Tobacco: The Silent Killer
[pib] Tobacco Board of India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tobacco Board, Tobacco Cultivation in India
Why in the News?
The Tobacco Board of India, established on January 1, 1976, under the Tobacco Board Act, 1975, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the growth and sustainability of the tobacco industry.
PYQ:[2008] Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
Code: A B C D (a) 2 4 3 1 (b) 1 3 4 2 (c) 2 3 4 1 (d) 1 4 3 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
Vasco da Gama’s toxic legacy is now a ‘pandemic’ that kills 8 million globally
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tobacoo industry in India
Mains level: CRISPR can reduce the impact of Tobacoo
Why in the news?
On July 8th, 1497, Vasco da Gama’s historic voyage began, reshaping global maritime routes and leaving a lasting impact on trade and culture. This era of exploration introduced and disseminated tobacco, profoundly affecting societies in numerous ways.
Cultivation and Production of Tobacco
- Historical Introduction: Tobacco was originally cultivated by Native Americans and brought to Europe in the 16th century. It was introduced to South Asia by European traders and colonizers, notably the Portuguese, Dutch, and British.
- Economic Significance: Tobacco is a drought-tolerant crop providing livelihoods to many. It accounts for about 2% of India’s agricultural exports and employs over 45 million people.
- Revenue Generation: The tobacco industry is a major source of revenue through taxation and exports, generating over ₹22,000 crores annually.
Implications on Human Health
- Health Issues: Tobacco use contributes to various cancers (lung, mouth, throat, oesophagus, pancreas, and bladder), respiratory diseases (COPD, emphysema, chronic bronchitis), cardiovascular problems (heart disease, stroke, hypertension), and other conditions like diabetes, infertility, weakened immune system, and complications in pregnancy.
- Addiction: Nicotine, a highly addictive substance in tobacco, alters brain function leading to severe addiction.
- Health Crisis: In India, tobacco use causes over 1.2 million deaths annually. It is responsible for 27% of all cancers and adds significant costs to healthcare and productivity losses, totaling approximately ₹1.82 trillion annually.
Ethical and Revenue Considerations
- Economic Benefits vs. Health Costs: While tobacco provides economic benefits and employment, it comes with tremendous human and financial costs due to tobacco-related illnesses.
- Constitutional Provisions: Under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution guarantees the right to life and health. The Directive Principles of State Policy mandate the state to improve public health and living standards.So,Govt. has responsibility to prevent tobacoo consumption.
Indian needs to Stack Up Its Priorities
- Institutional Conflict: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) focuses on eliminating tobacco to mitigate health impacts, while the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) aims to increase tobacco crop yields.
- Policy and Ethical Dilemma: The conflicting priorities between ICMR and ICAR create significant policy challenges. The constitutional mandate to prioritize public health should guide policy decisions.
Will CRISPR make a difference?
- Gene Editing Potential: CRISPR technology offers potential solutions by developing genetically modified tobacco plants with reduced nicotine content.
- Research Developments: Studies have shown promise in using CRISPR to significantly lower nicotine levels in tobacco plants. However, further characterization is needed to ensure these modifications do not negatively impact other important traits.
- Collaborative Efforts: Collaboration between ICMR and ICAR is crucial to align scientific advancements with public health goals and agricultural sustainability.
The Tobacco Lobby and Surrogate Advertising
- Circumventing Regulations: The tobacco industry employs surrogate advertising to promote its products despite stringent advertising bans. These tactics perpetuate tobacco consumption, especially among youth, undermining public health efforts.
- Aggressive Lobbying: The tobacco industry has a large network of 1,027 registered lobbyists at the state level in 2024, many of whom are former government employees. They engage in extensive lobbying to weaken, delay or block life-saving tobacco control measures.
Way forward:
- Implement Stricter Regulations: Enforce stringent regulations on tobacco advertising, including surrogate advertising, and ensure compliance through regular monitoring and penalties.
- Ban on Public Smoking: Implement and strictly enforce smoking bans in public places to reduce exposure to second-hand smoke.
Mains PYQ:
Q What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (UPSC IAS/2021)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
The Tobacco Epidemic in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Reports on Tobacco Consumption in India
Mains level: Implementing and Catching Up with Industry
Why in the News?
