya.
Ixchiq: The Chikungunya Vaccine
- Developed by European vaccine manufacturer Valneva, this vaccine will be available under the brand name Ixchiq.
- It has been authorized for use in individuals aged 18 and above who are at elevated risk of chikungunya exposure.
- It is administered as a single dose via injection into the muscle.
- The vaccine contains a live, attenuated (weakened) form of the chikungunya virus. It may induce symptoms similar to those experienced by individuals with the disease.
Understanding Chikungunya
- Symptoms: Chikungunya is characterized by severe joint pain, limited mobility, and accompanying fever. It is a viral infection (CHIKV) primarily transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes, earning it the status of an “emerging global health threat.”
- Global Prevalence: Chikungunya is prevalent in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, with sporadic outbreaks reported in other regions. Since 2004, outbreaks have become more frequent and widespread, partly due to viral adaptations facilitating transmission by Aedes albopictus mosquitoes.
- Symptoms: Alongside joint pain, chikungunya symptoms include joint swelling, muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash. While severe cases and deaths are rare, they may be underreported due to misdiagnosis, often confused with dengue or zika.
- No Cure: Currently, there is no cure for chikungunya, and treatment is primarily focused on symptomatic relief, including analgesics for pain, antipyretics for fever, rest, and adequate fluid intake.
- Prevention: Prevention efforts primarily revolve around mosquito control through public health initiatives, civic maintenance, and personal measures such as using medicated mosquito nets and eliminating stagnant water sources to hinder mosquito breeding.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
H. Pylori Detection and Drug-Resistance Identification
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: H. pylori
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Indian researchers have developed a groundbreaking two-step PCR-based assay for detecting Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, determining clarithromycin resistance, and distinguishing drug-sensitive strains.
- This molecular diagnostic tool reduces the detection time from weeks to just six-seven hours and exhibits remarkable accuracy, boasting 100% sensitivity and specificity.
About H. Pylori Detection
- Helicobacter pylori, often abbreviated as H. pylori, is a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine.
- It is a common bacterial infection associated with various gastrointestinal conditions, including gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) and peptic ulcers (sores or lesions in the lining of the stomach or the duodenum, which is the first part of the small intestine).
Why discuss this?
- Increasing Resistance: India faces a growing challenge of clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori strains, resulting in decreased treatment efficacy.
- Asymptomatic Infections: While most H. pylori infections are asymptomatic, 10–15% of cases lead to peptic ulcer disorders or stomach cancer.
- Prevalence in India: H. pylori infections affect 60-70% of the Indian population, acquired in childhood and persisting if not treated.
- Gastric Cancer Risk: H. pylori infection is a significant risk factor for gastric cancer.
Understanding Drug Resistance Mechanism in H. Pylori
- Genome Sequencing: Researchers identified a point mutation (A to G mutation at position 2143) in the 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene as the cause of clarithromycin resistance.
- Confirmation: They isolated and transferred the 617 base pairs containing the mutation to drug-sensitive bacteria, which became resistant, confirming the mutation’s role.
- Published Findings: The study’s results were published in the journal Gut Pathogens.
- Exploring Binding Affinity: Bioinformatics analysis revealed that drug-resistant strains had weaker binding affinity to clarithromycin compared to drug-sensitive strains.
- Impact of Weak Binding: Weaker binding limits the drug’s penetration into bacteria, rendering it ineffective against resistant strains.
Development of the PCR-Based Assay
- Biopsy Samples: The DNA template used for the assay was prepared by amplifying a small segment containing the point mutation directly from biopsy samples.
- Validation: DNA templates from cultured bacteria were compared with those from biopsy samples to validate their accuracy.
- Two-Step PCR: The assay employs a two-step PCR approach to detect H. pylori infection and differentiate resistant from sensitive isolates.
- Allele-Specific Primers: Resistant-specific and sensitive-specific primers exploit the point mutation for selective amplification.
- High Accuracy: Evaluation against conventional methods and sequencing analysis demonstrated 100% sensitivity and specificity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
NexCAR19: India’s own CAR-T Cell Therapy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAR-T Cell Therapy
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- India has achieved a significant milestone in the field of cancer treatment with the approval of NexCAR19, its first indigenous CAR-T Cell Therapy, by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- Developed by ImmunoACT, an incubated company of IIT Bombay, NexCAR19 is set to transform cancer treatment in India and make it more affordable.
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
- Revolutionary Approach: CAR-T cell therapy involves modifying T-cells, a type of white blood cell, into potent cancer-fighting cells.
- Targeting Cancer: These genetically enhanced cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they identify and eliminate cancer cells, particularly effective against blood cancers like leukemia and lymphomas.
- Game-Changer: Unlike chemotherapy or immunotherapy, CAR-T therapy offers the potential for a cure and lifelong benefits, making it a transformative treatment option.
NexCAR19: India’s Indigenously Developed CAR-T Therapy
- NexCAR19 is designed to target cancer cells carrying the CD19 protein, a marker on cancer cells, enhancing precision in treatment.
- India joins a select group of nations with its own CAR-T and gene therapy platform, reducing dependence on imports.
- Initially approved for patients aged 15 and above with B-cell lymphomas who did not respond to standard treatments, leading to relapse or recurrence.
Effectiveness and Unique Features
- Approximately 70% of patients respond to NexCAR19 treatment, with some achieving complete remission.
- Lab and animal studies indicate lower drug-related toxicities, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
- Trials for paediatric patients are underway at Tata Memorial Hospital, ensuring broader applicability.
Availability and Affordability
- ImmunoACT is in the process of securing licenses and partnering with hospitals, including Tata Memorial, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, across multiple cities.
- CAR-T therapy is expected to be available in a matter of weeks to a few months, pending final government approvals.
- Initially priced at Rs 30-40 lakh, ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
- Approval by regulatory agencies like CDSCO should lead to insurance coverage, but the extent may vary, and discussions with insurers and the government are ongoing.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Haemoglobin isn’t used only in Blood: Scientists
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Haemoglobin , RBCs
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- A groundbreaking study published in Nature has unveiled an unexpected revelation: haemoglobin is not exclusive to RBCs.
- Scientists from China have discovered that chondrocytes, the cells responsible for cartilage production, also produce haemoglobin, which appears vital for their survival.
- For decades, textbooks have taught that haemoglobin resides solely in red blood cells (RBCs), responsible for making blood red and transporting oxygen.
| Cartilage: A tough, flexible connective tissue found throughout the human body, providing structural support and reducing friction between bones. |
About Haemoglobin
| Fact | Description |
| Definition | A protein found in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs. |
| Molecular Structure | Composed of four subunits: two alpha-globin chains and two beta-globin chains. |
| Iron-Binding | Each subunit contains an iron atom that binds to oxygen, forming oxy-hemoglobin. |
| Oxygen Transport | Carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and releases oxygen for cellular respiration. |
| Color | Gives red blood cells their red color when oxygenated and appears bluish when deoxygenated. |
| Carbon Dioxide Transport | Aids in transporting carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions from tissues back to the lungs for exhalation. |
| Hemoglobin Variants | Different types of hemoglobin, with HbA being the most common. Variants can result from genetic mutations. |
| Hemoglobin Levels | Vary by individual and are measured in grams per deciliter (g/dL). Normal levels range from 12 to 18 g/dL. |
| Hemoglobin Disorders | Genetic disorders like sickle cell disease and thalassemia are characterized by abnormal hemoglobin production. |
| Iron Metabolism | Adequate iron levels are essential for hemoglobin synthesis. Iron is a key component of heme in hemoglobin. |
| Fetal Hemoglobin | Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) has a higher oxygen affinity and aids in oxygen transfer from mother to fetus. |
| Hemoglobin Tests | Used for diagnosing anemia, assessing health, and monitoring medical conditions. |
| Oxygen Saturation | Measured as the percentage of hemoglobin molecules bound to oxygen, often using a pulse oximeter. |
New Breakthrough: Haemoglobin Bodies (Hedy)
- Pathologists in China researching bone development, stumbled upon spherical structures resembling RBCs within chondrocytes.
- These structures, termed “haemoglobin bodies” or Hedy, contained haemoglobin and formed large, membraneless blobs, akin to phase separation in oil and water.
Functionality of Hedy
- Essential for Survival: Experiments on genetically modified mice revealed that chondrocytes without haemoglobin experienced cell death, emphasizing Hedy’s vital role.
- Oxygen Transport: Similar to RBCs, haemoglobin in chondrocytes likely serves as an oxygen store and supplier, preventing hypoxic stress (low-oxygen conditions) in cartilage cells.
Haemoglobin’s Broader Implications
- New Research Avenues: The discovery bridges gaps between haematology and skeletal biology, paving the way for further exploration into the relationship between haemoglobin and stem cell fate in growth plates.
- Potential for Joint Disease Insights: Functional haemoglobin in cartilage raises possibilities of its involvement in joint diseases and bone deformities, offering fresh insights into disease mechanisms.
Try this PYQ:
Excessive release of the pollutant carbon monoxide (CO) into the air may produce a condition in which oxygen supply in the human body decrease. What causes this condition?
(a) When inhaled into the human body, CO is converted into CO2
(b) The inhaled CO has much higher affinity for haemoglobin as compared to oxygen
(c) The inhaled CO destroys the chemical structure of hemoglobin
(d) The inhaled CO adversely affects the respiratory center in the brain
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Bats: Extraordinary Creatures and Genomic Secrets
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bats and their ecological significance
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Bats, by many measures, are truly remarkable organisms.
- Their lives are notably extended, and they enjoy a unique defense against a range of diseases, including cancer.
Bats in Numbers
- Significant Population: Bats constitute a substantial part of the mammal world, making up 20% of all mammal species globally. The planet is home to over 1,400 bat species, each exhibiting its own unique characteristics.
- Diverse Characteristics: Bats exhibit a wide range of sizes, from the tiny 2-gram bumblebee bat to the formidable flying foxes, boasting a 1.5-meter wingspan and weighing up to 1.6 kg.
- Ecological Importance: Bats play pivotal roles in maintaining ecological balance by contributing to essential processes such as pollination and insect population control.
Bats as Virus Reservoirs
- Notorious Reputation: Bats have come under scrutiny primarily due to their role as hosts for various deadly viruses, including coronaviruses, Nipah, Ebola, Marburg virus, and Hendra virus.
- COVID-19 Spotlight: The COVID-19 pandemic has thrust bats into the spotlight, raising concerns about their potential impact on human health.
- Natural Pathogen Hosts: Bats are unique in their ability to harbour numerous pathogens without falling victim to infections, sparking scientific interest in understanding the source of their resistance.
Unlocking Bat Genomes
- Genomic Exploration: Scientists have embarked on comprehensive studies of bat genomes, revealing invaluable insights into their distinctive biology.
- Compact Genomes: Bats boast relatively small genomes, typically consisting of around 2 billion bases, making them ideal subjects for genomic research.
- Metagenomic Sequencing: The ambitious Bat1K global genome consortium is currently undertaking the task of sequencing genomes of all bat species worldwide, promising further revelations about their genetic makeup.
Immune Insights from Bat Genomes
- Crucial Immune Genes: The immune-related genes of bats have been a major focus of research, with these creatures exhibiting unique genomic features.
- Reduced Immune Genes: Bats possess a smaller percentage of immune-related genes, approximately 2.7-3.5% compared to humans, who have around 7%.
- Positive Selection: Certain immune genes in bats have undergone positive selection, equipping them to control the spread of viruses while mitigating the inflammatory responses that often prove detrimental to humans.
Long-Read Sequencing and Deeper Insights
- Sequencing Advancements: Long-read sequencing technologies have revolutionized our ability to assemble complete genomes quickly and accurately.
- Immune Response Alterations: Recent research employing long-read technology has revealed significant changes in genes responsible for immune responses in bats.
- Interferon Dynamics: There has been a shift in the relative proportions of interferon-alpha (IFN-α) and interferon-omega (IFN-ω) in bats, impacting their immune properties.
- Tumor Suppression and Longevity: Genes linked to tumor suppression and DNA repair in bats exhibit signs of positive selection, contributing to their extended lifespans and reduced cancer risk.
Future Prospects
- Emerging Zoonotic Threats: The ongoing processes of deforestation, ecological degradation, and heightened human-animal interactions are anticipated to result in more frequent zoonotic disease outbreaks.
- Genomic Tools: Advanced genome sequencing techniques hold the promise of aiding in the management of these outbreaks while preserving ecological balance, providing insights without disrupting the delicate equilibrium of nature.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CAR-T Cell Therapy approved for Cancer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAR-T Cell Therapy
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) has granted market authorization to CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T) cell therapy, a groundbreaking cancer treatment developed by ImmunoACT, an IIT-Bombay spin-off.
- This authorization paves the way for its commercial introduction in India.
About CAR-T Cell Therapy
What is it? |
|
How does it work? |
|
Therapy Process |
The process involves several steps, including:
1. Collecting T Cells: Blood is drawn from the patient’s arm, and T cells are separated from the blood using an apheresis machine. 2. Engineering T Cells: In a laboratory, the T cells are modified by adding a manufactured CAR, and they are allowed to multiply and grow. 3. Infusing CAR-T Cells: Once enough CAR-T cells are prepared, they are injected back into the patient’s arm.
|
Cancers Treated |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DNA Methylation
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) is spearheading a groundbreaking research endeavour called the “Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)”.
- This integrated genomics and epigenomics study aims to unravel the genetic underpinnings of NCD’s prevalent in diverse populations, including South Asians.
Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP)
- DEEP is an integrated genomics and epigenomics study focused on understanding the genetic factors behind Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in diverse populations, including South Asians.
- The project spans five years.
- It aims to uncover the impact of genomic and environmental diversity on disease risk observed in people worldwide, including those in Asia, Africa, North America, and South America.
- It will study individuals from various genetic and environmental contexts to identify DNA methylation patterns contributing to disease risk in each context.
- It will develop software, infrastructure, and conduct advanced statistical analyses to create new resources.
- This will complement international health and genetics databases and examine trends in DNA methylation variation.
DNA Methylation
|
Significance of this initiative
- This research will enable the identification of disease-causing mechanisms that are common worldwide and those which are unique to particular groups or regions.
- It will help with answering questions such as whether medicines developed in one part of the world will be effective for all.
- Ultimately the DEEP study hopes to enable targeted interventions or treatments and reduce global health disparity and inequity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Novel R21/Matrix-M Vaccine for Malaria
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: R21/Matrix-M Vaccine
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- In a momentous development in the fight against malaria, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued a recommendation for the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine on October 2.
- This pioneering vaccine, developed by the University of Oxford and manufactured by India’s Serum Institute, has already gained approval for use in children under 36 months in Nigeria, Ghana, and Burkina Faso.
R21/Matrix-M Vaccine
- Extensive Testing: The vaccine’s efficacy was rigorously assessed in a phase-3 trial involving 4,800 children across five sites in Mali, Burkina Faso, Kenya, and Tanzania. These sites vary in malaria transmission intensity and seasonality.
- Blind Trial: Participants were randomly assigned to receive either the malaria vaccine or a control (approved rabies vaccine) in a double-blind study, ensuring impartiality.
- Multi-Dose Regimen: The vaccination schedule comprised three doses administered 4 weeks apart, with a booster shot administered 12 months after the last dose.
- Strategic Timing: Primary vaccinations occurred before the malaria season in seasonal transmission regions or at any time of the year in perennial transmission regions.
Impressive Results
- According to preprint data (pending peer review), the vaccine demonstrated a remarkable efficacy of 75% in children aged 5-36 months in seasonal malaria regions and 68% in perennial malaria regions after one year.
- Notably, children aged 5-17 months, more vulnerable to severe malaria, exhibited even higher vaccine efficacy of 79% in seasonal regions and 75% in perennial regions.
- Vaccine efficacy remained substantial for 18 months, further reinforced by a booster dose administered 12 months after the primary series.
Seasonality Matters
- Optimal Timing: Results suggest that the vaccine performs more effectively in regions with seasonal malaria compared to perennial transmission areas.
- Seasonal Patterns: In seasonal sites, 82% of malaria episodes occurred in the first six months of follow-up, while only 26% occurred in the initial six months in perennial sites.
- Vaccination Timing: Since the vaccine is administered just before the malaria season, its protection is more pronounced when malaria is seasonal.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Advancements in Xenotransplantation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Xenotransplantation
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- A groundbreaking study published in Nature showcases a remarkable feat by successfully modifying pig genomes and transplanting kidney grafts from these genetically engineered pigs into non-human primates.
- This preclinical achievement holds great promise, potentially advancing the prospects of using genetically modified pig kidneys for human transplantation.
About Xenotransplantation
- Xenotransplantation Potential: The concept of transplanting animal organs into humans, known as xenotransplantation, offers a potential solution to the chronic shortage of transplantable organs worldwide.
- Pig Donors Show Promise: Pigs are emerging as promising donor animals. However, several significant hurdles, including organ rejection and the risk of zoonosis (transmission of animal viruses to humans), must be overcome for this approach to be considered clinically viable.
Recent advances
- Genome Alterations for Success: Led by Wenning Qin in Cambridge, Massachusetts, the research team took a giant stride by introducing 69 genomic edits into a donor pig, a Yucatan miniature pig.
- Eliminating Glycan Antigens: Three glycan antigens, culprits for organ rejection, were removed, paving the way for successful transplantation.
- Human Transgenes Introduced: Seven human transgenes were strategically inserted into the pig’s genome to reduce the primate immune system’s hostility.
- Porcine Retrovirus Gene Deactivated: The scientists also inactivated all copies of the porcine retrovirus gene.
Advancement achieved so far
- Glycan Antigens Identified: Prior research pinpointed three glycan antigens in pigs that trigger rejection when recognized by human antibodies.
- Zoonotic Concerns: The porcine endogenous retrovirus has raised concerns about the potential transmission of animal viruses to humans during transplantation.
- Extended Graft Survival: Kidney grafts from genetically engineered pigs exhibited remarkable longevity, far surpassing previous attempts.
- Enhanced Immunity: Kidney grafts with glycan antigen knockouts and human transgene expression survived significantly longer than those with only glycan antigen knockouts (176 days versus 24 days).
- Immune Suppression Support: Combining these genetically modified grafts with immunosuppressive treatment resulted in long-term survival for the primate recipients, with survival durations extending up to an impressive 758 days.
A Step Closer to Clinical Trials
- Promising Outlook: This groundbreaking research underscores the potential of pig organs for future human transplantation, addressing the organ shortage crisis.
- Clinical Trials on the Horizon: The successful preclinical study brings the possibility of clinical testing of genetically engineered pig renal grafts within reach, marking a crucial milestone in organ transplantation.
Issues with Xenotransplantation
- Animal rights: Many, including animal rights groups, strongly oppose killing animals to harvest their organs for human use.
- Decreased life expectancy: In the 1960s, many organs came from the chimpanzees, and were transferred into people that were deathly ill, and in turn, did not live much longer afterwards.
- Religious violations: Certain animals such as pork are strictly forbidden in Islam and many other religions.
- Informed consent: Autonomy and informed consent are important when considering the future uses of xenotransplantation.
- Persistent threats of zoonosis: The safety of public health is a factor to be considered. We are already battling the biggest zoonotic disease threat.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Uterus Transplants: Procedure, Challenges, and Future Prospects
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Uterus Transplants
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- In the UK, doctors at the Churchill Hospital Oxford conducted the nation’s first uterus transplant.
- The procedure involved removing a uterus from a 40-year-old woman and transplanting it into her 34-year-old sister, who faced reproductive challenges due to a rare medical condition.
Why discuss this?
- While the transplanted womb is functional, its success can only be confirmed by a live birth in the future.
Understanding Uterus Transplants
- Not Life-Saving: Unlike heart or liver transplants, uterus transplants are not life-saving procedures. Instead, they are akin to limb or skin transplants, significantly enhancing individuals’ quality of life.
- Addressing Uterine Infertility: Uterus transplants offer hope to women facing uterine factor infertility, enabling them to fulfill their reproductive aspirations.
Pioneering Success in Sweden
- Historical Context: In 2014, Sweden achieved a milestone by witnessing the first live birth following a uterus transplant. This success paved the way for addressing uterine factor infertility.
- Affordability Challenge: Efforts are ongoing to make uterus transplants more accessible, especially in countries like the UK, where the National Health Service estimates the procedure’s cost at GBP 25,000 (Rs 25.26 lakh).
Uterus Transplants in India
- Indian Achievement: India joined the ranks of countries with successful uterus transplants, alongside Turkey, Sweden, and the United States. The country celebrated its first uterine transplant baby’s birth on October 18, 2018, approximately 17 months after the recipient underwent the procedure.
- Affordable Option: The cost of uterine transplant surgery in India currently ranges from Rs 15-17 lakh, making it a more cost-effective choice for many.
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Recipient Evaluation: Before transplantation, recipients undergo thorough evaluations to assess their physical and mental health.
- Donor Assessment: Whether the donor is living or deceased, their uterus undergoes viability checks before qualifying for donation. Live donors also undergo comprehensive gynecological examinations, including imaging scans and cancer screenings.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Uterus transplants do not connect the uterus to the fallopian tubes, necessitating IVF to create embryos. These embryos are then cryopreserved until the transplanted uterus is ready for implantation.
- Harvesting and Transplantation: The donor’s uterus is carefully removed, with the procedure becoming less invasive due to advancements in robot-assisted laparoscopy. The uterine vasculature and other critical connections are meticulously re-established during transplantation.
Pregnancy after Transplant
- The success of the transplant is assessed through three stages: the first three months focus on graft viability, followed by six months to one year for monitoring uterine function.
- Only after this period can the recipient attempt conception.
Issues with such transplants
- Challenges and Risks: Pregnancy after a uterine transplant entails a higher risk of rejection, spontaneous abortion, intrauterine complications, low birth weight, and premature birth. Close monitoring and follow-ups are essential.
- Immunosuppressant Use: Recipients must take immune-suppressing drugs to prevent rejection of the transplanted uterus. These drugs are selected to ensure they do not harm foetal development but can cause side effects such as kidney toxicity, bone marrow issues, and an increased risk of diabetes and cancer.
- Long-Term Follow-Ups: Post-uterus removal, recipients are advised to undergo regular follow-ups for at least a decade to monitor potential long-term effects of immunosuppressant drugs.
Exploring Artificial Uteri
- Future Possibilities: Successful uterus transplants have opened doors to exploring artificial uteri. These bioengineered organs, grown from stem cells on 3D scaffolds, could eliminate the need for live donors and ethical concerns. However, research is still in its early stages, and it may take about a decade before artificial uteri becomes efficient and safe for human use.
- Inclusivity Considerations: Artificial uteri could benefit not only women but also members of the LGBTQ+ community. However, certain complications, such as hormone-related considerations for trans-women recipients, remain to be addressed.
Conclusion
- Uterus transplants represent a remarkable medical advancement offering hope and possibilities for individuals facing uterine factor infertility.
- While challenges persist, ongoing research and technological progress continue to expand the horizons of reproductive medicine.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Alzheimer’s Research: Mystery of Brain Cell Death
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brain Cell Death
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Scientists have long sought medical treatments for Alzheimer’s disease but have faced limited success.
- The approval of the drug Lecanemab by the US FDA in 2023 has brought renewed optimism, as it shows promise in slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s in its early stages.
How brain cells die?
- Revealing the Connection: Researchers from Belgium and UK have shed light on the connection between abnormal proteins (amyloid and tau) and a process called necroptosis, which leads to cell death.
- Cell Death Mechanism: Necroptosis is a form of cell death typically triggered by immune responses to infection or inflammation, serving to eliminate damaged cells.
- Inflammatory Response: The study suggests that in Alzheimer’s patients, amyloid protein entering brain neurons triggers inflammation and alters the internal chemistry of the cells. Amyloid forms plaques, while tau forms tangles.
- MEG3 Molecule: When amyloid and tau processes occur simultaneously, brain cells produce a molecule called MEG3, which appears to be linked to cell death.
- Blocking MEG3: The researchers experimented by blocking the MEG3 molecule and found that brain cells survived when this molecule was inhibited.
- Experimental Approach: Human brain cells were transplanted into genetically modified mice that produced significant amyloid, allowing researchers to make these groundbreaking observations.
Hope for Alzheimer’s Treatment
- Historic Discovery: Researchers highlighted that this discovery marks the first time, after several decades of speculation, that scientists have found a plausible explanation for cell death in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Path to New Medicines: Some are optimistic that their findings will pave the way for new medical treatments targeting Alzheimer’s.
- Lecanemab’s Target: Lecanemab, a drug that specifically targets the amyloid protein, aligns with the potential to block the MEG3 molecule, offering the prospect of halting brain cell death in Alzheimer’s disease.
Understanding Brain’s Complex Processes
- Brain’s Enigma: The development of Alzheimer’s drugs has been hampered by a lack of understanding of the disease’s mechanisms within the brain.
- Amyloid and Tau: Amyloid and tau proteins are known to accumulate in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients, but their precise roles and how they contribute to cell death remained unclear.
Alzheimer’s Global Challenge
- Widespread Impact: Approximately 55 million people worldwide are affected by various forms of dementia, with Alzheimer’s being one of the prominent diseases.
- Disproportionate Burden: Two-thirds of dementia cases are found in developing countries, and with the aging global population, projections indicate that the number of dementia cases could reach 139 million by 2050, with China, India, Latin America, and Sub-Saharan Africa facing the greatest challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
TrueNat Test to detect Nipah
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TrueNat Test
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- Kerala has been accorded sanction by the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) to use TrueNat test to diagnose Nipah.
- Hospitals with BSL 2 level labs can perform the test.
What is TrueNat Test?
- The TrueNat test is a molecular diagnostic test used for the detection of infectious diseases, including tuberculosis (TB) and COVID-19.
- It is a portable, chip-based and battery-operated machine developed by a Goa-based company.
- It is based on real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, which allows for the amplification and detection of specific genetic material (RNA or DNA) from the target pathogen.
- The WHO has approved TrueNat for detecting TB as it is cost-effective and a miniature version of the PCR test.
Benefits offered
- TrueNat machines are designed to be portable and easy to use in various settings, including remote or resource-limited areas.
- This feature has been particularly useful for TB diagnosis in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure.
About RT-PCR
- Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology is a molecular biology method used to detect and quantify DNA or RNA sequences in biological samples.
- It combines PCR amplification with fluorescent probes to monitor DNA amplification in real-time.
- This allows for the quantification of specific genetic material, making it valuable for applications such as gene expression analysis, disease diagnosis, and genetic research.
- It provides high sensitivity, specificity, and rapid results, making it a widely used tool in molecular biology and clinical diagnostics.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Monoclonal Antibody
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- India has reached out to Australia in its efforts to procure monoclonal antibody doses for combating the Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala.
- The monoclonal antibody has successfully passed phase-one trials and has been administered to 14 individuals globally.
Why use it for Nipah?
- Currently, there is no effective treatment for Nipah virus infection apart from symptom relief.
- The virus carries a high mortality rate ranging from 40% to 75%, making it a formidable threat.
- In comparison, even during the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the case fatality ratio (CFR) remained at around three percent.
What are Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)?
- Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are a class of therapeutic proteins that have revolutionized medicine and healthcare.
- They are used in a wide range of applications, from treating diseases to diagnosing conditions and conducting scientific research.
Structure of mAbs
- Monoclonal antibodies are proteins produced by a single type of immune cell, known as a B cell.
- They are called “monoclonal” because they are derived from a single, cloned parent cell.
- These antibodies have a specific Y-shaped structure consisting of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains.
- The variable region of the antibody binds to a specific antigen with high precision.
Applications of Monoclonal Antibodies
- Monoclonal antibodies have a wide range of applications in medicine, science, and diagnostics:
- MAbs are used to treat various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and more.
- They are used in diagnostic tests, such as ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), to detect specific molecules like antigens or antibodies.
- Scientists use mAbs to study and manipulate biological processes. They can be labeled with fluorescent markers for imaging and are crucial tools in cell biology and molecular biology research.
- Monoclonal antibodies labelled with radioactive isotopes or fluorescent markers can be used for diagnostic imaging techniques like PET (positron emission tomography) scans.
- They can target specific molecules on cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells during cancer treatment.
Challenges and Advancements
- Despite their significant benefits, monoclonal antibodies can have limitations, such as high production costs and the potential for immune responses.
- Advances in technology, such as the development of humanized antibodies (antibodies with human components to reduce immune reactions), have addressed some of these challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Vagus Nerve: Stimulation and Health Implications
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vagus Nerve
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- There’s a growing buzz online about the vagus nerve—ways to stimulate it and the potential benefits for various health issues, from anxiety to obesity.
- Videos and devices abound, offering suggestions for vagus nerve stimulation.
- Recent research has even linked vagus nerve dysfunction to long COVID.
What is the Vagus Nerve?
- A Pair of Nerves: The vagus nerve consists of two nerves, one on each side of the body. They run from the brainstem through the neck, chest, and stomach.
- Part of the Parasympathetic Nervous System: These nerves are a vital component of the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for relaxing and resting the body, regulating functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion. They also play a role in the immune system.
Why is the Vagus Nerve being researched?
Several aspects make the vagus nerve a subject of intense research:
- Extensive Reach: The vagal nerves are the longest cranial nerves, connecting the brain to the large intestine and passing through or connecting with crucial areas in the neck, heart, lungs, abdomen, and digestive tract.
- Communication Hub: These nerves contain 75% of the nerve fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system, facilitating bidirectional communication between the brain and the body.
- Health Implications: Researchers explore how stimulating these “sensory superhighways” could trigger the parasympathetic nervous system and potentially benefit various health conditions.
Conditions Treated by Vagus Nerve Stimulation
- Epilepsy and Depression: Implantable vagus nerve stimulators are used to treat epilepsy and depression, particularly when conventional treatments are ineffective. These devices stimulate areas of the brain associated with seizures and mood regulation.
- Inflammation Regulation: The vagus nerve plays a role in regulating inflammation. Suppressing inflammation after an infection is resolved has implications for treating various conditions.
Vagus Nerve and Long COVID
- A study suggests a connection between vagus nerve dysfunction and post-COVID-19 condition (PCC) or long COVID. Patients with PCC exhibited symptoms related to vagus nerve dysfunction, indicating its potential role in the pathophysiology of PCC.
- Other research explores impaired vagal activity in long COVID patients and potential therapeutic approaches involving vagal nerve stimulation.
Natural Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Numerous natural methods are believed to stimulate the vagus nerve, including:
- Meditation: Focusing on longer exhales than inhales.
- Exercise: Engaging in physical activity.
- Massage: Techniques like reflexology.
- Music: Humming and singing.
- Cold Exposure: Placing a cold pack on your face or using icy water immersion.
Limitations
- Implanted vagus nerve stimulation is not a one-size-fits-all solution and should not replace conventional treatment.
- It serves as an adjunctive treatment for most conditions and requires further research to explore its potential therapeutic effects comprehensively.
- Vagus nerve stimulation devices should only be used under medical supervision due to their influence on heart rate and blood pressure.
- Different protocols must be followed, making clinic-based usage essential.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
IISc develops Hybrid Nanoparticles to detect and kill cancer cells
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gold and Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have pioneered a novel approach with the potential to detect and eradicate cancer cells, particularly those forming solid tumour masses.
Gold and Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles
- Innovative Nanoparticles: IISc scientists have engineered hybrid nanoparticles that blend gold and copper sulfide, resulting in multifunctional nanoparticles with promising implications for cancer detection and treatment.
- Photothermal and Oxidative Properties: These nanoparticles exhibit photothermal capabilities, where they absorb light and convert it into heat, effectively killing cancer cells. Moreover, they produce singlet oxygen atoms, which further contribute to the cells’ toxicity.
- Combining Mechanisms: The nanoparticles employ both photothermal and oxidative mechanisms to target and eliminate cancer cells effectively.
Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis
- Ultrasound Waves: Beyond cancer treatment, these hybrid nanoparticles hold potential for cancer diagnosis. Their photoacoustic property enables them to absorb light and generate ultrasound waves.
- High Contrast Detection: The ultrasound waves enhance the contrast for detecting cancer cells once the nanoparticles reach them. This method offers superior image resolution compared to traditional CT and MRI scans.
- Clarity and Oxygen Saturation Measurement: Scans generated through ultrasound waves boast greater clarity and the ability to measure oxygen saturation within tumors, enhancing cancer detection accuracy.
- Integration with Existing Systems: The nanoparticles can be seamlessly integrated with current detection and treatment systems. For instance, endoscopes used for cancer screening can trigger nanoparticle-induced heat generation with focused light.
Overcoming Size Limitations
- Size Advantages: These hybrid nanoparticles, measuring less than 8 nm, possess a critical advantage in terms of mobility within tissues and their ability to reach tumors.
- Potential Safe Elimination: Due to their diminutive size, researchers anticipate that these nanoparticles can exit the human body naturally without accumulating. However, extensive safety studies are essential to confirm their suitability for internal use.
- Successful Lab Testing: In laboratory settings, the researchers conducted successful tests using these nanoparticles on lung and cervical cancer cell lines, demonstrating their potential.
- Clinical Development: The promising outcomes from this study propel the nanoparticles closer to clinical development.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Lab-Grown Human Embryos: A Breakthrough in Science
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lab-Grown Human Embryos
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Scientists have successfully developed a “human embryo” in a laboratory without using traditional egg or sperm cells.
- The model was constructed using a combination of stem cells, which possess the ability to differentiate into various cell types, resulting in a structure resembling an early human embryo.
Creating Human Embryo artificially
- This model is considered one of the most comprehensive representations of a 14-day-old human embryo.
- Multiple research teams worldwide have been working on similar embryo-like models, with approximately six such models published in the current year.
- While none fully replicate early embryo development processes, they collectively contribute to scientific understanding.
Challenges in Creating the Model
- Researchers in Israel utilized stem cells and chemical components, but only a small fraction spontaneously assembled into different cell types.
- Approximately 1% of the mixture exhibited this spontaneous assembly, making the process inefficient.
Importance of Embryo Models and Research
- Ethical constraints prevent direct research on early embryo development after implantation in the uterus.
- Understanding early stages of embryo development is crucial as most miscarriages and birth defects occur during this period.
- Such research aids in the comprehension of genetic and hereditary diseases.
- Insights into why some embryos develop normally and implant successfully can enhance in vitro fertilization success rates.
Potential of Embryo-Like Models
- These models enable the study of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental influences on embryo development.
- They facilitate the investigation of genetic defects and the development of potential genetic therapies.
Limits of Lab-Grown Embryos
- Lab-grown embryos are solely for studying the early stages of foetal development.
- Implantation attempts are prohibited, and these models are typically destroyed after 14 days.
- Originating from a UK committee proposal in 1979, the 14-day limit aligns with natural embryo implantation completion.
- Beyond this point, embryos begin exhibiting characteristics of individuality and cannot split into twins.
- The ethical considerations shift as embryos progress from a clump of cells to entities with individual potential, often marked by the Primitive Streak.
Insights from Embryo Models
- Models like the one developed in Israel shed light on DNA duplication errors and chromosome imbalances.
- These errors are now understood to occur earlier in the development process, during ongoing DNA duplication.
- Such models aid in identifying the roles of various genes in fetal development, enabling gene manipulation for research purposes.
Conclusion
- Lab-grown human embryo models represent a significant scientific achievement.
- They provide a unique window into early embryo development and the understanding of genetic and developmental processes.
- While not suitable for reproduction, these models hold promise for advancing genetic and medical research.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
HC allows Stem Cell Therapy for autistic kids
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Stem Cells, Autism
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Delhi High Court granted permission for two children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to undergo Stem Cell Therapy for their condition.
- The court’s decision followed a challenge against the Ethics and Medical Registration Board’s (EMRB) recommendation against stem cell treatment for ASD.
Understanding Stem Cells
- Stem cells are the foundational cells that can differentiate into specialized cells with distinct functions.
- Two main categories: pluripotent stem cells (can differentiate into various adult cells) and adult stem cells (tissue/organ-specific).
- Pluripotent stem cells are found in embryos; reprogramming of adult cells leads to induced pluripotent stem cells.
Stem Cells in Medicine
- Stem cells’ regenerative properties make them valuable in regenerative medicine.
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation treats conditions like leukaemia.
- Challenges: Limited adult stem cells post-removal, focus on making them pluripotent.
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
- ASD is a neurological and developmental disorder affecting communication, behaviour, and interactions.
- Conventional therapies focus on symptom management, social skills training, behaviour analysis, and speech and occupational therapy.
Potential of Stem Cell Therapy for ASD
- Some experts suggest stem cells could enhance immune system regulation and neural connectivity in the brain.
- Current clinical trials show mixed results; treatment is experimental, lacks sufficient data.
- EMRB recommendations against stem cell therapy due to limited evidence, risks, side effects, and absence of established protocol.
EMRB’s Concerns
- EMRB’s recommendation stemmed from “predatory marketing” of stem cell therapy, giving false hope to parents about “curing” ASD.
- The Delhi HC ruling doesn’t assess the general validity of stem cell therapy but permits ongoing treatment for specific cases.
Conclusion
- The court’s verdict allows continued stem cell therapy for ASD, acknowledging the ongoing uncertainty and potential of the treatment.
- The decision underlines the need for further research and data to establish stem cell therapy’s efficacy and safety for treating autism.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Y Chromosome: Unveiling its Secrets and Evolution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Y Chromosome
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The enigmatic Y chromosome, harboring the genetic blueprint of maleness and sperm production, has long intrigued researchers and captured public curiosity.
- Despite its small size and abundant “junk DNA,” technological advancements have finally granted scientists a comprehensive sequence of the entire Y chromosome.
What are Chromosomes?
- Chromosomes are fundamental components of cells that play a vital role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
- These structures contain genes, which carry instructions for the development, functioning, and inheritance of traits.
- Chromosomes consist of tightly coiled DNA molecules wrapped around proteins called histones, forming chromatin.
- Before cell division, chromosomes replicate into identical sister chromatids held together at the centromere.
Types of Chromosomes:
- Autosomes: Non-sex chromosomes (22 pairs in humans) determine most traits.
- Sex Chromosomes: Determine biological sex (XX for females, XY for males).
Functions of Chromosomes
- Genetic Information Storage: Genes on chromosomes encode instructions for protein production and cellular processes.
- Inheritance: Chromosomes transmit genetic information during sexual reproduction through meiosis, ensuring genetic diversity in offspring.
- Gene Expression Regulation: Chromosomes control gene activation or silencing, crucial for development and cell functioning.
Significance of Chromosomes
- Understanding Genetic Disorders: Abnormalities in chromosomes cause conditions like Down syndrome, aiding diagnosis and comprehension.
- Evolutionary Insights: Comparative analysis of chromosomes reveals evolutionary relationships and genetic material changes over time.
- Advancements in Genetic Research: Chromosomes are crucial for genome sequencing, mapping, and studying gene expression, leading to improved understanding of human health, diseases, and targeted therapies.
Our focus: Y Chromosome
- Genetic Origins: The Y chromosome is believed to have emerged approximately 200-300 million years ago in a common ancestor of mammals. Its genetic sequence, published in 2003, revealed that it accounts for only 2% of the genetic material inside a cell, encoding around 55 genes.
- Quirks and Challenges: Referred to as the “juvenile delinquent” among chromosomes, the Y chromosome has repetitive sequences, a limited number of genes, and a reluctance to recombine with other chromosomes. These characteristics have led to debates about its functional utility and evolutionary trajectory.
Significance of the Y Chromosome
- Historical Insights: Researchers have extensively studied the Y chromosome to understand human migration and evolution. It has provided valuable insights into paternity, genetic diversity, and our shared past.
- Beyond Sex Determination: Contrary to earlier assumptions, recent studies have revealed that the Y chromosome plays a role in biological functions beyond sex determination. It contains genes associated with aging, lifespan regulation, and other vital processes.
Influence of the Y chromosome on Health
- Sex Differences in Lifespan: In the animal kingdom, including mammals, females tend to live longer than males. The absence of a second Y chromosome in males exposes detrimental mutations in the X chromosome, potentially contributing to shorter lifespans.
- Age-Related Loss of the Y Chromosome: Studies have shown that men experience a loss of the Y chromosome (LoY) with age, which has been associated with a higher risk of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. Research on mice models supports these findings, indicating a correlation between LoY and shorter lifespans and memory deficiencies.
- Phenotypic Sex and Longevity: Recent research on fruit flies challenges the notion that the presence of a Y chromosome directly influences longevity. Instead, the phenotypic sex of an individual, determined by external genitalia, may play a more significant role.
Future of the Y Chromosome
- Species-Specific Evolution: Some species, like rodents, have naturally lost their Y chromosome, offering insights into sex-chromosome turnover. These species serve as models for understanding the process and the potential repurposing of other chromosomes as sex chromosomes.
- Signs of Replacement: Genomic analysis of Neanderthal DNA indicates that the Y chromosome has undergone replacement in the lineage leading to modern humans. This suggests that the Y chromosome’s role as the “master of maleness” may eventually be overtaken by another chromosome in the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Organoid Intelligence: Biology and the future of computing
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Organoid Intelligence and apliactions
Mains level: Organoid Intelligence, applications and ethical concerns
What’s the news?
- By utilizing brain organoids derived from stem cells, Organoid Intelligence (OI) seeks to explore new frontiers in information processing, offering potential breakthroughs in understanding brain functionality, learning, and memory.
Central Idea
- In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has brought forth remarkable technological advancements. Yet, the realm of cognitive computing is being further extended by Organoid Intelligence (OI), a burgeoning interdisciplinary domain that envisions innovative biocomputing models.
What is an Organoid?
- An organoid is a specialized type of tissue culture that is generated from stem cells and intended to mimic the structure and function of specific organs.
- These three-dimensional structures are cultivated in vitro, or outside the body, under controlled conditions that attempt to recreate the microenvironment of the target organ.
- The term organoid encompasses diverse structures that imitate different organs or tissues.
What is Organoid Intelligence (OI)?
- Organoid Intelligence is an emerging multidisciplinary field that merges the realms of biology and computing to explore the potential of using brain organoids to achieve cognitive capabilities and enhance our understanding of brain function.
- This novel concept envisions harnessing the unique properties of brain organoids, which mimic certain aspects of brain structure and function, to develop biocomputing models that could process information and potentially exhibit rudimentary cognitive abilities.
Potential applications of OI
- Cognitive Computing: Integrating brain organoids and computation for information processing and adaptive learning.
- Disease Modeling and Drug Testing: Using organoids to simulate diseases, test treatments, and study cognitive aspects.
- Understanding Brain Development: Analyzing Organoids to grasp early brain stages and cellular memory processes.
- Personalized Brain Organoids: Tailoring organoids to study genetics, medicine, and cognitive conditions.
- Advantages over Traditional Computing: Exploring organoids’ capabilities for intricate data tasks and energy-efficient processing.
- Biocomputers and Energy Efficiency: Developing faster, greener biocomputers with brain organoids.
- Ethical Considerations: Addressing ethical concerns like informed consent, gene editing rules, and inclusive access.
- Sustainable Alternatives: Offering eco-friendly options for intensive cognitive tasks and learning, amidst technology advancement.
Case Study: DishBrain System Experiment
- The DishBrain system stands as a compelling case study illustrating the application of Organoid Intelligence (OI). This innovative experiment, led by a team of researchers from Cortical Labs in Melbourne, demonstrates the integration of brain organoids with computational systems to achieve rudimentary cognitive capabilities.
- Experiment Overview:
- Brain Organoid Culturing: The researchers cultivated brain organoids, which are complex three-dimensional structures derived from stem cells. These organoids simulate certain aspects of brain development and function.
- In Silico Integration: Brain organoids were interfaced with computational simulations and algorithms through in silico computing. This integration aimed to enable enhanced neural processing and cognitive functions.
- Gameplay: Pong’: The brain organoids were trained to engage in the classic video game Pong. They were programmed to respond to key in-game variables, such as the movement of the virtual ball.
- Learning Mechanism: When the brain organoids failed to respond correctly in the game, the system provided feedback in the form of electrical pulses. This approach mimics the concept of reinforcement learning observed in living organisms.
- Application of the Free-Energy Principle: In the absence of real-time incentive systems like dopamine pathways, the researchers employed the free-energy principle. This principle suggests that living systems strive to minimize unpredictability. Brain organoids adapted their behavior to make the game environment more predictable.
- Key Outcomes: Within an astonishingly short span of five minutes, the brain organoids demonstrated signs of learning in response to the game stimuli. The utilization of the free-energy principle showcased the potential to guide the behavior of brain organoids using computational principles, driving them toward predictable responses.
Challenges and ethical considerations associated with Organoid Intelligence
- Challenges:
- Technological Advancements: Scaling up brain organoids and enhancing their cognitive capacities pose significant technical hurdles. Developing more sophisticated blood flow systems and introducing diverse cell types are among the challenges.
- Complexity of Learning: Despite promising results, achieving advanced cognitive capabilities in brain organoids remains a complex task. Imitating the intricacies of learning and memory seen in human brains is a challenge that requires further research.
- Gap in Knowledge: There are aspects of OI technology that are yet to be fully understood and developed. This includes improving memory storage mechanisms within brain organoids to enable more complex cognitive functions.
- Ethical Considerations:
- Informed Consent: Obtaining voluntary informed consent for cell donation is crucial to upholding donors’ rights and dignity.
- Selection Bias and Discrimination: Preventing selection biases during organoid development is essential to avoid potential discrimination risks and ensure neurodiversity.
- Gene Editing Regulations: Balancing commercial interests with ethical gene editing regulations is necessary to ensure the responsible and ethical culturing of brain organoids.
- Data Sharing and Open Access: Ensuring data sharing and open access to OI technology promotes inclusivity and diverse knowledge generation.
- Stakeholder-Informed Regulations: Developing regulations for the ethical use of OI technology requires stakeholder input to ensure responsible applications.
- Consciousness and Suffering Concerns: Ethical concerns range from the potential consciousness of brain organoids to addressing the possibility of suffering in these bioengineered systems.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects
- Scaling up brain organoids, introducing diverse cell types, and enhancing memory storage are essential steps for augmenting OI’s cognitive potential.
- A 100-fold increase in the number of cells could yield complex cognitive capabilities, necessitating innovations in blood flow systems and cell diversity incorporation.
- The rudimentary success of DishBrain’s Pong experiment signifies the journey towards intelligence through OI.
- Although complete realization is distant, the limitations of current AI and silicon technologies in complex cognition, learning, and energy efficiency emphasize the urgency to explore sustainable alternatives.
Conclusion
- Through brain organoids, researchers are poised to unlock an unprecedented understanding of cognitive processes and revolutionize the ways we approach learning, memory, and neurological disorders. As OI advances, navigating ethical considerations and embracing technological innovations will be pivotal in ensuring a responsible and impactful journey toward an era of more sustainable and intelligent computing solutions.
Also read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
HeLa Cells: Everything you need to know about
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hela Cells
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- HeLa cells, an extraordinary line of human cells recovered from a woman suffering from cancer has helped various realms of scientific discovery and medical progress.
What are HeLa Cells?
- Unveiling the Unknown: In 1951, Henrietta Lacks was diagnosed with cervical cancer and underwent a tissue biopsy at Johns Hopkins Hospital.
- Pioneering Phenomenon: A fraction of Lacks’ tumor cells, later termed HeLa cells, displayed an exceptional trait – the ability to perpetually divide and multiply in laboratory conditions.
Distinctive Attributes of HeLa Cells
- Endless Proliferation: Unlike typical human cells that have finite lifespans, HeLa cells displayed continuous division, enabling their perpetual growth.
- Scientific Marvel: This property revolutionized research by offering a consistent and adaptable medium for experiments.
Utility for Scientific Progress
- Polio Vaccine: HeLa cells played a pivotal role in cultivating the poliovirus, facilitating the development of the polio vaccine.
- Cancer Research: HeLa cells fueled insights into cancer biology, aiding in testing treatments and understanding disease mechanisms.
- Genetic Insights: These cells were the first human cells to be cloned, deepening our grasp of genetics and cellular biology.
- Drug Testing: HeLa cells revolutionized drug testing, aiding in drug development and assessing safety profiles.
- Space Exploration: Their journey extended to space, contributing to the understanding of cellular behavior in microgravity.
Ethical Dilemmas and Controversies
- Informed Consent Absence: HeLa cells’ use without Henrietta Lacks’ consent raised ethical concerns, especially in the context of medical experimentation on African American patients.
- Patient Rights and Acknowledgment: Discussions emerged about patient rights, equitable compensation, and the acknowledgement of individuals whose contributions fuel scientific progress.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Potential of Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) in Disease Research
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cell Free DNA vs. Normal DNA
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Researchers worldwide are increasingly using Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) as a valuable tool to better comprehend human diseases, improve diagnosis, monitoring, and prognosis.
What is Cell-free DNA?
- CfDNA refers to small fragments of nucleic acids that are released from cells and found outside the cell in body fluids.
- Its discovery dates back to the late 1940s when it was first observed in the blood of pregnant women.
- cfDNA can be generated and released from cells in various situations, such as cell death and other physiological processes.
- The release of cfDNA is associated with several disease processes, including autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus.
How is it different from normal DNA?
Cell-free DNA |
Normal DNA |
| Found in the bloodstream and other bodily fluids | Found within the cell nucleus or mitochondria |
| Released from dying or dead cells into the circulation | Remains within the cell’s nucleus or mitochondria |
| Exists in a fragmented form | Exists as an intact double-stranded helix |
| Can be isolated and analyzed from blood samples | Requires cell extraction and purification for analysis |
| Provides valuable genetic information for personalized medicine | Forms the basis of genetic inheritance and traits |
| Valuable in infectious disease diagnosis and monitoring | Not used for infectious disease diagnosis |
| Used in forensics for DNA profiling and crime investigations | Not typically used in forensics |
Applications of CfDNA
| Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) | Detect genetic abnormalities in foetuses
Screening for Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome |
| Cancer Screening and Monitoring | Identify genetic mutations in tumour cells
Determine cancer type Monitor treatment response and disease progression |
| Transplant Rejection Monitoring | Monitor immune response after organ transplantation
Early detection of organ rejection |
| Infectious Disease Diagnosis | Identify viruses and bacteria in the bloodstream
Aid in diagnosing infections and guiding treatment |
| Personalized Medicine | Provide genetic information for tailored treatment plans
Enable precision medicine based on individual genetic profile |
| Tracking Tumour Mutations | Monitor drug-resistant mutations in cancer patients for treatment adjustments |
Recent Advances in Therapeutics
- GEMINI Test: Researchers at Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Centre developed a new test called ‘GEMINI’ that uses cfDNA for early cancer detection. By analyzing genetic mutations and using machine learning, they achieved over 90% accuracy in detecting lung cancer, even in early-stage cases.
- Potential Impact: Early detection of cancers using cfDNA could significantly improve patient outcomes and survival rates.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Donanemab: A promising drug for Alzheimer’s
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Donanemab
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Donanemab, a drug in trials has shown significant potential in slowing cognitive decline in individuals with early Alzheimer’s.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive and irreversible neurological disorder.
- Beta-amyloid, a protein that is crucial for brain function, turns toxic in Alzheimer’s patients, forming clumps that disrupt brain cell connections, leading to cognitive issues like memory loss.
- These protein deposits disrupt communication between neurons, leading to their deterioration and death.
- Early signs include forgetfulness, difficulty finding words, problem-solving challenges, confusion, and disorientation.
- The exact cause of Alzheimer’s is not fully understood but is believed to involve genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Family history, genetic mutations, head injuries, cardiovascular disease, and certain lifestyle factors are also risk factors.
Donanemab: An antedote
- Development: Donanemab is a drug developed by Eli Lilly and aims to treat individuals with early Alzheimer’s disease.
- Targeting Amyloid Plaques: The drug targets a common hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease: amyloid plaques in the brain.
Breakthrough in Slowing Cognitive Decline
- Alarming Burden: With an estimated 14 million cases of dementia, including Alzheimer’s, expected in India by 2050, the need for effective treatments is urgent.
- Phase III Trial: In a phase III trial, Donanemab demonstrated promising results, slowing cognitive decline by 35% compared to a placebo.
- Significance: This marks a significant milestone in Alzheimer’s research, as it is the second drug, within a year, to show effectiveness in checking cognitive decline in early-stage Alzheimer’s patients.
- Limitations: It is essential to note that Donanemab and the previous drug do not stop or reverse Alzheimer’s disease. However, slowing cognitive decline can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals and their families.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Bacteriophages: The Good Viruses that fight Bacteria
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Viromes, bacteriophages
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Viruses have had a significant impact on human history, causing deadly outbreaks of diseases.
- However, not all viruses are harmful, and scientists are discovering the importance of the virome (bacteriophages).
Do you know?Viromes and bacteriophages are closely related because bacteriophages, or phages for short, are a type of virus that specifically infects bacteria. Bacteriophages are considered part of the virome, as they contribute to the overall viral genetic material present in a given environment or organism. |
What are Virome?
- What is it: They are the collection of viruses in our bodies contributing to our health, similar to the bacterial microbiome.
- Bacteriophages: The majority of viruses inside us are bacteriophages, which kill bacteria in our microbiomes without affecting human cells.
- Vast in Numbers: Our bodies host around 380 trillion virus particles, 10x more than the number of bacteria.
- Beneficial Viruses: Some viruses play beneficial roles, such as killing cancer cells, aiding immune system training, fighting pathogens, and regulating gene expression during pregnancy.
Bacteriophages and Phage Therapy
- Bacteriophages’ Mechanism: Bacteriophages hunt down bacteria, attach to their surface, inject viral DNA, and replicate inside the bacteria before causing the bacterial cell to burst and release new viral particles.
- Historical Background: In the early 20th century, scientists explored phages as potential treatments for bacterial infections, but antibiotic development overshadowed this research.
- Antibiotic Resistance: With the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, scientists are revisiting phage therapy as an alternative to combat bacterial infections.
- Advantages of Phages: Phages effectively target multi-resistant pathogens, are precise in eliminating bacterial strains, and do not disrupt the gut microbiome like antibiotics do.
Phage Therapy in Practice
- Historical Use: Phage therapy persisted in countries like Georgia, Ukraine, and Russia, where antibiotics were scarce. These regions have witnessed successful treatment outcomes against antibiotic-resistant infections.
- Expanding Use: Phage therapy is gaining attention in countries like Belgium, the US, and Germany, with specialized therapy centres and calls for increased exploration and utilization.
- Challenges and Safety: Standardization of therapy and tailoring phages to specific bacteria causing the infection remain challenges. However, phage therapies have a good safety record, and human bodies can tolerate them well.
Future Prospects
- Complementary Approach: Phages are unlikely to replace antibiotics but could be used in combination to enhance antibiotic effectiveness, particularly against resistant bacterial strains.
- Research and Clinical Projects: Further large-scale research and clinical projects are recommended to establish effective phage therapies for different types of infections.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Affordable treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Researchers in India are collaborating to develop an affordable treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), a rare and incurable genetic disorder.
- The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Jodhpur, is collaborating to develop affordable therapeutics for DMD.
What is DMD?
- DMD is a progressive muscle degeneration disorder caused by alterations in the dystrophin protein.
- It is the most common and fatal type of muscular dystrophy, primarily affecting boys.
- It leads to progressive muscle degeneration, weakness, and eventually wheelchair dependency, assisted ventilation, and premature death.
Symptoms and Impact of DMD
- Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness is the primary symptom of DMD, initially affecting proximal muscles and later distal limb muscles. Difficulties in jumping, running, and walking are common.
- Other Symptoms: Enlargement of calves, a waddling gait, lumbar lordosis (inward curve of the spine), and later heart and respiratory muscle involvement. Pulmonary function impairment and respiratory failure may occur.
Current Challenges
- Costly treatment: Current therapeutic options for DMD are minimal and expensive, with costs reaching up to Rs 2-3 crore per child per year.
- Limited Treatment Options: The treatments are predominantly imported, making them financially unattainable for most families.
Efforts to Develop Affordable Therapeutics
[A] Antisense Oligonucleotide (AON)-Based Therapeutics
- The IIT Jodhpur researchers are working on enhancing the efficacy of AON-based therapeutics.
- AONs can mask specific exons in a gene sequence, addressing the challenges faced in DMD patients.
- Personalized medicine is necessary due to the variations in mutations among DMD patients.
[B] Clinical Trials and Molecular Tags
- The research team has received approval from the Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) to conduct multi-centric clinical trials on AON-based exon skipping in DMD patients.
- They are also working on reducing the therapeutic dose of AON through new molecular tags.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Bio-Banks
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Biobanks
Mains level: Transformative potential of Bioeconomy, India's potential and leadership capacity for global south
Central Idea
- The biotechnology economy, commonly known as the bioeconomy, has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by advancements in genetic research, healthcare applications, and innovations in food security and bioproduction. However, the responsible collection, storage, and sharing of biological data, particularly in the form of biobanks, necessitate robust governance to ensure equitable access and benefit sharing.
*Relevance of the topic*
India’s participation in healthcare advancements, including vaccine development and deployment, highlights its potential in the bioeconomy.
The pharmaceutical industry, coupled with expertise in medical research, positions India as a global leader in healthcare innovation and the production of drugs and therapies.
Considering its vast populations and challenges in healthcare, personalised healthcare is the need of the hour which makes biobanks is crucial factor for India
What is the biotechnology economy?
- The biotechnology economy, also known as the bioeconomy, refers to the sector that encompasses various activities related to biotechnology, genetic research, and the utilization of biological resources for industrial and commercial purposes.
- It encompasses the application of biological knowledge, principles, and techniques to develop innovative products, processes, and services in sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, food production, energy, environmental conservation, and more.
- The biotechnology economy relies on advancements in genetic engineering, genomics, bioinformatics, and other fields to understand and manipulate biological systems for practical purposes.
- It involves the development of new drugs, therapies, and medical treatments, the improvement of agricultural crops and livestock, the production of biofuels and renewable materials, and the creation of sustainable solutions for various industries.
India’s potential in the Bioeconomy
- Bioeconomy Market Value: India’s Bioeconomy Report projects a potential market value of US$300 billion for the bioeconomy in India by 2030. This indicates significant growth and economic prospects in the sector.
- Biotech Start-up Growth: The number of biotech start-ups in India has witnessed exponential growth, increasing from 50 to over 5,300 in the last ten years. This thriving ecosystem reflects a robust foundation for research, development, and industrial participation in the bioeconomy.
- Biobanking Landscape: India currently hosts 19 registered biobanks out of a total of 340 global biobanks. This infrastructure plays a crucial role in the collection, preservation, and sharing of biological data for research and development purposes.
Significance of biobanks for India
- Medical Research and Advancements: Biobanks store biological samples, such as blood, tissue, and DNA, along with associated health information. These samples and data enable researchers to study diseases, understand genetic factors, identify biomarkers, and develop new diagnostic tools and therapies.
- Disease Understanding and Treatment: By collecting samples and health information from individuals with specific diseases or genetic conditions, biobanks facilitate research on disease etiology, progression, and treatment options.
- Precision Medicine and Personalized Healthcare: By analyzing genetic and molecular data stored in biobanks, researchers can identify individual variations and develop tailored treatment approaches based on a person’s unique genetic makeup.
- Public Health and Epidemiology: By analyzing large-scale data sets from biobanks, researchers can identify risk factors, understand disease prevalence, monitor disease trends, and develop strategies for disease prevention and public health interventions.
- Drug Development and Clinical Trials: Biobanks play a crucial role in drug development and clinical trials. They provide researchers and pharmaceutical companies with access to well-characterized biological samples and associated health data, which are essential for evaluating drug efficacy, safety, and side effects.
Inequitable Data Collection and Benefit Deployment
- Global South Underrepresentation: The the majority of biobanks are housed in North America and Europe, covering about 95 percent of the biobanks globally. In contrast, the Global South, including India, only hosts approximately 5 percent of the world’s biobanks. This underrepresentation limits the Global South’s participation in health research and the deployment of health initiatives.
- Research Bias: Due to the concentration of biobanks in the Global North, there is a bias in research and funding, focusing on genetic conditions and diseases that are prevalent in those regions. This bias hamper research on health challenges specific to the Global South, limiting the relevance and applicability of the findings to the populations in these regions.
- Dissonance in Results: There is a dissonance in using samples from the Global South to cater to health requirements primarily in the Global North. This dissonance implies that research outcomes derived from data collected in the Global South may not adequately address the healthcare needs and challenges faced by the populations in that region.
- Lack of Equitable Benefit Sharing: The lack of explicit return on results policies leads to inadequate sharing of benefits derived from the data collected in the Global South. The benefits and outcomes of research conducted using biobank data from the Global South are not shared equitably among the countries and populations from which the data originated.
- Inequities During the Pandemic: The article cites an example of inequity during the COVID-19 pandemic, where the capacity of Afrigen, a biotech firm responsible for vaccine production in Cape Town, was limited due to the desire of private sector participants like Moderna and Pfizer to preserve their knowledge. This resulted in Africa’s reliance on global vaccine manufacturing, with only 1 percent of vaccines consumed on the continent being manufactured within Africa.
India’s contributions and leadership in the bioeconomy
- Healthcare and Vaccine Development: India has actively contributed to healthcare and vaccine development. The country has been involved in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development, deployment, and diplomacy. Its expertise and participation have played a crucial role in addressing global health challenges.
- Global South Representation: India’s involvement in advocating for global South representation in biobanking governance and global platforms demonstrates its commitment to addressing inequities. India’s leadership contributes to fostering collaboration, trust, and fair participation among countries in the Global South.
- Multilateral Engagement: India’s association with the Quadrilateral Alliance and its G20 presidency provide platforms for global diplomacy and collaboration. These engagements enable India to advocate for global governance structures and mechanisms that promote equitable access, benefit sharing, and funding in the bioeconomy.
- National Guidelines and Best Practices: India has established guidelines and best practices for biobanking, ethical data storage, sharing, and benefit distribution. The Department of Biotechnology and the Ministry of Science and Technology have played key roles in formulating these guidelines, ensuring responsible practices in the bioeconomy.
- Exporting Health Information and Data: India has a history of exporting health information and data, which positions it as a contributor to global health initiatives. Leveraging its experience, India can emphasize the prioritization of diseases relevant to the Global South, prevent biopiracy, and establish rules for benefit sharing to benefit countries in these regions.
- Global Diplomacy and Platforms: India’s involvement in global platforms, such as the G20 presidency, has enabled it to expand its national regulations and contribute to the establishment of a global governance structure for biobanking and data sharing. This allows India to advocate for relief from trust issues, mechanisms for benefit sharing, and incentives for funding in the Global South.
Way forward: Addressing Inequities through Global Governance
- Global South Representation: There is a need for greater representation of the Global South in global governance structures. This ensures that the specific requirements and perspectives of the Global South are considered in decision-making processes and policies.
- Global Guidelines for Biobanking: There is need of the formulation of global guidelines for biobanking to establish standards and best practices. These guidelines would address ethical data collection, storage, sharing, and benefit distribution, taking into account the specific needs and concerns of the Global South.
- Equitable Benefit Sharing: It is important to explicit return on results policies to ensure equitable benefit sharing. These policies would ensure that the benefits derived from data collected in the Global South are shared back with the countries and populations from which the data originated.
- Collaboration and Knowledge Exchange: Global governance in the bioeconomy should foster collaboration, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer between countries and regions. This collaboration helps address disparities, build trust, and promote capacity-building efforts in the Global South.
- Addressing Obstacles and Barriers: Global governance should address obstacles and barriers to data hosting, collection, and sharing in the Global South. This may include financial constraints, technological limitations, and infrastructure gaps that hinder effective participation and contribution.
- Private Sector Engagement: It is essential to define the role of the private sector in research and emergencies. Global governance should encourage responsible and ethical private sector engagement, fostering investment, innovation, and knowledge sharing in the Global South.
Conclusion
- The promotion of equitable governance in biobanking is crucial for advancing scientific research, ensuring equitable healthcare, and addressing the unique healthcare challenges faced by the global South. The time is ripe for India to champion this cause and drive transformative change in the field of biobanking on a global scale.
Also read:
Mainstreaming Biodiversity: A Pivotal Step Towards a Sustainable Future
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Antibiotics with promise — a lifeline India awaits
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AMR and EUA
Mains level: India's innovative mechanism for antibiotics
Central Idea
- The battle against highly drug-resistant infections has reached a critical stage, where the need for effective antibiotics cannot be overstated. In a recent incident, a team of doctors encountered a challenging situation that showcased the critical importance of taking immediate action.
Relevance of the topic
Relate it with the antimicrobial resistance (AMR). AMR often also called antibiotic resistance, is a global health challenge and a looming public health crisis.
The Case of Extensively Drug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- In an intensive care room, a brave 18-year-old patient fought not only T-cell leukemia but also an aggressive and resistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- With limited treatment options due to the bacterium’s high resistance to antibiotics, the patient’s condition deteriorated rapidly.
- The infection attacked his lungs, resulting in persisting fever spikes and severe damage to his face. Time was running out, and his life hung in the balance.
Indian Innovation in antibiotic development
- Effective Combination: Cefepime/zidebactam is an innovative antibiotic developed by Indian researchers. It combines two active components to combat drug-resistant gram-negative pathogens, including the formidable Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Promising Results: This Indian innovation has shown remarkable potential in combating highly drug-resistant infections. It has undergone phase 3 trials internationally, demonstrating its effectiveness and safety profile.
- Compassionate Use: In a compelling case, an 18-year-old patient suffering from T-cell leukemia and an extensively drug-resistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa experienced a miraculous recovery after receiving cefepime/zidebactam under a compassionate use protocol. This highlights the life-saving impact of this innovative antibiotic.
- Urgent Need for EUA: The extraordinary case of the patient’s recovery emphasizes the urgent need for Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for antibiotics like cefepime/zidebactam that have shown promising results in phase 3 trials or have been licensed from other countries. Granting EUA would enable timely access to this effective treatment option.
- Strengthening the Arsenal: By recognizing the importance of cefepime/zidebactam and expediting its EUA, India can strengthen its arsenal against drug-resistant infections. This Indian innovation can contribute significantly to addressing the global challenge of drug resistance.
- Potential Global Impact: Granting EUA for cefepime/zidebactam not only saves lives within India but also extends a helping hand globally to countless individuals in desperate need of effective treatment options. India’s scientific achievements can make a substantial impact on the world stage.
- Scientific Prowess: Cefepime/zidebactam stands as a shining example of India’s scientific prowess in the field of antibiotic development. It showcases the nation’s ability to innovate and provide solutions to combat drug-resistant infections.
The Dire Situation and the Devastating Reality
- Scarcity of Potent Antibiotics: The dire situation arises from the scarcity of potent antibiotics to combat highly drug-resistant infections. The available antibiotics have lost their effectiveness due to rising resistance, leaving healthcare professionals with limited treatment options.
- Lives at Risk: The devastating reality is that countless lives are at risk due to inadequate antibiotics. Patients, particularly those who are critically ill or immunocompromised, are succumbing to infections that were once treatable. This results in significant morbidity and mortality rates.
- Ineffectiveness of Current Antibiotics: Rising drug resistance has rendered once-effective antibiotics ineffective against formidable pathogens. The constant evolution and mutation of bacteria pose a significant challenge to doctors in providing effective treatment.
- Multifaceted Challenges: Doctors face multifaceted challenges in combating drug-resistant infections. They must navigate through a shrinking arsenal of effective antibiotics, leading to limited choices and the use of suboptimal treatments. This situation adds immense pressure and helplessness to doctors on the front lines.
- High Death Toll: The dire situation and devastating reality contribute to a high death toll attributed to drug-resistant infections. Millions of lives are lost each year due to the inadequacy of available antibiotics in effectively treating these formidable pathogens.
- Race Against Time: Healthcare professionals are constantly racing against time, trying to stay one step ahead of mutating bacteria. The urgency to find effective solutions and the frustration of not having access to life-saving antibiotics in critical situations weigh heavily on doctors.
- Global Concern: The dire situation and devastating reality of drug-resistant infections are a global concern. It requires collaborative efforts from healthcare authorities, policymakers, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies to address the challenge and develop effective solutions.
What is Emergency Use Authorization (EUA)?
- EUA is a regulatory pathway that allows for the expedited authorization and use of medical products during public health emergencies.
- Under EUA, medical products, including vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics, can be made available for use in emergency situations before they receive full approval or licensure. This allows for a more rapid response to public health crises, such as outbreaks or pandemics, by providing access to potentially life-saving interventions.
- EUA involves a rigorous evaluation process by regulatory authorities, who assess the available scientific evidence, safety data, and potential benefits and risks of the medical product.
The Urgent Need for EUA
- Limited Treatment Options: In the face of highly drug-resistant infections, the available treatment options become limited and often ineffective. Conventional antibiotics may not be effective against these infections, leading to prolonged illness and increased mortality rates.
- Life-Threatening Infections: Drug-resistant infections can pose significant risks to patients’ lives, especially those who are immunocompromised or critically ill. Immediate access to effective treatments is crucial to combat these infections and improve patient outcomes.
- Time-Sensitive Situations: In some cases, time is of the essence, and delays in accessing effective treatments can have severe consequences. EUA allows for expedited authorization and access to potentially life-saving interventions in emergency situations.
- Addressing Public Health Emergencies: EUA plays a crucial role in responding to public health emergencies, such as outbreaks or pandemics, where swift action is needed to deploy interventions that can save lives and mitigate the spread of infections.
- Balancing Safety and Efficacy: While EUA expedites access to treatments, safety and efficacy remain critical considerations. Rigorous evaluation and monitoring are essential to ensure that authorized treatments meet the necessary standards for patient safety and effectiveness.
- Supporting Research and Development: EUA can provide a pathway for essential treatments that are still in clinical trials to be made available to patients who have no other viable options. This allows for the collection of real-world data and insights that can further inform research and development efforts.
- Global Collaboration: EUA for essential treatments can also enable collaboration and sharing of knowledge and resources on a global scale. It allows countries to work together in addressing public health challenges and ensures equitable access to life-saving interventions.
Conclusion
- The story of the 18-year-old patient’s recovery highlights the critical need for Emergency Use Authorization for essential antibiotics. The scarcity of potent antibiotics and the rising threat of drug-resistant infections demand urgent action. By granting EUA for promising antibiotics like cefepime/zidebactam and cefiderocol, we can save lives and make a significant impact globally. It is time for India to demonstrate its scientific prowess and commitment to combatting the challenges posed by drug-resistant infections
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Fibonacci Spirals in Plants and Fossil Discoveries
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fibonacci Spirals
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Nature’s mathematical patterns: Observing Fibonacci spirals in plants reveals intriguing mathematical patterns in nature.
- Fascination surrounding Fibonacci spirals: Scientists have been captivated by the prevalence of these spirals in various natural elements.
- Aim of the study: Re-evaluating the ancient origins of Fibonacci spirals in plants through fossil analysis.
What are Fibonacci Spirals?
- In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones.
- Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers.
- A Fibonacci spiral approximates the golden spiral using quarter-circle arcs inscribed in squares derived from the Fibonacci sequence.
Fibonacci Spirals in Nature: Exploring Patterns and Significance
- Spirals occur frequently in nature: Found in plant leaves, animal shells, and DNA’s double helix.
- Connection to the Fibonacci sequence: Spirals often adhere to the numerical Fibonacci sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, etc.).
- Notable examples: Pinecones, leaves, and animal shells exhibit Fibonacci spirals.
- Visible spirals in plants: By closely examining plants, clockwise and anticlockwise spirals can be observed.
Widespread Presence of Fibonacci Spirals in Living Plants
- Fibonacci spirals in pinecones: Extensive study of 6,000 pinecones revealed 97% exhibiting Fibonacci spirals.
- Fibonacci spirals in other plant organs: Over 90% of 12,000 spirals analyzed in 650 plant species adhered to the Fibonacci sequence.
- Investigation of Ancient Fossils: Non-Fibonacci Spirals Discovered
- Study focus: Fossils of clubmoss species Asteroxylon mackiei.
- Analysis techniques: Imaging and digital reconstruction employed to visualize and quantify spirals.
- Surprising findings: Ancient fossil exhibited high variability, with non-Fibonacci spirals as the most common pattern.
- Rarity of non-Fibonacci spirals in modern plants: Contradicts the prevailing assumption based on the scarcity of such patterns today.
Implications for Understanding Fibonacci Spirals in Land Plants
- Re-evaluating ancient origins: Discovery of non-Fibonacci spirals challenges the belief that all leafy plants originated with Fibonacci patterns.
- Challenging universality: Indicates separate emergence of Fibonacci spirals during plant evolution.
- Distinct evolutionary history: Clubmosses’ leaf evolution and Fibonacci spirals differed from other plant groups.
- Multiple independent emergences: Suggests Fibonacci spirals emerged multiple times independently.
Unanswered Questions and Debates
- Significance of Fibonacci spirals in modern plants: Ongoing debate on their adaptive advantages.
- Hypotheses: Functions of Fibonacci spirals include maximizing light exposure and efficient seed packing.
- Insights from fossils and clubmosses: Valuable for unraveling the significance of Fibonacci spirals in plants.
Conclusion
- Revising understanding of Fibonacci spirals in plants: Ancient fossils challenge the assumption of universal presence.
- Unique evolutionary history: Clubmosses demonstrate a distinct trajectory of Fibonacci spirals.
- Role of fossils in uncovering answers: Further research may provide insights into the adaptive advantages and functions of Fibonacci spirals in plants.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Endosymbiotic Relationships: Archaea, Mitochondria, and Plant Evolution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Archaea , Mitochondria
Mains level: NA

