Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
PM Gram Sadak Yojana
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) asked states to add QR codes to Prime Minister Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) rural road boards to boost public monitoring and streamline upkeep via the eMARG platform.
About PM Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY):
- Launch: It was launched on December 25, 2000, by then PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee as a Central Sector Scheme to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected rural habitations.
- Objective: The scheme helps bridge the rural-urban divide and improves access to markets, healthcare, education, and public services.
- Implementation: It is now a centrally sponsored scheme led by the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) and supported by state governments.
- Monitoring: Progress is tracked using e-MARG, a digital platform for monitoring road construction and maintenance.
- Implementation Phases:
-
- Phase I (2000): Focus on connecting unconnected habitations.
- Phase II (2013): Upgrading roads built in Phase I to enhance rural infrastructure.
- Phase III (2019–2025): Consolidation of 1.25 lakh km of rural roads connecting habitations to Gramin Agricultural Markets, Higher Secondary Schools, and Hospitals. Cost: ₹80,250 crore (2019-2025). Funding: 60:40 (Centre), 90:10 for North-East and Himalayan States.
- Phase IV (2024–2029): Aims at constructing 62,500 km of all-weather roads to provide connectivity to 25,000 unconnected habitations with a focus on Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) areas, tribal areas, and remote regions.
Key Features of PMGSY:
- Rural Connectivity Focus: Targets habitations based on population thresholds (e.g., 500+ in plains, 250+ in hill/NE areas).
- Funding Pattern: Initially 100% central funding; since 2015–16, it follows a 60:40 split (90:10 for NE and Himalayan states).
- Maintenance Period: Contractors are responsible for road upkeep for 5 years post-construction.
- Quality Assurance: Involves routine inspections and geo-tagged photographs to evaluate maintenance performance.
- Economic Impact: Improves rural livelihoods, reduces migration, and enhances access to markets and services.
| [UPSC 2001] Consider the following schemes launched by the Union Government: I. Antyodaya Anna II. Gram Sadak Yojana III. Sarvapriya IV. Jawahar Gram Samriddhi Yojana. Which of these were announced in the year 2000?
Options: (a) I and II* (b) II and IV (c) III and IV (d) I, II and III |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
FASTag Annual Pass Scheme
Why in the News?
Union Transport Minister announced a new FASTag-based Annual Pass system for private non-commercial vehicles (cars, jeeps, vans) to ensure smoother travel across National Highways.
What are FASTags?
|
About the FASTag Annual Pass Scheme:
- Overview: It is a new initiative announced by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways to provide cost-effective and hassle-free travel for private non-commercial vehicles.
- Implementation: The pass will be effective from August 15, 2025, and is optional, intended for cars, jeeps, and vans (not for commercial vehicles).
- Objectives: The scheme is designed to reduce per-trip costs (as low as ₹15/toll) and provide savings of up to ₹7,000 annually for frequent travelers.
- Benefits: It allows unlimited passage at National Highway (NH) and National Expressway (NE) toll plazas for either:
- One year, or
- 200 toll crossings, whichever is earlier.
Key Features:
- Eligibility: Applicable only for non-commercial private vehicles with a valid, active FASTag linked to a registered vehicle number.
- Activation: Can be activated via the Rajmargyatra mobile app or NHAI website with a one-time payment of ₹3,000 for FY 2025–26.
- Validity: Covers 200 trips or one year and then reverts to regular FASTag mode unless renewed.
- Trip Count:
- Point-based plazas: Each pass counts as one trip per crossing.
- Closed toll systems: Entry and exit combined count as one trip.
- Transfer Restrictions: The pass is non-transferable and valid only for the vehicle on which the FASTag is registered.
- Coverage: Valid only at NH and NE toll plazas managed by the Centre. It does not apply to state highway or local toll plazas.
- Fee Revision: The base fee may be revised annually starting April 1 every year.
- Existing Users: No need for a new FASTag if one is already affixed and active. The pass can be added on top of the existing tag after eligibility verification.
| [UPSC 2023] With reference to India’s projects on connectivity, consider the following statements:
1. East-West Corridor under Golden Quadrilateral Project connects Dibrugarh and Surat. 2. Trilateral Highway connects Moreh in Manipur and Chiang Mai in Thailand via Myanmar. 3. Bangladesh-China -India -Myanmar Economic Corridor connects Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh with Kunming in China. How many of the above statements are correct? Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Rishikesh-Karnaprayag Railway Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Rishikesh-Karnaprayag Railway Tunnel
Why in the News?