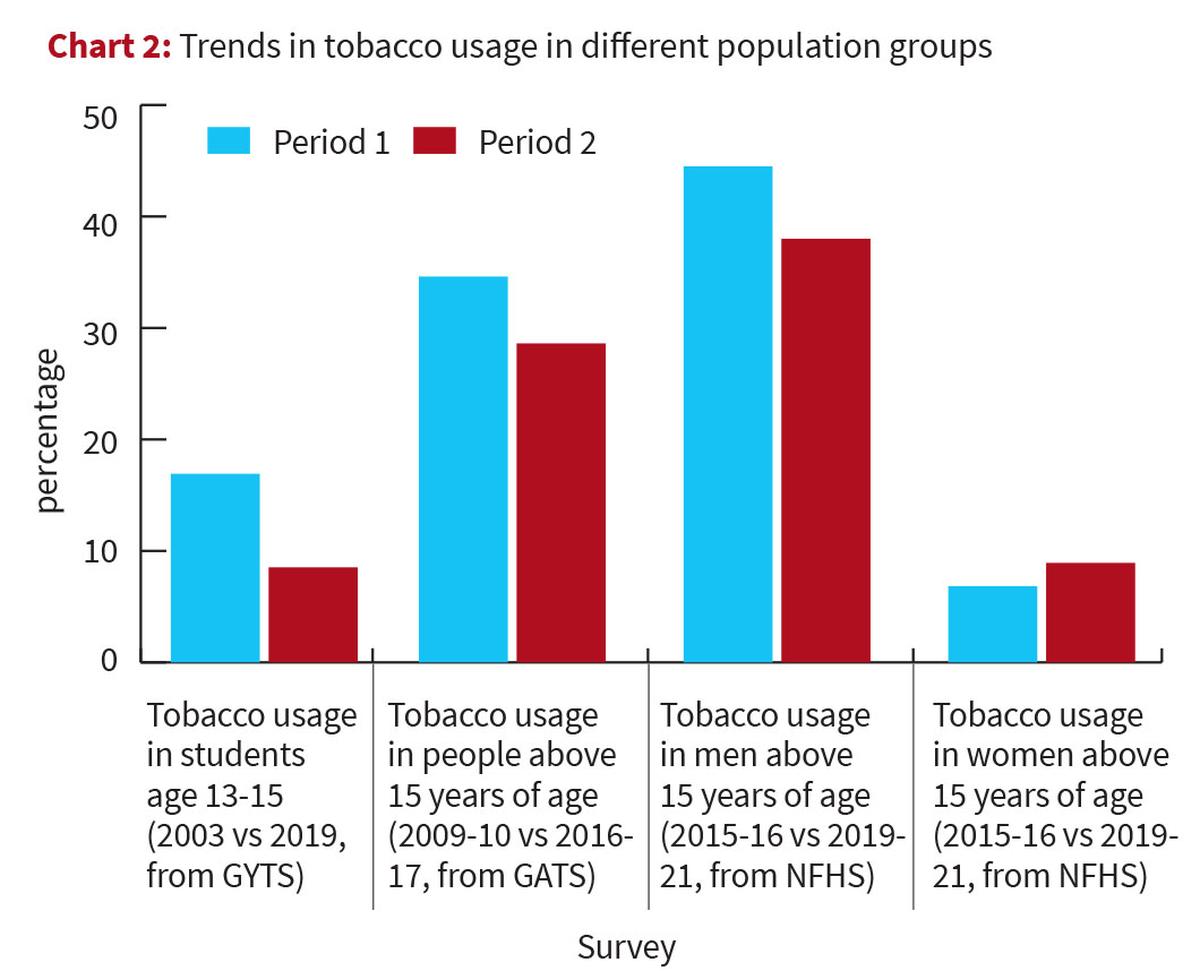
Tobacco is a leading preventable cause of disease which affects nearly 26 crore Indians and 60 lakh industry workers, posing significant health risks.
Reports on Tobacco Consumption in India
|
What is the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC)?
- The WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is an international treaty adopted by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2003. It is a legally binding treaty.