Central Idea
- Organisms on Earth are categorized into prokaryotes and eukaryotes, with distinct characteristics and evolutionary lineages.
- Archaea, a subset of unicellular organisms, were discovered to have a different lineage than bacteria and are found in extreme environments.
- Some archaea, known as the Asgard, exhibit similarities to eukaryotes, leading to insights into the origins of mitochondria and the evolution of complex life forms.
This article explores the endosymbiotic relationships between archaea and bacteria, the origins of mitochondria, and the unique evolutionary paths taken by plants.
Archaea and Unique Lineages
- Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes: Organisms are broadly divided into prokaryotes (unicellular, lacking organelles and nucleus) and eukaryotes (contain organelles and nucleus, often complex and multicellular).
- Archaea’s Distinct Lineage: Archaea differ from bacteria in cell wall composition and gene sequence and were initially found in extreme environments.
- Asgard Archaea: Asgard archaea, named after Norse mythology, exhibit proteins resembling eukaryotic proteins and are found in unique ecosystems.
Origins of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
- Endosymbiotic Theory: Mitochondria and chloroplasts, responsible for energy generation and photosynthesis, respectively, evolved from free-living bacteria through endosymbiosis.
- Mitochondria’s Origin: Mitochondria evolved from a proteobacteria that was engulfed by an Asgard archaea, leading to the development of animals, fungi, and plants.
- Plant Evolution: In plants, the Asgard-mitochondrial union was followed by the incorporation of a photosynthesizing cyanobacterium, which became the chloroplast.
Complexity of such Relationships
- Challenges of Symbiosis: Establishing a functional symbiotic relationship between independent life forms presents challenges.
- Plant Approach: Plants made choices to optimize gene retention, favoring archaean genes for information technology processes and bacterial genes for operations and housekeeping tasks.
- Gene Transfer to the Nucleus: Over time, many mitochondrial genes were transferred to the nucleus, creating a more efficient arrangement.
Insights from Cellular Process Studies
- Reconfiguring Cellular Processes: The research of Rajan Sankaranarayanan’s group at CCMB focuses on understanding the reconfiguration of cellular processes in endosymbiotic relationships.
- Animal and Fungal Adaptations: Animals and fungi adapt by inducing changes in mitochondria to work around discrepancies in amino acid discrimination mechanisms.
- Plant Evolution Complexity: Plants handle the complexity of three gene sets involved in their evolution by segregating policing machineries in the cytoplasm and mitochondria.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Cell-Cultivated Chicken gets US FDA Approval
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cell-Cultivated Chicken
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- Two US-based companies have received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to produce and sell cell-cultivated chicken, a type of lab-grown meat.
- This development is seen as a significant step towards reducing carbon emissions associated with the food industry.
Cell-Cultivated Chicken: How is it made?
- Cell Isolation: The companies isolate cells from live animals that are likely to taste good and reproduce consistently.
- Nutrient-Rich Mixture: The isolated cells are combined with a broth-like mixture containing essential nutrients, such as amino acids, fatty acids, sugars, salts, vitamins, and others required for cell growth.
- Cultivation in Bioreactors: The cells are placed in bioreactors or cultivators, creating a controlled environment that supports cell growth.
- Rapid Proliferation: Within two to three weeks, the cells multiply and form either large sheets (Upside Foods) or cell aggregates (Good Meat).
- Processing and Shaping: The cellular materials are collected, processed, and shaped into various meat products such as cutlets, sausages, or other forms.
Forms of Cell-Cultivated Meat
- Focus on Chicken: Good Meat and Upside Foods initially concentrate on cell-cultivated chicken, given its global consumption demand.
- Expansion Plans: These companies aim to extend their offerings to include other meats in the future. Research is underway for cell-cultivated versions of beef, sea bass, tuna, and shrimp.
Motivations behind Cell-Cultivated Meat
- Climate Mitigation: Cell-cultivated meat has the potential to reduce carbon emissions and land use associated with livestock production, addressing climate change concerns.
- Animal Welfare: By eliminating traditional animal farming, it aims to prevent animal cruelty.
- Food Security: Advocates view alternative meat as a means to meet nutritional demands worldwide.
Challenges to Overcome
- Consumer Acceptance: Ensuring that cell-cultivated meat matches the taste, texture, and appearance of traditional meat remains a challenge for widespread adoption.
- Cost Factors: The cost of cell-cultivated meat is expected to remain high in the near future, with concerns regarding quality control at scale.
- Resource Requirements: High-quality cells, suitable growth mediums, and other resources are necessary for successful cultivation.
- Environmental Impact: Studies highlight uncertainties regarding the environmental impact of cell-cultivated meat production, particularly concerning the growth medium used.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Evolutionary Journey of the Y Chromosome
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chromosomes
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- The Y chromosome, often known as the “master of maleness,” has fascinated scientists and historians for its role in determining sex and its unique genetic characteristics.
- This article explores the intriguing journey of the Y chromosome, its significance, and recent discoveries that challenge previous assumptions.
What are Chromosomes?
- Chromosomes are fundamental components of cells that play a vital role in storing and transmitting genetic information.
- These structures contain genes, which carry instructions for the development, functioning, and inheritance of traits.
- Chromosomes consist of tightly coiled DNA molecules wrapped around proteins called histones, forming chromatin.
- Before cell division, chromosomes replicate into identical sister chromatids held together at the centromere.
Types of Chromosomes:
- Autosomes: Non-sex chromosomes (22 pairs in humans) determine most traits.
- Sex Chromosomes: Determine biological sex (XX for females, XY for males).
Functions of Chromosomes
- Genetic Information Storage: Genes on chromosomes encode instructions for protein production and cellular processes.
- Inheritance: Chromosomes transmit genetic information during sexual reproduction through meiosis, ensuring genetic diversity in offspring.
- Gene Expression Regulation: Chromosomes control gene activation or silencing, crucial for development and cell functioning.
Significance of Chromosomes
- Understanding Genetic Disorders: Abnormalities in chromosomes cause conditions like Down syndrome, aiding diagnosis and comprehension.
- Evolutionary Insights: Comparative analysis of chromosomes reveals evolutionary relationships and genetic material changes over time.
- Advancements in Genetic Research: Chromosomes are crucial for genome sequencing, mapping, and studying gene expression, leading to improved understanding of human health, diseases, and targeted therapies.
Our focus: Y Chromosome
- Genetic Origins: The Y chromosome is believed to have emerged approximately 200-300 million years ago in a common ancestor of mammals. Its genetic sequence, published in 2003, revealed that it accounts for only 2% of the genetic material inside a cell, encoding around 55 genes.
- Quirks and Challenges: Referred to as the “juvenile delinquent” among chromosomes, the Y chromosome has repetitive sequences, a limited number of genes, and a reluctance to recombine with other chromosomes. These characteristics have led to debates about its functional utility and evolutionary trajectory.
Significance of the Y Chromosome
- Historical Insights: Researchers have extensively studied the Y chromosome to understand human migration and evolution. It has provided valuable insights into paternity, genetic diversity, and our shared past.
- Beyond Sex Determination: Contrary to earlier assumptions, recent studies have revealed that the Y chromosome plays a role in biological functions beyond sex determination. It contains genes associated with aging, lifespan regulation, and other vital processes.
Influence of the Y chromosome on Health
- Sex Differences in Lifespan: In the animal kingdom, including mammals, females tend to live longer than males. The absence of a second Y chromosome in males exposes detrimental mutations in the X chromosome, potentially contributing to shorter lifespans.
- Age-Related Loss of the Y Chromosome: Studies have shown that men experience a loss of the Y chromosome (LoY) with age, which has been associated with a higher risk of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. Research on mice models supports these findings, indicating a correlation between LoY and shorter lifespans and memory deficiencies.
- Phenotypic Sex and Longevity: Recent research on fruit flies challenges the notion that the presence of a Y chromosome directly influences longevity. Instead, the phenotypic sex of an individual, determined by external genitalia, may play a more significant role.
Future of the Y Chromosome
- Species-Specific Evolution: Some species, like rodents, have naturally lost their Y chromosome, offering insights into sex-chromosome turnover. These species serve as models for understanding the process and the potential repurposing of other chromosomes as sex chromosomes.
- Signs of Replacement: Genomic analysis of Neanderthal DNA indicates that the Y chromosome has undergone replacement in the lineage leading to modern humans. This suggests that the Y chromosome’s role as the “master of maleness” may eventually be overtaken by another chromosome in the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Implantable Brain-Computer Interface
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nuralink technology and probable applications
Mains level: Nuralink, its applications, Concerns , Data transparency, challenges and way ahead
Central Idea
- On May 25, the USFDA granted approval for clinical trials of Neuralink’s implantable Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), developed by tech mogul Elon Musk’s neurotech startup. While Neuralink’s ambitions are revolutionary, promising to treat brain disorders and fuse human consciousness with AI, there are significant concerns regarding the safety, viability, and transparency of the technology.
What is Implantable Brain-Computer Interface?
- An implantable Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is a technology that allows direct communication between the human brain and external devices.
- It involves the surgical implantation of a chip containing electrodes into the brain, which can detect and transmit neural signals.
- These signals are then decoded by a device connected to the chip, enabling individuals to control devices or interact with technology using their thoughts alone.
- The goal of implantable BCIs is to enhance human capabilities, treat neurological disorders, and potentially merge human consciousness with artificial intelligence (AI).
Simplified: What Is Neuralink?
- A device to be inserted in brain: Neuralink is a gadget that will be surgically inserted into the brain using robotics. In this procedure, a chipset called the link is implanted in the skull.
- Insulated wires connected to electrodes: It has a number of insulated wires connected from the electrodes that are used in the process.
- Can be operated by smartphones: This device can then be used to operate smartphones and computers without having to touch it
Neuralink’s Claims and Lack of Data Transparency
- Limited Published Data: Neuralink has only published one article, co-authored by Elon Musk and the Neuralink team, which describes the chip and implantation process. However, this article was not published in a prominent journal and does not provide comprehensive data supporting the claims made by Neuralink.
- Episodic Launch Videos: Instead of presenting robust scientific evidence, Neuralink relies on episodic launch videos and show-and-tell events live-streamed on YouTube. While these videos generate excitement and capture public interest, they do not provide in-depth data or transparency regarding the technology’s safety and efficacy.
- Lack of Preclinical Assessment: Before human trials, it is crucial to conduct thorough preclinical assessments on complex mammals to evaluate the safety and feasibility of the technology. However, Neuralink has not shared comprehensive data on preclinical studies involving animals such as pigs, sheep, or monkeys, leaving questions about the device’s effectiveness and potential risks.
- Limited Quantitative Data: Neuralink has not released sufficient quantitative data to the public regarding the safety and efficacy of their implantable device. There is a lack of published imaging or quantitative data from their histology unit, making it challenging to assess the device’s performance, mortality rates, or the success rate of the surgical procedure.
- Limited Disclosure of FDA-submitted Data: Private companies like Neuralink have the privilege of protecting proprietary technologies, and they are not obligated to disclose or publish the data they submit to regulatory authorities like the USFDA. This lack of transparency prevents public scrutiny and raises concerns about the thorough evaluation of the technology by independent experts.
Facts for prelims
What are Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)?
|
Safety concerns associated with Neuralink’s BCI technology
- Heat Generation and Wire Stability: With thousands of thin wires implanted in the brain, the issue of heat generation arises. The high density of wires and the transmission of signals can potentially generate heat, which may pose a risk to the surrounding brain tissue. Furthermore, ensuring the stability and secure placement of these thin wires in a freely moving human presents additional challenges.
- Brain Tissue Response and Injury: Implanting foreign objects into the brain can cause tissue response and potential injury. The impact of movement on the surrounding brain tissue, the potential for micro-injuries that may accumulate over time, and the resulting complications and disabilities need to be thoroughly assessed.
- Immune Reaction and Scar Tissue Formation: The brain has a natural defense mechanism that responds to injuries by forming scar tissue. Scar tissue can be seizure-prone and may have implications for the overall functioning of the implanted device. The immune reaction and scar tissue formation around the brain in response to the implant need to be carefully studied and understood.
Concerns about Work Environment and Material Stability
- Pressure Cooker Work Environment: Reports have emerged suggesting a high-pressure work environment at Neuralink. There have been claims of Elon Musk creating unrealistic timelines and expectations for employees, potentially fostering a culture that prioritizes speed over thoroughness. This kind of work environment can have negative effects on employee well-being and may compromise the quality and safety of the technology being developed.
- Material Stability: The long-term stability and inertness of the materials used in the fabrication of Neuralink’s implantable device have come into question. Competitor companies, such as InBrain, have raised doubts about the stability of the material (PEDOT) used for the implant wires.
Regulatory Challenges for Neuralink and Proprietary Protection
- Regulatory Challenges: The regulatory process may face challenges in terms of ensuring thorough evaluation, transparency, and adherence to safety standards. The FDA rejected Neuralink’s initial application due to safety concerns with the implanted chip’s lithium batteries, but the basis for subsequent approval remains unclear.
- Proprietary Protection: Neuralink have been granted latitude in protecting proprietary and patented technologies. This protection allows companies to safeguard their intellectual property, maintain a competitive advantage, and control the release of information. While proprietary protection is a common practice in business, it can limit public access to critical data and impede independent scrutiny of the technology’s safety and efficacy.
Way Forward
- Rigorous Evaluation: Comprehensive and independent evaluation of Neuralink’s technology is necessary to assess its safety, efficacy, and long-term viability. This evaluation should involve transparent data sharing, peer review, and collaboration with regulatory agencies, independent experts, and the scientific community.
- Preclinical Assessment: Thorough preclinical assessments, including studies in complex mammals, should be conducted to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and potential risks of Neuralink’s BCI. Comprehensive data on mortality rates, surgical success rates, and long-term effects should be disclosed to ensure a robust understanding of the technology’s impact.
- Transparency and Data Sharing: Neuralink should prioritize transparency and data sharing to address concerns about the lack of quantitative data, animal welfare, and material stability. Publishing quantitative data, sharing research findings, and providing access to independent researchers for scrutiny can enhance trust and facilitate a more thorough evaluation of the technology.
- Ethical Considerations: The ethical implications of merging humans with AI should be carefully examined and discussed. Engaging in open and inclusive dialogues involving experts from various disciplines can help navigate the ethical challenges associated with the potential fusion of human consciousness and AI.
- Regulatory Oversight: Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA, should ensure rigorous evaluation and oversight of Neuralink’s BCI technology. Striking the right balance between proprietary protection and the need for transparency and accountability is crucial to safeguard public safety and promote responsible innovation.
- Independent Monitoring and Accountability: Independent monitoring of Neuralink’s practices, including animal welfare and work environment, should be in place to ensure adherence to ethical standards. This can involve external audits, collaborations with animal welfare organizations, and enhanced regulatory scrutiny.
Conclusion
- Before delving into the ethical debates surrounding merging humans with AI, it is crucial to address the concerns surrounding Neuralink’s implantable BCI. Safety, data transparency, and animal welfare should be paramount. By promoting transparency, rigorous evaluation, and responsible practices, Neuralink can build trust, ensure patient safety, and foster a constructive dialogue about the future implications of this groundbreaking technology.
Also read:
| Neuralink and the unnecessary suffering of animals |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
IIT-M generates Hydrogen from Seawater
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Green Hydrogen
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Researchers from IIT-Madras have developed components for a cost-effective method of electrolyzing seawater to produce green hydrogen.
- The current alkaline water electrolyzer technology is energy-intensive, requires an expensive oxide-polymer separator, and uses fresh water.
Generating Green Hydrogen
- Instead of using fresh water, the researchers developed an electrolyzer that utilizes alkaline seawater.
- Carbon-based support material was used for the electrodes to minimize corrosion.
- Transition metal-based catalysts were designed to catalyze both oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions, improving the production of hydrogen and oxygen.
- A cellulose-based separator was developed to allow hydroxide ions to pass through while preventing crossover of oxygen and hydrogen.
How does Electrolysis take place?
- The alkaline water electrolyzer involves two half-reactions at the anode and cathode.
- At the cathode, water dissociates into H+ and hydroxide ions, with H+ ions converting into hydrogen.
- Hydroxide ions produced at the cathode pass through the separator, and oxygen is generated at the anode.
- When seawater is used, hypochlorite formation occurs at the anode, causing corrosion and reducing oxygen production. Impurities also affect the hydrogen evolution reaction at the cathode.
How were the Catalyst and Electrode designed?
- The carbon-based support material was used for both anode and cathode electrodes to prevent corrosion.
- The catalyst coating on the support material enhances hydrogen production at the cathode and oxygen production at the anode.
- Transition bimetals in the catalyst are selective toward oxygen evolution reaction, overcoming the challenge of hypochlorite formation.
- Despite impurities adsorbed on the cathode, the catalyst promotes hydrogen evolution, increasing hydrogen production.
What made this device novel?
- The team developed a cellulose-based separator to separate the anode and cathode.
- The separator allows hydroxide ions to pass through but minimizes the crossover of hydrogen and oxygen.
- The separator shows high resistance to degradation in seawater.
Experimental Results and Performance
- The assembled electrolyzer achieved a seawater splitting voltage of 1.73 V at 10 mA/sq.cm and 26 degrees C.
- The optimized parameters enable the electrolyzer to directly use photovoltaic-derived voltage for green hydrogen production.
- Two prototypes of different dimensions were developed, producing hydrogen at rates of 250 ml/hour and 1 liter/hour.
- A stack of three cells produced hydrogen at a rate of about 4 liters/hour.
Back2Basics: Hydrogen Categories
| Production Method | Carbon Emissions | |
| Gray Hydrogen | Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) from fossil fuels | High emissions |
| Blue Hydrogen | Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS) or carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) | Reduced emissions compared to gray hydrogen |
| Green Hydrogen | Electrolysis using renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro) | No carbon emissions |
| Turquoise Hydrogen | Methane pyrolysis from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS) or carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS) | Reduced emissions compared to gray hydrogen |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Fruit Flies: Unveiling their Contributions to Science and Medicine
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fruit Flies
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Flies’ negative perception: Fruit flies often considered annoying pests, but their significance in biological and medical science is immense.
- Economic and environmental importance: Flies, including fruit flies, play crucial roles as pollinators for plants and contribute to decomposition processes.
Fruit Flies (Drosophila melanogaster)
- Overview: Fruit or vinegar fly species known for its nuisance during summer.
- Scientific significance: Drosophila melanogaster is a well-understood animal organism globally and has contributed to numerous Nobel Prize-winning discoveries in physiology and medicine.
Partnership between Science and Flies
- Early collaborations with flies: Biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan’s experiments with fruit flies revolutionized evolutionary and genetic research.
- Discoveries in genetics: Fruit flies provided insights into genetic mutations, inheritance patterns, and the mapping of genes on chromosomes.
- Understanding biological processes: Studies in fruit flies helped unravel mechanisms of development, gene regulation, and protein synthesis.
Insights from Drosophila Research
- Embryo studies: Microscopic examination of Drosophila embryos aided in understanding genetic defects and gene networks that control development.
- Contribution to genetic medicine: Research on fruit flies helped decipher the genetic code, map DNA structure, and investigate inherited disorders.
- Remarkable genetic similarity: Fruit flies and humans share striking biological similarities, allowing for the study of human biology and disease in flies.
Versatility and Applications of Drosophila Research
- Efficient and cost-effective research: Fruit flies offer a fast and versatile model organism for studying various aspects of human biology and disease.
- Neuroscience and behavioral research: Fruit flies provide insights into learning, memory, sleep, aggression, addiction, and neural disorders.
- Broad range of applications: Fruit flies are used to study cancer, aging, development, gut microbiome, stem cells, muscles, and the heart.
Bridging Knowledge Gaps
- Complementary to human studies: Fruit flies serve as a bridge to understanding complex human diseases and physiological processes.
- Insights into neurodegenerative diseases: Although flies cannot fully mimic personality loss in Alzheimer’s disease, they contribute to studying neuronal death and related mechanisms.
Paradigm for Scientific Discoveries
- Accelerating research in complex organisms: Knowledge gained from fruit flies can be applied to more complex organisms, expediting scientific progress.
- Global research community: Over 10,000 researchers worldwide utilize fruit flies for diverse areas of study, enriching our understanding of human biology and disease.
Shifting Perspectives
- Appreciating the significance: Fruit flies, despite their annoyance, play a vital role in advancing scientific knowledge and medical breakthroughs.
- Rethinking flies’ presence: Viewing fruit flies in a different light, recognizing their value in research and their contributions to understanding the world around us.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Devastating Frog Disease: Chytridiomycosis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chytridiomycosis
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- A multinational study has recently published a breakthrough method in the journal Transboundary and Emerging Diseases to detect all known strains of the amphibian chytrid fungus.
- This method will enhance our ability to detect and research the disease and work towards finding a widely available cure.
Chytridiomycosis: The deadly frog disease
- Chytridiomycosis, also known as chytrid, is a fungal disease that has been decimating frog populations worldwide for the past 40 years.
- The disease has caused severe declines in over 500 frog species and led to 90 extinctions, making it the deadliest animal disease known.
How does it infect?
- Chytrid infects frogs by reproducing in their skin, damaging their ability to balance water and salt levels.
- The mortality rate is extreme, and the disease has affected a high number of species, causing devastating declines and extinctions.
- The disease originated in Asia and spread globally through amphibian trade and travel.
Limitations in diagnosis
- Researchers traditionally used swabs and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) tests, similar to COVID-19 testing, to detect chytrid in frogs.
- The existing qPCR test could not detect chytrid strains from Asia, limiting research efforts.
New and Improved qPCR Test
- Researchers in India, Australia, and Panama have developed a new qPCR test that can detect strains of chytrid from Asia.
- The test is also more sensitive, allowing for the detection of low infection levels and expanding the range of species that can be studied.
- The test can also detect a closely related species of chytrid that infects salamanders.
Understanding natural immunity in frogs
- Some amphibian species, even those without an evolutionary history with chytrid, do not become sick when carrying the fungus, indicating natural immune resistance.
- Frog immunity is complex, involving anti-microbial chemicals, symbiotic bacteria, white blood cells, antibodies, and more.
- Research in Asia, where chytrid declines have not been observed, may provide insights into how resistance evolves and aid in finding a cure for affected regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Study reveals unique Nervous System in Comb Jellies
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Comb Jellies, Neurons, Neural Network
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Comb jellies, or ctenophores, are marine animals with jelly-like bodies and iridescent combs.
- They represent an ancient animal lineage and have a distinct nervous system.
- A recent study published in Science examined the comb jelly nervous system and made surprising discoveries.
What are Comb Jellies?
- Comb jellies, also known as ctenophores, are marine animals that belong to the phylum Ctenophora. They are fascinating creatures with a unique and delicate appearance.
- Despite their name, comb jellies are not actually true jellyfish.
- They have a gelatinous, transparent body that is often luminescent and adorned with rows of cilia, or comb-like structures, which give them their characteristic shimmering appearance.
Findings of the new study
- The researchers aimed to investigate how nerve net neurons in comb jellies connect.
- Contrary to expectations, synapses (junctions between neurons) were absent in the nerve net.
- Instead, nerve-net neurons were continuously connected by a single plasma membrane.
Significance of ctenophores
- In the 1950s, electron microscopy confirmed the separate-cell nature of neurons connected by synapses.
- Ctenophores challenge this notion by having a syncytial nerve net, as observed in the new study.
- Ctenophores attracted attention due to their status as a potential early animal lineage.
- Whole-genome sequencing studies supported the theory that ctenophores branched off early in animal evolution.
Evolution of ctenophore nervous systems
- The evolution of ctenophore nervous systems remains unclear to biologists.
- Leonid Moroz proposed a controversial theory of independent nervous system evolution in ctenophores and other animals.
- Ctenophores exhibit a unique nervous system lacking classical neurotransmitter pathways and common neuronal genes.
- The absence of muscle-based movement and reliance on cilia might have driven the evolution of a different signal conduction system.
Questions for further research
- Researchers aim to study the development of nerve net neurons in ctenophores.
- They seek to determine if adult ctenophores retain syncytial nerve nets or develop synapses.
- The uniqueness of ctenophore nervous systems provides valuable insights into the evolution of the nervous system.
- Comparative analyses of unique animal systems like ctenophores aid in understanding neuronal function and treating disorders.
Conclusion
- Understanding the functional and evolutionary significance of syncytial nerve net neurons in ctenophores requires further research.
- This study serves as a crucial foundation for investigating the evolution of nervous systems in animals.
- Comparative studies on small marine creatures like ctenophores offer insights into the fundamental principles of brain function.
Key Terminologies
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Did Neanderthals shape our noses?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Neanderthals , Read the attached story
Mains level: Evolutionary features of Humans