India has marked a significant achievement in its railway infrastructure development with the “tunnel breakthrough” of Tunnel No. 8 on the Rishikesh-Karnaprayag Railway Line.

About Rishikesh-Karnaprayag Railway Tunnel:
- Tunnel No. 8 is a major part of the Rishikesh-Karnaprayag railway project, spanning 14.58 km, making it the longest transport tunnel under construction in India.
- The tunnel is the first railway tunnel in the Himalayan region to use a Tunnel Boring Machine (TBM) (combining with the New Austrian Tunneling Method (NATM)) which reduces environmental disruption and increases efficiency compared to traditional blasting methods.
- It is located on the Devprayag to Janasu stretch, which is part of the larger Rishikesh-Karnaprayag railway line project in Uttarakhand.
- It is part of a larger plan to build a 125.20 km rail link, with 83% of the line to be tunnelled.
- It will feature 12 new stations, 16 tunnels, and 19 bridges across five districts of Uttarakhand.
- Safety measures include 12 escape tunnels and 7.05 km of cross passages to ensure passenger safety in case of emergencies.
- This link will significantly improve connectivity to Uttarakhand’s hilly areas, reduce travel time, and boost economic activity in the region.
| [UPSC 2005] Consider the following statements concerning the Indian Railways:
1. The Head Quarters of the North Western Railway are located at Jodhpur. 2. ‘Indrail pass’ – a travel-as-you-please ticket has been created especially for freedom fighters and sportspersons who have represented India in any game/sport. 3. Fairy Queen is a train using the world’s oldest working engine and the Indian Railways conduct a journey of wildlife and heritage sites on it. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? Options: (a) 2 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 2 (d) None* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
How will the govt. produce the required fuel ethanol?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Ethanol production ;
Why in the News?
Union Minister Nitin Gadkari announced that India will reach its goal of blending 20% ethanol with petrol in the next two months, a year earlier than planned. This will require producing about 1,100 crore litres of ethanol in a year.
Does India’s ethanol distillery industry have the capacity to produce large ethanol?
- Current Production Capacity: India’s ethanol distillery capacity has significantly increased to 1,600 crore litres as of 2024-25, up from 423 crore litres in 2019-20. This expansion has been driven by government incentives and a stable market for ethanol.
- Projected Production: To meet the target of 20% blending of ethanol in petrol, approximately 1,100 crore litres of fuel ethanol will be produced annually, with sugarcane expected to contribute around 400 crore litres this ethanol year.
- Diverse Feedstocks: Ethanol production is now utilizing not just sugarcane but also high-grade molasses, broken rice, and maize, indicating a shift towards a more diversified feedstock strategy.
- Government Support: The Indian government has implemented various measures to boost ethanol production, including reducing the Goods & Services Tax on ethanol and encouraging the establishment of grain-based distilleries.
Why have maize imports increased substantially in the past year?
- Rising Demand for Ethanol: The increase in maize imports can be attributed to the government’s restrictions on using sugar and high-quality molasses for ethanol production, leading to a greater reliance on maize as an alternative feedstock for ethanol.
- Import Figures: From April to June 2024, approximately ₹100 crore worth of maize was imported. For the fiscal year 2023-24, maize imports reached about $33 million, with total imports from April to November 2024 valued at $188 million.
- Impact on Domestic Production: As farmers shift towards maize cultivation due to its lucrative potential for ethanol production, maize output is projected to reach around 42 million tonnes for the 2024-25 ethanol year, with an estimated 9 million tonnes available for ethanol production.
- Market Adjustments: The growth in maize cultivation is expected to continue without necessitating further imports due to favourable conditions for Kharif crops this year. Farmers are increasingly diverting maize from traditional uses to meet the demands of the ethanol market.
What are the significance of the ethanol distillery industry?
- Energy Security and Reduced Import Dependence: The ethanol distillery industry plays a crucial role in enhancing India’s energy security by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. By blending ethanol with petrol, India aims to substitute a significant portion of its crude oil imports, which account for over 87% of its needs.
- Environmental Benefits: Ethanol production and blending contribute to significant reductions in carbon emissions and urban air pollution. Ethanol’s chemical properties allow for more complete combustion, which lowers harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide and particulate matter.
- Economic Growth and Rural Development: The ethanol industry stimulates economic growth by providing additional income streams for farmers through the cultivation of sugarcane, maize, and other biofuel crops. This has led to increased investments in distilleries and agro-processing industries, creating jobs and revitalizing rural economies.