- It means that countries that have ratified it are obligated to implement the measures outlined in the convention within their national jurisdictions.
- It addresses the global health risks associated with tobacco use and provides a comprehensive framework for governments and organizations to implement effective tobacco control policies and strategies.
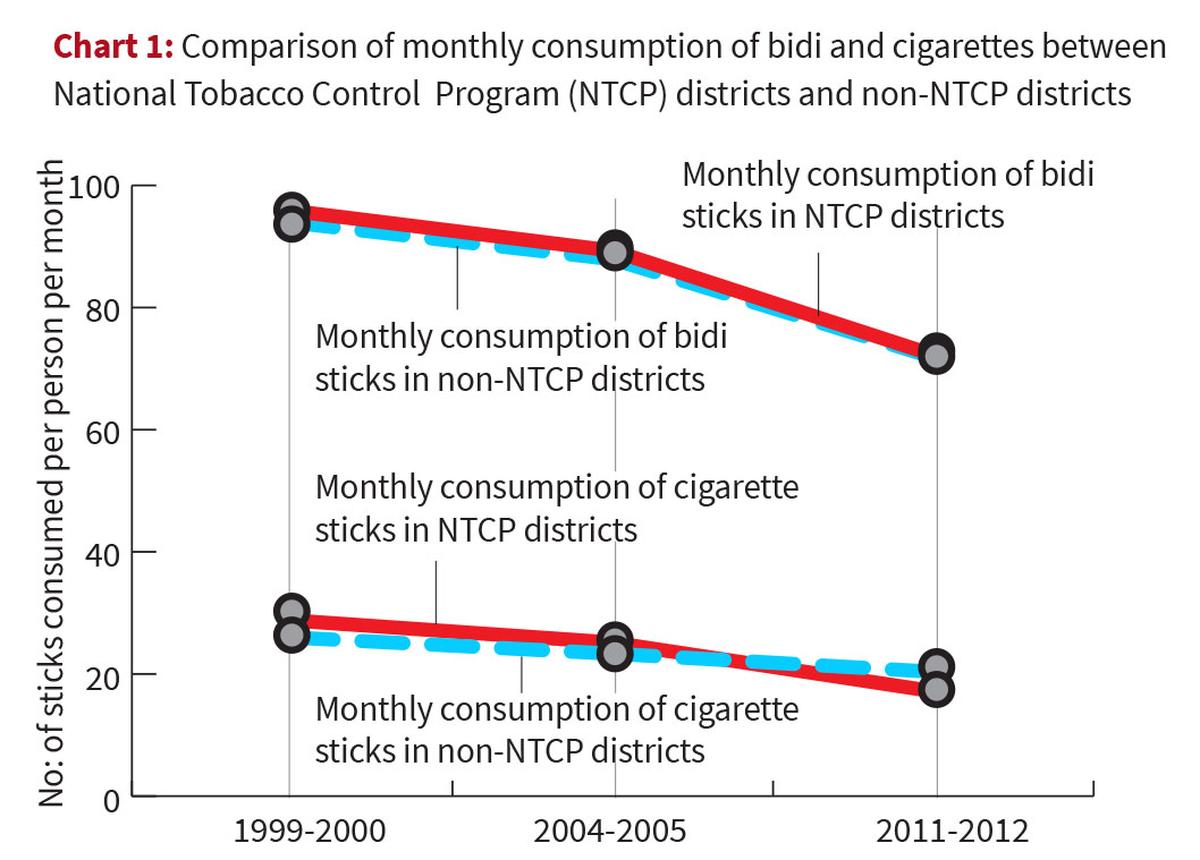
Challenges in India: Lobbying by the Tobacco Industry
- The tobacco industry exerts substantial influence on policy-making to maintain low tax rates and evade stricter regulations.
- Government Engagement: Both in-service and retired government officials often engage with the tobacco industry. Example: A retired Indian Administrative Services officer joined the board of Godfrey Phillips as an independent director.
- Government Stake: The Central government holds a 7.8% stake in ITC Ltd., India’s largest tobacco company.
- Tax Exemptions: Continuous exemptions of cess on bidis and smaller tobacco manufacturers. Persistent extensions of these exemptions despite the harmful effects of tobacco.