Central Idea
- The human nose has historical and cultural importance beyond its practical functions.
- Different societies have their own standards of beauty related to nose shape and proportion.
- The nose is significant in art, literature, and remnants of ancient civilizations.
Who were the Neanderthals?
| Description | |
| Time Period | Lived approximately 400,000 to 40,000 years ago during the Middle Paleolithic and Late Pleistocene epochs |
| Physical Appearance | Robust build with a barrel-shaped chest, shorter limbs, and distinctive anatomical features such as pronounced brow ridges and a projecting mid-face |
| Tools and Technology | Skilled toolmakers who used a variety of tools made from stone, bone, and antler |
| Culture and Behavior | Complex social structures and likely lived in small groups or bands, exhibited advanced hunting techniques, made use of fire, and engaged in symbolic expressions through personal ornamentation and cave art |
| Adaptation to Environments | Adapted to cold and temperate environments, had robust bodies, large noses, and other physiological characteristics were advantageous for survival in harsh conditions |
| Interactions with Modern Humans | Interbred with early modern humans who migrated out of Africa. As a result, some individuals today carry a small percentage of Neanderthal DNA in their genomes, particularly in non-African populations |
| Extinction | Around 40,000 years ago |
| Scientific Significance | Closest extinct relatives, and understanding their anatomy, behavior, and interactions with modern humans helps reconstruct our shared past |
Genetic association study on Human Nose
- A recent study used 2D images and automated measurements of facial landmarks to conduct a genetic association study.
- The study involved over 6,000 Latin American individuals and identified 42 new genetic loci associated with the human nose.
- Some of these loci, including 1q32.3, were replicated in other populations like Asians, Europeans, and Africans.
Role of Neanderthal Genes and ATF3 Gene
- The genetic locus 1q32.3, associated with midface height, has contributions from Neanderthals.
- The ATF3 gene, located in this locus, is regulated by FOXL2, which is involved in skull and face development.
- Changes in nose shape may have evolutionary implications, helping humans adapt to different climates.
Neanderthal Genomes and Human Traits
- Genomic loci from Neanderthals and Denisovans have influenced various traits and diseases in modern humans.
- Evidence suggests these genomic contributions affect pathogen response, skin conditions, blood conditions, cancers, and mental health.
- Understanding the genetic interactions between archaic and modern human genomes aids in comprehending genetic diversity and adaptability.
Human Origins and Interbreeding
- Human migrations out of Africa, interbreeding with Neanderthals and Denisovans, and extinct archaic hominids have shaped human traits.
- Recent studies highlight that early humans diverged in Africa from multiple ancestral roots, with varying degrees of genetic components from archaic humans in different populations.
Implications and Future Research
- Studying the interbreeding event and its consequences deepens our understanding of genetic heritage.
- The knowledge gained could lead to new avenues for disease study, treatment, and appreciation of human genetic diversity.
- Continued research on the interplay between archaic and modern human genomes is an exciting frontier in genomics.
Key TerminologiesLoci/Locus: The position of a specific gene on a chromosome. Introgression: The transfer of genetic information between different species or populations through interbreeding. Neanderthals: Archaic hominids closely related to modern humans, believed to have interbred with early humans. Denisovans: A subspecies of archaic humans who lived until around 30,000 years ago. Genomic Loci: Specific locations on chromosomes associated with certain traits or characteristics. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Understanding a Human Pangenome Map
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Human Pangenome Map
Mains level: Genetic studies

Central Idea
- A study published in the Nature journal presents a pangenome reference map built using genomes from 47 anonymous individuals.
- The individuals included in the study are from various regions, including Africa, the Caribbean, Americas, East Asia, and Europe.
Understanding Genomes and Reference Genomes
- The genome refers to the collection of all genes and regions between genes found in our chromosomes.
- Each chromosome is composed of millions of nucleotides (A, T, G, and C) arranged in different combinations.
- Genome sequencing helps understand genetic diversity and susceptibility to diseases.
- A reference genome is a map used to compare newly sequenced genomes and identify differences.
- The first reference genome, created in 2001, had limitations and did not represent human diversity accurately.
What is Pangenome Map?
- The new study focuses on building a pangenome map, which is a graph representing genetic diversity among individuals.
- Pangenome maps use long-read DNA sequencing technologies to assemble sequences accurately.
Importance of Pangenome Map
- Although humans are more than 99% similar in their DNA, there is still a 0.4% difference between individuals.
- A complete and error-free pangenome map helps understand genetic differences and human diversity.
- It aids in identifying genetic variants linked to health conditions, such as the discovery of 150 new genes associated with autism.
- The current pangenome map lacks representation from certain populations, including Indians.
Implications for Indian Genomes
- The pangenome map, despite not including Indian genomes, will assist in mapping Indian genomes against existing reference genomes.
- Future pangenome maps with Indian genome data will provide insights into disease prevalence, rare gene discovery, diagnostic methods, and drug development.
Key TerminologiesGenome: The complete set of genes and regions between genes in an organism. Reference Genome: A map used to compare newly sequenced genomes and identify differences. Pangenome: A graph representing genetic diversity among individuals rather than a linear sequence. Nucleotides: The building blocks of DNA (A, T, G, C). Long-Read DNA Sequencing: A technology that produces longer and contiguous DNA strands for more accurate sequencing. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Strengthening Quad: The Need for a Biomanufacturing Hub in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Biomanufacturing, QUAD's CET working group, ICET and other such developments
Mains level: Strengthening Quad Cooperation in Biotechnology, India as a biomanufacturing hub
Central Idea
- The Quad, comprised of Australia, India, Japan, and the United States, established a Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group in March 2021 to foster collaboration and explore opportunities in critical and emerging technologies, including biotechnology. However, there remains untapped potential for Quad cooperation in the field of biotechnology. The need of the hour is to establish a Quad-led biomanufacturing hub in India to enhance cooperation and leverage the complementary strengths of Quad nations.
What is QUAD’s Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group?
- The Quad’s Critical and Emerging Technology Working Group is a collaborative initiative established by the Quad countries.
- It was formed in March 2021 with the aim of facilitating cooperation, monitoring trends, and exploring opportunities related to critical and emerging technologies. The working group focuses on identifying and addressing key issues and challenges in areas such as biotechnology, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, quantum technologies, and other cutting-edge fields.
- It serves as a platform for the Quad countries to share expertise, exchange information, and coordinate efforts in order to harness the potential of these technologies for economic growth, national security, and societal development.
- For instance, in the field of 5G, the Quad members have worked on developing telecommunications networks to counter the pervasive presence of China’s Huawei through the use of open radio access (O-RAN) networks.
Facts for prelims
Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies (ICET)?
|
What is mean by Biomanufacturing?
- Biomanufacturing refers to the use of biological systems, such as living organisms (microorganisms, cell cultures, or plants), to produce commercially valuable products on a large scale. It involves harnessing the power of biological processes and utilizing them in industrial applications.
- In biomanufacturing, living organisms are employed as “factories” to perform specific tasks or produce desired molecules. These organisms can be genetically engineered or naturally occurring, depending on the desired outcome.
- The organisms are cultivated in controlled environments, such as bioreactors, where they are provided with optimal conditions for growth and production. They are fed with specific nutrients, and their growth and metabolic activities are carefully regulated.
- Biomanufacturing can encompass a wide range of products, including pharmaceuticals, enzymes, biofuels, specialty chemicals, biomaterials, and more.
- Biomanufacturing is often more sustainable and environmentally friendly, as it relies on renewable resources and has the potential to reduce waste and pollution.
Why India stands as the ideal choice to host the biomanufacturing hub?
- India’s ambition of biomanufacturing: India’s National Biotechnology Development Strategy sets a target of reaching $100 billion in the biomanufacturing sector.
- Existing Infrastructure: India already has existing infrastructure in place, including pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities and research institutions, that can be utilized to establish and expand biomanufacturing capabilities. This infrastructure provides a solid foundation for the development of a biomanufacturing hub.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Expertise: India has a long-standing reputation as a major player in the global pharmaceutical industry. The country has established expertise in manufacturing and quality control processes, which can be leveraged for biomanufacturing. The experience gained in pharmaceutical manufacturing can be applied to biomanufacturing, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maintaining high-quality production.
- Skilled Workforce: India possesses a large pool of skilled professionals in the life sciences and biotechnology sectors. The country’s workforce includes scientists, engineers, and technicians with expertise in various aspects of biomanufacturing. This skilled workforce can contribute to the success of the biomanufacturing hub by driving research, development, and production activities.
- Research Output: India has demonstrated its research capabilities in biomanufacturing, ranking high in terms of the quality of research output and the share of research publications. The country’s strong research base provides a solid foundation for innovation and advancements in biomanufacturing processes and technologies.
- Cost-Effectiveness: India has a competitive advantage in terms of cost-effectiveness. The cost of manufacturing in India is generally lower compared to countries like the United States, making it an attractive destination for cost-efficient biomanufacturing. This cost advantage can contribute to the affordability and accessibility of biomanufactured products.
- Potential for Affordable Scale: India has the potential to provide affordable scalability in biomanufacturing processes. With its large population and manufacturing capabilities, India can meet the demand for biomanufactured products on a large scale, leading to cost-effective production and availability of essential biopharmaceuticals and other biotechnological products.
Complementary Strengths of Quad Nations
- Advanced Biotechnology Innovation Ecosystems: Japan, Australia, and the United States have well-established and advanced biotechnology innovation ecosystems. These ecosystems comprise research institutions, universities, biotech companies, and startups that drive innovation and technological advancements in biotechnology.
- Funding Capability: The United States, being one of the Quad nations, brings significant funding capability to the table. The U.S. government and private sector invest heavily in research, development, and commercialization of biotechnology.
- Skilled Workforce: India, as a Quad member, offers a large pool of skilled manpower, particularly in the life sciences field. Collaborative efforts can facilitate knowledge sharing and capacity building to enhance the skills of the workforce across the Quad nations.
- Manufacturing and Scale-Up Capabilities: India has well-established pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. The country has a robust infrastructure and expertise in large-scale production, which can be harnessed for biomanufacturing purposes.
- Intellectual Property and Technology Transfer: The Quad nations, particularly Japan and the United States, have strong intellectual property protection systems and expertise in technology transfer. Sharing intellectual property and facilitating technology transfer can accelerate the development and commercialization of biomanufacturing technologies, benefiting all Quad nations.
- Research Output and Innovation: All Quad nations contribute significantly to global research output in the field of biotechnology. They produce high-quality research publications and drive innovation in various subfields of biotechnology. Collaboration within the Quad can facilitate knowledge exchange, joint research projects, and the development of innovative solutions in biomanufacturing.
Way ahead
- Collaborative Research and Development: Foster collaborative research and development initiatives between the Quad nations and India. This can involve joint projects, knowledge sharing, and technology transfer to accelerate the development of biomanufacturing processes, products, and technologies.
- Capacity Building and Skill Development: Establish training programs, workshops, and exchange programs to enhance the skills and knowledge of professionals in biomanufacturing. This can include specialized training in areas such as advanced bioprocessing techniques, quality control, regulatory compliance, and technology transfer.
- Infrastructure Investment: Allocate resources for infrastructure development, including the establishment of specialized bioreactor facilities, research centers, and manufacturing capabilities.
- Regulatory Framework Alignment: Collaboratively work towards aligning regulatory frameworks among the Quad nations and India. This involves harmonizing regulations, streamlining approval processes, and ensuring consistent quality standards.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Foster public-private partnerships to leverage the expertise, resources, and capabilities of both sectors. Engaging industry stakeholders, academia, research institutions, and government agencies in collaborative initiatives can drive innovation, facilitate technology transfer, and accelerate the commercialization of biomanufactured products.
- International Collaboration: Explore collaborations beyond the Quad nations to foster international cooperation in biomanufacturing. Engaging with countries outside the Quad can expand opportunities for knowledge exchange, market access, and research collaboration.\
Must read:
| QUAD and the Telecom network security |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
DNA Analysis in Criminal Cases: Ensuring Credibility and Admissibility
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DNA analysis applications
Mains level: DNA analysis in criminal investigations and and issues
Central Idea
- The recent judgments by the Supreme Court have raised concerns about the admissibility of DNA reports as conclusive evidence in criminal cases. Highlighting issues of suspicion, lack of examination of underlying findings, and reliable application of techniques, the Court has emphasized the need to establish a robust framework for the acceptance of DNA analysis.
What is DNA analysis?
- DNA analysis, also known as DNA profiling or DNA testing, is a scientific method used to identify and analyze genetic material present in an individual’s cells.
- It involves examining specific regions of DNA to create a unique DNA profile for identification purposes.
- DNA analysis is widely used in forensic investigations, paternity testing, ancestry research, and other fields where genetic identification is required.
Facts for prelims: Basics
| Characteristic | DNA | RNA |
| Structure | Double-stranded | Single-stranded |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) | Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) |
| Base Pairing | A-T, C-G | A-U, C-G |
| Primary Function | Stores genetic information | Transfers and expresses genetic information, protein synthesis |
| Types of RNA | Not applicable | Messenger RNA (mRNA), Transfer RNA (tRNA), Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
| Presence in Viruses | Yes | Yes |
| Stability | Relatively stable | More prone to degradation |
The process of DNA analysis
- Sample Collection: Biological samples such as blood, saliva, semen, hair, or tissues are collected from the individual or the crime scene.
- DNA Extraction: The collected sample undergoes a process of DNA extraction, which involves isolating the DNA from other cellular components.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is used to amplify specific regions of the DNA. This technique allows the production of numerous copies of the targeted DNA sequences.
- Short Tandem Repeats (STR) Analysis: STR analysis is performed by examining specific regions of DNA called short tandem repeats. These regions consist of repeating DNA sequences that vary in length among individuals. The number of repeats at each STR locus is determined and used to create a DNA profile.
- Electrophoresis: The amplified DNA fragments are separated by size using a technique called electrophoresis. The DNA fragments are placed in a gel matrix and subjected to an electric current, causing them to migrate through the gel. This process separates the DNA fragments based on their sizes.
- DNA Profile Generation: The separated DNA fragments are visualized, and the resulting pattern is captured as an individual’s DNA profile. The DNA profile consists of a series of bands corresponding to the sizes of the amplified STR regions.
- Comparison and Interpretation: The generated DNA profile is compared to known reference samples, such as those from suspects or victims. The comparison is used to determine if there is a match or exclusion. Statistical calculations, such as the random match probability (RMP), may be used to assess the significance of the match.
Role of DNA analysis in criminal investigations
- Identification: DNA analysis is used to identify individuals involved in a crime. By comparing DNA profiles from crime scene samples to reference samples, such as those collected from suspects or victims, investigators can establish or exclude a person’s presence at the crime scene.
- Linking Suspects to Crime Scenes: DNA evidence can be compared to a suspect’s DNA profile to determine if they were present at the crime scene. If a match is found, it provides strong evidence connecting the suspect to the crime.
- Exclusion of Innocent Individuals: DNA analysis can be used to exclude individuals who are not connected to a crime. If a DNA profile from the crime scene does not match a suspect’s DNA, it can help establish their innocence.
- Cold Case Investigations: DNA analysis has been instrumental in solving cold cases where conventional evidence has been limited. Revisiting old DNA samples or re-analyzing evidence using advanced techniques can lead to the identification of previously unknown suspects or the exoneration of wrongly convicted individuals.
- Establishing Biological Relationships: DNA analysis is employed in cases involving missing persons, unidentified bodies, and disputed paternity or maternity claims. By comparing DNA profiles, investigators can determine familial relationships or confirm parentage.
- Sexual Assault Cases: DNA analysis is particularly significant in sexual assault cases. DNA evidence collected from the crime scene, victim, or perpetrator can provide crucial information for identifying and convicting the offender.
- Decoding Crime Scene Evidence: DNA analysis can help decipher complex crime scene evidence. By analyzing DNA profiles from different sources, such as mixed DNA samples, touch DNA, or degraded DNA, forensic experts can unravel critical information about the sequence of events and potential contributors.
- Corroboration of Witness Testimony: DNA evidence can corroborate or challenge witness testimony. When witness accounts are in question, DNA analysis can provide objective evidence to support or refute their claims.
Critical Examination of DNA Reports
- In recent judgments, such as Rahul v. State of Delhi, Ministry of Home Affairs (2022) and Manoj v. State of Madhya Pradesh (2022), the Supreme Court has raised concerns about the reliability and admissibility of DNA evidence in criminal cases.
- Rahul v. State of Delhi:
- In Rahul v. State of Delhi, the Court expressed reservations about the reliability of DNA evidence based on the suspicion surrounding the collection and sealing of samples sent for examination.
- Despite a match result and other findings, the Court acquitted all three individuals accused of rape and murder.
- Manoj v. State of Madhya Pradesh:
- In Manoj v. State of Madhya Pradesh, the Court identified the likelihood of contamination in the DNA analysis due to the absence of mentioning the random occurrence ratio.
- The Court emphasized the importance of considering the statistical ratio or ‘random match probability’ (RMP), which indicates the frequency of a particular DNA profile in a population. The lack of mention of RMP led to the exclusion of the DNA evidence in this case.
Concerns over the admissibility of DNA reports
- Reliability of Techniques: The Court has questioned whether the techniques used in DNA analysis were reliably applied. It is crucial to ensure that the methods employed are scientifically sound and that the experts conducting the analysis possess the necessary expertise.
- Examination of Underlying Findings: The Court has criticized the failure of trial courts and higher courts to examine the underlying basis of the findings in DNA reports. It is essential to scrutinize the methodology, procedures, and conclusions drawn from the analysis to determine the accuracy and reliability of the results.
- Chain of Custody: The Court has expressed concerns about the integrity of DNA samples and their handling throughout the chain of custody. Proper documentation and maintenance of the chain of custody are vital to establish the authenticity and reliability of the evidence.
- Possibility of Contamination: Contamination of DNA samples can significantly impact the reliability and accuracy of the analysis. The Court has highlighted instances where contamination may have occurred, such as improper collection, storage, or handling of samples.
- Random Occurrence Ratio (RMP): The Court has emphasized the importance of including the random occurrence ratio or RMP in DNA reports.
Way ahead
- Standardized Guidelines: Establish standardized guidelines for DNA analysis in forensic laboratories, including protocols for sample collection, handling, storage, and analysis. These guidelines should encompass best practices to minimize the risk of contamination and ensure the integrity of DNA evidence.
- Quality Control Measures: Implement rigorous quality control measures in DNA analysis processes. This includes regular proficiency testing, accreditation of forensic laboratories, and adherence to international quality standards.
- Chain of Custody: Emphasize the importance of maintaining a proper chain of custody for DNA samples. Accurate documentation and strict adherence to protocols will help ensure the integrity and admissibility of DNA evidence in court.
- Research and Technological Advancements: Encourage research and development in the field of DNA analysis to further enhance the reliability and accuracy of techniques. Explore emerging technologies, methodologies, and advancements in forensic genetics that can improve the analysis of DNA evidence.
- Expert Testimony: Enhance the understanding of DNA analysis among legal professionals, judges, and juries. Training programs and workshops can help educate stakeholders about the principles, limitations, and significance of DNA evidence. This will facilitate better comprehension and assessment of DNA reports during legal proceedings.
- Collaboration and Peer Review: Foster collaboration among forensic laboratories, DNA experts, and legal professionals to promote knowledge sharing and peer review. This will help maintain high standards of DNA analysis and ensure continuous improvement in the field.
Conclusion
- Despite recent concerns, DNA analysis continues to be a valuable tool in criminal cases. By addressing the raised issues through standardized guidelines, quality control, and improved understanding, the admissibility and reliability of DNA reports can be enhanced, contributing to a fair administration of justice.
Also Read:
| What is DNA Fingerprinting? |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Scientists help find new kind of Molecular Motor
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Molecular Motor
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea: Researchers from the National Centre for Biological Sciences have discovered a new kind of molecular motor that has potential applications in biology and medicine.
What is a molecular motor?
- Cells use molecular motors to move things like organelles and molecules, and disruption of these processes can lead to diseases.
- Molecular motors use biochemical energy to do mechanical work.
What did the new study find?
- The study found that EEA1, a long protein, can regain its rigid shape to create a new kind of two-part molecular motor.
- EEA1 regains its rigid shape through a reaction called GTP hydrolysis, mediated by enzymes called GTPases.
- The researchers believe this could mark a new class of molecular machines that operate as motors in a unique way with novel collective effects.
Why is the finding significant?
- The motor is different from most motors because it doesn’t produce a lever-like back-and-forth action and it uses GTP instead of ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate) for energy.
- EEA1 exerts an entropic force on the membranes that it pulls, which is a unique feature.
- The finding could have potential applications for understanding membrane fusion and for many other mechanochemical proteins or assemblies.
What are the potential applications?
- The discovery of the molecular motor could have potential applications in biology and medicine.
- The study provides a general mechanism that is applicable to many mechanochemical proteins or assemblies that harness chemical energy for mechanical work in cells.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Microbes found near Mt. Everest
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Microbes
Mains level: NA
Central idea
- Researchers conducted a genetic analysis of microbial communities on the South Col of Sagarmatha (Mount Everest).
- The article examines the human microbiota on the inhospitable slopes of Mount Everest esp. the South Col ridge.
Microbial Communities on the South Col
- Microbial communities were collected from sediment samples left by human climbers on the South Col, 7,900 meters above sea level (msl).
- The South Col is inhospitable due to low oxygen, strong winds, high levels of UV radiation, and temperatures below minus 15 degrees Celsius.
- Visible signs of life are absent above 6,700 msl except for a few species of moss and a jumping spider.
- Microbes are carried to high altitudes by birds, animals, winds, and dust particles.
Microbes found
- Using sophisticated methods such as 16S and 18S rRNA sequencing, the microbe hunters were able to identify the bacteria and other microorganisms found on the South Col.
- 16s rRNA is a component of the 30S subunit in prokaryotic ribosomes while 18s rRNA is a component of the 40S subunit in eukaryotic ribosomes.
- 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequencing is an amplicon sequencing technique used to identify and compare species of bacteria present within a given sample.
- 16S rRNA gene sequencing is used to study phylogeny and taxonomy of samples from complex microbiomes or environments that are difficult or impossible to study.
- Microbes like Modestobacter altitudinis and the fungus, naganishia, which are known to be UV-resistant survivors are found there.
History of Mount Everest and Naming
- Nepal’s eminent historian, late Baburam Acharya, gave the Nepali name Sagarmatha to Mount Everest in the 1960s.
- Andrew Waugh, British Surveyor General of India, discovered Mount Everest in 1847 and named it after his predecessor, Sir George Everest.
- Radhanath Sikdar, an Indian mathematician and surveyor, was the first person to show that Mount Everest was the world’s highest peak in 1852, with the help of a special device.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Novel compound to treat Kala-Azar Infection
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kala Azar
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: The Kolkata-based Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) have established the potential of quinoline derivatives to treat drug-resistant leishmaniasis, which is also called kala-azar or black fever.
What is Kala Azar?
- Kala-Azar is a vector-borne (sandfly) neglected tropical disease caused by the protozoan parasites of the genus leishmania.
- It afflicts the world’s poorest populations in over 90 countries throughout Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Central and South America.
- Current annual estimates of kala-azar are about 1,00,000.
- More than 95% of cases reported to the WHO are from India and other tropical countries, most importantly co-infection with HIV, which leads to an immunocompromised state.
How does Quinoline work over this?
- The quinoline derivative is a potent inhibitor of an enzyme called topoisomerase 1 (LdTop1).
- This enzyme is essential for the maintenance of DNA architecture in parasites and is distinct from the one found in humans.
- Poisoning LdTop1 imparts significant cytotoxicity to both Leishmania parasites found in the gut of sandfly vectors (promastigotes) and those found in infected humans (amastigotes) of both the wild type and the antimony-resistant isolates.
- This is done without inducing lethality to human and mice host cells.
Significance of quinoline treatment
- Overcoming drug resistance in clinical leishmaniasis is a severe challenge in rural India.
- The current treatment regimens against kala-azar use formulations that are toxic and induce high levels of drug-resistance.
What is the breakthrough?
- The novel inhibitor targeting the leishmania parasites was identified by screening them against recombinant Leishmania topoisomerase 1 enzyme.
- In all, 21 derivatives were prepared and evaluated for their antileishmanial activity, and one of them was found to be effective.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Scientists devise ‘Glowscope’ to bring fluorescent microscopy to schools
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fluorescence Microscopy
Mains level: NA