- The government’s initiatives, such as the PM-JI-VAN Yojana, further incentivize ethanol production, ensuring stable farmer incomes and promoting diversification in agricultural practices.
Way forward:
- Enhancing Domestic Maize Production: Strengthen R&D in high-yield maize varieties, improve irrigation infrastructure, and provide financial incentives to farmers to ensure a stable domestic supply for ethanol production, reducing import dependency.
- Sustainable Feedstock Diversification: Promote second-generation (2G) biofuels using agricultural waste and non-food biomass to minimize food security concerns while maintaining ethanol production growth.
PYQ:
Q With reference to the usefulness of the by-products of sugar industry, which of the following statements is/are correct? (UPSC IAS/2022)
- Bagasse can be used as biomass fuel for the generation of energy.
- Molasses can be used as one of the feed stocks for the production of synthetic chemical fertilizers.
- Molasses can be used for the production of ethanol.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
LEADS 2024’ Report Released
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report;
Mains level: Significance of LEADS;
Why in the News?
The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024 report, released by the Union Minister, outlines key objectives and performance metrics aimed at enhancing India’s logistics sector.
What are the Aims and Objectives of Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- The primary aim is to improve logistics efficiency across states and union territories (UTs), thereby facilitating trade and reducing transaction costs essential for economic growth.
- States are encouraged to collaborate with the private sector to develop action plans that attract investments in logistics.
- Emphasis is placed on promoting green logistics and adopting sustainable practices in logistics operations.
- The report advocates for the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Data Analytics to enhance operational efficiency.
- There is a focus on workforce inclusivity and skill development to boost the logistics sector’s capabilities.
LEADS 2024 evaluates logistics performance based on four key pillars:
|
Key Performance Highlights of 2024
- Achievers by Group:
-
- Coastal Group Achievers: Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Tamil Nadu.
- Landlocked Group Achievers: Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand.
- North-Eastern Group Achievers: Assam, Arunachal Pradesh.
- Union Territories Achievers: Chandigarh, Delhi.
- Fast Movers and Aspirers:
-
- Fast Movers include states like Andhra Pradesh, Goa (Coastal); Bihar, Himachal Pradesh (Landlocked); Meghalaya, Mizoram (North-Eastern).
- Aspirers include Kerala, West Bengal (Coastal); Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand (Landlocked); Manipur (North-Eastern).
What is the role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) and skill development in transforming India’s logistics sector as per the recommendations in the LEADS 2024 report?Role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Role of Skill Development
|
Way forward:
- Strengthen Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Foster collaboration between states and the private sector to develop multimodal logistics hubs, enhance last-mile connectivity, and improve infrastructure transparency through competitive bidding processes.
- Promote Sustainability and Skill Development: Integrate green logistics practices, adopt advanced technologies (AI, ML), and implement comprehensive skill development programs to create an inclusive and efficient logistics ecosystem.
Mains PYQ:
Q What is the significance of Industrial Corridors in India? Identifying industrial corridors, explain their main characteristics. (UPSC IAS/2018)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
What is Automated & Intelligent Machine-aided Construction (AIMC) system?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AIMC system and its features
Why in the News?
- The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways (MoRTH) is moving toward large-scale use of Automated & Intelligent Machine-aided Construction (AIMC) for National Highway projects.
- AIMC will provide real-time data at each stage of road construction, which will be sent directly to stakeholders, including MoRTH.
About Automated & Intelligent Machine-aided Construction (AIMC) System
| Details | |
| What is it? |
|
| Features of the System |
|
| Significance of the System |
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
India’s First Bio-Bitumen National Highway Inaugurated
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bio-Bitumen
Why in the News?
India’s first bio-bitumen-based National Highway stretch was inaugurated on NH-44 in Mansar, Nagpur, Maharashtra by Union Minister Nitin Gadkari.
About Bio-Bitumen
- Bio-bitumen is a bio-based binder derived from renewable, sustainable sources such as: Vegetable oils, Crop stubble, Algae, Lignin (a component of wood), Animal manure.
- It serves as an alternative to traditional bitumen, which is primarily derived from the distillation of crude oil.
- The production of bio-bitumen reduces dependence on petroleum and is a step toward sustainable road construction and infrastructure development.
Significance and Features of Bio-Bitumen:
- Bio-bitumen reduces the carbon footprint associated with the traditional bitumen production process.
- By using renewable sources such as lignin (a byproduct of wood), it helps mitigate environmental concerns like stubble burning and contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, potentially by as much as 70% compared to fossil-based bitumen.