Tax Measures and Lobbying
|
- Thus, India’s score has worsened since 2021, indicating increased interference by the tobacco industry in governance.
Initiatives taken by the Government:
- Cigarette and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) 2003: It regulates the advertisement, promotion, and sponsorship of tobacco products, prohibits smoking in public places, mandates pictorial health warnings on tobacco product packaging, and sets rules for the sale of tobacco products to minors.
- Awareness on Media: India is the first country in the world to implement the larger steps through implementing warnings on OTT platform content when actors are seen using tobacco products.
- Awareness of Product: India has implemented prominent and graphic pictorial health warnings on tobacco product packaging.
Challenges in Implementation
- Poor Enforcement: Existing measures are not strictly implemented, leading to widespread non-compliance, especially among smokeless tobacco products (SLTs).
- Indirect Advertisements: Surrogate advertisements (e.g., using elaichi to promote tobacco brands) circumvent direct advertising bans, undermining control efforts.
- Inadequate Fines: Penalties for violations of COTPA regulations have not been updated since 2003, making them ineffective deterrents.
Way forward:
- Update COTPA Fines and Penalties: Revise and significantly increase fines for violations of COTPA regulations to create a stronger deterrent.
- Strengthen Border and Market Surveillance: Improve customs and market surveillance to combat smuggling and illicit trade of tobacco products.
Mains question for practice:
Q Discuss the various measures undertaken by the Indian government to control tobacco consumption. Evaluate the effectiveness of these measures and suggest improvements. 15M
Tobacco Board of India
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
In news: Tobacco Board
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tobacco Board, Tobacco Crop, Flue-cured Virginia (FCV) tobacco
Mains level: NA
Why in the news?
- The Tobacco Board has authorised a crop size of 100 million kg for Karnataka during the year 2024-25.
Tobacco in Indian Economy
|
About Tobacco Board
- The Tobacco Board was constituted as a Statutory Body on 1st January, 1976 under Section (4) of the Tobacco Board Act, 1975.
- It operates under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is headquartered in Guntur, Andhra Pradesh.
The primary objective of the Tobacco Board is-
- To promote the orderly development of the tobacco industry in India, particularly in the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu, which are the major tobacco-growing regions in the country.
Key Functions and Responsibilities
- Regulation and Control: The Tobacco Board regulates the production, curing, grading, and marketing of Virginia tobacco, which includes Flue-Cured Virginia (FCV) and Burley tobacco varieties.
- Licensing and Registration: It monitors and issues licenses and registrations to tobacco growers, manufacturers, exporters, and dealers involved in various stages of the tobacco supply chain.
- Research and Development: It collaborates with agricultural research institutes, universities, and industry stakeholders to introduce new technologies, best practices, and crop varieties to enhance the productivity and profitability of tobacco farming.
- Market Promotion: It promotes Indian tobacco products in domestic and international markets through trade fairs, exhibitions, buyer-seller meets, and promotional campaigns.
- Price Stabilization: It intervenes in the market to stabilize prices, mitigate price fluctuations, and protect the interests of farmers against adverse market conditions.
- Quality Control and Grading: It operates grading centers and quality testing laboratories to assess the quality characteristics of tobacco and facilitate fair trade practices in the industry.
PYQ:
Q.With reference to the “Tea Board” in India, consider the following statements:
- The Tea Board is a statutory body.
- It is a regulatory body attached to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The Tea Board’s Head Office is situated in Bengaluru.
- The Board has overseas offices at Dubai and Moscow.
Which of the statements given above are correct? (2022)
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
- 1 and 4
Practice MCQ:
Consider the following statements regarding the cultivation of Tobacco in India:
- Tobacco is a drought tolerant, hardy and short duration crop.
- India is the 2nd largest producer and exporter after China and Brazil respectively
- In the global scenario, Indian tobacco accounts for 10% of the area and 9% of the total production.
How many of the given statements is/are correct?
- One
- Two
- Three
- None
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
Tobacco Warnings on OTT Platforms: A Closer Look at the Debate
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Tobacco Warnings on OTT Platforms

Central Idea
- The Central government’s regulations mandated long-duration smoking warnings for films and TV series on OTT platforms like Hotstar, Amazon, and Netflix.