Central idea: Researchers at Winona State University, Minnesota, have created a design for a rudimentary fluorescence microscope.
Why in news?
- The development can be put together at a cost of $30-50 (Rs 2,500-4,100) using products purchased on online marketplaces.
- The device aims to democratize access to fluorescence microscopy.
What is Fluorescence Microscopy?
- An optical microscope views an object by studying how it absorbs, reflects or scatters visible light.
- A fluorescence microscope views an object by studying how it reemits light that it has absorbed, i.e. how it fluoresces.
- The object is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength.
- Particles in the object absorb this light and reemit it at a higher wavelength.
- These particles are called fluorophores; the object is infused with them before being placed under the microscope.
How does it work?
- The setup consists of two plexiglass surfaces, an LED flashlight, three theatre stage-lighting filters, a clip-on macro lens, and a smartphone.
- The smartphone (with the lens attached) is placed on one surface that is suspended at a height (say, a foot above).
- The second sheet is placed below and holds the object.
- One of the stage-lighting filters is held between the flashlight and the object and the other two were held between the object and the smartphone.
- The sources of illumination were also LED flashlights emitting light of correspondingly different wavelengths.
Key observations
- With this setup, the researchers were able to image the creatures’ brain, spinal cord, heart, and head and jaw bones.
- They were able to zoom in and out using the smartphone camera and the clip-on lens.
How accessible is this?
- Using a ‘glowscope’ still requires access to fluorophores, suitable biological samples, the know-how to combine the two, and some knowledge of physics to work out which LED flashlight to buy.
- The Foldscope was truly remarkable because all its required components were simple to understand.
- However, the fact that a simple fluorescent microscope can be set up with a few thousand rupees means researchers can prepare samples and take them to schools, where students can observe them.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What are ‘Bio-Computers’ and what can they tell us about the human brain?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bio-Computers
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: Johns Hopkins University scientists have proposed creation of Bio-Computers’ using a new area of research called “organoid intelligence”.
Background
- JHU scientists will harness the processing power of the brain and help understand the biological basis of human cognition, learning, and neurological disorders.
- Traditional methods of studying the human brain involve using rat brains, which are structurally and functionally different from human brains.
Building brain organoids in the lab
- Scientists are building 3D cultures of brain tissue in the lab, called brain organoids, using human stem cells.
- Brain organoids capture many structural and functional features of a developing human brain and are being used to study human brain development and test drugs.
- However, brain organoids developed in the lab lack sensory inputs and blood circulation, which limits their growth and sophistication.
Transplanting brain organoids
- Scientists have transplanted human brain organoid cultures into rat brains, where they formed connections with the rat brain and were functionally active.
- However, human brain organoids are still nested in the rat-brain microenvironment, which limits their relevance to humans.
What is the new “bio-computer”?
- The JHU researchers’ scheme combines brain organoids with modern computing methods to create “bio-computers”.
- Brain organoids will be grown inside flexible structures affixed with multiple electrodes to record the firing patterns of neurons and deliver electrical stimuli.
- Machine-learning techniques will be used to analyze the response patterns of neurons and their effect on human behavior or biology.
Opportunities for “bio-computers”
- Brain organoids can be developed using stem cells from individuals with neurodegenerative diseases or cognitive disorders to reveal the biological basis of human cognition, learning, and memory.
- “Bio-computers” could help decode the pathology of and develop drugs for neurodevelopmental and degenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and microcephaly.
Challenges for bio-computers
- Brain organoids have a diameter of less than 1 mm and have fewer than 100,000 cells on average, limiting their computing capacity.
- Researchers will have to develop microfluidic systems to transport oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products.
- The hybrid systems will generate large amounts of data that will need to be stored and analyzed using “Big Data” infrastructure and advanced analytical techniques.
- An ethics team is proposed to identify, discuss, and analyze ethical issues as they arise in the course of this work.
Conclusion
- Biocomputers will harness the processing power of the brain and help understand the biological basis of human cognition, learning, and various neurological disorders.
- Scaling up brain organoids and developing microfluidic systems and analytical techniques are the key challenges.
- Ethical issues arising from the development of biocomputers will be analyzed by an ethics team.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Foldscope: A new paper microscope
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Foldscope
Mains level: NA

Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, have developed a cheap paper microscope (foldscope) connected to a smartphone camera that could find wider application in a variety of research areas, and in some cases potentially replace more expensive equipment.
What is Foldscope?
- The Foldscope is a handheld microscope made mostly of paper that can be easily linked to a smartphone camera.
- It has a magnification of around 140x and can identify objects just 2 micrometres wide.
- It was first created by researchers at Stanford University in 2014.
- IISc version of Foldscope costs around Rs 400, much cheaper than that of Stanford’s one.
How is Foldscope comparable to electron microscope?
- The researchers found that Foldscope could capture the roundness and aspect ratio of an object to within 5% of those imaged by a state-of-the-art instrument called a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
- SEM costs more than Rs 50 lakh each.
- Preparing a sample for study through a Foldscope takes less than an hour, whereas the same process for an SEM was “tedious and time-consuming”.
Potential applications
- Foldscopes can be used in pharmaceuticals (to inspect drug products), environmental science (to observe pollutants), and cosmetics (to observe powders and emulsions), among other fields.
- They can also be used to study “soil particles’ morphology,” which can “help understand soil structure, nutrient availability, and plant growth” in agriculture.
- It allows for in-field soil analysis and visualisation of soil structure per Indian Standard Soil Classification System which earlier required bulky microscopes with high resolution.
Are you an IAS Worthy Aspirant? Get a reality check with the All India Smash UPSC Scholarship Test
Get upto 100% Scholarship | 900 Registration till now | Only 100 Slots Left
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Proton Beam Therapy out of reach for many
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Proton Beam Therapy
Mains level: Not Much

There is currently a demand-supply gap of proton beam therapy machines in India, leaving many cancer patients in a difficult situation.
What is Proton Beam Therapy?
- Proton beam therapy is a type of radiation therapy — a treatment that uses high-energy beams to treat tumors.
- Radiation therapy using X-rays has long been used to treat cancers and noncancerous (benign) tumors.
- It uses protons rather than x-rays to treat cancer. At high energy, protons can destroy cancer cells.
- It can also be combined with x-ray radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, and/or immunotherapy.
- Like x-ray radiation, proton therapy is a type of external-beam radiation therapy.
How it works?

- Fundamentally, all tissue cells are made up of molecules with atoms as their building blocks.
- In the center of every atom is the nucleus. Orbiting the nucleus of the atom are negatively charged electrons.
- When energized protons pass near orbiting electrons, the positive charge of the protons attracts the negatively charged electrons, pulling them out of their orbits. This is called ionization.
- It changes the characteristics of the atom and consequentially the character of the molecule within which the atom resides.
- Because of ionization, the radiation damages molecules within the cells, especially the DNA.
- Damaging the DNA destroys specific cell functions, particularly the ability to divide or proliferate.
- While both normal and cancerous cells go through this repair process, a cancer cell’s ability to repair molecular injury is frequently inferior.
- As a result, cancer cells sustain more permanent damage and subsequent cell death than occurs in the normal cell population.
Why in news?
- There is currently a significant demand-supply gap of proton beam therapy machines in India, with only a few machines available in the country.
- This has resulted in long wait times for patients who need the treatment, and many patients are forced to travel abroad to access the treatment, which can be prohibitively expensive.
Various challenges
- Huge demand: The demand for PBT machines is also increasing, as more and more patients are being diagnosed with cancer and are seeking the latest and most effective treatments available.
- High cost: One of the major challenges in setting up PBT machines is the high cost involved, as the machines are complex and require a significant investment.
- Shortage of personnel: In addition, there is a shortage of trained personnel who can operate and maintain the machines, which further limits their availability.
Way Forward
- The government and private sector need to invest more in setting up and maintaining the machines. This could include-
- Offering tax incentives and subsidies to private healthcare providers who invest in PBT machines
- Providing training and education to personnel who can operate and maintain the machines
- Setting up more public hospitals that offer proton beam therapy, which would help to make the treatment more accessible and affordable to patients who need it
Attempt UPSC 2024 Smash Scholarship Test | FLAT* 100% OFF on UPSC Foundation & Mentorship programs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CCR5-delta 32 Gene Transplant: Permanent cure of HIV
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CCR5-delta 32 mutation
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: This article discusses recent developments in the field of HIV research that have led to the possibility of a cure for the disease.
What is HIV/AIDS?
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.
- First identified in 1981, HIV is the cause of one of humanity’s deadliest and most persistent epidemics.
- It is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with HIV, most commonly during unprotected sex, or through sharing injection drug equipment.
- If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
- The human body can’t get rid of HIV and no effective HIV cure exists.
Present treatment of HIV
- However, by taking HIV medicine (called antiretroviral therapy or ART), people with HIV can live long and healthy lives and prevent transmitting HIV to their sexual partners.
- In addition, there are effective methods to prevent getting HIV through sex or drug use, including pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP).
What is the new breakthrough?
- Doctors selected a donor carrying two copies of a CCR5-delta 32 genetic mutation – a mutation that is known to make the carriers almost immune to HIV.
- The CCR5-delta 32 genetic mutation is a rare genetic mutation that affects the CCR5 gene, which is involved in the immune system’s response to infection.
- The mutation causes a deletion of 32 nucleotides in the gene, resulting in a truncated or shortened version of the CCR5 protein.
- This truncated protein is not able to function normally, and people with this mutation are largely resistant to HIV infection.
How has the CCR5-delta 32 mutation been used in HIV research?
- Researchers have been studying the CCR5-delta 32 mutation as a potential avenue for developing an HIV cure.
- One approach involves using gene editing technologies like CRISPR to induce the mutation in HIV-positive individuals, effectively making their immune cells resistant to HIV infection.
- Another approach involves bone marrow transplantation from donors with the CCR5-delta 32 mutation.
What are the risks associated?
- Gene editing technologies like CRISPR are still in their early stages, and there are concerns about the safety and effectiveness of these methods.
- Additionally, bone marrow transplantation is a complex and risky procedure that is not feasible for all HIV-positive individuals.
- Finally, it is important to note that not all HIV infections are caused by the CCR5 strain of the virus, and therefore the use of the CCR5-delta 32 mutation as an HIV cure would not be effective for all cases of HIV.
Prevalence of HIV/AIDS in India
- As per the India HIV Estimation 2019 report, the estimated adult (15 to 49 years) HIV prevalence trend has been declining in India since the epidemic’s peak in the year 2000 and has been stabilizing in recent years.
- In 2019, HIV prevalence among adult males (15–49 years) was estimated at 0.24% and among adult females at 0.20% of the population.
- There were 23.48 lakh Indians living with HIV in 2019.
- Maharashtra had the maximum at 3.96 lakh followed by Andhra Pradesh (3.14 lakh) and Karnataka.
- ART is freely available to all those who require and there are deputed centres across the country where they can be availed from.
Attempt UPSC 2024 Smash Scholarship Test | FLAT* 100% OFF on UPSC Foundation & Mentorship programs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
AI to improve maternal and child health in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Use of AI for health
Context
- With the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other digital technologies, there is potential for these tools to support maternal and neonatal healthcare in low-resource settings, although their development in this field is still in its early stages. AI has the capability of transforming maternal and child health in low and middle-income countries by supplementing conventional practices with advanced technology, thus improving the accuracy of diagnoses, increasing access to care, and ultimately saving lives.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) target
- The SDGs have set a target to eliminate preventable deaths of newborns and children under five years of age by 2030, with a specific aim to lower neonatal mortality (NMR) to a minimum of 12 deaths per 1,000 live births and under-five mortality (U5MR) to a minimum of 25 deaths per 1,000 live births across all nations.
Challenges and the current state of maternal and child health in India
- One of the main challenges is the high maternal and infant mortality rates: According to the latest SRS Bulletin, India’s maternal mortality rate (MMR) was 97 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018-2020, and the infant mortality rate (IMR) was 35.2 deaths per 1,000 live births in 2019-21.
- Rates are higher than the SDG targets: According to the latest National Family Health Survey (NFHS) data, the NMR and U5MR in India are 24.9 and 41.9 respectively. These rates are higher than the SDG targets and are a cause for concern.
- Lack of access to healthcare for many women and children in India: Many rural and remote areas lack basic healthcare facilities, and even when facilities are available, they may not be staffed with qualified healthcare providers. Additionally, cultural and societal barriers can prevent women and children from accessing healthcare.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition is a major contributor to high maternal, neonatal, and infant mortality rates in India, with about 68 percent of child deaths being linked to malnutrition.
- Low birth weight: In low- and middle-income countries like India, low birth weight is a leading cause of death in the first month of life. Prematurity and low birth weight account for 45.5 percent of deaths during the first 29 days of a newborn in India. Presently, around 18.2 percent of children reported having low birth weight.
Some positive developments in maternal and child health in India in recent years
- Programs and policies aimed at reducing maternal and infant mortality: The government has implemented several programs and policies aimed at reducing maternal and infant mortality, such as the Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) and the Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA) which provides cash incentives for pregnant women to deliver in health facilities and free health check-up respectively.
- Efforts to increase access and quality health facilities: There have also been efforts to increase the number of healthcare facilities in rural and remote areas and to improve the quality of care provided at these facilities.
- Using technology in Healthcare: In addition, India has also been working on using technology to improve maternal and child health.
- For example: Telemedicine has been implemented in remote areas, and the government has also launched an application, RCH ANMOL, for tracking pregnant women, infants and children for their health, vaccination, and nutrition status. Other digital initiatives include the Draft Health Data Management Policy, Health Data Retention Policy, Unified Health Interface, and Health Facility Registry.
Potential applications of AI
- Predictive modelling of risk factors: By analysing large amounts of medical data, AI algorithms can identify risk factors for maternal and fetal complications and predict the likelihood of certain outcomes. This can help healthcare providers to identify high-risk pregnancies early on and take steps to mitigate the risks.
- Predicting birth weights for effective nutrition programme: Malnutrition is responsible for lowering newborn immunity to infections and diseases. Predicting birth weight for newborns can aid doctors and parents to adopt putative measures such as effective utilisation of Nutrition Rehabilitation Centres (NRCs) pre-emptively.
- AI can make a big impact is in the detection of fetal abnormalities: In LMICs, access to ultrasound technology is often limited, and the quality of images may be poor. By using AI to analyse ultrasound images, healthcare providers can improve the accuracy of diagnoses and detect abnormalities that may otherwise be missed.
- AI can also be used to improve access to care: Virtual care technologies, such as AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, can provide expectant mothers in LMICs with information and support. It has been demonstrated that sending personalised, timed voice messages about pregnancy via mobile phone can positively impact maternal healthcare practices and improve maternal health outcomes.
- Manage and analyse large amounts of medical records: By identifying trends and patterns in this data, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions and improve outcomes for mothers and children.
Challenges to using AI to improve maternal and child health in India
- One of the biggest challenges is data availability and quality: AI relies on large amounts of data to train models, however, in India, there is a lack of data on maternal and child health, and the data that is available may be of poor quality. This can make it difficult to develop accurate and reliable AI-based solutions.
- Limited infrastructure: In many parts of India, there is a lack of basic infrastructure such as electricity and internet connectivity, which makes it difficult to implement AI-based solutions. This can be a particular problem in rural areas where access to healthcare is already limited.
- Ethical concerns: AI-based solutions raise a number of ethical concerns, including issues around privacy, bias, and accountability. It is important to address these concerns to ensure that AI-based solutions are used in a responsible and ethical manner.
- Language and dialects: India has a wide variety of languages and dialects, which can make it difficult to develop AI-based solutions that are accessible to everyone. The lack of data in certain languages or dialects can make it difficult to develop accurate and reliable AI-based solutions that are tailored to the specific needs of different linguistic communities.
- Socio-Economic status: As people living in poverty may not have access to the technology and services provided by AI-based solutions.
Conclusion
- AI has the capability of bringing about a substantial difference in maternal and child health in India. Nevertheless, it is crucial to keep in mind that these innovative technologies should not be utilised as a substitute for conventional healthcare practices, but rather as an additional tool. The integration of AI with the already existing healthcare systems would bring about the best results. It is also essential to involve healthcare providers and local communities in the development and implementation process of AI-based solutions. This way, the solutions can be made more relevant, accessible, and in line with the local context, thereby, maximising their positive impact.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CAR T-Cell Therapy for treatment of Cancer
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAR T-Cell Cancer Therapy
Mains level: Not Much

The new CAR T-Cell Immunotherapy holds promise for Ovarian Cancer patients over other forms of treatment.
What are CAR T-cells?
- Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies represent a quantum leap in the sophistication of cancer treatment.
- Unlike chemotherapy or immunotherapy, which require mass-produced injectable or oral medication, CAR T-cell therapies use a patient’s own cells.
- They are modified in the laboratory to activate T-cells, a component of immune cells, to attack tumours.
- These modified cells are then infused back into the patient’s bloodstream after conditioning them to multiply more effectively.
- The cells are even more specific than targeted agents and directly activate the patient’s immune system against cancer, making the treatment more clinically effective.
- This is why they’re called ‘living drugs’.
How does the therapy work?
- In CAR T-cell therapy, the patient’s blood is drawn to harvest T-cells which are immune cells that play a major role in destroying tumour cells.
- Researchers modify these cells in the laboratory so that they express specific proteins on their surface, known as chimeric antigen receptors (CAR).
- They have an affinity for proteins on the surface of tumour cells.
- This modification in the cellular structure allows CAR T-cells to effectively bind to the tumour and destroy it.
- The final step in the tumour’s destruction involves its clearance by the patient’s immune system.
Where is it used?
- As of today, CAR T-cell therapy has been approved for leukaemias (cancers arising from the cells that produce white blood cells) and lymphomas (arising from the lymphatic system).
- These cancers occur through the unregulated reproduction of a single clone of cells, that is, following the cancerous transformation of a single type of cell, it produces millions of identical copies.
- As a result, the target for CAR T-cells is consistent and reliable.
- CAR T-cell therapy is also used among patients with cancers that have returned after an initial successful treatment or which haven’t responded to previous combinations of chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
- Its response rate is variable. In certain kinds of leukaemias and lymphomas, the efficacy is as high as 90%, whereas in other types of cancers it is significantly lower.
How widespread is its use?
- The complexity of preparing CAR T-cells has been a major barrier to their use.
- The first clinical trial showing they were effective was published almost a decade ago; the first indigenously developed therapy in India was successfully performed only in 2022.
- The technical and human resources required to administer this therapy are also considerable.
- Treatments in the US cost more than a million dollars.
- Trials are underway in India, with companies looking to indigenously manufacture CAR T-cells at a fraction of the cost.
- The preliminary results have been encouraging.
What are conventional cancer therapies?
- The three major forms of treatment for any cancer are surgery (removing the cancer), radiotherapy (delivering ionising radiation to the tumour), and systemic therapy (chemotherapy- administering medicines that act on the tumour only).
- Surgery and radiotherapy have been refined significantly over time whereas advances in systemic therapy have been unparalleled.
- A new development on this front, currently holding the attention of many researchers worldwide, is the CAR T-cell therapy.
Will this therapy be expensive in India as well?
- In India, introducing any new therapy faces the twin challenges of cost and value.
- Critics argue that developing facilities in India may be redundant and/or inappropriate as even when it becomes cheaper, CAR T-cell therapy will be unaffordable to most Indians.
- Those who are affluent and require the therapy currently receive it abroad anyway.
- While this is true, it may be the right answer to the wrong question.
- Having access to a global standard of care is every patient’s right; how it can be made more affordable can be the next step.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Why banyan, peepal trees live longer?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Multiple Signs of Adaptive-evolution (MSA)
Mains level: NA

Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Bhopal have found out the carried out whole genome sequencing of banyan and peepal from leaf tissue samples.
Science behind long life: Multiple Signs of Adaptive-evolution (MSA)
- Scientists identified 25,016 coding gene sequences in banyan and 23,929 in peepal.
- Both trees faced a population bottleneck around 0.8 million years ago and evolved genes with multiple signs of adaptive evolution (MSA).
- In banyan, the MSA genes are mainly involved in root growth, pollen tube and seed development, leaf formation, cell wall synthesis, metabolism and other developmental processes.
How MSA prolongs the life?
- Disease resistance and other stress tolerance gene families showed expansion as well as high expression, contributing to the plants’ long lifespan.
- The MSA genes of peepal are associated with root cell elongation, cell proliferation, seed and pollen tube growth, lateral organ development, controlling flowering time, metabolism and intracellular transport.
- The team zeroed in on 17 MSA genes in banyan and 19 MSA genes in peepal that are mainly related to well-developed morphology, and tolerance against drought, oxidative stress and pathogens.
- Genes involved in growth-regulating auxin signalling and plant senescence-regulating pathways also showed evolutionary signatures.
- Also, 88% and 89% of the MSA genes in banyan and peepal trees, respectively, are associated with tolerance against biotic and abiotic stress responses.
- This, in turn, helps these plants to survive when faced with environmental challenges.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How can mRNA vaccines help fight cancer?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: mRNA Vaccine
Mains level: Not Much

The results of a trial of an experimental cancer vaccine built on the mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) platform, made by Moderna and MSD (Merck&Co.), have shown promising results.
What is mRNA?

- Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single-stranded RNA (Ribo Nucleic Acid) molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene.
- The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made.
- During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, and uses the genetic code to translate each three-base triplet, or codon, into its corresponding amino acid.
What are mRNA vaccines?
- mRNA vaccines work by introducing a piece of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein, usually a small piece of a protein found on the virus’s outer membrane.
- Individuals who get an mRNA vaccine are not exposed to the virus, nor can they become infected with the virus by the vaccine.
- As part of a normal immune response, the immune system recognizes that the protein is foreign and produces specialized proteins called antibodies.
- Antibodies help protect the body against infection by recognizing individual viruses or other pathogens, attaching to them, and marking the pathogens for destruction.
- Once produced, antibodies remain in the body, even after the body has rid itself of the pathogen, so that the immune system can quickly respond if exposed again.
How does the vaccine work?
- The personalized cancer vaccine uses the same messenger-RNA technology that was used to produce the COVID vaccine.
- It allows the body’s immune system to seek and destroy cancerous cells, in this case melanoma, but with the hope that it could lead to new ways to fight other types of cancers too.
Why is it a significant feat?
- The cancer vaccine showed a 44% reduction in the risk of dying of cancer or having the cancer progress.
- As a personalized cancer vaccine, it is tailor-made for every patient.
- As a consequence, it is expected to be very expensive to make.
- But oncologists across the world have welcomed this as an exciting new opportunity in cancer care.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DNA Fingerprinting
Mains level: Advanced criminology

Delhi Police has established identity of a victim of brutal murder and mutilation by DNA fingerprinting.
What is DNA fingerprinting?
- DNA fingerprinting was first developed in 1984 by Alec Jeffreys in the UK, after Jeffreys discovered that no two people could have the same DNA sequence.
- Within three years of the discovery, the UK achieved the world’s first conviction based on DNA evidence in a case of rape and murder.
How is DNA fingerprinting done?
- Each person’s DNA, except for identical twins, is unique.
- By analyzing selected DNA sequences (called loci), a crime laboratory can develop a profile to be used in identifying a suspect.
- DNA can be extracted from many sources, such as hair, bone, teeth, saliva, and blood.
- Because there is DNA in most cells in the human body, even a minuscule amount of bodily fluid or tissue can yield useful information.
- Samples may even be extracted from used clothes, linen, combs, or other frequently used items.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
|
How it is used in criminal investigation?
- DNA evidence is used to solve crimes in two ways:
- If a suspect is known, that person’s DNA sample can be compared to biological evidence found at a crime scene to establish whether the suspect was at the crime scene or whether they committed the crime.
- If a suspect is not known, biological evidence from the crime scene can be analyzed and compared to offender profiles in existing DNA databases to assist in identifying a suspect.
- Beyond its accuracy, DNA fingerprinting can also sift through crime scene evidence in different ways, previously unavailable to investigators.
- For instance, advanced DNA fingerprinting can make separate prints of various individuals even from a sample mixture found at the crime scene — this is of help during gang rape investigations as each perpetrator can be individually identified.
DNA fingerprinting in India
- By 1988, Lalji Singh, who had been in the UK from 1974 to 1987 on a Commonwealth Fellowship, developed DNA fingerprinting for crime investigations in Hyderabad.
- Today, Lalji Singh, who passed away in 2017, is known as “the father of DNA fingerprinting in India.”
- In 1989, DNA fingerprinting was first used in a case by the Kerala Police.
- By the early 1990s, the technology had begun to be used for establishing paternity, and to link criminals and identify victims in sensational crimes.
- From the 2000s onwards, the technology became a staple in rape cases where vaginal swab samples were matched with semen samples from suspects.
Challenges with DNA fingerprinting in India
- It is vital to ensure that the DNA of the investigators does not get mixed with that of the victims or the suspects.
- Thus, picking up samples from a crime scene with sterile tools and storing samples in a proper manner are crucial for the evidence to stand a judicial test.
- While India has rules and guidelines regarding this, India’s police forces have a lot of catching up to do with counterparts overseas.
- While central agencies such as CBI have the expertise to ensure that crime scenes are protected and correct procedure is followed, state police forces are inadequately trained or fully equipped.
Issues with such technology
- The problem is not limited to the police awareness.
- The capacity for DNA fingerprinting in the country itself is lacking.
- DNA fingerprinting is available only at a few places — Maharashtra, West Bengal, Delhi, Hyderabad and Chandigarh.
- Advanced practices in the technology are limited to the Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics (CDFD) in Hyderabad.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Base Editing?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Base Editing
Mains level: Not Much
A teenage cancer patient suffering from T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL) has defeated her seemingly incurable cancer with the help of base editing technique.
Base Editing
- Bases are the language of life. The four types of base – adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T) – are the building blocks of our genetic code.
- Just as letters in the alphabet spell out words that carry meaning, the billions of bases in our DNA spell out the instruction manual for our body.
- Base editing allows scientists to zoom to a precise part of the genetic code and then alter the molecular structure of just one base, converting it into another and changing the genetic instructions.
- The large team of doctors and scientists used this tool to engineer a new type of T-cell that was capable of hunting down and killing cancerous T-cells.

What is T-Cell?
- T (thymus) cells are type of white blood cell.
- They are part of the immune system and develop from stem cells in the bone marrow.
- They help protect the body from infection and may help fight cancer.
- Also called T lymphocyte and thymocyte.
How base editing helped this teenage cancer patient?
- Doctors started with healthy T-cells that came from a donor and set about modifying them.
- The first base edit disabled the T-cells targeting mechanism so they would not assault patient’s body.
- The second removed a chemical marking, called CD7, which is on all T-cells.
- The third edit was an invisibility cloak that prevented the cells being killed by a chemotherapy drug.
- The final stage of genetic modification instructed the T-cells to go hunting for anything with the CD7 marking on it so that it would destroy every T-cell in patient’s body – including the cancerous ones.
- That’s why this marking has to be removed from the therapy – otherwise it would just destroy itself.
- If the therapy works, the patient’s immune system – including T-cells – will be rebuilt with the second bone-marrow transplant.
Click and get your FREE Copy of CURRENT AFFAIRS Micro Notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Gold-Mushroom Nanoparticle to ease Drug Delivery
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gold Nanoparticle
Mains level: Not Much
Cordy gold nanoparticles (Cor-AuNPs), the outcome of a collaborative experiment by scientists from four Indian institutions, has earned an international patent from Germany.
What is Cordy gold nanoparticles ?
- Cordy gold nanoparticles (Cor-AuNPs) are derived from the synthesis of the extracts of Cordyceps militaris and gold salts.
- They could make drug delivery in the human body faster and surer.
- Cordyceps militaris is a high-value parasitic fungus, lab-grown at the Department of Biotechnology’s Technology Incubation Centre (TIC) in Bodoland University.
- Gold salts are ionic chemical compounds of gold generally used in medicine.
Benefits offered by this nanoparticle
- Penetration in the cells is more when the drug particles are smaller.
- Cordyceps militaris adds bioactive components to the synthesis of gold nanoparticles for better penetration.
- It can be delivered as ointments, tablets, capsules, and in other forms.
Back2Basics: Gold Nanoparticles for Medicines
- Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are small gold particles with a diameter of 1 to 100 nm which, once dispersed in water, are also known as colloidal gold.
- Functionalized gold nanoparticles with controlled geometrical and optical properties are the subject of intensive studies and biomedical applications.
- They find applications in genomics, biosensorics, immunoassays, clinical chemistry, laser phototherapy of cancer cells and tumors, the targeted delivery of drugs etc.
Click and get your FREE copy of Current Affairs micro notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
GI in news: Kalanamak Rice
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kalanamak Rice
Mains level: NA

Kalanamak, a traditional variety of paddy is all set to get a new look and name.
Kalanamak Rice
- Kalanamak rice is a paddy with black husk and strong fragrance, which is considered a gift from Lord Buddha to the people of Sravasti when he visited the region after enlightenment,
- It is grown in 11 districts of the Terai region of northeastern Uttar Pradesh and in Nepal.
- The traditional Kalanamak rice is protected under the Geographical Indication (GI) tag
- It’s recorded in the GI application that Lord Budhha gifted Kalanamak paddy to the people of Sravasti so that they remembered him by its fragrance.
What is the upgrade?
- The traditional paddy has been prone to ‘lodging’, a reason for its low yield.
- Lodging is a condition in which the top of the plant becomes heavy because of grain formation, the stem becomes weak, and the plant falls on the ground.
- Addressing the problem, the Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI) has successfully developed two dwarf varieties of Kalanamak rice.
- They have been named Pusa Narendra Kalanamak 1638 and Pusa Narendra Kalanamak 1652.
Back2Basics: Geographical Indication
- A GI is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin.
- Nodal Agency: Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- India, as a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO), enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 w.e.f. September 2003.
- GIs have been defined under Article 22 (1) of the WTO Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement.
- GI is granted for a term of 10 years in India. As of today, more than 300 GI tags has been allocated so far in India (*Wikipedia).
- The tag stands valid for 10 years.
Click and Get your FREE copy of Current Affairs Micro notes
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
An Indian Pioneer of ORT
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ORT Everyday application
Mains level: ORT, Diseases treated by ORT, Cholera outbreak
Context
- In the demise of Dilip Mahalabnis on October 16 we lost a pioneering public health physician the ORS pioneer who helped save millions of lives. In 1978, a Lancet editorial termed ORS the most important medical advance in this century.
Background
- ORT was first introduced worldwide in the 1970s to treat millions of children suffering from severe dehydration in crisis-stricken and impoverished areas. At the time, the world’s leading general medical journal The Lancet called ORT “potentially the most important medical advance since penicillin.”
- A Lancet editorial in 1978 termed it “potentially the most important medical advance this century”.
Interesting story of Dilip Mahalabnis and invention of ORT
- Mahalanabis was trained as a paediatrician and joined the Cholera Research Programme of the Johns Hopkins University Center for Medical Research and Training (JHCMRT) in Calcutta in 1966.
- His team was treating cases of the cholera epidemic in a camp in Bangaon, West Bengal that housed 3,50,000 refugees but ran out of intravenous fluids. He thought that it would be opportune to use ORS. As no ORS packets were available, they mixed salt and sugar solution (ORS) in drums and administered it to the cholera patients in the camps.
- The library of the JHCMRT was converted into a factory. This was not a mandated mode of treatment and at great personal risk, Mahalanabis chose to respond to the humanitarian crisis in this manner.
- It was evident in two to three weeks’ time that not only was the therapy working but that it was possible to administer ORT through volunteers (in the absence of a sufficient number of trained workers).
- It was subsequently analyzed that ORS reduced mortality due to cholera or acute diarrhoeal diseases in these camps from 40 per cent to 5 per cent. They coined the term “oral saline” and rest is the story.
What is Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT)?
- A fluid to correct dehydration: Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORT) entails drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium to correct dehydration due to fluid losses from diarrhoea.
- ORT ingredients: ORT combines three ingredients such as salts, sugars and water to quickly reverse the signs of dehydration. Through the process of osmosis, the salts and sugars pull water into your bloodstream and speed up rehydration.
- Essential electrolytes which replenish Blood: ORT also replenishes your blood with essential electrolytes (minerals) that are lost due to intense exercise, exposure to extreme weather conditions, or diarrhea and other illnesses. Water doesn’t contain electrolytes and so, ironically, water alone cannot cure dehydration like ORT.
- An effective electrolyte: Administration of fluids through the intravenous route used to be the mainstay of management of cholera till the results of a study demonstrated that an oral solution of glucose and electrolytes was effective for replacing water and electrolyte losses.
- Quick and efficient: The translation of the basic science concept to quick and efficient practice was, however, not easy. And that is the fascinating story and sterling contribution of Mahalanabis and his co-workers on ORT.
What is Dehydration?
- Dehydration occurs when you use or lose more fluid than you take in, and your body doesn’t have enough water and other fluids to carry out its normal functions. If you don’t replace lost fluids, you will get dehydrated.
What is Disease Cholera?
- Cholera is an acute diarrhoeal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae that can kill within hours if left untreated.
- Most of those infected will have no or mild symptoms and can be successfully treated with oral rehydration solution. Cholera affects both children and adults.
- Provision of safe water and sanitation is critical to prevent and control the transmission of cholera and other waterborne diseases.
- Cholera remains a global threat to public health and an indicator of inequity and lack of social development.
Recent outbreak of cholera In India
- Cholera is said to be endemic in India. However, the reported cases in India tend to be much lesser than the actual numbers, say doctors and experts.
- The number of cases is rising in India because we still lack the basic sanitation, hygiene and access to clean water in many communities,
- The country reports nearly 20,000 to 30,000 cases of cholera every year, usually during the monsoon season of July to September.
- Climate change adds up another layer to the cholera outbreak.
Contribution of ORT to the world.
- As a perfect alternative over the prevailing doctrine: ORT was in marked contrast to the then prevailing doctrine of patients being given only sips of water without food, euphemistically called “resting the stomach”, often worsening the underlying malnutrition.
- For Diarrhoea: An estimated 54 million diarrhoeal deaths were averted by ORT alone between 1978 and 2008, such was the magnitude of its beneficial impacts. ORT for the management of severe diarrhea was developed in the latter half 1960s. WHO launched a worldwide campaign in 1978 to reduce mortality related to diarrhea, with ORT as one of the key elements.
- For cholera: Administration of fluids through the intravenous route used to be the mainstay of management of cholera till the results of a study demonstrated that an oral solution of glucose and electrolytes was effective for replacing water and electrolyte losses
- Cholera pandemic: This period coincided with the seventh cholera pandemic (El Tor biotype) that started in Indonesia in 1961 and spread to East Pakistan (Bangladesh) by 1963 and to India in 1964. Though experiments with ORS were underway, the WHO responded in 1970 by distributing large amounts of intravenous fluids – a move marked by high transportation costs and limited utilization on account of a shortage of a trained health workforce. The focus of the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO), through the Cholera Research Laboratory in Dhaka, was to find a vaccine to protect the US troops from cholera attacks in Southeast Asia.
- One solution for everyone: Athletes; people with illnesses, especially babies and toddlers; seniors; military personnel stationed in extreme climates; air travelers who lose electrolytes every time they fly: They all stand to dramatically improve their health and well-being with ORT.
Conclusion
- Dilip Mahalanabis pioneered a simple and effective solution for diarrhoea that saves millions of lives which can be considered as one of the greatest contributions of Indian in medical sciences. To carry the carry legacy forward young scientists should step in.
Mains Question
Q. What do you Understand by Oral Rehydration Therapy? How it could be effective in tackling the yearly outbreaks of Cholera in India and the world. Discuss.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is RNA Origami?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: RNA Origami
Mains level: Not Much