- India, which heavily imports traditional bitumen, can reduce its import dependency by switching to bio-bitumen made from locally available materials.
- The use of bio-bitumen stimulates bio-refineries, creating opportunities for revenue generation and providing economic benefits to farmers and the bio-refining industry.
India’s Bitumen Scenario:
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
In news: Bharatmala Pariyojana
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bharatmala Pariyojana
Why in the News?
- Bharatmala Pariyojana is a comprehensive road development project initiated by the Government of India to improve connectivity and reduce logistics costs across the country.
- The total length covered under the scheme is 34,800 km, with an estimated cost of Rs. 5.35 lakh crore.
About Bharatmala Pariyojana
| Details |
Key Components:
|
| Aims and Objectives |
|
| Funding and Implementation |
|
Do you know?
|
PYQ:[2017] With reference to ‘National Investment and Infrastructure Fund’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Z-Morh Tunnel Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Z-Morh Tunnel Project

Why in the News?
Some militants attacked workers building the Z-Morh tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway, killing seven people.
What is the Z-Morh Tunnel?
- The Z-Morh tunnel is a 6.4-kilometer tunnel located near Gagangir village, connecting the Sonamarg health resort to Kangan town in the Ganderbal district of central Kashmir.
- It is part of the larger Zojila tunnel project, which aims to provide year-round road connectivity between Srinagar and Ladakh.
- It is part of the Srinagar-Sonamarg-Leh highway.
- It is being constructed at an altitude of over 8,500 feet.
- It derives its name from the Z-shaped road stretch where it is being built.
- The project was originally conceived by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) in 2012.
- A soft opening of the tunnel was held in February 2024, although the full inauguration has been delayed.
Significance of the Z-Morh Tunnel
- The tunnel provides all-weather road connectivity to the Sonamarg health resort, ensuring that the popular tourist destination remains accessible year-round.
- It is essential for maintaining all-weather connectivity to Ladakh, a region of strategic importance for India, particularly due to the military presence along the border with Pakistan and China.
- The tunnel is strategically important for the Indian Army, as it provides quick and safe access to forward areas in Ladakh, reducing the dependence on air transport for the movement of troops and supplies.
- It will also reduce expenditure on air maintenance of forward locations, thereby increasing the lifespan of Indian Air Force aircraft.
- The tunnel will boost economic growth by improving accessibility to Sonamarg, thereby supporting tourism in the region.
PYQ:[2016] Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] ‘Humsafar Policy’ for Wayside Amenities along the National Highways
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: 'Humsafar Policy' and its features
Why in the News?
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has launched the ‘Humsafar Policy’ in New Delhi to improve travel convenience on National Highways and boost the development of Wayside Amenities.
About the ‘Humsafar Policy’
- The Humsafar Policy is an initiative launched by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways to enhance the convenience and experience of travelers on National Highways (NHs).
- It focuses on developing Wayside Amenities along highways to provide a range of facilities for highway users, ensuring smooth, safe, and comfortable journeys.
- The policy also emphasizes environmental sustainability by incorporating eco-friendly practices like water conservation, solar energy, and waste recycling.
Features of the Humsafar Policy
- Wayside Amenities: Includes food courts, fuel stations, EV charging stations, parking, toilets, ATMs, and pharmacies.
- Standardized Facilities: Ensures well-maintained and hygienic services for commuters.
- Visibility for Service Providers: Featured on the ‘Rajmarg Yatra’ app, with signage space and renewal fee waivers for high-rated providers.
- Monitoring & Inspection: Regular third-party checks to maintain service quality, with alerts for low-rated facilities.
- Green Focus: Encourages solar energy, water conservation, and waste recycling.
Significance
- Better User Experience: Enhances travel with high-quality facilities.
- Economic Impact: Creates jobs and supports local communities.
- Standardization: Ensures consistent quality and accountability.
- Technological Integration: The ‘Rajmarg Yatra’ app gives real-time facility info and allows feedback from users.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Why Supreme Court bar unregulated soil extraction for linear projects?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Environment Protection Act,1986; National Green Tribunal (NGT);
Mains level: Judiciary; National Green Tribunal (NGT);
Why in the News?
Recently, the SC revoked the notification given by the Environment Ministry to exempt the extraction of ordinary earth for linear projects, such as road and railway construction.
- It was challenged before the National Green Tribunal (NGT), which asked the Ministry to review it within three months. However, the Ministry did not take any action, leading the matter to reach the SC.