- Streaming websites voiced objections, raising concerns about user experience.
Recent Development
- According to a recent report, the government has agreed to find “pragmatic solutions” for stricter tobacco warnings on OTT platforms.
- A closed-door meeting saw streaming executives engage with Health Ministry and Information and Broadcasting (I&B) Ministry officials.
Why Smoking Warnings in Indian Entertainment?
- Linking Health Impact and Public Perception: The introduction of smoking warnings in Indian entertainment stems from the connection between smoking’s health impact and its portrayal to the public. The goal is to communicate clear information about the health risks associated with smoking and discourage its use.
- Regulation Evolution: The Indian government has a history of regulating how smoking is portrayed. The Cinematograph Act of 1952 prohibited the “glamorization” of tobacco in movies, and the Cable Television Networks Amendment Act of 2000 banned tobacco and alcohol advertising on cable TV.
Historical Context
- Factors Leading to Consensus: Several factors contributed to a growing national consensus on tobacco control, including increased health awareness, new laws and enforcement, judicial rulings (e.g., the 2008 ban on public smoking), civil society efforts, global support for tobacco control, and the influence of the World Health Organization.
- COTPA and Health Ministry Notification: Under the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA), signed into law in May 2003, the Health Ministry introduced a notification prohibiting the display of tobacco products in cinema and television programs.
- Content Rules: This notification required films and shows produced before it to include health warnings regarding smoking as a prominent scroll at the bottom of the screen. It also recommended prohibiting smoking in public places and using pictorial health warnings covering 85% of tobacco product display areas.
- Legal Challenges: Legal challenges arose as some filmmakers and actors argued that these rules violated their freedom of speech. The Delhi HC quashed the notification in 2009, but the Supreme Court later upheld the rules.
Introduction of Health Spots
- Consensus-Building Efforts: Amid legal disputes, I&B Ministry appointed a new minister, leading to attempts to reach consensus. In 2011, the Health Ministry introduced new rules after consultations with I&B Ministry, aiming to make them more practical and implementable.
- Health Spots in Old Content: For films and shows made before these rules, anti-tobacco health spots or messages were required at the beginning and middle of television programs, made available to the Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC).
- Requirements for New Content: New films and TV shows with smoking scenes were to provide an “editorial justification” to the CBFC, include anti-tobacco health spots, display a prominent static message during tobacco product scenes, and feature an audio-visual disclaimer on the ill effects of tobacco use.
Implementation Challenges
- A study revealed that while many movies implemented at least one element of the film rules on tobacco imagery, few fully complied.
- Compliance with other aspects of COTPA, such as restrictions on selling cigarettes near schools, has also been lacking.
Debate over OTT Smoking Warnings
- Content Library Concerns: I&B Ministry which regulates streaming platforms, expressed concerns about implementing warnings in existing content, foreign content, and health spots. It suggested displaying an appropriate health warning when users log in.
- OTT Industry Concerns: In May, India ordered OTT platforms to insert static health warnings and anti-tobacco disclaimers. OTT executives raised concerns about the potential need to edit vast amounts of existing content, impacting user experience and creators’ freedom of expression.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
WHO Report on Tobacco Control
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Tobacco consumption and issues
Central Idea
- The WHO has released a report on the progress made in global tobacco control in the last 15 years.
- The report highlights the impact of the MPOWER measures, introduced by WHO, to combat tobacco use and protect public health.
What are MPOWER measures by WHO?
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has introduced a set of global health targets known as “MPOWER measures” to address the global tobacco epidemic.
- These measures are evidence-based strategies aimed at reducing tobacco use and its associated health risks.
- The MPOWER measures were developed to assist countries in implementing effective tobacco control policies and interventions.
- The term “MPOWER” is an acronym, with each letter representing a specific area of focus:
- M – Monitor tobacco use and prevention policies
- P – Protect people from tobacco smoke
- O– Offer help to quit tobacco use
- W – Warn about the dangers of tobacco
- E – Enforce bans on tobacco advertising, promotion, and sponsorship
- R – Raise taxes on tobacco products
Key Findings of the Report
- Reduction in Smoking: Globally, there are 300 million fewer smokers today, with smoking prevalence declining from 22.8% in 2007 to 17% in 2021. In a city-specific example, hundreds of enforcement drives and awareness campaigns resulted in a 27% reduction in smoking in public places.