This newscard is an excerpt of the original article published in The Hindu.
Note: It appears to be too much biological. And suddenly out of our ease of understanding.
What is Ribo Nucleic Acid (RNA)?
- RNA is an important biological macromolecule that is present in all biological cells.
- It is principally involved in the synthesis of proteins, carrying the messenger instructions from DNA, which itself contains the genetic instructions required for the development and maintenance of life.
- In some viruses, RNA, rather than DNA, carries genetic information.
- The type of RNA dictates the function that this molecule will have within the cell.
- Aside from the coding region of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules that will be translated into proteins, other cellular RNA elements are involved in different processes.
What are RNA Origami?
- RNA origami is the nanoscale folding of RNA, enabling the RNA to create particular shapes to organize these molecules.
- It is an attempt to generate complex human-made RNA-based devices.
- They are stable in cells, interact with other biomolecules, including other RNA and proteins, and enable unique applications, particularly in the context of gene regulation.
Why are they used?
So far there have been two approaches in RNA origami and both attempt to regulate the production of protein.
(1) To achieve precise control of protein production
- Self-inhibiting protein expression cassettes were made by installing a strong binding site for the expressed protein in its own gene.
- Afterwards, RNA origami decorated with the same protein-binding sites was expressed in large excess.
- In this way, the RNA origami serves as a protein-sponge that sequesters proteins in the cell and allows expression of the self-inhibited protein.
- This approach helped to regulate several proteins simultaneously and turn on enzymatic pathways for improved product yields.
(2) Using for gene editing
- The RNA origamis were integrated in the small RNAs that guide CRISPR-Cas9 enzyme to target specific sequences in the DNA genome.
- Its scaffolds were decorated with protein-binding sites capable of recruiting transcription factors.
- By targeting the RNA scaffolds to promoter regions, the transcription factors activated gene expression.
- Researchers have shown that the expression strength can be tuned by the orienting the scaffold and level of transcription factors recruited.
- These multi-enzyme pathways could be controlled for high-yield production of the anti-cancer drug violacein.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Dr. Mahalanabis: the man behind ORS no more
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ORS, Dr. Mahalanabis
Mains level: NA

While Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) as a simple, effective remedy for dehydration is known around the world, the physician who pioneered the treatment, Dr. Dilip Mahalanabis, passed away.
What is ORS?
- Oral rehydration therapy is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea.
- It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium.
- Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube.
About Dr. Mahalanabis
- Born on November 12, 1934 in West Bengal, Dr Mahalanabis studied in Kolkata and London.
- He joined the Johns Hopkins University International Centre for Medical Research and Training in Kolkata in the 1960s, where he carried out research in oral rehydration therapy.
- When the 1971 war broke out, millions of people from then East Pakistan took refuge in India.
- Clean drinking water and sanitation were problems at these refugee camps, and cholera and diarrhoea broke out among people anyway exhausted and dehydrated.
- Dr Mahalanabis and his team were working in one such camp at Bongaon.
- Stocks of intravenous fluids were running out, on top of which there weren’t enough trained personnel to administer the IV treatment.
How he discovered ORS?
- From his research, Dr Mahalanabis knew that a solution of sugar and salt, which would increase water absorption by the body, could save lives from Cholera.
- He and his team then prepared solutions of salt and glucose in water and began storing them in large drums, from where patients or their relatives could help themselves.
- The oral solution then consisted of 22 gm glucose (as commercial monohydrate), 3.5 gm sodium chloride (as table salt) and 2.5 gm sodium bicarbonate (as baking soda) per liter of water.
- This was the simplest formula, containing the minimum number of ingredients, previously found to be effective in severely ill patients with cholera.
His legacy
- While initially, the medical fraternity was septical, the WHO eventually adopted ORS as the standard method for treating cholera and other diarrhoeal diseases.
- Today, the WHO recommends a combination of sodium chloride, anhydrous glucose, potassium chloride and Trisodium citrate dihydrate as the ORS formula.
- In India, July 29 is observed as ORS Day.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
MeFSAT Database for Medicinal Fungi
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: MeFSAT
Mains level: Not Much

An analytical study of medicinal fungi using MeFSAT carried out by researchers from Chennai shows that some chemicals they secrete may find use as novel drugs.
What is MeFSAT?
- MeFSAT (Medicinal Fungi Secondary Metabolites and Therapeutics) is a database that compiles information on 184 medicinal fungi, including mushrooms.
- It is a manually curated database that compiles information on secondary metabolites and reported therapeutic uses of medicinal fungi from published research articles and specialized books on the subject.
Why in news?
- Chennai-based researchers analysed the structure of 1,830 secondary metabolites of medicinal fungi.
- Secondary metabolites are chemical compounds that fungi produce when they are stressed.
- They enhance the fungus’ ability to survive.
What are medicinal fungi?
- Medicinal fungi belongs to two taxonomic divisions namely, basidiomycota and ascomycota.
- Mushrooms belong to the basidiomycota division. An example is Agaricus bisporus, the button mushroom, which can be consumed.
- Fungi belonging to the ascomycota division are generally not mushrooms.
Examples of fungi-based medicines
- Cordycepin, a secondary metabolite produced by Cordyceps species of fungus, is known to have anti-tumor properties.
- Not only cordycepin, in general, but several secondary metabolites are also known to be beneficial for humans in terms of both therapy and health.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Private: Fruit Fly: Novel method to study Nuclear Matrix
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Nuclear Matrix
Mains level: NA

Now, using a novel method, Indian researchers have established a way of studying the nuclear matrix of the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) without removing the nucleus from the embryo.
Nuclear Matrix of fruit flies
- Every cell that makes up an organism contains a copy of its genome.
- This genome is packaged in special ways with the help of a structure known as the nuclear matrix.
- The nuclear matrix gives an organisation and architecture to the nucleus.
- A familiar figure, the nuclear matrix of fruit flies, for instance, has been studied for many years, mainly by isolating it in nuclei that have been taken out from fruit fly embryos.
- This allows comparative study of nuclear matrix in different cells within the embryo, giving a boost for fruit fly genetics.
- Two of the most recent papers on this work have been published in the journals Nucleus and Molecular and Cell Proteomics.
What exactly is Nuclear Matrix?
- The nuclear matrix is like a scaffolding.
- Using biochemical means, if the nucleus is taken out and treated with an enzyme that digests all the DNA.
- It is then washed with a solution of high salt concentration so that viable DNA proteins or protein-protein interactions are removed.
- What is then left is a fibrous meshwork of proteins called the nuclear matrix.
- This is like a building from which all movables have been sucked out, leaving only the beams, ceiling, and walls, plug points, etc.
- Analogous to the building, the nuclear matrix creates the architecture in which the genome is packaged.
Why study them?
- Studying the nuclear matrix is, therefore, very important to get a better picture of how precisely development progresses every time a new individual is born.
- We have 220 different types of cells in the body, but all contain identical genomes.
- The same genome sequence is present in neurons, where it works for thinking; in the liver, the same sequence enacts metabolism; and in the intestine, it works to digest.
- So, this information is packaged differently in different cell types.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Private: Species in news: Tasmanian Tiger
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tasmanian Tiger
Mains level: Not Much

Scientists in the US and Australia have embarked on a $15-million project to resurrect the thylacine or Tasmanian Tiger, a marsupial that went extinct in the 1930s, using gene-editing technology.
Tasmanian Tiger
- The Tasmanian tiger or thylacine (a dog-headed pouched dog) was an exclusively carnivorous marsupial that is considered to be extinct.
- It has a resemblance to a dog, with its distinguishing features being the dark stripes beginning at the rear of its body and extending into its tail, its stiff tail and abdominal pouch.
- The last known thylacine died in captivity over 80 years ago, in Tasmania’s Hobart Zoo in 1936.
- It may also be the only mammal to have become extinct in Tasmania since the European settlement.
Why did they become extinct?
- It was confined to Tasmania in recent times and disappeared from mainland Australia over 2000 years ago, mainly because of over-hunting by humans, diseases and competition from the Dingo (Canis lupus), a wild dog native to Australia.
- The Thylacine was also persecuted because it was believed to be a threat to sheep and in its latter years it was hunted for the purposes of collection by museums and zoos.
- As per some accounts, the introduction of sheep in 1824 led to a conflict between the settlers and thylacine.
Why in news?
- The ambitious project aims to reintroduce the animal to its native place Tasmania to revive the region’s lost ecological balance.
- Interestingly, this is not the first attempt to revive thylacines.
- In 1999, an Australian scientist, Dr Michael Archer, embarked on an unsuccessful journey to resurrect the animal using cloning technology from a perfectly preserved specimen in a museum.
The resurrection process
- Even though the last living thylacine died over 86 years ago, many embryos and young specimens of the species have been preserved.
- Scientists will be using a genome sequenced from a DNA extracted from a 108-year-old specimen held at Australia’s Victoria Museum.
- This genome will be compared with the closest living animal of the species– the fat tailed dunnart — to identify all the differences.
- Once all the differences are identified, scientists will engineer the living cell’s DNA where it is different, essentially engineering the extinct species back.
- The fat-tailed dunnart is a mouse-like species in the Dasyuridae family in Australia. With an average body length of 2.4–3.5 inches, they are one of the smallest carnivorous marsupials.
Criticisms of the move
- Researchers have raised concerns about the practicality of the technology.
- De-extinction is a fairytale science a/c to them and is more about media attention for the scientists and less about doing serious science.
Back2Basics: De-extinction technology
- De-extinction, or resurrection biology, is the method of creating a species that went extinct or is endangered, in order to revitalise ecological diversity and balance shattered due to reasons ranging from biodiversity loss to climate change.
- While cloning is the most widely used method of de-extinction, genome editing and selective breeding are also considered effective ways.
- The Pyrenean ibex, a subspecies of Spanish ibex, was one of the first extinct animals that have been resurrected using somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT).
- However, the baby Ibex died minutes after its birth from lung defect.
- One of the challenges of de-extinction is that reintroducing the species to its former habitat may make it an invasive species, which will also impact the balance of the current ecological system.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Edible coating to prolong shelf life of fruits and vegetables
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dunaliella tertiolecta
Mains level: Not Much

A team of researchers at the IIT — Guwahati has developed an edible coating using marine alga that coated on vegetables and fruits, substantially extends their shelf-life.
Dunaliella tertiolecta: The Edible coating
- The team used a mix of an extract of a marine microalga called Dunaliella tertiolecta and polysaccharides to produce it.
- The microalga is known for its antioxidant properties and has various bioactive compounds such as carotenoids and proteins.
- It is also used to produce algal oil, a non-animal source of omega-3 fatty acid and is considered a good source of biofuel.
- After the oil is extracted, the residue is usually discarded.
- The researchers used extracts from this residue in formulating their film, in combination with chitosan, which is a carbohydrate.
- It also has antimicrobial and antifungal properties and can be made into an edible film.
Benefits of this Edible coating
- The films displayed superior antioxidant activity, thermal stability, mechanical strength, total phenolic content and water vapour barrier property.
- They also had excellent UV-Vis light-blocking properties.
- The researchers also tested the biosafety of these coatings.
Why is it viable?
- The new coatings can be mass-produced.
- They are very stable to light, heat, and temperature up to 40C, edible, and can be safely eaten as part of the product formulation and do not add unfavourable properties to it.
- They retain texture, colour, appearance, flavour and nutritional value.
- The material can be either directly coated on the vegetables and fruits or made into a vegetable storage pouch.
- In both cases, the shelf-life of the vegetables can be extended.
- It is a simple dip coating technique with no significant cost added to the post-harvest processing.
Economic significance of Edible coating
- According to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, between 4.6 and 15.9 per cent of fruits and vegetables go waste post-harvest, partly due to poor storage conditions.
- In fact, post-harvest loss in certain produce items like potato, onion, and tomato could even be as high as 19%, which results in high prices for this highly consumed commodity.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Genome Sequencing?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Genome sequencing, APOBEC3 protein
Mains level: NA

Researchers from across the world have made available over 650 complete genome sequences of monkeypox isolates to date in public domain databases including GISAID and GenBank.
What is Genome Sequencing?
- Genome sequence is the unique code of genetic material of any organism, and determines the characteristic of any organism.
- Whole genome sequencing is the process of determining the complete DNA sequence of an organism’s genome at a single time.
- The gene composition of novel coronavirus, for instance, is different from that of the influenza virus. Every organism has a unique genome sequence.
- Laboratories in various countries have been isolating and sharing the genome sequences of the virus on an international platform.
Why are so many genome sequences being isolated?
- When viruses multiply, or reproduce, there is a copying mechanism that transfers the gene information to the next generation.
- However, no copying mechanism is perfect. When the virus multiplies, there will be small changes, which are called mutations.
- These mutations accumulate over time, and after prolonged periods, are responsible for evolution into new organisms.
- Within a single reproduction, the changes are extremely minor. More than 95 per cent of the gene structure remains the same.
How does it help scientists?
- However, the small changes that occur are crucial to understanding the nature and behaviour of the organism.
- In this case, for example, the small changes could provide scientists with information about the origin, transmission, and impact of the virus on the patient.
- It could also hold clues to the differing effects the virus could have on patients with different health parameters.
Accelerated evolution of Monkeypox
- The monkeypox virus has a DNA genome of around 2,00,000 base pairs, roughly six times larger than that of SARS-CoV-2.
- Like other viruses, the monkeypox virus evolves by the accumulation of genetic errors, or mutations, in its genome when it replicates inside a host.
- Being a DNA virus, the monkeypox virus like other poxviruses was believed to have a small rate of accumulating genetic changes compared to viruses with an RNA genome like SARS-CoV-2, which have a much larger rate of mutations.
- For poxviruses, this rate is estimated to be as low as a couple of genetic changes every year.
- A recent study, however, revealed that the observed rate of genetic changes in the virus was higher than expected — average of around 50 genetic changes.
Key findings
Ans. APOBEC3 protein
- The study also suggests that several mutations that have been identified in the new sequences of the monkeypox virus.
- This may have emerged due to interaction between the virus genome and an important family of proteins coded by the human genome known as the Apolipoprotein B Editing Complex (or APOBEC3).
- These proteins offer protection against certain viral infections by editing the genome sequence of the virus while it replicates in the cell.
- Some researchers suggest that many of the genetic mutations in the monkeypox genomes from the current outbreak are relics of the effect of APOBEC3.
Conclusion
- Genomic surveillance of pathogens provides interesting insights by following a molecular approach for contact tracing and understanding the transmission of the virus across the world.
- As cases of monkeypox continue to rise, it is therefore important to strengthen the genomic surveillance for the monkeypox virus.
- Since data from the present outbreak suggest a sustained human-to-human transmission, continuous genomic surveillance is important to understand the evolution and adaptation of the virus, apart from providing useful data to epidemiologists.
- With COVID-19 continuing unabated and monkeypox around the corner, the time has never been better, and the need never more acute, to build a sustainable system for genomic surveillance in India.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Dostarlimab: The New Wonder Cancer Drug
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dostarlimab
Mains level: NA
A trial on 18 colorectal cancer patients in the US found that cancer could be treated without chemotherapy or surgery. The world is sitting up and taking note of Dostarlimab, which has been called a wonder drug.
What is Dostarlimab?
- Dostarlimab is an experimental drug. It contains laboratory-produced molecules.
- It acts as substitute antibodies. It is sold under the brand name Jemperli.
- It was approved for medical use in the United States and the European Union in 2021.
- Its side-effects include vomiting, joint pain, itching, rash, fever etc.
What are the findings?
- The trial showed that immunotherapy alone – without any chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery that have been staples of cancer treatment.
- It could completely cure the patients with a particular kind of rectal cancer called ‘mismatch repair deficient’ cancer”.
- All 12 patients had completed the treatment and were followed for six to 25 months after.
- No cases of progression or recurrence had been reported during the follow-up.
- The response too was rapid, with symptoms resolving in 81% of the patients within nine weeks of starting the therapy.
Is Dostarlimab actually very effective?
- Dostarlimab is not a new drug but a combination of drugs that are already approved for use in immunotherapy.
- There is a possibility that Dostarlimab may improve the outcome and survival rate in rectal cancer patients but to say it as a magic drug for cancer is completely going overboard.
How does this drug cure?

- PD1 is a protein that regulates immune function and can sometimes keep T cells from killing cancer cells.
- The therapy in the trial used PD1 blockades, allowing T cells to kill cancer cells.
- ‘Mismatch repair deficient’ cancer is most common among colorectal, gastrointestinal, and endometrial cancers.
- Patients suffering from this condition lack the genes to correct typos in the DNA that occur naturally while cells make copies.
- Immunotherapy belongs to a category called PD1 blockades that are now recommended for the treatment of such cancers rather than chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Will Indian patients get access to the drug?
- At present, Indian doctors seem to be generally wary of prescribing Dostarlimab for their patients.
- Experts have termed as optimistic the findings of an ongoing trial—a group of rectal cancer patients showed no signs of a tumour after taking the drug for six months.
- None of the participants reported any severe side-effects either.
- Yet, doctors say they want to assess the duration of the response.
What do we know about the clinical trial?
- Cancer was treated in all the patients and could not be detected by physical examination, endoscopy, positron emission tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging.
- Thus, there is a thought that cancer can be treated without chemotherapy or surgery.
Is it too early to celebrate?
- Cancer specialists said initial signals show how precision medicine is building the future but they need to test more patients from different areas and other types of cancers.
- The combination of drugs was administered to a small number of patients and for a specific type of cancer.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
Mains level: Not Much
A team of scientists from Australia have found that babies at risk of the mysterious Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, or SIDS, generally have low levels of an enzyme called butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) in their blood.
What is SIDS?
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome refers to the sudden and unexpected death of an otherwise healthy infant under the age of one, generally while they are sleeping.
- Most SIDS-related deaths occur in infants between the age of 1-4 months.
- According to the NHS website, parents can reduce the risk of SIDS by not smoking while pregnant or after the baby is born and ensuring that the baby is placed on their back when they sleep.
- Some health experts have said that it is associated with issues in the part of an infant’s brain that controls breathing and waking up.
Prevalence of SIDS
- SIDS, also known as ‘cot death’, has claimed the lives of thousands of children across the West.
- US estimates that about 3,400 babies die suddenly and unexpectedly every year.
- Meanwhile, the United Kingdom reports about 200 such deaths annually.
What does the new study say?
- The study assessed whether there was something inherently different in babies that succumbed to SIDS.
- The researchers compared dried blood samples from 655 healthy babies, 26 babies who died due to SIDS and 41 babies who died of other causes.
- The team found that around nine of ten babies who died from SIDS had lower levels of BChE enzymes than the babies in the other two groups.
What is the BChE (Butyrylcholinesterase) enzyme responsible for?
- These enzymes are responsible for sending out signals that make a baby wake up, turn her head, or gasp for breath.
- It is part of the autonomic system, and controls function like blood pressure and breathing.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
RNA granules to treat neurodegenerative disorders
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: mRNA, RNA granules
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers at IISc Bangalore have identified a protein in yeast cells that dissolves RNA-protein complexes, also known as RNA granules.
What is mRNA?

- Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single-stranded RNA (Ribo Nucleic Acid) molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene.
- The mRNA is an RNA version of the gene that leaves the cell nucleus and moves to the cytoplasm where proteins are made.
- During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, and uses the genetic code to translate each three-base triplet, or codon, into its corresponding amino acid.
What are RNA granules?
- Inside the cytoplasm of any cell there are structures made of messenger RNA (mRNA) and proteins known as RNA granules.
- Unlike other structures in the cell (such as mitochondria), the RNA granules are not covered and confined by a membrane.
- This makes them highly dynamic in nature, thereby allowing them to constantly exchange components with the surrounding.
- RNA granules are present in the cytoplasm at low numbers under normal conditions but increase in number and size under stressful conditions including diseases.
Why are they unique?
- A defining feature which does not change from one organism to another (conserved) of the RNA granule protein components is the presence of stretches containing repeats of certain amino acids.
- Such stretches are referred to as low complexity regions.
- Repeats of arginine (R), glycine (G) and glycine (G) — known as RGG — are an example of low complexity sequence.
Functions of RNA granules
- Messenger RNAs are converted to proteins (building blocks of the cell) by the process of translation.
- RNA granules determine messenger RNA (mRNA) fate by deciding when and how much protein would be produced from mRNA.
- Protein synthesis is a multi-step and energy-expensive process.
- Therefore, a common strategy used by cells when it encounters unfavorable conditions is to shut down protein production and conserve energy to deal with a stressful situation.
- RNA granules help in the process of shutting down protein production.
- Some RNA granule types (such as Processing bodies or P-bodies) not only regulate protein production but also accomplish degradation and elimination of the mRNAs, which in turn helps in reducing protein production.
What is the recent study?
- Researchers concluded that low complexity sequences which normally promote granule formation, in this case promote the disintegration of RNA granules in yeast cells.
- They observed that the identified protein Sbp1 is specific for dissolving P-bodies and not stress granules which are related RNA granule type also present in the cytoplasm.
Significance of the study
- This study has highlighted the potential of amino acid repeats (RGG) as a therapeutic intervention.
- The study may help analyze the effect of repeat sequences in genetically engineered mice that accumulate insoluble pathological aggregates in brain cells.
- This could possibly help in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Microbots for Drug Delivery
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Microbots for drug delivery
Mains level: NA

An Indian researcher has found that it is possible to use light as a fuel to move microbots in real-body conditions with intelligent drug delivery that is selectively sensitive to cancer cells
Microswimmers for drug delivery
- Made from the two-dimensional compound poly (heptazine imide) carbon nitride (aka PHI carbon nitride), these microbots are nothing like the miniaturised humans.
- They range from 1-10 micrometre (a micrometre is one-millionth of a metre) in size, and can self-propel when energised by shining light.
- While carbon nitride is an excellent photo-catalyst, the two-dimensional PHI has a sponge-like structure full of pores and voids and charge storage properties.
- The researchers found that the ions in the salty solution passed through the pores of PHI carbon nitride.
- Thus, there was little or no resistance from the salt ions.
How do they swim across the blood?
- The PHI carbon nitride microparticles are photocatalytic.
- Like in a solar cell, the incident light is converted into electrons and holes.
- These charges drive reactions in the surrounding liquid. The charges react with the fluid surrounding them.
- This reaction, combined with the particle’s electric field, makes the microbots (micro-swimmers) swim.
- As long as there is light, electrons and holes are produced on the surface of the swimmers, which in turn react to form ions and an electric field around the swimmer.
- These ions move around the particle and cause fluid to flow around the particle.
- So this fluid flow causes the micro-swimmers to move.
How does the ion movement occur?
- The ions move from the bright surface of the micro-swimmer to the rear end.
- The diffusion of the swimming medium in one direction propels the micro-swimmer in the opposite direction.
- This is like a boat moving in the direction opposite to the oar strokes.
- The particles are nearly spherical, and the incident light illuminates one-half of the sphere, leaving the other dark.
- As photocatalysis is light-driven, it occurs only on the brightened hemisphere.
- As the ions move from the bright side to the dark side, micro-swimmers march in the direction of the light source.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
India’s first indigenous Bio-Sample Collection Kit: mWRAPR
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: mWRAPR
Mains level: NA
The Indian Institute of Science (IISc.) led start-up has launched mWRAPR, a biological transport and storage medium for genomic sequencing labs, biobanks, and research labs handling biological samples for molecular analysis.
mWRAPR
- It is India’s first indigenous bio-sample kit, a biological transport and storage medium.
- It would help in preserving genetic content in all types of biological samples, including microbiomes, saliva, cells, tissues, blood, body fluids, and fecal tubes.
- It is the only Molecular Transport Medium to be manufactured in India that competes with sample stabilisation and transporting media of notable foreign brands.
Significance
- The disruptions in global supply chain limits accessibility to materials for molecular diagnostics.
- India required to move to molecular tests (PCR/ RT-PCR test), but sample collection kits currently used were very cheap and not of molecular grade.
- RNA WRAPR is the kind of molecular grade sample collection medium that India needs right now.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Xeno-Transplantation and Related Issues
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Xenotransplantation
Mains level: Bio-ethics associated with Xenotransplantation
Recently, the University Of Maryland School Of Medicine announced that it had successfully transplanted a genetically-modified pig heart into a patient with severe ailments.
What is Xenotransplantation?

- Xenotransplantation, or transplanting organs across different species, was first tried in humans in the 1980s.
- The experiment was abandoned after the famous case of the American Baby Fae who was born with a congenital heart defect and received a baboon heart in 1984.
- However, pig heart valves have been used for replacing damaged valves in humans for over 50 years now.
- Nowadays, harvesting organs from genetically engineered pigs is seen as a viable alternative to meet organs shortage.
How the pigs are genetically engineered?
- The donor pig underwent 10 genetic modifications, by which the genes responsible for the rapid rejection of foreign organs by the human body were inactivated or knocked out.
- Four pig genes were removed, and six human genes were added.
- “GalSafe” pigs, or pigs that had undergone editing to knock out a gene that codes for Alpha-gal (a sugar molecule) were used.
- Alpha-gal can elicit a devastating immune response in humans.
- GalSafe pigs have been well studied, and are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in pharmacology.
Why pursue xenotransplantation?
- Modern scientific supporters of xenotransplantation argue that the potential benefits to society outweigh the risks, making pursuing xenotransplantation the moral choice.
- None of the major religions object to the use of genetically modified pig organs for life-saving transplantation.
A crucial case in India
- Harvesting organs from genetically engineered pigs is seen as a viable alternative to meet organs shortage.
- According to the health ministry, around 0.18 million people in India are estimated to suffer from renal failure every year, but only about 6,000 renal transplants are carried out in the country.
- About 25,000-30,000 liver transplants are needed annually in India but only about 1,500 are being performed.
- In the case of the heart, 50,000 people suffer from heart failure and are in need of a heart transplant.
- Yet, only 10-15 heart transplants are carried out in India each year.
Issues with Xenotransplantation
Besides scientific challenges, there are several ethical challenges to overcome:
- Animal rights: Many, including animal rights groups, strongly oppose killing animals to harvest their organs for human use.
- Decreased life expectancy: In the 1960s, many organs came from the chimpanzees, and were transferred into people that were deathly ill, and in turn, did not live much longer afterwards.
- Religious violations: Certain animals such as pork are strictly forbidden in Islam and many other religions.
- Informed consent: Autonomy and informed consent are important when considering the future uses of xenotransplantation.
- Threats of zoonosis: The safety of public health is a factor to be considered. We are already battling the biggest zoonotic disease threat.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Zebrafish study reveals how the brain makes its connections
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Synapses, Human Brain
Mains level: NA

Recent work by researchers at the National Centre of Biological Sciences, Bengaluru, has thrown light on what stimulates the synapses (connection of nerve cells) to form.
What are Synapses?

- Neurons, or nerve cells, in the brain connect by means of junctions known as synapses through which they transmit signals.
- There are two types of synapses – chemical and electrical:
(1) Chemical Synapse
- In this, there is a space of about 20 nanometres between two neurons, and the way they communicate is this: One neuron converts electrical signal into chemical signals.
- This chemical is released into the synaptic space and the receiving neuron converts the chemical signal back into an electrical signal.
(2) Electrical synapse
- In these synapses, the two neurons have a physical connection and the conversion of electrical to chemical need not occur, and they communicate directly.
- Electrical synapses are like a physical wire, communication is faster but they are also fewer in number.
Observing these synapses
- Researchers from TIFR-National Centre of Biological Sciences, Bengaluru, have chosen Zebrafish as a model organism to study this process.
- Zebrafish are transparent and neuron development in larval zebrafish can be observed from day to day by injecting a dye or by engineering the fish to express fluorescent proteins.
- It was observed that electrical synapses are formed before chemical synapses, they are like a blueprint in which neurons make a handshake. This results in the making of chemical synapses.
- Research on organisms such as leeches showed that if you remove electrical synapses, the chemical synapses do not form.
- However, the mechanism of how it happens in higher organisms such as vertebrates was not known.
What induces these synapses?
- The group observed that knocking out a particular protein known as the gap junction delta 2b (gjd2b) in the cerebellum of zebrafish affected levels of the enzyme CaMKII.
- Levels of CaMKII were seen to increase in the Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum.
- These neurons and the cerebellum itself control coordination of movements in the organism.
Why study this?
- In humans for example, excess abuse of alcohol leads to damage of these cells, which results in lack of coordination in movement.
- The cerebellum shows an evolutionary continuity in all vertebrates, so, too, the Purkinje neurons.
- Even though fish and humans diverged from a common ancestor about 500 million years ago, the cerebellum has been evolutionarily conserved.
- While zebrafish have about 300-400 Purkinje neurons, humans have thousands of these.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The functioning of INSACOG
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INSACOG
Mains level: Not Much
The Indian SARS-CoV-2 Consortium on Genomics (INSACOG) has sequenced about 1,00,000 samples.
What is INSACOG?
- INSACOG is a consortium of 10 labs and 18 satellite labs across India tasked with scanning COVID samples from patients and finding the variants that has led to spike in transmission.
- The institutes involved include the laboratories of the Department of Biotechnology, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Indian Council of Medical Research, and the Health Ministry.
- Its work began in January 2020, by sequencing all samples with a history of travel from the U.K. and a proportion of positive samples in the community.
Tasks of INSACOG
- The NCDC is tasked with coordinating collections of samples from the States as well as correlating disease with certain mutations.
- It is mainly involved in genomic sequencing which is done by isolating the genetic material of the coronavirus samples.
- It is also tasked with tracking certain combinations of mutations that become more widespread in India.
What has it found so far?
- The INSACOG sequenced about 1,00,000 samples as of early December 2021 when this data was last made publicly available.
- The bulk of its effort has been focussed on identifying international ‘variants of concern’ (VoC) that are marked out by the WHO as being particularly infectious or pathogenic.
- International travellers who arrive in India and test positive are the ones whose samples usually get sent to INSACOG for determining the genomic variant.
Why is genome sequencing useful?
- Understanding mutations: The purpose of genome sequencing is to understand the role of certain mutations in increasing the virus’s infectivity.
- Immune response: Some mutations have also been linked to immune escape, or the virus’s ability to evade antibodies, and this has consequences for vaccines.
- Effectiveness of vaccines: Labs across the world, including many in India, have been studying if the vaccines developed so far are effective against such mutant strains of the virus.
- Evolution of viruses: Studies such as this have shown that Omicron, for instance, has evolved to evade antibodies much better than the Alpha or Delta variant. This prompted the push towards booster doses.
How is it done?
- Genomic sequencing is done by isolating the genetic material (RNA) of the coronavirus samples.
- RNA consists of millions of nucleotide bases and genomic sequencing is about identifying and comparing the sequence in a given sample to a reference sample.
- Changes in the sequence are clues to mutations that show that the virus may have undergone distinct changes at some key locations.
- There are several approaches to genome sequencing — whole genome sequencing, next-generation sequencing — that have different advantages.
- It has now evolved to a stage where large sequencers can process even thousands of samples simultaneously.
Various challenges that INSACOG faces
- Geographical variations: Given that COVID-19 is spreading, mutating and showing geographical variations, the original aim of the group was to sequence at least 5% of COVID-19 samples.
- Shortage of funds: But only 1% has been achieved yet, primarily due to a shortage of funds, insufficient reagents and tools necessary to rapidly scale up.
- Red-tapism: The INSACOG, in spite of being peopled by expert scientists, is ultimately within the Central government’s communication structure.
- Infrastructure lacunae: Not all INSACOG labs have the same quality of equipment and manpower and therefore a surge or spike in some cities can mean difficulties in processing.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What are Chaperone Proteins?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chaperone Protein
Mains level: NA
Chaperones are a functionally related group of proteins assisting protein folding in the cell under physiological and stress conditions.
What are Chaperones?

- DNA is a linear chain of nucleotides, portions of which are faithfully transcribed into linear messenger RNA.
- The message in this RNA is translated into strings of amino acids – proteins.
- Proteins need to take a precise three-dimensional shape to become functional entities.
- This protein folding does not happen all by itself, at least most of the time.
- A special bunch of proteins called molecular chaperones assist in correctly folding the protein.
Functions of chaperone proteins
- In biological systems, Chaperones play crucial roles.
- Many molecular chaperones belong to the class of “heat shock” proteins (or stress-response proteins).
- This is because whenever an organism is subjected to elevated temperatures – a heat shock – proteins in the system begin to lose their native shapes, and chaperones are produced in large quantities to restore order.
General need of chaperones
Chaperones are needed under physiological conditions too, for normal cellular function since misfolding of proteins can cause a number of diseases.
- Alpha-synuclein protein, present in neurons, is wrongly folded in Parkinson’s disease.
- Brains of Alzheimer’s patients have plaques formed from aggregates of amyloid beta-peptide.
- This accumulation of amyloid fibrils is toxic, leading to widespread destruction of neurons – a ‘neurodegenerative’ disorder.
- Aberrant folding of crystallins of the eye lens leads to cataracts.
Types of Chaperones
- Major chaperones in humans include HSP70, HSC70 and HSP90: the numbers express the size of the proteins in kilodaltons.
- In normal cells 1%–2% of all proteins present are heat shock proteins.
- This number rises threefold during stressful conditions.
HSC70: The molecular thermometer
- HSC70 appears to be more like a molecular thermometer, with an ability to sense cold temperatures.
- It is induced by heat, whereas HSC70 is always present at high levels in normal cells.
- This knowledge comes from the study of an intriguing set of disorders, exemplified by Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS).
HSC70 and HSP90: Role in Cancer
- Cancer cells divide at a break-neck pace, and heat shock proteins are very important in maintaining the stressful cancerous state.
- An overabundance of heat shock proteins in cancer cells is an indicator of a poor prognosis. Cancerous cells accumulate mutations in proteins that would normally suppress tumours.
- HSP70 and HSP90 play the roles of villains, as they continue to fold the mutated proteins, thus allowing tumor progression.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Punjab farmers create Bio-Enzymes from Kinnow
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bio-Enzymes
Mains level: Not Much

Some farmers in Punjab, especially in the Kinnow belt, have started making Bio-Enzymes (BEs) from this waste fruit — peel and ‘D’ grade, very small kinnows.
What is a Kinnow?
- The ‘Kinnow’ is a high yield citrus fruit cultivated extensively in the wider Punjab region of India and Pakistan.
- It is a year-long duration crop and the main harvesting period is from November-end to March.
- It looks similar to orange but is smaller in size.
Agricultural significance of Kinnows
- Fallen fruit is a major challenge for kinnow farmers in the state as one needs to dig up small pits to bury them, otherwise the fallen fruit rot and invite a fly attack on the healthy fruit still on the plants.
- But now, some farmers are using this waste kinnow to improve the pH level and soil fertility of their land by making BEs from this waste fruit.
What are Bio-Enzymes?
- Chemically, the Bio Enzymes are a mixture of complex organic substances such as proteins, salts and other materials that are by-products of the bacteria/yeast.
- They produced through fermentation of organic waste including various fruits, vegetable peels and flowers, by mixing in sugar, jaggery/molasses and water.
- BE’s also have a lot of usage in our daily lives. They can be used as natural cleansers.
Benefits offered by BEs
- BEs have a lot of good microbes and one of the major methods which helps overall improvement of our ecology.
- It helps in mitigating the imbalance occurred due to overuse of chemicals, in our soil, air and water.
- In a state like Punjab where water table is depleting fast and water contamination is also major issue, BEs can bring the soil back to life.
- It helps in better water recharging and also stops the contamination of water by improving the health of soil.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Zeolite Oxygen Concentrators: Chemistry in 3-D
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zeolite
Mains level: NA

To meet the demand of oxygen supply in the country during the peak of pandemic, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) had chartered the Air India to import ‘Zeolite’ from different countries.
What are Zeolites?