What are the linear projects?Linear projects refer to Construction or Development Projects. It includes the construction of linear structures like utility lines, pipelines, railroad tracks, highways, stormwater channels, and stream restoration activities. |
What was the 2020 exemption?
- September 2006: The Environment Ministry issued a notification under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, on activities that would require prior Environmental Clearance.
- January 2016: A second notification was issued, exempting certain categories of projects from this requirement.
- March 2020: It added “Extraction or sourcing or borrowing of ordinary earth for the linear projects such as roads, pipelines, etc” to the list of exempted activities.
- The general purpose of the 2020 notification was to conform to the amendments made to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, in March 2020, allowing new lessees to continue mining for two years with the statutory clearances and licenses issued to their predecessors.
Nexus between the Judiciary and the Union Government (Ground for Challenges)
-
- Judicial stand: The SC invalidated the broad and random exception, highlighting that the announcement was rushed during the COVID-19 lockdown without seeking feedback or objections through prior notification.
- The exemption granted without incorporating safeguards was deemed arbitrary and violative of Article 14 of the Constitution.
- The court emphasized that the absence of safeguards defeats the purpose of the Environment Protection Act (EP Act).
- An argument by the center: The Center contended that the exemption was essential “to benefit the general public” and would support “the kumhars (potters), farmers, gram panchayats, banjaras, roads of Gujarat,” and all non-mining activities recognized by the states.
- However, the Apex court stated that the Centre had failed to provide reasons for concluding that the notification was issued in the public interest.
Similar Judicial Scrutiny in the Past:
|
Conclusion: The Supreme Court invalidated the Environment Ministry’s exemption for earth extraction in linear projects due to a lack of justification and safeguards, emphasizing compliance with Environmental Clearance to minimize environmental harm, safeguarding the Environment Protection Act’s purpose.
Mains PYQ
Q How does the draft EnvironmentImpact Assessment(EIA)Notification, 2020 differ from the existing EIA Notification, 2006? (UPSC IAS/2020)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
GPS-based Highway Toll Collection: The New Proposed System
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: GAGAN, Fastags
Mains level: NA
In the news
- The government’s plan to implement a new highway toll collection system based on the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) before the 2024 election model code of conduct kicks in.
- In this article, we delve into the details of the proposed system, its challenges, privacy safeguards, and its relationship with the existing FASTag system.
New Proposed Highway Tolling System
- Utilization of GNSS: The system will employ an On-Board Unit (OBU) or tracking device fitted inside vehicles, leveraging the Indian satellite navigation system, GAGAN, for accurate location mapping.
- ANPR Technology: It will use an automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) system through cameras installed on highways and deduct tolls based on the distance travelled by a vehicle.
- Digital Image Processing: Co-ordinates of national highways will be logged digitally, and toll rates will be assigned based on the distance travelled by a vehicle, with toll amounts deducted from a wallet linked to the OBU.
- Enforcement Mechanisms: Gantries mounted with CCTV cameras will monitor highways, capturing high-security registration plate images to prevent evasion, ensuring compliance with the tolling system.
Challenges in Implementation
- Recovery of Unpaid Tolls: Recovering toll amounts from non-compliant users poses a challenge, especially when digital wallets linked to OBUs are empty.
- Evasion and Non-Compliance: Vehicles traveling without OBUs or deliberately switching them off, or misuse of OBUs to pay lower tolls, present enforcement challenges.
- Infrastructure and Legal Amendments: Setting up ANPR-based systems and amending toll collection rules are essential for the effective implementation of the new system.
Privacy Safeguards
- Usage of GAGAN: Utilizing the indigenous GAGAN system instead of GPS ensures data security within the country, addressing privacy concerns.
- Legal Framework: The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, aims to safeguard privacy, although concerns regarding increased state surveillance exist.
Co-Existence with FASTags
- Complementary Systems: The new tolling system will co-exist with FASTags, with no decision yet on mandating OBUs for all vehicles.
- Operational Efficiency: While FASTags have achieved robust compliance, the GNSS-based system offers lower operational costs and streamlines toll collection processes.
Key Statistics
- FASTag Compliance: By December 2023, 98.9% of vehicles passing through toll fee plazas at national highways were FASTag compliant, reflecting widespread adoption.
- Toll Collection Growth: Toll collection increased 1.5 times from ₹17,942 crore in 2016-2017 to ₹27,744 crore in 2020-2021 at National Highway fee plazas, showcasing the effectiveness of existing mechanisms.
Conclusion
- The proposed GNSS-based toll collection system represents a paradigm shift in highway tolling mechanisms, promising greater accuracy, efficiency, and compliance.