- Impact of MPOWER Measures: The MPOWER measures have positively impacted tobacco control efforts worldwide. 71% of the global population, or 5.6 billion people, are protected by at least one MPOWER measure, up from 5% in 2008. The number of countries implementing at least one measure has increased from 44 to 151.
- Global Challenges: Despite progress, 44 countries still do not implement any MPOWER measure, and there are shortcomings in enforcing smoke-free policies in healthcare facilities and restaurants.
- Focus on Second-Hand Smoke: The report emphasizes the importance of curbing second-hand smoke, which causes significant health risks, including 1.3 million tobacco-related deaths among non-smokers annually. India is among the countries making efforts to control this aspect.
India’s Achievements and Areas for Improvement
- Health Warning Labels: India ranks among the top 10 countries for having health warning labels on cigarette packs, with 85% of packs carrying warnings on both sides.
- Ban on E-cigarettes: India has implemented a ban on the sale of e-cigarettes, which WHO recognizes as an essential step in curbing the tobacco epidemic.
- Smoking Bans: India has banned smoking in healthcare facilities and educational institutions, although there is scope for improvement in terms of enforcement.
- Warnings on OTT Platforms: India is taking significant steps to implement warnings on over-the-top (OTT) platform content showing tobacco use, making it the first country to do so. This move is crucial, given the increased subscriptions to OTT platforms during the pandemic.
Expert Perspectives
- Experts suggest the need for further amendments to India’s comprehensive tobacco control laws, with specific attention to banning the loose sale of cigarettes.
- Implementing warnings on OTT platforms is seen as a necessary measure to reach a broader audience, especially young viewers.
Conclusion
- The WHO report highlights the global progress in reducing smoking prevalence and implementing tobacco control measures.
- While India has made significant strides in certain aspects of tobacco control, there are areas that require continued attention and action.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
Mandatory Anti-Tobacco Warnings on OTT Platforms
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Tobacco consumption and issues

Central Idea
- Over-the-top (OTT) streaming platforms must display anti-tobacco warnings similar to those seen in movies screened in theatres and on TV.
- The requirement is based on a Union Health Ministry notification that amends the rules under the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA), 2004.
What is COTPA, 2004?
| Description | |
| Purpose | Regulate production, sale, distribution, and consumption of tobacco products |
| Prohibition of Smoking in Public Places | Smoking prohibited in public areas like offices, restaurants, parks, public transport, etc. |
| Health Warnings on Tobacco Products | Mandatory display of health warnings on cigarette packages and other tobacco products |
| Ban on Advertisement and Promotion | Prohibition on direct and indirect advertising of tobacco products |
| Prohibition on Sale to Minors | Selling tobacco products to individuals below 18 years of age is strictly prohibited |
| Packaging and Labelling Requirements | Health warnings and pictorial representations of harmful effects on cigarette packages |
| Powers of Enforcement | Authorities empowered to enforce the act, conduct inspections, and seize contraband products |
New requirements for Anti-Tobacco Warnings
- Publishers of online curated content displaying tobacco products or their use must show anti-tobacco health spots at the beginning and middle of the program.
- When tobacco products or their use are displayed during the program, an anti-tobacco health warning must be prominently displayed as a static message at the bottom of the screen.
- The warning message should be legible and readable, with black font on a white background.
- The specified warnings are ‘Tobacco causes cancer’ or ‘Tobacco kills.’
- Health spots, warnings, and audio-visual disclaimers should be in the same language as used in the show.
Negative health impacts of tobacco
- Cancer: Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable cancer. It can cause cancer of the lungs, mouth, throat, larynx, pancreas, bladder, kidney, and cervix.
- Respiratory diseases: It may cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It can also worsen asthma symptoms.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Consumption increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Reproductive health: Tobacco use can lead to infertility, premature birth, and low birth weight in babies.
Socio-economic impact
(1) On an individual level:
- Decreased productivity: Smoking-related illnesses can result in absenteeism from work, decreased work performance, and increased medical expenses.