- Zeolites are highly porous, 3-dimensional meshes of silica and alumina.
- In nature, they occur where volcanic outflows have met water.
- Synthetic zeolites have proven to be a big and low-cost boon.
Uses in Oxygen Concentrator
- One biomedical device that has entered our lexicon during the pandemic is the oxygen concentrator.
- This device has brought down the scale of oxygen purification from industrial-size plants to the volumes needed for a single person.
- At the heart of this technology are synthetic frameworks of silica and alumina with nanometer-sized pores that are rigid and inflexible.
- Beads of one such material, zeolite 13X, about a millimeter in diameter, are packed into two cylindrical columns in an oxygen concentrator.
How does it work?
- Zeolite performs the chemistry of separating oxygen from nitrogen in air.
- Being highly porous, zeolite beads have a surface area of about 500 square meters per gram.
- At high pressures in the column, nitrogen is in a tight embrace, chemically speaking, with the zeolite.
- Interaction between the negatively charged zeolite and the asymmetric nucleus (quadrupole moment) of nitrogen causes it to be preferentially adsorbed on the surface of the zeolite.
- Oxygen remains free, and is thus enriched.
- Once nitrogen is captured, what flows out from the column is 90%-plus oxygen.
- After this, lowering the pressure in the column releases the nitrogen, which is flushed out, and the cycle is repeated with fresh air.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Linear No-Threshold (LNT) Model for Radiation Safety
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LNT Model
Mains level: Not Much
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) decisively upheld the Linear No-Threshold (LNT) model to prescribe radiation safety standards, ending the protracted controversy on the topic.
What is the LNT Model?
- The LNT is a dose-response model used in radiation protection to estimate stochastic health effects such as radiation-induced cancer, genetic mutations etc. on the human body due to exposure to ionizing radiation.
- The LNT model states that biological effects such as cancer and hereditary effects due to exposure to ionising radiation increase as a linear function of dose, without threshold.
- It provides a sound regulatory basis for minimizing the risk of unnecessary radiation exposure to both members of the public and radiation workers.
Why in news?
- LNT model continues to provide a sound basis for a conservative radiation protection regulatory framework that protects both the public and occupational workers.
- The model helps the agencies to regulate radiation exposures to diverse categories of licensees, from commercial nuclear power plants to individual industrial radiographers and nuclear medical practices.
- There are also studies and findings that support the continued use of the LNT model, including those by national and international authoritative scientific advisory bodies.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Mosquirix: First malaria vaccine to get WHO nod
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Malaria and it vaccines
Mains level: Malaria menace in India
In a historic move, the World Health Organization (WHO) has endorsed the first anti-malarial vaccine, as mankind enters a key turning point in a battle waged relentlessly over decades between man and mosquito, the vector.
Mosquirix
- RTS,S/ASO1 (RTS.S), trade name Mosquirix acts against P. falciparum, the most deadly malaria parasite globally, and the most prevalent in Africa.
- The vaccine was able to prevent approximately 4 in 10 cases of malaria over a 4-year period in Africa.
- This is the first malaria vaccine that has completed the clinical development process.
- It is also the first malaria vaccine to be introduced by three national ministries of health through their childhood immunization programs — more than 800,000 children in Ghana, Kenya, and Malawi.
- have been vaccinated, and are benefiting from the added protection provided by the vaccine as part of a pilot program.
How the vaccine can help?
- WHO’s recommendation is based on the advice of its two global advisory bodies, one for immunization and the other for malaria.
- WHO has recommended that in the context of comprehensive malaria control, the RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine be used for the prevention of P. falciparum malaria in children living in regions with moderate to high transmission as defined by it.
- The malaria vaccine should be provided in a schedule of 4 doses in children from 5 months of age for the reduction of malaria disease and burden.
Back2Basics: Malaria
- Malaria is caused by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito if the mosquito itself is infected with a malarial parasite.
- There are five kinds of malarial parasites — Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax (the commonest ones), Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi.
- Therefore, to say that someone has contracted the Plasmodium ovale type of malaria means that the person has been infected by that particular parasite.
- Malaria is treated with prescription drugs to kill the parasite. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug.
Countries that have eliminated malaria
- Globally, the elimination net is widening, with more countries moving towards the goal of zero malaria.
- In 2019, 27 countries reported fewer than 100 indigenous cases of the disease, up from 6 countries in 2000.
- Countries that have achieved at least 3 consecutive years of zero indigenous cases of malaria are eligible to apply for the WHO certification of malaria elimination.
- 11 countries have been certified as malaria-free: United Arab Emirates (2007), Morocco (2010), Turkmenistan (2010), Armenia (2011), Sri Lanka (2016), Kyrgyzstan (2016), Paraguay (2018), Uzbekistan (2018), Algeria (2019), Argentina (2019), and El Salvador (2021).
Burden of Malaria in India
- In 2018, the National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) estimated that approximately 5 lakh people suffered from malaria.
- 63% of the cases were of Plasmodium falciparum.
- The recent World Malaria Report 2020 said cases in India dropped from about 20 million in 2000 to about 5.6 million in 2019.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Computer Tomography?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Computer Tomography (CT) and its working
Mains level: NA
The first computed tomography image – a CT scan – of the human brain was made 50 years ago, on Oct. 1, 1971.
A few months back, almost all of us have heard about the High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan being conducted on our relatives for diagnosing the damage of lungs caused due to the Wuhan Virus.
About Computer Tomography (CT)
- A CT scan is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to get detailed images of the body noninvasively for diagnostic purposes.
- The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using reconstruction algorithms to produce tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual “slices”) of a body.
How does it work?
- They use a narrow X-ray beam that circles around one part of your body. This provides a series of images from many different angles.
- A computer uses this information to create a cross-sectional picture. Like one piece in a loaf of bread, this two-dimensional (2D) scan shows a “slice” of the inside of your body.
- This process is repeated to produce a number of slices.
- The computer stacks these scans one on top of the other to create a detailed image of your organs, bones, or blood vessels.
- For example, a surgeon may use this type of scan to look at all sides of a tumor to prepare for an operation.
Its development
- Since its development in the 1970s, CT has proven to be a versatile imaging technique.
- While CT is most prominently used in diagnostic medicine, it also may be used to form images of non-living objects.
- The 1979 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded jointly to South African-American physicist Allan M. Cormack and British electrical engineer Godfrey N. Hounsfield “for the development of computer-assisted tomography”.
Threats
- CT scans use X-rays, which produce ionizing radiation.
- Such radiation may damage your DNA and lead to cancer.
- The risk increases with every CT scan we get.
- Ionizing radiation may be more harmful in children.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] What is Pollen Calendar?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pollen Calender
Mains level: NA
Chandigarh now has its first pollen calendar, which can identify potential allergy triggers and provide a clear understanding for clinicians as well as allergy sufferers about their causes to help limit their exposure during high pollen loads.
What is a Pollen Calendar?
- Pollen calendars represent the time dynamics of airborne pollen present in a particular geographical area.
- They yield readily accessible visual details about various airborne pollen present throughout the year in a single picture.
Is this a new concept in India? Where else in the west has this calendar been used?
- Though the concept is not essentially new, this is one of the major environmental concerns that had not been addressed for the Indian cities.
- Such calendars are location-specific, as pollen concentrations are closely related to locally distributed flora.
- Europe, UK and the US are using regional pollen calendars in a big way to prevent and diagnose allergic rhinitis/hay fever and predict the timing and severity of the pollen season.
Why is it important to study pollen?
- Pollen grains are male biological structures with the primary role of fertilization, but when inhaled by humans, they may strain the respiratory system and cause allergies.
- Pollen found suspended in air can cause widespread upper respiratory tract and naso-bronchial allergy with manifestations like asthma, seasonal rhinitis, and bronchial irritation.
- About 20-30 percent of the population suffers from allergic rhinitis/hay fever in India, and approximately 15 percent develop asthma.
- Pollen is considered a major outdoor airborne allergen responsible for allergic rhinitis, asthma, and atopic dermatitis in humans.
What were the key findings?
- The study highlights the variability of crucial pollen types in different seasons.
- Spring and autumn are two seasons when airborne pollen dominate.
- The findings will enhance the understanding of pollen seasons, which will in turn help minimize pollen allergies.
How will a pollen calendar benefit people, especially those who have respiratory issues?
- A pollen calendar provides a clear understanding for clinicians, as well as people with allergies to identify the potential allergy triggers and help to limit their exposure during high pollen load season.
- The early advisories can be prepared and disseminated through media channels to the citizens so that they can use protective gear during the period when the concentration of allergic pollen will be high.
Does the study infer that gardens and parks in the city contribute to the pollen and thus there must be proper scientific tree plantation?
- It is important to involve experts while designing parks.
- We should try to plant trees/shrubs that release no or little pollen.
- Trees such as palms, nettle, safeda, white mulberry (shahtoot), congress grass, pine, have a high incidence of pollen.
What kind of trees must be grown alongside our roads or in parks?
- Plant monoecious plants (male and female flowers on the same plant).
- Hibiscus, lilies, and holly that are grown widely in Chandigarh are examples of such plants.
- Cucumbers and squashes are also monoecious. Select plants with low to moderate pollen production.
- Non-allergic or entomophilous plant species should be chosen to provide an allergen-free atmosphere.
- Examples of such plants include rose, jasmine, salvia, Bougainvillea, Raat Rani, and sunflower.
With inputs from:
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Wood Wide Web?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Wood wide web
Mains level: Not Much

Plants appear to be simple enough in their organization. Whether small shrubs or tall trees, all they seem to be made up of is leaves, flowers, fruits, stems, and roots. But simple they are not. Being rooted in one spot has required very special personality traits.
Wood Wide Web
- Trees in the forest share resources by using an underground network.
- A scientist from the University of British Columbia, Dr. Suzanne Simard, revealed this network and called it the wood wide web.
- In the wood wide web, mycorrhizal fungi colonize the plant roots, and their tiny fungal filaments, or mycelia, connect hairy root tips of different trees together.
- Mycorrhizal fungi refer to the role they play in the plant’s root system—as symbionts.
- These root-associated fungi are harmless to plants. Instead, they form harmonious symbiotic relationships with plants.
An ancient association
- The association between plants and fungi is ancient.
- Fossils of plants from about 400 million years ago show the first evidence of roots, and these roots are fungus associations – rhizoids – suggesting that roots co-evolved with fungi.
- One good example is species of Penicillium, the fungus from which Alexander Fleming isolated the antibiotic penicillin.
- Fungus–root associations, called mycorrhizae, appear at first glance to be simple mutualisms that are beneficial to both.
- The root-invading fungus gains nutrients made by the plant, and the plants get difficult-to-find minerals like phosphorus from the microbe. But the association is deeper.
How does it work?
- The wood wide web works by offering a win-win situation for all parties: mycorrhizal fungi and trees.
- The fungal filaments transport nitrogen, phosphorous, water, and other hard-to-capture nutrients from the soil to the trees, in exchange for carbon-rich sugars made by the plants.
- The fungi also help deliver substances from one tree to its neighboring trees.
- By using the network, mature trees feed their seedlings with nutrients to boost their survival.
- When a plant is sick or dying, it can allocate its nutrients to the other plants nearby through the wood wide web.
Benefits offered
- Bacteria that associate with roots are called rhizobacteria, and a very wide range of these species are plant growth promoters.
- Like the fungi, mutualism operates in these relationships too. In exchange for sugars, these bacteria offer plants a wide range of benefits.
- They may help plants ward off pathogens that cause diseases of the root. They may even trigger systemic resistance to a pathogen throughout the plant.
Back2Basics: Symbiotic Relationship
Parasitism
- It is a type of interaction between two species that results in damage and harm to one member and benefit to another member.
- Ex. As in the case of the tick-host relationship, the tick gains benefit by sucking blood while the host is harmed as it loses blood.
Commensalism
- In this type of relationship one species benefits without affecting the other.
- Barnacles growing on the back of the whale, orchids growing as an epiphyte on some mango branch, cattle egret and grazing cattle in close association, Sea anemone, and the Clown Fish are some of the classic examples of Commensalism.
Amensalism
- In this relationship, one species is harmed while the other is neither harmed nor benefitted and remains unaffected.
- When an organism excretes the chemicals as a part of the normal metabolism of its own, but which may severely impact other nearby species, this kind of relationship is seen.
Mutualism
- In this type of relationship both the partners benefit from one another. When similar interaction occurs within a species, it is known as cooperation.
- Lichens a mutual relationship between algae and fungus. In this mutual cooperation, fungus gives protection and raw material for the preparation of the food while Green Algae synthesizes the food for both.
Saprophytism
- In this kind of biotic interaction, certain organisms live on dead and decaying organic matter.
- Dung Beetles, Vultures, Fungi, Bacteria, Protozoa are the example of Saprophytism.
Predation
- In this type of biological interaction, a predator feeds upon its prey and in this type of relationship, one species is benefitted while the other is harmed.
Competition
- In this type of interaction both the species compete with each other for the resources like food, shelter, mating, and both the species get harmed out of the process of competition.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Milky Sea Phenomenon?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Milky Sea Phenomenon
Mains level: NA

Some researchers would use satellites to study the elusive milky sea phenomenon.
What is the Milky Sea?
- Milky seas, also called mareel, is a luminous phenomenon in the ocean in which large areas of seawater appear to glow translucently (in varying shades of blue).
- Such occurrences glow brightly enough at night to be visible from satellites orbiting Earth.
- They are a rare nocturnal phenomenon in which the ocean’s surface emits a steady bright glow.
Why do they glow?
- Luminous bacteria cause the particles they colonize to glow.
- The purpose of this glow could be to attract fish that eat them.
- These bacteria thrive in the guts of fishes, so when their populations get too big for their main food supply, a fish’s stomach makes a great second option.
How do they occur?
- It is typically caused by Noctiluca scintillans (popularly known as “sea sparkle”), a dinoflagellate that glows when disturbed and is found in oceans throughout much of the world.
- Once their population gets large enough – about 100 million individual cells per millilitre of water – a sort of internal biological switch is flipped and they all start glowing steadily.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Absorption Spectroscopy?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Absorption Spectroscopy
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers from IIT Madras and IISER Kolkata have developed a method to detect minute quantities of chemicals in solution using Absorption Spectroscopy.
Note: These days there has been a rise in questions from biology (rather cell biology in particular).
Absorption Spectroscopy
- Absorption spectroscopy is a tool to detect the presence of elements in a medium.
- Light is shone on the sample, and after it passes through the sample is examined using a spectroscope.
- Dark lines are seen in the observed spectrum of the light passed through the substance, which correspond to the wavelengths of light absorbed by the intervening substance and are characteristic of the elements present in it.
- In usual methods, about a cubic centimeter of the sample is needed to do this experiment.
- In the method developed here, minute amounts of dissolved substances can be detected easily.
- Usually in absorption spectroscopy, the principle used is that light because of its wavelike nature, shows diffraction patterns, that is, dark and light fringes, when it scatters off any object.
Studying small objects
- A related concept called the Abbe criterion sets a natural limit on the size of the object being studied.
- According to this criterion, the size of the observed object has to be at least of the order of the wavelength of the light being shone on it.
- If one wants to perform absorption spectroscopy using visible light, namely, blue, green and red, the wavelengths [of these colours] are about 400 nm, 500 nm and 600 nm, respectively.
What has Indian researchers achieved?
- In the method used by the researchers here, tiny, nano-sized particles that can absorb light being shone on them and re-emit red, blue and green light were employed.
- The particles emit electric fields that are analogous to how a tiny magnet would give off magnetic lines of force – this is called a dipole, and the particle is like a tiny mobile phone’s antenna.
- This dipole generates an electromagnetic field depending upon the quantum properties of the erbium dopants in the glass.
- The absorption leaves a gap in the reflected light, which is what is observed and used to analyse the nature of the absorbing material.
Applications of this technology
- There are many potential applications.
- Small molecules almost ten-millionth of an mm in diameter can be detected while these pass the emission region of the glass particle.
- The future is to use it to measure individual molecules, see absorption spectroscopy of a single DNA or protein molecule.
Try this
Q.Which of the following statements are correct regarding the general difference between plant and animal cells?
- Plant cells have cellulose cell walls whilst animal cells do not.
- Plant cells do not have plasma membranes unlike animal cells which do.
- Mature plant cell has one large vacuole whilst an animal cell has many small vacuoles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer this PYQ here:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is the Human Genome Project?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Human Genome Project
Mains level: Genome Sequencing and its health applications
Since the release of the draft human genome sequence in 2001, sections were left unsequenced, and some sequence information was incorrect. Now, two decades later, we have a much more complete version.
What is the human genome sequence?

- The human genome sequence is contained in our DNA and is made up of long chains of “base pairs” that form our 23 chromosomes.
- Along our chromosomes are the base pair sequences that form our 30,000 genes.
- All humans share a great degree of similarity in their genome sequences – the same genes are ordered in the same manner across the same chromosomes.
- Each of us is unique (except for identical twins) in terms of the exact base pair sequence that makes up our genes and thus our DNA/chromosomes.
- It is this similarity that, in a genetic sense, defines us as “human” and the specific variation that defines us as individuals.
The Human Genome Project
- As early as the 1980s, momentum was gathering behind activities that supported, and would eventually define, the Human Genome Project.
- Conversations had turned into workshops that likened characterization of the human genome to characterization of the human anatomy that had centuries earlier revolutionized the practice of medicine.
- In 1990, with continued support from the US and widespread international collaboration and cooperation, the $3 billion dollar Human Genome Project was launched.
- The project aimed to determine the sequence of the human genome within 15 years.
- By 2000 (well ahead of schedule) a working draft of the human genome was announced.
- This was followed by regular updates and refinements and today we all have access to a human “reference genome sequence”.
Why did it take 20 years?
- Much of the newly sequenced material is the “heterochromatic” part of the genome.
- This is more “tightly packed” than the euchromatic genome and contains many highly repetitive sequences that are very challenging to read accurately.
- These regions were once thought not to contain any important genetic information but they are now known to contain genes that are involved in fundamentally important processes such as the formation of organs during embryonic development.
- Among the 200 million newly sequenced base pairs are an estimated 115 genes predicted to be involved in producing proteins.
Two key factors made the completion of the human genome possible:
- Choosing a very special cell type
- The new sequence was created using human cells derived from a very rare type of tissue called a complete hydatidiform mole, which occurs when a fertilized egg loses all the genetic material contributed to it by the mother.
- Most cells contain two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent and each parent’s chromosome contributing a different DNA sequence.
- A cell from a complete hydatidiform mole has two copies of the father’s chromosomes only, and the genetic sequence of each pair of chromosomes is identical.
- This makes the full genome sequence much easier to piece together.
- Advances in sequencing technology
- A new method called “shotgun sequencing”, involved breaking the genome into very small fragments of about 200 base pairs, cloning them inside bacteria, deciphering their sequences, and then piecing them back together like a giant jigsaw.
- This was the main reason the original draft covered only the euchromatic regions of the genome — only these regions could be reliably sequenced using this method.
- The latest sequence was deduced using two complementary new DNA-sequencing technologies.
Is the genome now completely sequenced?
- Well, no. An obvious omission is the Y chromosome, because the complete hydatidiform mole cells used to compile this sequence contained two identical copies of the X chromosome.
- However, this work is underway and the researchers anticipate their method can also accurately sequence the Y chromosome, despite it having highly repetitive sequences.
- Even though sequencing the (almost) complete genome of a human cell is an extremely impressive landmark, it is just one of several crucial steps towards fully understanding humans’ genetic diversity.
What’s next?
- The next job will be to study the genomes of diverse populations (the complete hydatidiform mole cells were European).
- Once the new technology has matured it will be better positioned to make a more significant impact on our understanding of human history, biology and health.
- Both care and technological development are needed to ensure this research is conducted with a full understanding of the diversity of the human genome to prevent health disparities.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
(b) Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
(c) A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
(d) Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How blind people can navigate better using Echolocation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Echolocation
Mains level: NA
A technique used by animals such as dolphins, whales, and bats to navigate their surroundings can also be used by blind people to get around better and have greater independence and well-being, researchers at Durham University in the UK have shown.
What is Echolocation?
- Echolocation, also called biosonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species.
- Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them.
- They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects.
What has the new study found?
- The same technique can help blind people locate still objects by producing clicking sounds from their mouth and hands.
- The researchers organized a 10-week training programme, in which 12 blind and 14 sighted volunteers aged between 21 and 79 were taught click-based echolocation.
- The volunteers were trained in distinguishing between the size of objects, orientation perception and virtual navigation.
- At the end of the training, the participants had been able to improve their ability to navigate using clicking noises either from one’s mouth, walking cane taps or footsteps.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] India’s First Indigenous Tumour Antigen SPAG9
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SPAG9
Mains level: NA
The National Institute of Immunology (NII) has received a trademark for India’s First Indigenous Tumor Antigen SPAG9.
About SPAG9
- India’s first indigenous tumor antigen SPAG9 was discovered by Dr Anil Suri in 1998 who is heading the Cancer Research Program at NII.
- In a recent development, the SPAG9 antigen has received the trademark ASPAGNII-TM.
- Currently, ASPAGNIITM is being used in dendritic cell (DC) based immunotherapy in cervical, ovarian cancer and will also be used in breast cancer.
What is immunotherapy?
- Immunotherapy is a new approach that exploits the body’s inner capability to put up a fight against cancer.
- With this approach, either the immune system is given a boost, or the T cells are “trained’’ to identify recalcitrant cancer cells and kill them.
- In this personalized intervention, those patients expressing SPAG9 protein can be treated with DC-based vaccine approach.
- In DC-based vaccine, patient’s cells called monocytes from their blood are collected and modified into what are called dendritic cells.
- These dendritic cells are primed with ASPAGNIITM and are injected back to the patient to help the ‘fighter’ cells, or T-cells, in the body to kill the cancer cells.
Why need such therapy?
- DC-based immunotherapy is safe, affordable and can promote antitumor immune responses and prolonged survival of cancer patients.
- The ASPAGNIITM is a true example of translational cancer research and the Atmanirbhar Bharat spirit.
- This will be a real morale boost in affordable, personalized, and indigenous products for cancer treatment.
Answer this PYQ in the comment box:
Q.‘RNA Interference (RNAi)’ technology has gained popularity in the last few years. why?
- It is used in developing gene silencing therapies
- It can be used in developing therapies for the treatment of cancer
- It can be used to developer hormone replacement therapies
- It can be used to produce crop plants that are resistant to viral pathogens
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
a) 1, 2 and 4
b) 2 and 3
c) 1 and 3
d) 1 and 4 only
The burden of cancer in India
- Cancer kills 8.51 lakh people in India every year (International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2020).
- As per World Health Organization (WHO), one in 10 Indians will develop cancer during their lifetime, and one in 15 will die of cancer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What are the Diatoms?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Diatoms
Mains level: Not Much
The Maharashtra Anti-Terrorism Squad has relied on a forensic test known as diatom tests for leads in an alleged murder case of a person inviting high stage political drama.
What are Diatoms?

- Diatoms are photosynthesizing algae that are found in almost every aquatic environment including fresh and marine waters, soils, in fact, almost anywhere moist.
- Diatoms have cell walls made of silica, each species has a distinct pattern of tiny holes in the cell wall (frustule) through which they absorb nutrients and get rid of waste.
- A diatom is a photosynthetic, single-celled organism which means they manufacture their own food in the same way plants do.
Diatoms are important as they:
- provide the basis of the food chain for both marine and freshwater micro-organisms and animal larvae
- are a major source of atmospheric oxygen responsible for 20-30% of all carbon fixation on the planet
- can act as environmental indicators of climate change
- form the basis of some household goods such as pest/mite prevention and mild abrasive
Never underestimate UPSC. Try this PYQ before you reach any conclusion.
Q.Which one of the following is the correct sequence of a food chain?
(a) Diatoms-Crustaceans-Herrings
(b) Crustaceans-Diatoms-Herrings
(c) Diatoms-Herrings-Crustaceans
(d) Crustaceans-Herrings-Diatoms
What is a diatom test?
- Diagnosis of death by drowning is deemed as a difficult task in forensic pathology.
- A number of tests have been developed to confirm the cause of such deaths with the diatom test emerging as one of the most important tests.
- The test entails findings if there are diatoms in the body being tested.
The science behind
- A body recovered from a water body does not necessarily imply that the death was due to drowning.
- If the person is alive when he enters the water, the diatoms will enter the lungs when the person inhales water while drowning.
- These diatoms then get carried to various parts of the body, including the brain, kidneys, lungs and bone marrow by blood circulation.
- If a person is dead when is thrown in the water, then there is no circulation and there is no transport of diatom cells to various organs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] What is Artificial Photosynthesis?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Artificial Photosynthesis
Mains level: Carbon sequestration through AP
Scientists have found a method to mimic nature’s own process of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, namely photosynthesis, to capture excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Artificial Photosynthesis
- Artificial photosynthesis (AP) is a chemical process that mimics the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen.
- The term artificial photosynthesis is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of fuel (a solar fuel).
- Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into hydrogen and oxygen and is a major research topic of artificial photosynthesis.
- Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another process studied that replicates natural carbon fixation.
Try this PYQ:
Which of the following adds/add carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on the planet Earth?
- Volcanic action
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- Decay of organic matter
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Challenges in AP
- Research on this topic includes the engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight.
- This AP harnesses solar energy and converts the captured carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide (CO), which can be used as a fuel for internal combustion engines.
- In AP, scientists are essentially conducting the same fundamental process in natural photosynthesis but with simpler nanostructures.
- However, there are plenty of hurdles to overcome as a successful catalyst to carry out AP.
What have Indian researchers achieved?
- Indian researchers have designed and fabricated an integrated catalytic system based on a metal-organic framework (MOF-808) comprising of a photosensitizer that can harness solar power and a catalytic centre that can eventually reduce CO2.
- A photosensitizer is a molecule that absorbs light and transfers the electron from the incident light into another nearby molecule.
- The scientists have immobilized a photosensitizer, which is a chemical called ruthenium bipyridyl complex ([Ru (bpy)2Cl2]) and a catalytic part which is another chemical called rhenium carbonyl complex ([Re(CO)5Cl]).
- They have fabricated it inside the nano space of a metal-organic framework for artificial photosynthesis.
Outcomes of the research
- The developed catalyst exhibited excellent visible-light-driven CO2 reduction to CO with more than 99% selectivity.
- The catalyst also oxidizes water to produce oxygen (O2).
- The Photocatalytic assembly, when assessed for CO2 reduction under direct sunlight in a water medium without any additives, showed superior performance of CO production.
- Being heterogeneous, the integrated catalytic assembly can be reused for several catalytic cycles without losing its activity.
Back2Basics: Photosynthesis
- It is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.
- It is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism’s metabolic activities.
- This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Genetics of Eye Color
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Human eye and the applied genetics
Mains level: NA

Researchers from London have found that eye colour in Asians with different shades of brown is genetically similar to eye colour in Europeans ranging from dark brown to light blue.
Human Eye Colour
- Human eye colour ranges from black, brown to blue, green, and even red.
- Eye colour is primarily determined by melanin abundance within the iris pigment epithelium, which is greater in brown than in blue eyes.
- There are two forms of melanin – eumelanin and pheomelanin – and the ratio of the two within the iris as well as light absorption and scattering by extracellular components are additional factors that give irises their colour.
- Absolute melanin quantity and the eumelanin–pheomelanin ratio is higher in brown irises, while blue or green irises have very little of both pigments and relatively more pheomelanin.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Recently, LASIK (Lasser Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) procedure is being made popular for vision correction. Which one of the following statements in this context is not correct?
(a) LASIK procedure is used to correct refractive errors of the eye
(b) It is a procedure that permanently changes the shapes of the cornea
(c) It reduces a person’s dependence on glasses or contact lenses
(d) It is a procedure that can be done on the person of any age
What has the research found?
- Previously a dozen genes (mainly HERC2 and OCA2) were found to influence eye colour.
- The researchers have now identified 50 new genes for eye colour.
- Genetic analysis of nearly 0.2 million people across Europe and Asia helped the researchers to identify the new genes.
- The findings collectively explain over 53% of eye colour variation using common single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
Outcome of the research
- Overall, the study outcomes demonstrate that the genetic complexity of human eye colour considerably exceeds previous knowledge and expectations.
- These findings will help improve our understanding of eye diseases such as pigmentary glaucoma and ocular albinism where pigment levels play a role.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Novel Open Reading Frames (NORF)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: nORF
Mains level: Not Much
A team from the University of Cambridge set out to find whether new genes emerge in the genome of living organisms and if they do, how they do so. They have now catalogued 1,94,000 novel regions.
Genes/Genomes/DNA/RNA is all-time favourite of UPSC. You can easily find 1-2 questions every year since 2017 in Prelims.
Novel genomic regions
- The ‘novel’ genomic regions cannot be defined by our current ‘definition’ of a gene.
- Hence, researchers call these novel regions – novel Open Reading Frames or as nORFs.
- Researchers found that the mutations in nORFs do have physiological consequences and a majority of mutations that are often annotated as benign have to be re-interpreted.
What novel did the researchers find?
- nORF regions were uniquely present in the cancer tissues and not present in the control tissue.
- They found that some nORF disruptions strongly correlated with the survival of patients.
- nORFs proteins can form structures, can undergo biochemical regulation like known proteins and be targeted by drugs in case they are disrupted in diseases.
- The researchers also identified these nORFs in Plasmodium falciparum, the parasite which causes the deadliest form of malaria.
Connected to disease
- The research found that these regions are also broadly involved in diseases.
- The nORFs were seen as dysregulated in 22 cancer types.
- Dysregulated is a term which means that they could either be mutated, upregulated, or downregulated, or they could be uniquely present.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Intentional Genomic Alteration?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Intentional Genomic Alteration
Mains level: Gene Editing

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a first-of-its-kind intentional genomic alteration (IGA) in a line of domestic pigs referred to as GalSafe pigs.
Try this PYQ:
Q.What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news?
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal sub
What is Intentional Genomic Alteration?
- Intentional genomic alteration in animals’ means making specific changes to the genome of the organism using modern molecular technologies.
- These are popularly referred to as “genome editing” or “genetic engineering”. However, there are other technologies that can be used to make IGAs in animals.
- Such changes in the DNA sequence of an animal may be carried out for research purposes, to produce healthier meat for human consumption and to study disease resistance in animals among other reasons.
- One example is of using IGAs to make an animal more susceptible to certain diseases such as cancer, which helps researchers get a better understanding of the disease and develop new therapies to treat it.
What does FDA’s recent approval mean?
- The FDA made the announcement this week and allowed IGA in GalSafe pigs to eliminate a type of sugar found in mammals called alpha-gal.
- This sugar is present on the surface of these pigs’ cells and when they are used for products such as medicines or food.
- The sugar is found in red meats such as beef, pork and lamb, the sugar makes some people with Alpha-gal Syndrome (AGS) more susceptible to developing mild to severe allergic reactions.
- IGA will help eventually free these products from detectable alpha-gal sugar, thereby protecting their human consumers from potential allergies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Hydroponics: the art of soil-less farming
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hydroponics
Mains level: Hydroponics and its utility

This newscard is an excerpt from the original article published in TH.
Many questions related to agricultural techniques are being asked in the Prelims. UPSC has done away with traditional crop-related questions for the past two years.
For example, see this question from CSP 2020:
Q.What are the advantages of fertigation in agriculture?
- Controlling the alkalinity of irrigation water is possible.
2. Efficient application of Rock Phosphate and all other phosphatic fertilizers is possible.
3. Increased availability of nutrients to plants is possible.
4. Reduction in the leaching of chemical nutrients is possible.Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only(b) 1,2 and 4 only
(c) 1,3 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
What is hydroponics?

Hydroponics is the cultivation of plants without using soil.
- Hydroponic flowers, herbs, and vegetables are planted in inert growing media and supplied with nutrient-rich solutions, oxygen, and water.
- This system fosters rapid growth, stronger yields, and superior quality.
- When a plant is grown in soil, its roots are perpetually searching for the necessary nutrition to support the plant.
- If a plant’s root system is exposed directly to water and nutrition, the plant does not have to exert any energy in sustaining itself.
- The energy the roots would have expended acquiring food and water can be redirected into the plant’s maturation. As a result, leaf growth flourishes as does the blooming of fruits and flowers.
Why Hydroponics?
- Plants sustain themselves by a process called photosynthesis. But they do not need soil to photosynthesize.
- They need the soil to supply them with water and nutrients.
- When nutrients are dissolved in water they can be applied directly to the plant’s root system by flooding, misting, or immersion.
- Hydroponic innovations have proven direct exposure to nutrient-filled water can be a more effective and versatile method of growth than traditional irrigation.
How does hydroponics work?
- Hydroponic systems work by allowing minute control over environmental conditions like temperature and pH balance and maximized exposure to nutrients and water.
- It administers nutrient solutions tailored to the needs of the particular plant being grown.
- They allow you to control exactly how much light the plants receive and for how long.
- pH levels can be monitored and adjusted. In a highly customized and controlled environment, plant growth accelerates.
Components of Hydroponics
To maintain a flourishing hydroponic system, we need to become acquainted with a few components that make it run efficiently.
(1) Growing media
- Hydroponic plants are often grown in inert media that support the plant’s weight and anchor its root structure.
- Growing media is the substitute for soil, however, it does not provide any independent nutrition to the plant.
- Instead, this porous media retains moisture and nutrients from the nutrient solution which it then delivers to the plant.
(2) Air stones and air pumps
- Plants that are submerged in water can quickly drown if the water is not sufficiently aerated. Air stones disperse tiny bubbles of dissolved oxygen throughout your nutrient solution reservoir.
- These bubbles also help evenly distribute the dissolved nutrients in the solution. Air stones do not generate oxygen on their own.
- They need to be attached to an external air pump via opaque food grade plastic tubing
(3) Net pots
- Net pots are mesh planters that hold hydroponic plants. The latticed material allows roots to grow out of the sides and bottom of the pot, giving greater exposure to oxygen and nutrients.
- Net pots also provide superior drainage compared to traditional clay or plastic pots.
Benefits
By controlling the environment of the plant in hydroponics, many risk factors are reduced:
- Plants grown in gardens and fields are introduced to a host of variables that negatively impact their health and growth. Fungus in the soil can spread diseases to plants.
- Wildlife like rabbits can plunder ripening vegetables from your garden.
- Pests like locusts can descend on crops and obliterate them in an afternoon. Hydroponic systems end the unpredictability of growing plants outdoors and in the earth.
- Without the mechanical resistance of the soil, seedlings can mature much faster.
- By eliminating pesticides, hydroponics produces much healthier and high-quality fruits and vegetables. Without obstacles, plants are free to grow vigorously and rapidly.
Various limitations
- A hydroponic system isn’t cheap
- Constant monitoring is required
- Micro-organisms that are water-based can creep in rather easily
- Growing a hydroponic garden demands an expertise
- Production is limited compared to field conditions
- If a disease appears, all plants in the system will be affected
- Without soil to serve as a buffer if the system fails plant death will occur rapidly
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How epigenetics alters inherited genetics’ message
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Epigenetics
Mains level: Genetics and human health

Researchers have found the cause of vision impairment due to ageing as the accumulation of “epigenetic noise” that disrupts gene expression patterns leading to changes in inherent DNA function
Genetics is an all-time favourite of UPSC. Every year you can find a question in prelims. Try this one from CSP 2020:
Q.Consider the following statements:
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human-induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
What is Epigenetics?
- Epigenetics is the study of how your behaviours and environment can cause changes that affect the way your genes work.
- Unlike genetic changes, epigenetic changes are reversible and do not change your DNA sequence, but they can change how your body reads a DNA sequence.
- Environmental stimuli can cause genes to be turned off or turned on.
- This determines a cell’s specialization (e.g., skin cell, blood cell, hair cell, liver cells, etc.) as a fetus develops into a baby through gene expression (active) or silencing (dormant); and nurture.
- This normal epigenetic control on our genes can get altered during normal ageing, stress and disease conditions.
Cellular regulators
- The functioning of cells and tissues in our body are controlled by thousands of proteins that regulate various cellular functions.
- These proteins are in turn encoded by the respective genes which are a part of our genome or the cellular DNA.
- Any minor or major changes to our inherited DNA (addition or mutation) can result in altered protein production, which in turn leads to defective cellular functions.
- This forms the basis for many heritable genetic disorders affecting mankind.
A trigger for various inactivities
- Apart from DNA or protein sequence level alterations, there are other biochemical changes that influence and dictate if a gene should be active or inactive in a given cell type.
- For example, the gene that encodes for the insulin protein is present in the exact form, in every cell of the body.
- However, it is allowed to express only in the insulin-secreting beta cells of the pancreas and is kept inactive in the rest of the cells of the body.
- This phenomenon is tightly regulated by a combination of regulatory proteins that changes the expressivity of the gene.
- Also, the histone proteins that bind the DNA and help to compactly wrap it inside the chromosomes can undergo chemical modifications such as methylations and acetylations on different lysine amino acids within the protein.
- These modifications both on the DNA and its associated proteins alter the chromosomal conformations and regulate gene expression.
- These changes can either unwind the DNA and allow gene expression or can compact the DNA and render the genes in the region inactive or silent.
Epigenetics and the human eye
- The human (and mammalian) eye is a remarkable organ in the course of evolution which has allowed us to “see” the external world clearly and in colour.
- Earlier forms, such as microbes and plants, reacted to light in other ways (for absorption and use, such as photosynthesis).
- The front part of the human eye (cornea, lens and the vitreous humour gel) is transparent, colourless and helps focus the incoming light into the retina, helping us see colour.
- It is the retina that sends the message to the brain.
- Its main component, called the retinal ganglion cells (RGC) are the ones that help in this process of sending the message in the form of electrical signals, called neurons or nerve cells.
- Thus, RGCs are the ones that convert optics into electronics.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Plasmodium Ovale and Other types of Malaria
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Plasmodium parasite
Mains level: Malaria in India
A not very common type of malaria, Plasmodium Ovale, has been identified in a jawan in Kerala.
Try this PYQ:
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria.
Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine?
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
What is Malaria?
- Malaria is caused by the bite of the female Anopheles mosquito if the mosquito itself is infected with a malarial parasite.
- There are five kinds of malarial parasites — Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax (the commonest ones), Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium knowlesi.
- Therefore, to say that someone has contracted the Plasmodium ovale type of malaria means that the person has been infected by that particular parasite.
- Malaria is treated with prescription drugs to kill the parasite. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug.
Plasmodium Ovale
- P ovale rarely causes severe illness and there is no need for panic.
- Symptoms include fever for 48 hours, headache and nausea, and the treatment modality is the same as it is for a person infected with P vivax.
- P ovale is no more dangerous than getting a viral infection.
- It is termed ovale as about 20% of the parasitised cells are oval in shape.
Burden of Malaria in India
- In 2018, the National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVBDCP) estimated that approximately 5 lakh people suffered from malaria.
- 63% of the cases were of Plasmodium falciparum.
- The recent World Malaria Report 2020 said cases in India dropped from about 20 million in 2000 to about 5.6 million in 2019.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Zebrafish and its heart regeneration capacity
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zebrafish
Mains level: Not Much