- However, challenges such as recovery of unpaid tolls and infrastructure requirements need to be addressed for successful implementation.
- With adequate safeguards for privacy and co-existence with FASTags, the new system holds the potential to revolutionize highway toll collection in India.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Sela Tunnel: Enhancing Border Connectivity
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sela Tunnel Project
Mains level: All weather connectivity near LAC

In the news
- The inauguration of the Sela Tunnel by Prime Minister Narendra Modi marks a significant milestone in India’s border infrastructure development, particularly in the strategic Tawang sector.
About Sela Tunnel Project
| Details | |
| Location | West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh
On the Balipara-Chariduar-Tawang (BCT) Road |
| Feat | World’s longest bi-lane tunnel at an altitude above 13,000 feet. |
| Connectivity | Ensures all-weather connectivity between Guwahati in Assam and Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh. |
| Highway | Excavated below the Sela Pass on the NH-13 component of the Trans-Arunachal Highway system. |
| Construction | Built by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) under Project Vartak.
Construction commenced on April 1, 2019. |
| Project Details | Tunnel 1: Single-tube tunnel, 980m in length. –
Tunnel 2: Bi-lane tunnel, 1555m in length, including one escape tube for emergencies. Roads: Approach to Tunnel 1 (7100m), road between the two tunnels (1340m), approach to Tunnel 2 (340m). |
Infrastructure Details
- Strategic Location: Situated on the, the Sela Tunnel provides a crucial link between Guwahati and the strategically important Tawang sector in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Military Significance: The tunnel facilitates faster military movement to Tawang, home to the Indian Army’s IV Corps, ensuring swift deployment and operational readiness along the border.
- Operational Benefits: By bypassing foggy stretches at Nechiphu and snow-covered terrain at Sela Pass, the tunnel reduces travel distance by nearly 10 km and travel time by almost an hour for convoys, enhancing logistical efficiency.
- Technology and Safety: Constructed using the new Austrian tunnelling method, the Sela Tunnel incorporates state-of-the-art safety features, meeting the highest standards set by the Defence Ministry.
Geopolitical Context
- Strategic Considerations: Tawang’s geographical significance extends to its proximity to the Brahmaputra plains and its role as a vital axis to Tezpur in Assam, strengthening India’s military posture.
- Historical Significance: Tawang holds historical and cultural importance as the birthplace of the sixth Dalai Lama and a prominent centre of Tibetan Buddhism, adding to its strategic value.
- Security Imperatives: Given China’s territorial claims over Tawang and Arunachal Pradesh, India remains vigilant, fortifying its military presence and infrastructure to safeguard its sovereignty.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
India’s First Underwater Metro Line in Kolkata
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kolkata Underwater Metro Tunnel
Mains level: NA

In the news
- Prime Minister inaugurated India’s first underwater metro tunnel in Kolkata, marking a significant milestone in infrastructure development.
Kolkata Underwater Metro Tunnel
- Kolkata- Howrah Link: Part of the Howrah Maidan-Esplanade section of Kolkata Metro’s East-West corridor.
- Distance and Speed: Covers a distance of 8 km under the Hooghly River, with a rapid travel time of just 45 seconds across a 520-metre stretch.
- Station Configuration: Three out of six stations will be underground, enhancing connectivity and convenience.
- Submerged Train Operation: Trains will traverse 26 meters below the river’s surface and operate 16 meters beneath the riverbed.
About Kolkata Metro: India’s First Rapid Transit System
- Overview: Kolkata Metro is India’s first operational rapid transit system, established in 1984, serving Kolkata and its metropolitan region.
- Network Length: It boasts four operational lines, totalling 59.38 km and comprising 48 stations, with three additional lines under construction.
- Infrastructure Mix: Utilizes a combination of underground, at-grade, and elevated stations with broad-gauge and standard-gauge tracks.
- Operation and Ownership: Managed by Metro Railway, Kolkata, and Kolkata Metro Rail Corporation.
- Project Financing: Funded for Rs 4,965 crore through a loan from the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
About Hooghly River
- The Hooghly River, also known as the Bhagirathi-Hooghly, is a distributary of the Ganges River in West Bengal, India.
- The river originates at Tribeni, where it splits from the main channel of the Ganges.
- The Hooghly River stretches for approximately 260 km (162 miles), making it a significant water body in the region.
- It served as a crucial trade route during the colonial era, fostering commerce and cultural exchange.