- Decreased life expectancy: Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased life expectancy, which reduces the overall productive years of an individual.
(2) On a societal level:
- Healthcare cost: Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased economic development due to the increased burden of healthcare costs and decreased productivity.
- Increased social expenditure: According to a study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), tobacco-related illnesses cost India about $22.4 billion in healthcare costs and lost productivity annually
Why tobacco isn’t completely banned?
- Revenue loss: The industry contributes a significant amount of tax revenue to the government. Banning tobacco would result in the loss of these tax revenues, which are used for various public welfare programs and initiatives.
- Economic Impact: The tobacco industry provides employment to a large number of people, especially in the agricultural sector, where tobacco farming is prevalent.
- Not a psychotropic substance: While the harmful effects of tobacco are well-documented, banning a legal product entirely requires careful consideration and legal processes.
- Regulatory approach: Instead of a complete ban, the Indian government has adopted a regulatory approach to control tobacco use.
Way forward
- Strengthen tobacco control laws: Review and enhance existing laws to effectively reduce tobacco consumption.
- Conduct public awareness campaigns: Educate the public about the health risks of tobacco use and the benefits of quitting.
- Expand access to tobacco cessation programs: Increase availability of affordable and effective programs to support individuals who want to quit tobacco.
- Implement sin taxes on tobacco products: Increase taxes to discourage consumption, especially among price-sensitive populations.
- Enforce smoke-free environments: Strictly implement smoke-free laws in public places, workplaces, and public transport.
- Support tobacco farmers: Provide alternative livelihood options and assistance for farmers transitioning away from tobacco farming.
- Conduct research and surveillance: Invest in data collection and analysis to inform evidence-based policies and interventions.
- Collaborate with international organizations: Partner with global entities like WHO to leverage expertise and resources in tobacco control.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
Tobacco consumption: Higher Prices Could Be The Effective way
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Tobacco consumption, Health and socio economic impact
Central Idea
- The share of smokers is declining in India, but smokeless tobacco consumption continues unabated. Smokeless tobacco use is widespread and is a significant public health challenge. The use of smokeless tobacco in India is deeply ingrained in cultural and traditional practices, making it difficult to address through public health interventions.
DATA: Tobacco consumption in India
- High Consumption in north eastern states: In the north-eastern States of India, consumption of tobacco among men in both smokable and chewable forms was higher than the rest of India in 2019-21.
- Consumption in southern states is relatively low: In the southern States, the share was relatively low with regard to both forms of tobacco consumption. However, among those who smoked, the share of those who consumed more than five sticks a day was much higher in many southern States. So, while smokers were fewer in the south, those who smoked did so heavily.
- Smokable forms: If only the smokable forms were considered, the share was higher in the northern States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Haryana, J&K U.T. and the eastern State of West Bengal.
- Chewable forms: If only the chewable forms were considered, the share was higher in the east Jharkhand, Bihar and Odisha and in Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat.
- Share of cigarette/bidi smokers is coming down: Overall, in India, the share of cigarette/bidi smokers is coming down. Compared to 2005-06, the share of smokers came down by over 10% points in 2019-21.
Why is this trend?
- Increase in prices of smokable forms: According to health economists the reduction in cigarette smoking may be attributed to the increase in the prices of the commodity over time.
- Price of chewable form have not increased: On the other hand, the prices of bidis and other chewable forms have not increased much, and so consumption too has not reduced much.
Why price and taxation of tobacco matters?
- Effective way to reduce consumption: Research from many countries around the world including India shows that a price increase induces people to quit or reduce tobacco use as well as discourages non-users from getting into the habit of tobacco use.
- For example: a study conducted in India found that a 10% increase in the price of tobacco products led to a 6.4% reduction in tobacco consumption among adults.
- Higher prices can also discourage young people from taking up smoking: According to the World Health Organization, increasing tobacco prices by 10% can reduce tobacco use among young people by about 4%. This is particularly important as most tobacco users start smoking during adolescence.
Tobacco consumption: Negative health effects
- Cancer: Tobacco use is the leading cause of preventable cancer. It can cause cancer of the lungs, mouth, throat, larynx, pancreas, bladder, kidney, and cervix.