Indian scientists have used the Zebrafish model and identified its genes that can promote heart regeneration.
Try this PYQ:
Q.With reference to India’s Biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith Barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are-
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
Zebrafish
- Zebrafish is a small (2-3 cm long) freshwater fish found in the tropical and subtropical regions.
- The fish is native to South Asia’s Indo-Gangetic plains, where they are mostly found in the paddy fields and even in stagnant water and streams.
- The fish become adults at three months and survive 2-3 years in a laboratory condition.
- Its unique characteristics lie in its transparency during its embryonic stages, allowing observing all organs, including beating heart and blood circulation.
Ability to heal their heart
- The ability of Zebrafish to heal their heart after injury makes them an attractive model to investigate mechanisms governing the regenerative process.
- Researchers worldwide are actively working to understand the mechanism behind the heart regeneration in Zebrafish for the last two decades.
- Years of efforts have helped them identify the cellular communication network factor 2a (ccn2a), a gene that can promote heart regeneration by enhancing cardiomyocyte proliferation.
- They have also observed that this gene resolves the transient collagenous fibrotic scar resulting in faster regeneration.
Significance for humans
- Cardiovascular diseases are the number 1 cause of deaths globally, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year, according to the World Health Organisation.
- Humans cannot regenerate their hearts upon myocardial damage and a person who suffered a heart attack cannot functionally heal the damaged heart muscle, resulting in reduced pumping efficiency.
- While on the other hand, this unique fish has the full potential to regenerate its heart and restore its function after injury.
- Till now, there is no treatment available to restore the damaged heart function in humans. Hence scientists have sought to decode the heart regeneration processes using this model animal.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Federated Learning?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: IoT , AI
Mains level: AI and its applications
An improvement in a Machine Learning (ML) model, called ‘federated learning’, is said to enable companies to develop new ways of collecting anonymous data without compromising their privacy.
Data privacy is the right of a citizen to have control over how personal information is collected and used. Data protection is a subset Right of Privacy under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
What is ‘federated learning’?
- Federated learning is an ML method used to train an algorithm across multiple decentralised devices or servers holding data samples.
- It doesn’t exchange data with the devices, meaning there is no central dataset or server that stores the information.
- Standard ML models require all data to be centralised in a single server. Implementation of federated learning eliminates the need for maintaining a storage hub.
- The term was first introduced in a 2016 Google study titled ‘Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data.’
- Google emphasised mobile phones and tablets, stating that modern devices contain special features like speech recognition and image models that can store large amounts of data.
- Since then, Google has used the technique is various products, including Gboard, which provides text and phrase suggestions to the keyboard.
How this works
- Federated learning aims to train an algorithm, like deep neural networks, on multiple local datasets contained in local nodes, without explicitly exchanging data.
- The general principle involves simply exchanging parameters between these nodes. Parameters include a number of federated learning rounds, the total number of nodes, and learning rate.
- The distinct advantage of the model is its ability to reduce privacy and security risks by limiting the attack surface to only the device, rather than the device and the cloud, Google stated in the study.
Why need such technology?
- Smart home devices like speakers and smartwatches collect and share data with other devices and systems over the network.
- These Internet of Things (IoT) devices are equipped with sensors and software that store a user’s private information like body measurements and location.
- This large chunk of stored data is used by the device makers to improve their products and services.
Applications
- Federated learning is said to have application in healthcare, where hospitals and pharmaceutical companies can exchange data for treating diseases without sharing private clinical information.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Community Cord Blood Banking
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cord Blood Banking
Mains level: Stem Cells Therapy

Community Cord Blood Banking, a stem cell banking initiative, has recently helped save the life of a girl child making it India’s first dual cord blood transplant through an unrelated donor.
Must read:
What is Cord Blood Banking?
- Community Banking is a new sharing economy model of stem cell banking that was pioneered by LifeCell in India.
- Parents who choose to store their child’s cord blood in a community bank will have access, in the event of medical need, to all of the other cord blood units in the bank.
- A community bank is like a public cord blood bank in that the members are supporting each other, but it is also like a private bank because the members pay for this service and outsiders cannot participate.
- It can fill an unmet health need in a country like India, where there is no national network of public banks and the population has unique genetics that are not covered by banks elsewhere in the world.
- It is different from “hybrid” banking where both public and family banks share a laboratory, because in hybrid banks the pubic and family sides operate separately.
- In a community bank the public and family functions are blended.
Benefits of cord blood
- It gives protection to a baby against all conditions treatable using stem cells (own & donor).
- It gives protection to the baby’s siblings, parents and grandparents (maternal & paternal) by providing unrelated donor stem cells.
Back2Basics: Stem Cell Therapy
- It is a type of treatment option that uses a patient’s own stem cells to repair damaged tissue and repair injuries.
- It is used to treat more than 80 disorders including neuromuscular and degenerative disorders. Eg. Bone-marrow transplant is used in Leukemia (blood cancer), sickle-cell anemia, immunodeficiency disorders.
- Stem cells are usually taken from one of the two areas in the patient’s body: bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue in their upper thigh/abdomen.
- Because it is common to remove stem cells from areas of stored body fat, some refer to stem cell therapy as “Adipose Stem Cell Therapy” in some cases.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Anomaly over Normal Body Temperature
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: “Normal” body temperature
Mains level: NA

For several years now, doctors and researchers have known that 98.6°F is not really the gold-standard “normal” body temperature it was once considered to be.
The “normal” body temperature
- In 1851, Carl Reinhold August Wunderlich pioneered the use of the clinical thermometer.
- It was a rod a foot long, which he would stick under the armpits of patients at the hospital attached with Leipzig University, and then wait for 15 minutes for the temperature to register.
- He took over a million measurements of 25,000 patients, and published his findings in a book in 1868, in which he concluded that the average human body temperature is 98.6°F.
- Most modern scientists feel Wunderlich’s experiments were flawed, and his equipment inaccurate.
- Another study concluded that the average human body temperature is closer to 98.2°F, and suggested that the 98.6°F benchmark be discarded.
The anomaly
- Studies in the US and Europe have found average body temperatures declining over time.
- In recent years, however, different studies have found the human body temperature averaging out differently, including at 97.7°, 97.9° and 98.2°F.
- One of the largest such studies, published last year, found that body temperatures among Americans have been declining over the last two centuries.
Now try this PYQ based on health sciences
Q.Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing?
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) Only 1
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Discovering the Tubarial Glands
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tubarial glands
Mains level: Not Much

Researchers from the Netherlands have discovered a new location of salivary glands.
Try this PYQ:
Q.With references to the scientific progress of ancient India, which of the statements given below are correct?
- Different kinds of specialized surgical instruments were in common use by 1st century AD.
- Transplant of internal organs in the human body had begun by the beginning of 3rd century AD.
- The concept of sine of an angle was known in 5th century AD.
- The concept of cyclic quadrilaterals was known in 7th century AD.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Tubarial Glands
- The salivary gland system in the human body has three paired major glands and over 1,000 minor glands that are spread throughout the mucosa.
- These glands produce saliva necessary for swallowing, digestion, tasting, mastication and dental hygiene.
- When researchers were studying scans from about 100 people, they found a bilateral structure at the back of the nasopharynx and these glands had characteristics of salivary glands.
- Researchers have proposed the name “tubarial glands” for their discovery.
- The researchers believe that these glands would qualify as the fourth pair of major salivary glands.
- The proposed name is based on their anatomical location; the other three glands are called parotid, submandibular and sublingual.
Why are these glands being discovered only now?
- The location of these glands is at a poorly accessible anatomical location under the base of the skull, which is an area that can only be visualized using nasal endoscopy.
- Further, conventional imaging techniques such as a CT scan, MRI and ultrasound have not allowed the visualization of these glands.
- For the scans done on the 100 patients, a new type of scan called the PSMA PET/CT scan was used, which was able to provide the high sensitivity and specificity required to detect these glands.
What is the purpose of these glands?
- So far, researchers suspect that the physiological function of the glands is to moisten and lubricate the nasopharynx and the oropharynx.
- However, this interpretation needs to be confirmed with additional research.
Significance of this discovery
- The discovery is potentially good news for some cancer patients with head and neck cancers.
- Patients with head and neck cancers and tumours in the tongue or the throat are treated with radiation therapy that can damage the new salivary glands, whose location was not previously known.
- Oncologists will be able to circumvent these areas and protect them from the side effects of radiation which can lead to complications such as trouble speaking, swallowing and speaking.
- Some patients may even face an increased risk of caries and oral infections that can significantly impact their life.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Need for guidelines for gene-editing research in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CRISPR-Cas9
Mains level: Paper 3- CRISPR-Cas9-Important tool in gene editing
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2020 has been awarded for the discovery of CRISPR Cas9. The two scientists have pioneered the use of CRISPR – Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) system as a gene-editing tool.
Background of discovery of CRISPR
- In 1987a group of Japanese researchers observed an unusual homologous DNA sequence bearing direct repeats with spacing in a eubacterial gene.
- In subsequent years CRISPR was discovered and showed to be a bacterial adaptive immune system and to act on DNA targets.
- A notable discovery on the use of CRISPR as a gene-editing tool was by a Lithuanian biochemist, Virginijus Šikšnys, in 2012.
- Šikšnys showed that Cas9 could cut purified DNA in a test tube, the same discovery for which both Charpentier and Doudna were given the credit.
- Thus, the exclusion of Siksnys from this year’s Nobel is going to raise discussions.
Issue of gene-edited babies
- The world was alarmed by such a mission in 2018 when Chinese scientist edited genes in human embryos using the CRISPR-Cas9 system which resulted in the birth of twin girls.
- The incident became known as the case of the first gene-edited babies of the world.
- Following the incident, the World Health Organization formed a panel of gene-editing experts.
- The expert panel suggested a central registry of all human genome editing research in order to create an open and transparent database of ongoing work.
Guidelines and regulations in India
- In India, several rules, guidelines, and policies are notified under the Environment Protection Act, 1986 to regulate genetically modified organisms.
- The above Act and the National Ethical Guidelines for Biomedical and Health Research involving human participants, 2017, by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and the Biomedical and Health Research Regulation Bill implies regulation of the gene-editing process.
- This is especially so in the usage of its language “modification, deletion or removal of parts of heritable material”.
- However, there is no explicit mention of the term gene editing.
Consider the question “What is CRISPR-Cas9? How it helps in the gene-editing? What are the concerns with use of it for gene-editing?”
Conclusion
It is time that India came up with a specific law to ban germline editing and put out guidelines for conducting gene-editing research giving rise to modified organisms.
Back2Basics: What is CRISPR?
- CRISPRs: “CRISPR” stands for “clusters of regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats.”
- It is a specialized region of DNA with two distinct characteristics: the presence of nucleotide repeats and spacers.
- Repeated sequences of nucleotides — the building blocks of DNA — are distributed throughout a CRISPR region.
- Spacers are bits of DNA that are interspersed among these repeated sequences.
- In the case of bacteria, the spacers are taken from viruses that previously attacked the organism.
- They serve as a bank of memories, which enables bacteria to recognize the viruses and fight off future attacks.

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
FELUDA test for Covid-19
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FELUDA, CAS9, CRISPR
Mains level: CRISPR technology

Union Health Ministry will soon roll out the FELUDA paper strip test for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis.
Try this PYQ:
Q.What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news?
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
FELUDA test
- FELUDA is the acronym for FNCAS9 Editor Linked Uniform Detection Assay.
- It uses indigenously developed CRISPR gene-editing technology to identify and target the genetic material of SARS-CoV2, the virus that causes Covid-19.
- According to CSIR, the test matches accuracy levels of RT-PCR tests, considered the gold standard in the diagnosis of Covid-19, has a quicker turnaround time and requires less expensive equipment.
- It is also the world’s first diagnostic test to deploy a specially adapted Cas9 protein to successfully detect the virus.
How does it work?
- The Feluda test is similar to a pregnancy test strip that will just change colour upon detection of the virus and can be used in a simple pathological lab.
- The Cas9 protein is bar-coded to interact with the SARS-CoV2 sequence in the patient’s genetic material.
- The Cas9-SARS-CoV2 complex is then put on the paper strip, where using two lines (one control, one test) makes it possible to determine if the test sample was infected.
Back2Basics: CRISPR technology
- CRISPR is a short form for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats.
- It is a gene-editing technology and finds its use in correcting genetic defects and treating and preventing the spread of diseases.
- The technology can detect specific sequences of DNA within a gene and uses an enzyme functioning as molecular scissors to snip it.
- It also allows researchers to easily alter DNA sequences and modify gene function.
- Moreover, the technology can also be configured for detection of multiple other pathogens in the future.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Bio-Pesticide Formulation using Verticillium Lecanii
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Verticillium lecanii
Mains level: NA
Indian researchers have successfully developed new Aqueous Suspension formulation technology of bio-pesticide based on entomopathogenic fungus Verticillium lecanii.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) biodiesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
Verticillium lecanii
- This bio-pesticide formulation has been found very effective in controlling various insects in seed spice crops (fenugreek, cumin, and coriander).
- It has a good shelf life, safe to user & environment and it may be effectively used for controlling different agricultural insects especially in seed spice crops.
- This bio-pesticide may be used as a safer alternative to chemical pesticides to minimize pesticide residue problem.
- Besides, it may be used as a key input for crop protection from insects pest in organic agriculture and Integrated Pest Management.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
2020 Nobel for Hepatitis C Virus discovery
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hepatitis
Mains level: Not Much
Americans Harvey J Alter and Charles M Rice, and British scientist Michael Houghton were awarded the Nobel Prize for Medicine or Physiology on Monday for the discovery of the hepatitis C virus.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Which one of the following statements is not correct? (CSP 2019)
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B. unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Hepatitis C Virus
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a bloodborne virus and causes liver diseases. It refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver.
- The novel virus caused several deaths in the 1960s and 1970s — but remained unknown until its discovery in the late 1980s.
What are other Hepatitis Viruses?
- Before the discovery of the Hepatitis C virus, two other viruses were known to cause hepatitis in patients.
- The Hepatitis A virus was known to spread mainly through contaminated food and water and caused a relatively milder form of liver inflammation.
- Hepatitis B, discovered in the 1960s, was known to transmit mainly through infected blood and caused a more serious form of the disease.
- Incidentally, the discovery of the Hepatitis B virus too was rewarded with a Nobel Prize in Medicine, given to Baruch Blumberg in 1976. There are vaccines available for this disease now.
How Hepatitis C came to observation?
- The discovery and identification of the Hepatitis B virus facilitated the development of a diagnostic test to detect its presence in blood.
- Thereafter, only blood sanitized from this virus would be given to patients, but it was observed that even this sanitized blood was able to prevent only 20% of the blood-borne hepatitis cases.
- It was then that the search for the new virus began.
How is Hepatitis C treated?
- Presently there is no vaccine available for HCV. However, it can be treated with antiviral medication.
- Hepatitis A and B are preventable by vaccine.
Back2Basics:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Ketogenic Diet?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ketogenic Diet
Mains level: Not Much
Ketogenic or Keto Diet is popularly followed as a weight loss diet across the world.
Try this PYQ:
Q.Regular intake of fresh fruits and vegetables is recommended in the diet since they are a good source of antioxidants. How do antioxidants help a person maintain health and promote longevity? (CSP 2014)
(a) They activate the enzymes necessary for vitamin synthesis in the body and help prevent vitamin deficiency.
(b) They prevent excessive oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and help avoid unnecessary wastage of energy.
(c) They neutralize the free radicals produced in the body during metabolism.
(d) They activate certain genes in the cells of the body and help delay the ageing process.
What is Ketogenic Diet?
- The Keto Diet is one of the most popular weight-loss diets the world over.
- It consists of a high-fat, moderate-protein and low-carb diet.
- It helps in weight loss by achieving ketosis — a metabolic state where the liver burns body fat and provides fuel for the body, as there is limited access to glucose.
What constitutes a keto diet?
- A classic keto generally requires that 90 per cent of a person’s calories come from fat, 6 per cent from protein and 4 per cent from carbs.
- But there are many versions doing the rounds since this one was designed for children suffering from epilepsy to gain control over their seizures.
How does it impact the body?
- If we starve the body of carbohydrate, after burning out the glucose, the liver starts breaking down fats for energy.
- Ketosis is common in all kinds of fasting, but in a keto diet, when one is feeding it by giving a lot of fats from outside without carbs, it can become mildly toxic.
- It may lead to many nutrient deficiencies such as carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins (especially vitamin A, D, E, & K) and minerals like calcium, phosphorus, sodium.
- Extreme carbohydrate restriction can lead to hunger, fatigue, low mood, irritability, constipation, headaches, and brain fog, which may last days to weeks
What impact does it have on our kidneys?
- Even the moderate increase in protein needs to be carefully monitored, especially in those who are already suffering from chronic kidney disease, as it could lead to kidney failure.
- One should get a thorough assessment and make sure they have normal kidney function before choosing this diet.
- This diet could lead to increased stress on the kidneys and result in kidney stones, as they are made to work overtime.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is CBD Oil?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cannabidiol
Mains level: Not Much
These days, there are diverse opinions rising regarding the legalization of CBD oil in India after recent controversy rose after the alleged suicide of an actor.
What is CBD oil?
- CBD oil is an extract from the cannabis plant.
- The two main active substances in it are cannabidiol or CBD and delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC.
- The high that is caused by the consumption of cannabis is due to THC.
- CBD, however, does not cause a “high” or any form of intoxication.
- CBD oil is made by extracting CBD from the cannabis plant, then diluting it with a carrier oil like coconut or hemp seed oil.
What are the effects of Cannabidiol?
- Cannabidiol has effects on the brain, preventing the breakdown of a chemical that aggravates the pain and affects mood, and mental function. It can reduce pain and anxiety.
- It also reduces psychotic symptoms associated with conditions such as schizophrenia as well as epilepsy.
Is it legal in India?
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 (NDPS Act) outlaws the recreational use of cannabis.
- The NDPS Act, however, does not apply to the leaves and seeds of cannabis plants. In case the CBD is extracted from the leaves of the cannabis, then technically it is not illegal.
- CBD oil manufactured under a licence issued by the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 can be legally used.
- However, the use of cannabis as a medicine is not much prevalent in India.
Now try this PYQ:
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine?
A) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
B) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
C) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
D) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
CBD Oil
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Research and development is medical science
Context- Earlier this week, late actor Irrfan Khan’s wife Sutapa Sikdar made an appeal to legalise CBD oil in India for its potential to treat cancer. Her appeal followed the criticism of actor Rhea Chakrabaorty after it was reported that she had administered CBD oil, used as a pain reliever for some, to Sushant Singh Rajput when he was alive.
About CBD oil ?
- CBD oil is an extract from the cannabis plant. The two main active substances in it are cannabidiol or CBD and delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC.
- The high that is caused by the consumption of cannabis is due to THC. CBD, however, does not cause a “high” or any form of intoxication.
- CBD oil is made by extracting CBD from the cannabis plant, then diluting it with a carrier oil like coconut or hemp seed oil.
- Cannabidiol can reduce pain and anxiety. It also reduces psychotic symptoms associated with conditions such as schizophrenia as well as epilepsy.
- There is not enough robust scientific evidence to prove that CBD oil can safely and effectively treat cancer.
- CBD oil manufactured under a license issued by the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 can be legally used. However, the use of cannabis as a medicine is not much prevalent in India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Raman Spectroscopy?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Scattering of light
Mains level: Paper 3- Raman spectroscopy
Mumbai-based researchers have turned to Raman Spectroscopy to detect RNA viruses present in saliva samples.
Try this question from CSP 2017
Q.Which Indian astrophysicist and Nobel laureate predicted rapidly rotating stars emit polarized light?
(a) Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar
(b) CV Raman
(c) Ramanujan
(d) Amartya Sen
The Raman Spectroscopy
- Raman spectroscopy is an analytical technique where scattered light is used to measure the vibrational energy modes of a sample.
- In 1928, Raman discovered that when a stream of light passes through a liquid, a fraction of the light scattered by the liquid is of a different colour.
- While Raman was returning from London in a 15-day voyage, he started thinking about the colour of the deep blue Mediterranean.
- He wasn’t convinced by the explanation that the colour of the sea was blue due to the reflection of the sky.
- As the ship docked in Bombay, he sent a letter to the editor of the journal Nature, in which he penned down his thoughts on this.
Subsequently, Raman was able to show that the blue colour of the water was due to the scattering of the sunlight by water molecules. - By this time he was obsessed with the phenomenon of light scattering.
How does it work?
- The Raman Effect is when the change in the energy of the light is affected by the vibrations of the molecule or material under observation, leading to a change in its wavelength.
- Significantly, it notes that the Raman effect is “very weak” — this is because when the object in question is small (smaller than a few nanometres), the light will pass through it undisturbed.
- But a few times in a billion, light waves may interact with the particle. This could also explain why it was not discovered before.
- In general, when light interacts with an object, it can either be reflected, refracted or transmitted.
- One of the things that scientists look at when light is scattered is if the particle it interacts with is able to change its energy.
Applications
- Raman spectroscopy is used in many varied fields – in fact, any application where non-destructive, microscopic, chemical analysis and imaging is required.
- Whether the goal is qualitative or quantitative data, Raman analysis can provide key information easily and quickly.
- It can be used to rapidly characterize the chemical composition and structure of a sample, whether solid, liquid, gas, gel, slurry or powder.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Gynandromorphism?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gynandromorphism
Mains level: NA
Recently, a rare biological phenomenon called Gynandromorphism was observed in dragonflies at Kole wetlands of Kerala.
Gynandromorphism is a core biology concept. We can expect a prelims question in a rare scenario.
Try this question from CSP 2013:
Q.Improper handling and storage of cereal grains and oilseeds result in the production of toxins known as aflatoxins which are not generally destroyed by normal cooking process. Aflatoxins are produced by
(a) Bacteria (b) Protozoa (c) Moulds (d) Viruses
Gynandromorphism
- Gynandromorphs are individual animals that have both genetically male and female tissues and often have observable male and female characteristics.
- They may be bilateral, appearing to divide down the middle into male and female sides, or they may be mosaic, with patches characteristic of one sex appearing in a body part characteristic of the other sex.
- Gynandromorphs occur in insects, spiders, crustaceans, and other arthropods as well as in birds, but they are extremely rare, and discovering one in the field or in the laboratory is a major event.
- Estimating how frequently they occur is difficult because they usually go unnoticed in species where sexual dimorphism is less pronounced.
- Gynandromorphs have been reported in mosquitoes, fruit flies, and in other insects, but they are most dramatic in those butterfly species in which the male and female wing colours and patterns are dramatically different.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Celebrating the contributors to agriculture
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various personalities that contributed to India's food reaserch
Mains level: Paper 3- Contributors to the India's agri-research
This article introduces us to the Indian winners of the prize that is considered as the Nobel for research in food. Their contribution has benefited agriculture immensely.Here, we’ll get a brief idea about their work.
Word Food Prize
- The World Food Prize is often described as the Nobel for research in food.
- It was set up by Ñorman Borlaug.
- Borlaug won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1972 for his work on hybridisation of wheat and rice.
- His work led to the Green Revolution in the mid-1960s.
Indian winners of the award
- The awards to eight Indians of the total of 50 given so far are a tribute to the country’s agricultural university education and research system.
- The country should celebrate their achievements unabashedly when 7-10 million new productive jobs need to be created annually.
- And when it accounts for a third of global undernourished.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has made job creation and improved nutrition and health more urgent than ever.
Let’s look at the contributions made by these personalities
Rattan Lal
- Rattan Lal was awarded for developing and mainstreaming a soil-centric approach to increasing food production.
- This approach also restores and conserves natural resources and mitigates climate change.
- His research has shown that growing crops on healthy soils produces more food from less land area, less use of agrochemicals, less tillage, less water, and less energy.
M S Swaminathan
- Swaminathan’s vision transformed India from a “begging bowl” to a “breadbasket” almost overnight.
- His work helped bringing the total crop yield of wheat from 12 million tonnes to 23 million tonnes in four crop seasons.
- Which helped in ending India’s dependence on grain imports.
Verghese Kurien
- Kurien, received the prize in 1989 for India’s white revolution.
- Under his leadership, milk production increased from 23.3 million tonnes (1968-69) to 100.9 million tonnes (2006-07).
- And now it is projected to reach 187 million tonnes for 2019-20.
- This helped in bringing millions of small and marginal farmers, including women into the marketplace.
Ramlal Barwale
- Barwale, a small farmer and entrepreneur, received the award in 1996.
- He made selling seeds of okra and sorghum “hip” and founded the Maharashtra Hybrid Seeds Company.
- The Crop Science Society of America has called him father of the seed industry in India.
- He introduced hybrid rice from China to India.
Surinder Vasal
- Vasal was given the prize in 2000 for developing quality protein maize (QPM).
- Integrating cereal chemistry and plant breeding techniques, Vasal and Villegas of Mexico collaborated to work on “opaque-2” maize variety using molecular biology techniques.
- In the mid-1980s, they produced a QPM germplasm with hard kernel characteristics and taste like that of the traditional grain.
- But it has much higher quality levels of lysine and tryptophan, thereby enhancing the nutrition value.
Mododugu Gupta
- Gupta received the award in 2005 for starting a blue revolution.
- He developed two exceptional approaches for increasing fish harvests among the very poor.
- This helped in increasing the protein and mineral content in the diets of over one million of the world’s most impoverished families.
- Gupta’s aquaculture technologies boosted Bangladesh’s fish yields from 304 kg per hectare to over 2,500 kg per hectare in less than a year — including 1,000 kg per hectare harvests in the dry season.
Sanjaya Rajaram
- Rajaram, who won the prize in 2014.
- He succeeded Borlaug in leading CIMMYT’s wheat breeding programme.
- There he went on to develop an astounding 480 varieties that have been widely adopted by both small and large-scale farmers.
- Rajaram was born near a small farming village in Uttar Pradesh and received his master’s degree from IARI.
Decreasing government support
- The awardees all come from the time of the green and rainbow revolutions (of dairy and aqua-culture).
- It was also the time when India invested heavily in agricultural science education and research and Indian scientists shone brightly in the global galaxy of science.
- Government support for state agricultural universities, and research conducted by the ICAR and the departments of science and technology and biotechnology has slipped in recent years.
- Today, not a single Indian university is counted among the top 100 in the world.
Consider the question asked by the UPSC in 2019 “How was India benefitted from the contributions of Sir M.Visvesvaraya and Dr M. S. Swaminathan in the fields of water engineering and agricultural science respectively?”
Conclusion
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Foldscope?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Foldscope
Mains level: NA

Indian researchers have explored and validated the clinical utility of Foldscope in the diagnosis of diseases using various patient samples.
Though trivial, Foldscope is a significant invention with most crucial applications. It somehow offers an alternative to costly microscopes for some basic diagnosis.
What is Foldscope?
- Foldscope is an affordable origami-based microscopy device composed of a series of paper clippings.
- Upon assembly, the device can hold a specimen slide for observation, and this specimen can be viewed via a mobile phone camera attached to it.
How does it work?
- Foldscope can be assembled using paper clips and mounted on a cell phone using coupler and glue drops.
- To do the assessment, a patient sample like urine is smeared on a transparent glass slide and visualized under a Foldscope mounted on a cell phone.
- Sample images can be enlarged using the zoom function of the mobile, which can be stored on the mobile memory card for later reference/patient records.
- Foldscope visualizes calcium oxalate crystals, which are a major cause of kidney stones.
Utility of Foldscope
- Foldscope is particularly convenient to diagnose urinary tract infection (UTI) and monitor kidney stone.
- The study evaluated the use of Foldscope in the clinical diagnosis of oral and urinary tract infections.
- Using this tool, one can easily monitor own-kidney stone status at home with a simple glass-slide, a Foldscope and a phone in hand.
- Such monitoring could perhaps avoid kidney stone reaching a painful state or surgery in recurring cases.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Crystalline Rubrene for Optoelectronic Devices
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Piezo-electric crystals
Mains level: Not much
Indian scientists have found a new process for synthesizing crystalline rubrene for the development of optoelectronic devices and also for preparation of Electronic Skin (E-Skin).
Note the difference between the Pyro-electric/ Piezo-electric/ Pyro-photonic effects. UPSC may shuffle the meaning of such terms in statement based prelims question.
What is crystalline rubrene?
- Crystalline rubrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-based thin film.
- It is a water-free, solvent-free, environmentally friendly one-step plasma process.
- It demonstrated optoelectronic properties (which detect and control light).
- A highly uniform pin-hole-free thin film can be deposited by this process, which is useful for the fabrication of high-end devices.
Working principle
- Devices made of pyro-electric materials (that generate electric charge when they are heated or cooled) and piezo-electric materials (that generate electric charge under the effect of mechanical pressure), can help detect change in temperature and pressure.
- Pyro-electric materials also show pyro-phototronic effect where pyro-electricity is associated with the change in temperature of a material when it absorbs photons.
- Pyro-electric infrared detectors are well known for application in infrared sensing for space research, defense, remote sensing, and household appliances.
Principle application: Human Skin
- These kinds of materials are available in biological systems such as – human skin, plant cellulose leading to their significance in the understanding of basic science of biological systems and also in their huge application prospect.
- The rubrene crystal has a thin amorphous oxide layer formed over the crystalline film.
- This induces surface layer polarization effect leading to pyro-phototronic effect.
Significance of the research
- Since last few years, scientists from around the world are working on the synthesis of organic materials for electronic applications.
- The conventional process for synthesis of organic electronic materials based on chemical processes provides very good quality materials, but the stability of the materials is not very good, and it requires use of solvents.
- Moreover, multiple steps are required for material synthesis and film deposition.
Applications
- This novel process developed by the Indian team is useful for developing advanced optoelectronic devices and preparation of Electronic Skin (E-Skin).
- It may prove to be useful tool for laboratory simulation of different biological systems for probing the organization and dynamics of those systems.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Rare-earth based Magnetocaloric materials for cancer treatment
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Magnetocaloric Effect
Mains level: Magnetocaloric Effect and its application in Cancer treatment
Indian scientists have developed a rare-earth-based magnetocaloric material that can be effectively used for cancer treatment.
Magnetocaloric Effect does have other applications like in the field of medical implants but for use in energy field, it is still in nascent stage.
From exam perspective, do understand what principles lies behind this effect.
What is Magnetocaloric Effect?

- Magnetocaloric effect (MCE) is a phenomenon where the application and removal of a magnetic field cause certain materials to get warmer and cooler, respectively.
- This effect normally occurs near its Curie temperature where the application of the field makes the material to warm up and cools up when the field is removed.
Issue of hyperthermia in cancer treatment
- Advancements in magnetic materials led to the development of magnetic hyperthermia to try to address the issues of side effects of cancer treatment like chemotherapy.
- In magnetic hyperthermia, magnetic nanoparticles are subjected to alternating magnetic fields of few Gauss, which produce heat due to magnetic relaxation losses.
- Usually, the temperature required to kill the tumour cells is between 40 and 45°C.
- However, the drawback in magnetic hyperthermia is the lack of control of temperature, which may damage the healthy cells in the body and also have side effects like increased BP, hair losses etc.
Here comes in, Magnetocaloric materials
- This hypothermia can be avoided by using magnetocaloric materials, as it can provide controlled heating.
- The advantage of magnetocaloric materials which heat up or cool down with the application and removal of the magnetic field, respectively is that as soon as the magnetic field is removed, the cooling effect is generated.
- The team at ARCI chose rare-earth-based alloy for studies as some of the rare earth materials are human body compatible.
- The heating capacity would increase with the increase in the magnetic field.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Serotonin Hormone causes Locust to form Swarms
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Serotonin
Mains level: Locusts invasion and its threats
Scientists have attempted to answer an important scientific question of how and why locusts collect together by the thousands in order to make a swarm.
Quite often, Oxytocin hormone is seen in the news for its commercial uses and associated ethical concerns. Kindly go through Oxytocin and issues over its commercial use
What causes Locusts to form huge swarms?
- When lone locusts happen to come near each other (looking for food) and happen to touch each other, this tactile stimulation, even just in a little area of the back limbs, causes their behaviour to change.
- This mechanical stimulation affects a couple of nerves in the animal’s body, their behaviour changes, leading to their coming together.
- The central nervous system of the locust, the most important among them being serotonin which regulates mood and social behaviour is the mystery behind swarms.
- Their coming together triggers a mechanical (touch) and neurochemical (serotonin) stimulations to make crowding occur.
What is Serotonin?
- It is a monoamine neurotransmitter.
- It has a popular image as a contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness.
- Its actual biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Species in news: Super mushroom “Cordyceps militaris”
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cordyceps militaris
Mains level: NA

A university in Assam has developed a fungal powder to help people boost their immunity to disease.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
Q.) Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) bio-diesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
A similar question related to Cordyceps militaris can be asked. UPSC may ask whether it is a Fungi, Algae, a Moss or a Lichen.
Cordyceps militaris
- The powder is from a parasitic but rare “super mushroom” called Cordyceps militaris.
- The militaris underwent powdering through lyophilisation or freeze-drying at –80°C.
- The earth has more than 400 species of Cordyceps, a fungus parasitic on insects as well as other fungi.
- Often referred to as a super mushroom, Cordyceps known for its anti-ageing, anti-viral, energy and immunity-boosting effect.
- Natural Cordyceps is hard to get and if dried, costs at least ₹8 lakh per kg.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Iron-Manganese based Biodegradable Alloy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Iron-Manganese based Biodegradable Alloy
Mains level: Affordable medical devices and implants in India

Indian scientists have jointly developed new generation Iron-Manganese based alloys for biodegradable metal implants for use in humans.
Do you remember the Johnson and Johnson’s faulty hip implants case?? The alloy mentioned in the newscard can prove to be a gamechanger in the field of medical implants.
Iron-Manganese based Biodegradable Alloy
- Biodegradable materials (Fe, Mg, Zn, and polymer) can participate in the healing process and then degrade gradually by maintaining mechanical integrity without leaving any implant residues in the human body.
- They are better alternatives to currently used metallic implants which remain permanently in the human body and can cause long-term side effects like systemic toxicity, chronic inflammation, and thrombosis.
- The ARCI team employed both conventional melting and powder metallurgy techniques in the manufacturing of the new Fe-Mn based biodegradable alloys.
- The alloy Fe-Mn (having Mn composition of more than 29% by weight) is a promising biodegradable metallic implant which exhibits a single austenitic phase (a non-magnetic form of iron) with MRI compatibility.
Easy degradation
- The alloy also showed a degradation rate in the range of 0.14-0.026 mm per year in the simulated body fluid.
- It means that the Fe-Mn alloy exhibits mechanical integrity for 3-6 months and completely, disappears from the body in 12-24 months.
- During the degradation process, calcium phosphate deposits on the implant due to local alkalization and saturation of calcium and phosphate, allow cells to adhere onto the surface to form tissues.
Benefits
- The Fe-Mn alloy produced at ARCI exhibited 99% density with impressive mechanical properties and behaved as a nonmagnetic material even under a strong magnetic field.
- These properties are comparable to presently used permanent Titanium (Ti) and stainless-steel metallic implants (which is very costly).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Species in news: Quinine Nongladew
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: HCQ, Quinine Nongladew
Mains level: NA

Quinine, the most primitive antimalarial avatar of Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), has made a village in Meghalaya latch on to its past for a curative future.
Relate Quinine Nongladew with the following question. Such peculiar names are very important.
Q. Recently, there was a growing awareness in our country about the importance of Himalayan nettle (Girardinia diversifolia) because it is found to be a sustainable source of (CSP 2019)
(a) anti-malarial drug
(b) bio-diesel
(c) pulp for paper industry
(d) textile fibre
Quinine Nongladew
- The herb Quinine Nongladew is the alkaloid quinine extracted from the bark of cinchona, a plant belonging to the Rubiaceae family and classified as either a large shrub or a small tree
- The tree is named after a village about 70 km south of Guwahati, on the highway to Meghalaya capital Shillong.
- The cinchona nursery was raised in the 19th century, probably around 1874, when Shillong became the British administrative headquarters for Assam Province.
- Large swathes of Meghalaya used to be, and still are, malaria-prone.
- The British had the foresight to start the plantation to combat malaria and other diseases caused by mosquitoes.
Back2Basics: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
- HCQ is an oral tablet used as an anti-malarial drug. It is used to treat malaria, lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- It may be used as part of a combination therapy where it is taken with other drugs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] BiPAP Non-Invasive Ventilator “SwasthVayu”
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SwasthVayu

National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) Bangalore, a constituent of the lab of CSIR has developed a Non-Invasive BiPAP Ventilator ‘SwasthVayu ’in a record time of 36 days to treat COVID-19 patients.
The name ‘SwasthVayu’ can be tricky to guess, specially after some days. In prelims, UPSC may throw some options related to air pollution.
SwasthVayu
- A ventilator is a machine that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently.
- BiPAP (Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure) Non-Invasive ventilator is a microcontroller-based precise closed-loop adaptive control system.
- It is a built-in biocompatible “3D printed manifold & coupler” with HEPA filter (Highly Efficient Particulate Air Filter).
Benefits of SwasthVayu
- The major advantage of this machine is that it is simple to use without any specialized nursing, cost-effective, compact and configured with the majority of indigenous components.
- This is ideal for treating COVID -19 patients in Wards, Makeshift Hospitals, dispensaries and home in current Indian COVID 19 scenario.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] UV Blaster: A UV Disinfection Tower
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: UV germicidal irradiation
Mains level: Can always be used as an example

The DRDO has developed an Ultra Violet (UV) Disinfection Tower for rapid and chemical-free disinfection of high infection-prone areas.
GYAN:
We have a UV filter in our home based water filter. Ever wondered, how do UV rays kill viruses/bacteria?
UV Blaster
- The UV blaster is a UV based area sanitizer designed and developed by Laser Science & Technology Centre (LASTEC), the Delhi based premier laboratory of DRDO.
- It is useful for high tech surfaces like electronic equipment, computers and other gadgets in laboratories and offices that are not suitable for disinfection with chemical methods.
- The product is also effective for areas with a large flow of people such as airports, shopping malls, metros, hotels, factories, offices, etc.
How does it work?
- The UV based area sanitizer may be used by remote operation through laptop/mobile phone using wifi link.
- The equipment has six lamps each with 43 watts of UV-C power at 254 nm wavelength for 360-degree illumination.
- For a room of about 12 x 12 feet dimension, the disinfection time is about 10 minutes and 30 minutes for 400 square feet area by positioning the equipment at different places within the room.
- This sanitizer switches off on the accidental opening of a room or human intervention.
Back2Basics: UV germicidal irradiation
- UV irradiation is a disinfection method that uses short-wavelength ultraviolet rays to kill or inactivate microorganisms by destroying nucleic acids and disrupting their DNA, leaving them unable to perform vital cellular functions.
- UVGI is used in a variety of applications, such as food, air, and water purification.
- UVGI devices can produce strong enough UVC light in circulating air or water systems to make them inhospitable environments to microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, moulds, and other pathogens.
- UVGI can be coupled with a filtration system to sanitize air and water.
- It has been used primarily in medical sanitation and sterile work facilities.
- Increasingly, it has been employed to sterilize drinking and wastewater since the holding facilities are enclosed and can be circulated to ensure a higher exposure to the UV.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Reverse Vaccinology and its benefits
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Reverse Vaccinology
Mains level: Coronovirus and the hunt for its vaccine
The Tamil Nadu Dr. MGR Medical University has developed a vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2 through ‘reverse vaccinology’.
A definition based prelims question can be expected on Reverse Vaccinology. Ex. Which of the following statements best describes ‘Reverse Vaccinology’?
Reverse Vaccinology
- Reverse vaccinology is an improvement on vaccinology that employs applied bioinformatics.
- The basic idea behind it is that an entire pathogenic genome can be screened using bioinformatics approaches to find genes.
- Some traits that the genes are monitored for may indicate antigenicity.
- Those genes are filtered for desirable attributes that would make good vaccine targets such as outer membrane proteins.
- Once the candidates are identified, they are produced synthetically and are screened in animal models of the infection.
- Since then, it has been used on several other bacterial vaccines.
Benefits
- Earlier researchers had to do a viral culture in the laboratory to develop a vaccine, and this was time-consuming.
- The major advantage for reverse vaccinology is finding vaccine targets quickly and efficiently.
- Traditional methods took decades to unravel pathogens and antigens, diseases and immunity
- With ‘reverse vaccinology’ scientists know what molecules make the genomic sequence.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Anastomosis surgery for re-implantation
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Anastomosis Surgery
Mains level: Not Much
The chopped off-hand of a Punjab Police officer has been successfully re-implanted after hours of surgery.
Anastomosis is a general term in surgical sciences used to join amputated limbs or organs. The term has made headline due to its recent application. A piece of general information regarding novelties of medical sciences should be known to the aspirants.
Anastomosis Surgery
- A surgical Anastomosis is a surgical technique used to make a new connection between two body structures that carry fluid, such as blood vessels or bowel.
- It involves conjoining various parts of the arm and the hand — bones, muscles, tendons, arteries, veins as well as nerves.
- Both radial and ulnar arteries, accompanying nerves and the dorsal vein were anastomosed successfully, allowing for the hand to receive adequate circulation.
- The bones are attached using K wires (used for orthopaedic surgery) which can be removed once the bones conjoin organically.
In which cases is re-implantation possible?
- When a surgeon makes that decision, the factors that he or she considers include how much time has elapsed since the injury.
- The condition of the severed organ and the nature of the injury are also taken into account.
Can a reattached hand get its function restored?
- That is the goal of doing such surgery. The extent of restored function, however, can vary from case to case.
- While a successful surgery can result in the good return of motor function, studies have shown that sensory recovery can often be poor.
- Whether the blood circulation is optimum after surgery can only be observed within the next few days.
- The patient also needs to attend regular physiotherapy sessions for total restoration of motor movement and sensation in his hand.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
TB diagnostic kit ‘Truenat’
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TrueNat
Mains level: Not Much