- It hosts iconic structures along its banks, including Howrah Bridge and Victoria Memorial, enrich Kolkata’s cultural landscape.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
India’s First Hydrogen Fuel Cell Ferry: A Technological Marvel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Mains level: Hydrogen as a clean fuel

In the news
- Prime Minister has unveiled India’s maiden indigenous hydrogen fuel cell ferry, a groundbreaking achievement in the country’s maritime sector.
About Harit Nauka Initiative
|
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Ferry: Key Features
- Design: The 24-meter-long catamaran ferry accommodates up to 50 passengers in its air-conditioned area, constructed with high-quality fiberglass reinforced plastic.
- Manufacture: Manufactured by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), the vessel will revolutionize water transportation and contribute to India’s green mobility initiatives.
- Propulsion: Powered by a 50-kW Proton-Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cell and Lithium-Ion Phosphate batteries, the vessel operates with zero emissions and minimal noise, offering enhanced energy efficiency.
- Energy Source: Hydrogen fuel, stored in five cylinders onboard, fuels the vessel’s propulsion system, supplemented by a 3-kW solar panel for additional energy generation.
Operational Mechanism
- Hydrogen Fuel Cells: The vessel utilizes hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity by harnessing the chemical energy of hydrogen, emitting only pure water as a byproduct.
- Continuous Operation: Unlike conventional batteries, hydrogen fuel cells do not require recharging, ensuring continuous operation with uninterrupted fuel and oxygen supply.
Indigenous Development
- Collaborative Effort: Cochin Shipyard Limited spearheaded the vessel’s construction, incorporating indigenous hydrogen fuel cell systems developed by KPIT Technologies and Council of Scientific and Industrial Research Labs.
- Early Mover Advantage: India’s pioneering hydrogen fuel cell ferry underscores the nation’s commitment to green technology and positions it as a frontrunner in maritime sustainability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Sudarshan Setu: India’s Longest Cable-Stayed Bridge
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sudarshan Setu
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- Prime Minister inaugurated ‘Sudarshan Setu’, the country’s longest cable-stayed bridge, connecting Beyt Dwarka Island to mainland Okha in Gujarat’s Devbhumi Dwarka district.
About Sudarshan Setu
- Length: Sudarshan Setu spans 2.32 km, making it India’s longest cable-stayed bridge.
- Location: Situated in the Gulf of Kutch, it links mainland Gujarat with Bet Dwarka island off the Okha coast in Devbhumi Dwarka.
Technical Details
- Cable-Stayed Design: The bridge is Gujarat’s longest cable-stayed bridge, featuring a total length of 4,772 meters. Unlike shorter cable-stayed bridges in the state, Sudarshan Setu’s 900-meter cable-stayed section sets it apart.
- Purpose: Designed to provide all-weather road connectivity to Bet Dwarka, it serves as a crucial link for the island’s residents and visitors.
- Navigation Section: Supported by 32 piers, the bridge features seven cable-stayed spans facilitating the movement of fishing boats to and from Dalda Bandar harbour.
Significance of Bet Dwarka
- Religious Hub: Bet Dwarka is renowned as a major pilgrimage and religious tourism destination, housing the revered Shree Dwarkadhish Mukhya Mandir and numerous Hindu temples.
- Economic Activities: Fishing and tourism are the primary economic activities on the island, attracting thousands of pilgrims and tourists annually.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Satellite-Based Toll Collection likely before General Elections
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Satellite -Based Toll Collection
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Satellite-based toll collection is slated for deployment before the onset of the 2024 general election Model Code of Conduct informed Union Transport Minister Nitin Gadkari.
- This technology will supersede FASTags, offering improved efficiency and convenience for drivers.
How Satellite -Based Toll Collection Works?
- GPS-Equipped Vehicles: Every vehicle will require a GPS device for toll collection, enabling real-time tracking of their movements.
- Micro-controller Integration: The government plans to equip vehicles with micro-controllers featuring third-generation (3G) and GPS connectivity to facilitate data transmission.
- Continuous Monitoring: By capturing GPS coordinates, authorities can monitor vehicle routes, track toll road usage, and calculate toll taxes based on distance travelled.