- Respiratory diseases: It may cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It can also worsen asthma symptoms.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Consumption increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Reproductive health: Tobacco use can lead to infertility, premature birth, and low birth weight in babies.
Tobacco consumption: Social-Economic Impact
- On an individual level:
- Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased productivity and increased healthcare costs.
- Smoking-related illnesses can result in absenteeism from work, decreased work performance, and increased medical expenses.
- In addition, tobacco consumption can lead to decreased life expectancy, which reduces the overall productive years of an individual.
- On a societal level:
- Tobacco consumption can lead to decreased economic development due to the increased burden of healthcare costs and decreased productivity.
- According to a study conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO), tobacco-related illnesses cost India about $22.4 billion in healthcare costs and lost productivity annually
Conclusion
- Tobacco consumption in India has significant socioeconomic and health impacts, particularly on the poor and marginalized sections of the population. Worryingly, after GST implementation, cigarette prices have not increased much. Increasing the price of tobacco products through taxation is a key strategy for reducing tobacco consumption and its associated health and economic costs.
Mains Question
Q. Tobacco consumption in India has significant socioeconomic and health impacts? Discuss. Do you think increase in price of tobacco commodities reduces its consumption?
Attempt UPSC 2024 Smash Scholarship Test | FLAT* 100% OFF on UPSC Foundation & Mentorship programs
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
Tobacco and related issues in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GST Council
Mains level: Paper 2- Use of taxation to discourage tobacco use
Context
Tobacco is a silent killer in our midst that kills an estimated 1.35 million Indians every year.
The harm caused by tobacco
- It is the use of tobacco as a result of which more than 3,500 Indians die every single day, as estimated by scientific studies.
- It also comes at a heavy cost: an annual economic burden of ₹1,77,340 crore to the country or more than 1% of India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
How price and taxation of tobacco matters
- Research from many countries around the world including India shows that a price increase induces people to quit or reduce tobacco use as well as discourages non-users from getting into the habit of tobacco use.
- There is overwhelming consensus within the research community that taxation is one of the most cost-effective measures to reduce demand for tobacco products.
- There has been no significant tax increase on any tobacco product for four years in a row.
- This is quite unlike the pre-GST years where the Union government and many State governments used to effect regular tax increases on tobacco products.
- As peer-reviewed studies show, the lack of tax increase over these years has made all tobacco products increasingly more affordable.
- The absence of a tax increase on tobacco has the potential to reverse the reduction in tobacco use prevalence that India saw during the last decade and now push more people into harm’s way.
- It would also mean foregone tax revenues for the Government.
Way forward
- The Union Budget exercise is not the only opportunity to initiate a tax increase on tobacco products.
- The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council could well raise either the GST rate or the compensation cess levied on tobacco products especially when the Government is looking to rationalise GST rates and increase them for certain items.
- For example, there is absolutely no public health rationale why a very harmful product such as the bidi does not have a cess levied on it under the GST while all other tobacco products attract a cess.
- GST Council meetings must strive to keep public health ahead of the interests of the tobacco industry and significantly increase either the GST rates or the GST compensation cess rates applied on all tobacco products.
Conclusion
The aim should be to arrest the increasing affordability of tobacco products in India and also rationalise tobacco taxation under the GST.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Tobacco: The Silent Killer
WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), WHO
Mains level: Not Much
The World Health Assembly (WHA) took the historic decision to form a global treaty to “strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness and response”.
Significance of the launch
- The launch of putting together this accord is the second such initiative taken under Article 19.
- The first initiative was the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC), which came into effect in 2005.
About FCTC
- The Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) is the world’s first modern-day global public health treaty.
- It is also the first treaty negotiated under the auspices of the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The treaty entered into force in February 2005.
- It was signed by 168 of the 192 WHO member states and more than 180 WHO member states have become parties to the convention.
Highlights of the FCTC
The FCTC provides an internationally coordinated response to combating the tobacco epidemic and sets out specific steps for governments addressing tobacco use, including:
- Adopting tax and price measures to reduce tobacco consumption
- Banning tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship
- Creating smoke-free work and public spaces
- Putting prominent health warnings on tobacco packages
- Combating illicit trade in tobacco products
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024