‘Truenat’, a diagnostic machine used to test drug-resistant TB has now been approved by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for conducting Covid-19 tests.
Truenat
- The Truenat TB test is a new molecular test that can diagnosis TB in one hour as well as testing for resistance to the drug rifampicin.
- This test for TB uses a sputum sample taken from each patient.
- It is a small battery operated device which requires minimal training and is usable even in smaller settings such as the Primary Health Centre.
- It uses a chip-based technology and takes just up to 60 minutes for a test, screening or confirmatory.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] Chitra Acrylosorb Secretion Solidification System
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Acrylosorb
Mains level: Advanced materials and thier applications

Scientists at Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) have designed and developed a highly efficient superabsorbent material for liquid respiratory and other body fluid solidification and disinfection for the safe management of infected respiratory secretions.
Chitra Acrylosorb Secretion Solidification System
- It is a highly efficient superabsorbent material for liquid respiratory and other body fluid solidification and disinfection.
- AcryloSorb can absorb liquids at least 20 times more than its dry weight and also contains a decontaminant for in situ disinfection.
- Containers filled with this material will immobilize the contaminated fluid by solidifying it (gel-like), thus avoiding spillage and will also disinfect it.
- The canister containing the solidified waste canister can then be decomposed as all other biomedical waste by incineration.
How it works?
- In the developed system, suction canisters, disposable spit bags have been designed with “AcryloSorb” technology.
- They are lined inside with the AcryloSorb material.
- The AcryloSorb suction canisters will collect the liquid respiratory secretions from ICU patients or those with copious secretions treated in the wards.
- The container will be spill-proof and can be sealed after use, making it safe and fit for disposal through the usual incineration system for biomedical wastes.
Significance of Acrylosorb
- Sealable and disposable spit bags can be provided for solidifying the sputum and saliva of ambulant patients with respiratory infections, which can then be incinerated.
- Thus it reduces the risk for the hospital staff, the need for personnel for disinfecting and cleaning the bottles and canisters for reusing them and makes the disposal safer and easier.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Man versus microbe
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Techniques used for detecting virus: RT-PCR, CRISPR and serological tests.
Mains level: Paper 3- Various techniques used in tests used to detect Covid-19 and their advantages.
Context
The present COVID-19 outbreak has brought to light the old struggle between humans and viruses.
The constant struggle between humans and viruses
- Hijacking the cell machinery of the host: Microbes, particularly viruses, have only one goal — to find a suitable host and multiply. Viruses, however, do not multiply by themselves. They need the cell machinery of the host for replication.
- Around two-thirds of all infections in humans are caused by viruses.
- The current COVID-19 outbreak caused by a coronavirus, SARS-CoV2, has brought this struggle to light once again.
- Coronavirus has the upper hand now: The virus seems highly successful because it spreads rapidly from human to human and has a lower rate of mortality.
- Humans have faced new viruses at regular intervals. These include the Ebola, Zika, HIV, the Flu virus H1N1, the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) — the latter two are from the coronavirus family.
- Animal to humans: These viruses have all appeared in the last few decades, having jumped from their animal reservoirs to humans.
- Many of these viruses have a much higher mortality rate than the SARS-CoV2 that caused COVID-19.
- Victory would be at huge costs: Like before, humans will come out of the present crisis as winners but that will happen at a huge cost, in every sense of the word.
- The loss would include untimely loss of human lives, economic losses and a general loss of confidence in the human ability to deal with a tiny unknown enemy.
Steps involved in dealing with the virus
- It involves dealing with any new viral outbreak is to be able to accurately test, detect and track the spread of the virus, and isolate the infected persons to stop further spread.
- Knowing the genetic makeup of virus matters: In order to implement the first step, it is important to obtain information on the genetic makeup of the virus, which forms the basis of developing highly specific diagnostic tests.
- Three types of tests are being used which have different advantages associated with them and are based on different technologies. These are described below-
1. What is the RT-PCR technique?
- Currently, the most reliable and widely-used test is based on a technique called RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription Time Polymerase Chain Reaction).
- This test aims to detect the viral RNA, the genetic material of SARS-CoV2.
- The testing begins with the careful collection of swabs taken from the nose or the back of the throat of the patient and extraction of the viral RNA.
- However, this extracted viral RNA from the swab is too tiny an amount for direct detection.
- Amplification: The RT-PCR, through many different reactions that include the conversion of viral RNA to DNA — its amplification and detection — makes it possible to confirm the presence or absence of the virus.
- The testing kits contain all chemicals and materials required for carrying out the RT-PCR based tests, which are performed by government-approved laboratories such as India’s National Institute of Virology.
- However, many more testing centres, including those run by private players, have now been allowed to carry out the tests in many countries to bridge the huge demand and supply gap.
- Why testing matters? It is now clear that countries which were able to scale up the testing of the virus in patients at an early stage were able to control the spread of the disease far better than those which did not.
- Only viable control measure: Given that there is no cure or vaccine for the control of COVID-19, testing of infected patients much more quickly and tracking their contacts to isolate them till they clear off the virus is currently the only viable control measure.
2. How CRISPR is proving helpful in scaling up the testing?
- There is good news of a relatively new but powerful technology called CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats).
- CRISPR is highly specific in directly detecting viral RNA and confirming the presence or absence of the virus.
- Interestingly, viruses also attack bacteria and the discovery of CRISPR itself was based on understanding how bacteria cut off the viruses.
- What are the advantages of CRISPR-based test? The CRISPR-based test is quick and circumvents the need for both expert handling as well as PCR machines and can be done at multiple locations in about half an hour.
- It can also fend off delays and other logistic problems in collection and transportation of test samples.
- These tests are being validated and readied for approval.
- Two companies, separately founded by the two scientists who discovered the CRISPR technique, have also announced that they are ready with their CRISPR-based test for validation and approval.
- Test in 10 minutes: They have claimed that these tests can be performed within 10 minutes and can be conducted by using a paper strip format.
- Test in 5 minutes: Another company, Abbott Laboratories, has recently announced the approval of their portable test for coronavirus, which the company claims can provide the results in five minutes.
- Such a point of care test will not only greatly enhance the speed of large-scale testing but will also relieve the tremendous pressure faced by frontline healthcare providers.
3. Serological tests to detect the realistic information on the spread of the virus
- Why we need serological tests? The above described RT-PCR and the newly developed CRISPR based tests are needed for scaling up the testing.
- But many individuals infected with the virus do not show symptoms of the disease and recover completely.
- How to test these cases to gather realistic information on the spread of the virus?
- Such information will be necessary for designing future control strategies.
- How serological tests work? This is done with serological tests, which are carried out in blood samples collected from a large population and are based on the detection of antibodies that are produced in response to the viral infection.
- Advantage of the serological tests: These tests are relatively easier to develop and use, less expensive, and also do not need much sophisticated infrastructure or highly trained manpower.
- Serological tests for COVID-19 have already been developed by many groups and are already in use.
- India also plans to carry out serological tests to examine the actual spread of the disease in different parts of the country.
Conclusion
Lockdowns are essential to control the disease but long-term strategies to deal with the disease would be based on the knowledge of its actual spread. The newly-developed point of care tests should be successfully able to bridge the existing gap in the testing of the virus. This will also assist in gearing up facilities to treat the severely sick as well as relieve and protect frontline health providers. Meanwhile, hopefully, efficient drugs therapies and efficacious vaccines against COVID-19 will also be discovered soon.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
The race to find a cure for COVID-19
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Vaccine development and trials.
Context
The world is dealing with an unprecedented and unimaginably serious crisis. Therefore, the speed of vaccine development is crucial.
Speeding up the vaccine development
- Availability of rationale and information: The race for developing an anti-COVID-19 vaccine has begun. Reasonable scientific rationale and the information needed for vaccine development are available to all stakeholders in academia and industry.
- Vaccine platforms: A large number of candidate vaccines based on different vaccine platforms, including delivering the virus genetic materials (RNA, DNA) or using synthetic biology to produce key viral proteins, have already been developed.
- Phase-I safety trials of an experimental vaccine, jointly developed by scientists at the National Institute of Health and at Moderna, a biotechnology company, has already been administered to healthy volunteers for its safety and immunogenicity.
- The speed with which the experimental vaccine has entered safety trials is unprecedented.
- Another vaccine jointly developed by China’s Academy of Military Medical Sciences and CanSino Biologics has reportedly been cleared for early-stage clinical trials.
- Development in India: The Serum Institute of India has also recently announced its readiness to start safety trials following animal experiments.
- According to a World Health Organization (WHO) report, more than 20 vaccine candidates are in advanced stages of development and will be ready for Phase-I safety trials.
- However, it is also clear that it will not be possible to roll-out any efficacious vaccine for at least another year.
Questions that need to be answered
- While these developments are encouraging, several questions will need to be answered for this vaccine development to move further.
- Triggering immune response safely: Although it is quite evident that humans mount a strong immune response and clear the viral load, the nature of the immune response and how to trigger it safely through vaccination will be key questions to address.
- Duration of the acquired immunity: How long the acquired immunity in humans will last is another important question to be asked before experimental vaccines move forward.
- We will need to know this because if the immunity is transient, then humans will be susceptible to reinfections.
- Ensuring no disease enhancement: Before moving to Phase-II trials in a large number of healthy volunteers, we also have to ensure that the immune response induced by vaccination does not lead to any disease enhancement.
Repurposing the already available drugs
- Therapeutic interventions, not only for curing severe cases of the disease but also for protecting all front-line healthcare workers, are urgently needed.
- Using already approved drugs: Since developing new drugs is a complex and lengthy process, scientists and pharmaceutical companies have rushed to investigate and use drugs that have already been approved by regulatory authorities.
- Using available molecular and structural biology information on the virus, a group of scientists have analysed all interactions of the viral proteins with human proteins that are crucial for the virus to enter human cells and use the host cell machinery to rapidly reproduce itself.
- Of the nearly 70 short-listed molecules that may interrupt these key interactions, 24 happen to be already approved drugs which can now be tested in laboratory animal models as well as humans.
- However, the re-purposing of several drugs, alone or in combinations to treat COVID-19 patients, have already been reported.
- More confusion than hope: There are many success stories of curing patients of COVID-19 doing the rounds in different parts of the world, but these have managed to create more confusion than hope.
- Without any appropriate controls, careful dosing and safety concerns, such small experiments can only do more harm than good.
Controlled randomised trials
- Given the urgency of finding a cure, it is absolutely necessary to find out unequivocally what works well and what does not. For that conducting carefully controlled randomised trials is the only way to go.
- In a welcome move, the WHO has announced clinical trials called the ‘Solidarity Project’.
- Under this project four drugs or drug, combinations will be tested in many countries around the world.
- These candidates include the anti-Ebola drug, Remdesivir, Chloroquine, anti-HIV drugs, and the Ritonavir/Lopinavir combination, with or without Interferon-beta.
- The European counterpart of the trial, Discovery, will conduct these trials in countries including France, Spain, Germany and the U.K.
- The pharma company Roche has also decided to initiate large, randomised Phase-III trials of its arthritis drug Actemra for its safety and efficacy in adult patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia.
- It is complex and tedious to conduct randomised, large multi-centric trials.
- Quickly getting all the stakeholders together is laudable and underscores the notion that everyone needs to fight the deadly virus together. Hopefully, these trials will lead to tangible drug therapies against COVID-19.
Conclusion
It is most heartening to see scientists in academia and industrial partners coming together to fight a monumental public health crisis. The battle between pathogens and humans will continue but let us hope that we win the present one sooner than later.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] How lipids play critical roles in infectious diseases
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Lipids, Non-polar compounds
Mains level: Not Much
A researcher from IIT Bombay is using biologically active lipid molecules as chemical biology tools to elucidate their biological disease-causing function.
About the research
- The research is focused to explore how lipids play critical roles in infectious diseases by intervening in cellular signaling, membrane trafficking, and protein function all of which are intimately involved in host-pathogen interplay.
- The research works with lipids from Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb), which synthesizes atypical lipids predisposed on its surface to interact with the human host membrane.
- Using Mtb lipids as tools, the research elucidates a direct correlation between human host lipid membrane modification and modulation of associated signaling pathways by these exogenous Mtb lipids.
What are Lipids?
- A lipid is a biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- Non-polar solvents are typically hydrocarbons used to dissolve other naturally occurring hydrocarbon lipid molecules that do not (or do not easily) dissolve in water, including fatty acids, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, and phospholipids.
- The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes.
- Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries as well as in nanotechnology.
Role of Lipids
- Lipids are important components of living cells and are responsible for maintaining the integrity of our cell membrane, which allows nutrients and drugs to pass through the cell.
- These are commonly breached during infection and in diseases.
- Lipids play a major role in altering cell membrane properties modulating lipid and protein diffusion and membrane organization.
- Thus, changes in membrane properties control the proper functioning of cells and are harnessed by pathogens for their survival and infection.
- Lipids critically dictate the molecular interactions of drugs with membranes influencing drug diffusion, partitioning, and accumulation, thereby underpinning lipid-composition specificity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Role of Glucose in Regulating Liver Functions
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SIRT1
Mains level: NA
A study by researchers from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Mumbai (TIFR) has revealed that glucose in the body controls the function of SIRT1 enzymes directly.
What is SIRT1?
- SIRT1 is an enzyme that deacetylates (removal of acetyl) proteins which contribute to cellular regulation.
- A shortage or absence of the control by glucose may lead to a diabetic-like state, while excess feeding and sustained low levels of SIRT1 can lead to obesity and enhanced ageing.
- This information is expected to tackle lifestyle disorders and ageing-related diseases.
How do they function?
- In normal healthy individuals, SIRT1 protein levels are known to increase during fasting and decrease during the feed, which is essential to maintain a balance between glucose and fat metabolism.
- The glucose controls the functions of a protein SIRT1 which in turn maintains everyday feed-fast cycles and is also associated with longevity.
- The feed-fast cycle is a basic pattern and the metabolism-related to this is largely taken care of by the liver.
- Thus, the study shows that both over-activation and under-activation of SIRT1 can lead to diseases.
- Glucose puts a check on the activity of SIRT1 in the fed state. In the absence of this check, SIRT1 activity increases and results in hyperglycemia in a fasted state, mimicking diabetic state.
- The constant feeding or high-calorie intake that leads to a sustained reduction in the levels of SIRT1 by glucose which is associated with ageing and obesity.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] ARI-516 Grape Variety
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: ARI-516
Mains level: Not Much
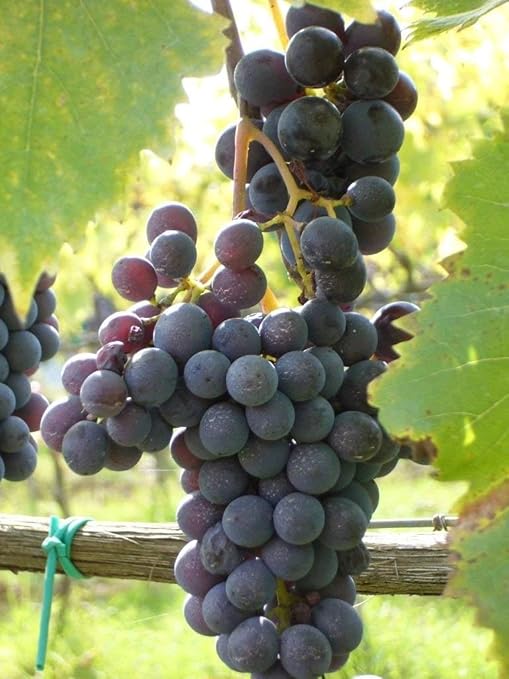

Pune’s Agharkar Research Institute (ARI), an autonomous institute of the DST has developed a hybrid variety of grapes which is resistant to fungal diseases, high yielding and has excellent juice quality.
ARI-516
- The hybrid variety ARI-516 has been developed by interbreeding of two species from the same genus — Catawba variety of Vitis labrusca and Beauty seedless variety of Vitis vinifera.
- It is a result of collaboration between Maharashtra Association for the Cultivation of Science (MACS) and ARCI and can benefit farmers, the processing industry and consumers.
- This variety of grapes is resistant to fungal diseases, high yielding and has excellent juice quality.
- The fungal resistance of ARI-516 has been derived from Catawba, which is an American grape variety.
Commercial benefits
- It is also suitable for preparation of juice, raisin, jam and red wine and farmers are enthusiastically adopting the variety.
- It has superior quality fruits and higher yield per unit area.
- An early ripening hybrid, it matures in 110 – 120 days after pruning.
- Being moderately resistant to a majority of fungal diseases, its cost of production is lower.
Back2Basics
Grape production in India
- India ranks twelfth in the world in terms of grape production.
- About 78% of grape production in India is utilized for consumption, 17-20 % for raisin production, 1.5 % for wine and 0.5 % for juice.
- Maharashtra leads in the production of grapes in India with a share of 81.22 %. A negligible share of grapes is used for juice production.
- A majority of farmers in Maharashtra cultivate ‘Thompson seedless’ and its clones for table purpose or raisin making.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
How plants dissipate excess sunlight as heat?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: Not Much

Photosynthesis is a life-sustaining process by which plants store solar energy as sugar molecules. However if sunlight is in excess it can lead to leaves being dehydrated and damaged.
What is Photosynthesis?
- Photosynthesis is the process used by plants, algae and certain bacteria to harness energy from sunlight and turn it into chemical energy.
- There are two types of photosynthetic processes: oxygenic photosynthesis and anoxygenic photosynthesis.
- The general principles of anoxygenic and oxygenic photosynthesis are very similar, but oxygenic photosynthesis is the most common and is seen in plants, algae and cyanobacteria.
- During oxygenic photosynthesis, light energy transfers electrons from water (H2O) to carbon dioxide (CO2), to produce carbohydrates.
- Ultimately, oxygen is produced along with carbohydrates. Oxygenic photosynthesis is written as follows:
6CO2 + 12H2O + Light Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Here, six molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) combine with 12 molecules of water (H2O) using light energy. The end result is the formation of a single carbohydrate molecule (C6H12O6, or glucose) along with six molecules each of breathable oxygen and water.
How do plants dissipate heat?
- To prevent such damage, plants dissipate extra light as heat.
- While this was known there has been a debate over the past several decades over how plants actually do so.
- Now for the first time researchers have directly observed one of the possible mechanisms through which plants dissipate extra sunlight.
- The new research has been able to determine–by using a highly sensitive type of spectroscopy–that excess energy is transferred from the pigment chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green colour, to other pigments called carotenoids.
- The carotenoids then release the energy as heat. After the carotenoids accept excess energy, most of it is released as heat, thus preventing damage to the cells.
Why does plant dissipate light?
- During photosynthesis, light-harvesting complexes play two seemingly contradictory roles.
- They absorb energy to drive water-splitting and photosynthesis, but at the same time, when there’s too much energy, they have to also be able to get rid of it.
- Plants quickly adapt to changes in sunlight intensity. Even in very sunny conditions, only 30 per cent available sunlight is converted into sugar, and the rest is released as heat.
- The excess energy, if not released, leads to the creation of free radicals that can damage proteins and other important cellular molecules.
Significance of the research
- So far, it had been difficult to observe the heat dissipation phenomenon, given that it occurs on a very fast time scale, in femtoseconds or quadrillionths of a second.
- Using the new technique, researchers could observe that chlorophylls absorb red light and carotenoids absorb blue and green light, thus being able to monitor energy transfer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Unguarded X hypothesis
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Unguarded X hypothesis, Chromosomes
Mains level: NA
Men outnumbered women by 37 million in the 2011 Census of India, but among those over the age of 60, there were more than 1 million more women than men. In general, men live shorter lives than women worldwide. This is due to the chromosomal differences between the two, points’ new study.
What are Chromosomes?
- The human body is made up of cells, and in the centre of each cell is the nucleus. Chromosomes, which are located inside the nucleus, are structures that hold the genes.
- It is the genes that determine the various traits of an individual including eye colour, blood type — and sex.
- The human cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes. One pair is of the sex chromosomes, named X and Y, which determine whether an individual is male or female.
- A female has two X chromosomes (XX) while a male has one X and one Y (XY).
Unguarded X hypothesis
- This hypothesis suggests that the Y chromosome in XY is less able to to protect an individual from harmful genes expressed on the X chromosome.
- In a male, as the Y chromosome is smaller than the X chromosome, it is unable to “hide” an X chromosome that carries harmful mutations, which may later expose the individual to health threats.
- On the other hand, the hypothesis goes, there is no such problem in a pair of X chromosomes (XX) in a female.
- If one of the X chromosomes has genes that have suffered mutations, then the other X chromosome, which is healthy, can stand in for the first, so that the harmful genes are not expressed.
- This maximizes the length of life, according to the hypothesis. And this is what the UNSW researchers set out to examine.
Testing the hypothesis
- In a statement issued by UNSW, PhD student and study first author Zoe Xirocostas said the
- Unguarded X hypothesis appears to stack up, after examining the lifespan data available on a wide range of animal species.
- Researchers studied lifespan data in not just primates but mammals and birds, but also reptiles, fish, amphibians, arachnids, cockroaches, grasshoppers, beetles, butterflies and moths among others.
- It was found that across that broad range of species, the heterogametic sex (XY in humans) does tend to die earlier than the homogametic sex (XX in humans).
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
[pib] CHITRA Flow Diverter Stents
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CHITRA stents
Mains level: Affordable medical devices and implants in India

The Sree Chitra Thirunal Institute of Medical Science and Tech. Thiruvanthapuram an Institute of National Importance under the Department of Science and Technology has developed an innovative intracranial flow diverter stent for the treatment of aneurysms of the blood vessels of the brain.
What is Aneurysms?
- Intracranial aneurysm is a localized ballooning, bulging or dilation of arteries in the brain caused by progressive weakening of the inner muscles of the wall of the blood vessels.
- Spontaneous rupture of the aneurysm can result in bleeding into the space around the brain resulting condition called a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) which can lead to paralysis, coma or death.
- Most often a ruptured brain aneurysm occurs in the space between the brain and the thin tissues covering the brain.
How to avert risks of Brain Aneurysms?
- Flow diverters stents when deployed in the artery in the brain bearing the aneurysms, diverts blood flow away from the aneurysm.
- This reduces the chances of its rupture from the pressure of blood flow.
- The Surgical treatment of an aneurysm involves opening the skull and a clip on the neck of aneurysm, so that it is cut off from the path of blood flow.
- There are three non surgical, minimally invasive endovascular treatments of aneurysms of the brain.
- In two of these procedures, the aneurismal sacis filled with platinum coils or occluded using high viscosity liquid polymer which solidifies when released into the sac thus sealing the sac.
- All these techniques have some limitation or the other.
Why are flow diverter stent preferable?
- A more attractive third minimally invasive option is deploying a flow diverter stent to bypass the segment of the blood vessel which has the aneurysm.
- Flow diverters have the advantages of being flexible and adaptable to the shape and course of the vessel.
- Also flow diverters promote healing of the vessel wall by removing the constant stress of blood flow on it.
What is CHITRA flow diverter?
- The Chitra flow diverter is designed to have better grip on the walls of arteries of complex shapes in order to reduce the risk of migration of the device.
- The unique design is in its weave also makes this stent resistant to kinking or twisting, when it is placed in tortuous arteries and those with complex shapes. Even a 180 degrees bend does not occlude the lumen of the stent.
- Portion of the wires is made radio opaque for better visibility in X –Rays and fluoroscopy thus aiding accurate delivery of the diverter in the blood vessel.
- Nitinol, a super elastic alloy with shape memory was acquired from National Aero Space Laboratories, Bengaluru (CSIR-NAL).
- When the device is deployed at the site, it is released from its crimped locked position and assumes the desired and originally designed shape because of the shape memory property of Nitinol.
Benefits of CHITRA
- The imported Flow diverter stents costs Rs 7-8 lakhs and is not manufactured in India.
- With the availability of the indigenous CHITRA, a well established industry would be able to manufacture and sell at a much lower price.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Species in news: Henneguya Salminicola
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Henneguya Salminicola
Mains level: NA
Researchers at Tel Aviv University have discovered a non-oxygen breathing animal, which significantly changes one of science’s assumptions about the animal world — that all animals use aerobic respiration and therefore, oxygen.
Henneguya Salminicola
- The organism is Henneguya salminicola, a fewer-than-10-celled microscopic parasite that lives in salmon muscle.
- It relies on anaerobic respiration (through which cells extract energy without using oxygen).
- In the case of this non-oxygen breathing organism, evolution turned it into a simpler organism that shed “unnecessary genes” responsible for aerobic respiration.
- Other organisms such as fungi and amoebas that are found in anaerobic environments lost the ability to breathe over time.
- The new study shows that the same can happen in the case of animals, too.
What is Aerobic respiration?
- Animals, including humans, need energy to perform the various tasks that are essential for survival.
- Aerobic respiration is one such chemical reaction through which organisms take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Through this mechanism, energy is transferred to cells, which can use it for multiple purposes — for instance, to burn food.
- Mitochondria is the “powerhouse” of the cell, which captures oxygen to make energy — its absence in the H. salminicola genome indicates that the parasite does not breathe oxygen.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Genome India Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Genome India Project
Mains level: Applications of Gene mapping
The Union Govt. has given clearance to an ambitious gene-mapping project, estimated to be worth Rs 238 crore.
Genome India Project
- The Genome India Project has been described by those involved as the “first scratching of the surface of the vast genetic diversity of India”.
- It involves over 20 scientists from institutions including the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in Bengaluru and a few IITs.
- One of the most comprehensive genome mapping projects in the world is the Human Genome Project (HGP), which began in 1990 and reached completion in 2003.
- The international project, which was coordinated by the National Institutes of Health and the US Department of Energy, was undertaken with the aim of sequencing the human genome and identifying the genes that contain it.
- The project was able to identify the locations of many human genes and provide information about their structure and organisation.
What is Genome Mapping?
- According to the Human Genome Project, there are estimated to be over 20,500 human genes.
- Genome refers to an organism’s complete set of DNA, which includes all its genes and mapping these genes simply means finding out the location of these genes in a chromosome.
- In humans, each cell consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes, which means that for 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell, there are roughly 20,500 genes located on them.
- Some of the genes are lined up in a row on each chromosome, while others are lined up quite close to one another and this arrangement might affect the way they are inherited.
- For example, if the genes are placed sufficiently close together, there is a probability that they get inherited as a pair.
- Genome mapping, therefore, essentially means figuring out the location of a specific gene on a particular region of the chromosome and also determining the location of and relative distances between other genes on that chromosome.
Applications
- Significantly, genome mapping enables scientists to gather evidence if a disease transmitted from the parent to the child is linked to one or more genes.
- Furthermore, mapping also helps in determining the particular chromosome which contains that gene and the location of that gene in the chromosome.
- Genome maps have been used to find out genes that are responsible for relatively rare, single-gene inherited disorders such as cystic fibrosis and Duchene muscular dystrophy.
- Genetic maps may also point out scientists to the genes that play a role in more common disorders and diseases such as asthma, cancer and heart disease among others.
- Researchers from several international institutions mapped the handful of genes whose mutation causes several different kinds of cancers.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
New rice variety: Muktoshri (IET 21845)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Muktoshri
Mains level: Arsenic poisoning through food, Rice Fortification
Researchers have developed and commercialized a rice variety that is resistant to arsenic.
Muktoshri
- The new rice variety, Muktoshri — also called IET 21845 —, was developed jointly by the Rice Research Station at Chinsurah coming under West Bengal’s Agriculture Department and the National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow.
- A gazette notification for the commercial use of Muktoshri was made by West Bengal last year.
- During our multilocational trials, it was found that this variety uptakes very less amount of arsenic from soil and water in comparison to other varieties of rice.
- The rice is long and thin, and aromatic. Across the State, thousands of farmers have started cultivation, even in areas where arsenic in groundwater is not an issue, because of the aroma and the yield.
Significance
- West Bengal is among the States with the highest concentration of arsenic in groundwater, with as many as 83 blocks across seven districts having higher arsenic levels than permissible limits.
- Several studies have shown that arsenic from groundwater and the soil can enter the food chain through paddy.
- According to the WHO, long-term exposure to arsenic, mainly through drinking water and food, can lead to poisoning. Skin lesions and skin cancer are the most characteristic effects.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
What is Fermentophone?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fermentophone
Mains level: NA

Fermentation, the chemical breakdown of a substance by microorganisms such as bacteria or yeasts, results in some of the most delicious foods and beverages, including cheese, chocolate and wine. Now, research has shown it can result in music, too.
Fermentophone
- The chemical processes of fermentation can be used to create spontaneous tunes.
- Researchers has built multiple art exhibits called Fermentophone to showcase how fermentation can make music.
- First, different fruits and veggies are placed in glass jars and fermented.
- As the fermentation kicks off, the yeast — or bacteria — present in the food chows down on the foods’ sugars, which results in the release of carbon dioxide bubbles.
- The release of these bubbles creates a tiny sound, which is picked up by underwater microphones.
- A computer processes the sounds and, with the help of algorithms plugged in, electronic music is created.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Cancer Gene Mapping
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mutation, Gene mapping
Mains level: Rising incidences of cancer in India and its prevention

A series of new papers in the journal Nature has revealed the most comprehensive gene map ever of the genes causing cancer. It shows departures from normal behaviour i.e. mutations trigger a cascade of genetic misbehaviours that eventually lead to cancer.
What is Mutation?
- A mutation is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors such as UV light and pollution etc.
- Structural variations mean deletion, amplification or reorganization of genomic segments that range in size from just a few bases to whole chromosomes.
- Bases are the structural units of genes.
- Over a lifetime our DNA can undergo changes or ‘mutations’ in the sequence of bases A, C, G and T.
Why study cancer?
- Cancer is known to be a disease of uncontrolled growth.
- The growth process, like all other physiological processes, has genetic controls so that the growth is self-limiting. When one or more genes malfunction, the growth process can go out of hand.
- Not just cancer, there are many other diseases with a genetic link in varying degrees.
- Just a handful of “driver” mutations could explain the occurrence of a large number of cancers, the researchers said, raising hopes of a cancer cure being nearer than ever.
How big is the cancer burden?
- Cancer is the second most-frequent cause of death worldwide, killing more than 8 million people every year; incidence of cancer is expected to increase by more than 50% over the coming decades.
- 1 in 10 Indians will develop cancer during their lifetime, and one in 15 Indians will die of cancer, according to the World Cancer Report by WHO.
- The Northeastern states, UP, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Haryana, Gujarat, Kerala, Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh account for 44% of the cancer burden in India, says a recent analysis, published in The Lancet.
Is the genetic link to cancer well established?
- Yes, it is. One such association, for example, is of breast cancer with the BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes; the actress Angelina Jolie, who discovered that she carried the former gene, chose to undergo a preventive double mastectomy.
- This is personalised therapeutics where, instead of traditional toxic medications like chemotherapy, drugs that specifically target the delinquent genetic mutation are already being used.
- Such therapy, however, remains very expensive.
What is the new study that has oncologists around the world excited?
- It is a major international collaboration called the Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG), in which researchers has published a series of papers after analysing some whole-cancer genomes and their matching normal tissues across 38 tumor types.
- They concluded that on average, cancer genomes contained 4-5 driver mutations when combining coding and non-coding genomic elements.
- This is the largest genome study ever of primary cancer.
- Various kinds of cancers required to be studied separately because cancers of different parts of the body often behave very differently from one another; so much so that it is often said that cancer is not one disease but many.
Breakthrough achievement of the study
- The mutations identified by the team have been catalogued. Identification and cataloguing of the genes is a very crucial step and has taken science’s understanding of cancer and its genesis ahead by several leaps.
- The catalogue, which is already available online, allows doctors and researchers from all over the world to look things up, consult and find information about the cancer of a given patient.
- The study has discovered causes of previously unexplained cancers, pinpointed cancer-causing events and zeroed in on mechanisms of development, opening new vistas of personalized cancer treatment to strike at the root of the problem.
- When it comes to drug development, however, the gene mapping is but a first step.
The next step
- The process of drug development will have to now kick in with pharmaceutical companies first identifying the compound(s) that target these gene mutations and then it being subjected to the rigours of clinical trials to prove its safety and efficacy.
- That could take anything from a few decades to a few years to cover all the mutations identified.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Species in news: Natrialba Swarupiae
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Natrialba Swarupiae, Sambhar Lake
Mains level: Not Much
- Scientists at the National Centre for Microbial Resource — National Centre for Cell Science (NCMR-NCCS) in Pune have reported a new archaeon (a kind of microorganism), which they discovered in Sambhar Salt Lake in Rajasthan.
- The new archaeon has been named Natrialba swarupiae, after Dr Renu Swarup, secretary, Department of Biotechnology, for her initiative in supporting microbial diversity studies in the country.
Archaea
- Archaea (singular archaeon) are a primitive group of microorganisms that thrive in extreme habitats such as hot springs, cold deserts and hypersaline lakes.
- These slow-growing organisms are also present in the human gut, and have a potential relationship with human health.
- They are known for producing antimicrobial molecules, and for anti-oxidant activity with applications in eco-friendly waste-water treatment.
- Archaea are extremely difficult to culture due to challenges in providing natural conditions in a laboratory setting.
- As archaea are relatively poorly studied, very little is known about how archaea behave in the human body.
- The organism has potential gene clusters that helps maintain the metabolism of the archaea to survive in extreme harsh conditions.
Search and discovery
- Sambhar Lake has been poorly studied for microbial ecology studies.
- With a salt production of 0.2 million tonnes per annum, it is also a hypersaline ecosystem which provides an opportunity for microbial ecologists to understand organisms that thrive in such concentrations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
IVF of White Rhinos
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: In-vitro fertilization, White Rhinos
Mains level: Ethical issues surrounding IVF
Researchers had created another embryo — the third — of the nearly extinct northern white rhino. This is seen as a remarkable success in an ongoing global mission to keep the species from going extinct.
What is IVF?
- IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment and gestational surrogacy.
- A fertilised egg may be implanted into a surrogate’s uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate.
- Some countries have banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism.
- Restrictions on the availability of IVF include costs and age, in order for a woman to carry a healthy pregnancy to term.
- IVF is generally not used until less invasive or expensive options have failed or been determined unlikely to work.
IVF process
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro (“in glass”).
- The process involves monitoring and stimulating a female ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the female ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a liquid in a laboratory.
- After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is implanted in the same or another female uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
Types of Rhinos
- The northern white is one of the two subspecies of the white (or square-lipped) rhinoceros, which once roamed several African countries south of the Sahara.
- The other subspecies, the southern white is, by contrast, the most numerous subspecies of rhino, and is found primarily in South Africa.
- There is also the black (or hook-lipped) rhinoceros in Africa, which too, is fighting for survival, and at least three of whose subspecies are already extinct.
- The Indian rhinoceros is different from its African cousins, most prominently in that it has only one horn.
- There is also a Javan rhino, which too, has one horn, and a Sumatran rhino which, like the African rhinos, has two horns.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Innovations in Biotechnology and Medical Sciences
Genome Sequencing of Cobra Venom
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Antivenom
Mains level: Genome sequencing and its applications
This week, an international team of researchers reported that they have sequenced the genome of the Indian cobra, in the process identifying the genes that define its venom. This has provided a blueprint for developing more effective antivenom.
Big four in Snake bites
- India alone accounts for about 50,000 deaths annually, and these are primarily attributed to the “big four”.
- The challenge has been producing antivenom for the species known collectively as the “big four” — the Indian cobra (Naja naja), common krait (Bungarus caeruleus), Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii), and saw-scaled viper (Echis carinatus).
- In India, common antivenom is marketed for the treatment of bites from the “big four”, but its effectiveness is questionable.
- While the common antivenom worked as marketed against the saw-scaled viper and the common cobra, it fell short against some neglected species and also against one of the “big four” — the common krait.
- Accidental contact with snakes leads to over 100,000 deaths across the world every year.
What is antivenom?
- Antivenom is currently produced by a century-old process — a small amount of venom is injected into a horse (or a sheep), which produces antibodies that are then collected and developed into antivenom.
- This is expensive, cumbersome and comes with complications. Some of the antibodies raised from the horse may be completely irrelevant.
Why has production of effective antivenom been challenging?
- Venom is a complex mixture of an estimated 140-odd protein or peptides.
- Only some of these constituents are toxins that cause the physiological symptoms seen after snakebite.
- But antivenom available today does not target these toxins specifically.
Issues with present antivenom
- The horse also has a lot of antibodies floating in its blood that have nothing to do with the venom toxins.
- One more problem with horse antibodies — our immune system recognises it as foreign and when antivenom is given our body mounts an antibody response. This leads to what is called serum sickness.
- Also, next time if one is unlucky and has a snakebite incident (even if it is a different snake) and they are given a horse-derived antivenom, the body is going to have a severe allergic reaction.
How does decoding the genome help?
- In the Indian cobra genome, the authors identified 19 key toxin genes, the only ones that should matter in snakebite treatment.
- They stress the need to leverage this knowledge for creation of antivenom using synthetic human antibodies.
- Targeting these 19 specific toxins using synthetic human antibodies should lead to a safe and effective antivenom for treating Indian cobra bites.
Back2Basics
Genome Sequencing
- Genome is an organism’s complete set of DNA, including all of its genes.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome—more than 3 billion DNA base pairs—is contained in all cells that have a nucleus.
- Genome sequencing is figuring out the order of DNA nucleotides, or bases, in a genome—the order of As, Cs, Gs, and Ts that make up an organism’s DNA.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024