- Toll Gate Configuration: Presently, toll gates are stationed at the end of each road stretch or project. Toll tax is calculated for distances up to 60 km, with rates fixed by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
Distinction from FASTag Technology
| FASTag | GPS-Based Toll Collection | |
| Technology Utilization | Relies on RFID technology for automatic toll deduction. | Utilizes GPS system within vehicles for tracking and toll deduction. |
| Toll Deduction Process | Deduction occurs only at toll booths upon approach. | Toll tax is deducted based on continuous GPS tracking throughout the journey. |
| Infrastructure Requirements | Requires installation of FASTag scanners at toll booths. | Eliminates the need for physical toll booths and plazas, relying solely on GPS tracking. |
| Implementation Status | Mandated since February 2021, offering streamlined toll payment at toll booths. | Anticipated implementation around March 2024, promising enhanced efficiency and convenience for travelers. |
Why is a GPS-based system preferred over FASTag?
- Infrastructure Elimination: GPS-based systems don’t require toll booths, reducing congestion and infrastructure costs.
- Continuous Tracking: They track vehicles continuously, enabling accurate toll calculations based on actual distance traveled.
- Flexibility and Scalability: GPS offers wider coverage and scalability, suitable for varied toll rates and distances.
- Reduced Administration: Automation reduces manual intervention and administrative burden.
- Enhanced User Experience: Drivers enjoy seamless travel without the need to stop at toll booths.
Operational Framework
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Integration: Vehicles will require on-board units (OBUs) linked to a satellite constellation (ex. GPS, GLONASS, IRNSS) for toll calculations and transactions.
- Barrier-Free Movement: OBUs, akin to vehicle tracking devices, will enable distance-based tolling, fostering unhindered highway transit.
- Regulatory Requirements: Geo-fencing of national highways and legislative amendments to permit distance-based tolling under National Highway Fee Rules and the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, are necessary for implementation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Mumbai Trans Harbour Link: India’s Longest Sea Bridge
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mumbai Trans Harbour Link
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Prime Minister is set to inaugurate the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL), officially named the Atal Setu Nhava Sheva Sea Link.
- This 22 km bridge, conceptualized six decades ago, represents a significant development in India’s infrastructure, promising to transform connectivity and economic prospects in the Mumbai Metropolitan Region.
Atal Setu: the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link
- Bridge Specifications: The MTHL is a 22-km-long, six-lane twin-carriageway bridge over the Thane Creek in the Arabian Sea. It connects Sewri in Mumbai to Chirle in Raigad district.
- Components: The structure comprises a 16.5 km sea link and 5.5 km of viaducts on land at both ends.
- Project Objective: Aimed at enhancing connectivity within the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the MTHL is expected to spur economic growth, reduce travel time, and alleviate congestion on existing routes.
Historical Context and Development
- Initial Proposal: The concept of a bay crossing was first proposed in 1963 by Wilbur Smith Associates but remained dormant for decades.
- Revival and Challenges: The project was revived in the late 90s, with the first tenders floated in 2006. After initial interest from Reliance Infrastructure and subsequent withdrawal, the project faced multiple bidding challenges.
- Funding and Execution: The Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA) partnered with the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) for funding, leading to the commencement of work in early 2018. The project cost totaled Rs 21,200 crore, with a significant loan from JICA.
Impact of the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link
- Travel Time Reduction: A study by MMRDA and JICA predicts that the MTHL will cut the average travel time between Sewri and Chirle from 61 minutes to less than 16 minutes.
- Economic and Connectivity Benefits: The bridge is expected to integrate Navi Mumbai’s economy with Mumbai and improve connectivity to key locations like the Navi Mumbai International Airport, Mumbai Pune Expressway, and the Mumbai-Goa Highway.
- Vehicle Usage: An estimated 40,000 vehicles are expected to use the link daily in its opening year.
Concerns and Challenges
- Accessibility for Commuters: Doubts remain about the bridge’s utility for daily commuters between Mumbai and Navi Mumbai, considering the high toll cost and the distance of landing points from main residential areas.
- Additional Commuting Costs: The toll fee of Rs 250 for a one-way crossing and the bridge’s landing points being over 10 km from major residential zones like Vashi and Nerul may increase commuting expenses.
- Lack of Public Transport Options: As of now, there are no announcements regarding public transport facilities, such as dedicated bus lanes, on the bridge.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Report, 2023
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LEADS Report
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The govt has released the LEADS (Logistics Ease across Different States) 2023 report, assessing logistics performance across Indian States and Union Territories (UTs).
- The report includes 11 States and two UTs, encompassing coastal, landlocked, North Eastern States, and UTs.
About LEADS Report
- The LEADS index was launched in 2018 by the Commerce and Industry Ministry and Deloitte.
- It was inspired by the Logistics Performance Index (LPI) of World Bank, and has evolved over time.
- It ranks states on the score of their logistics services and efficiency that are indicative of economic growth.
- States are ranked based on quality and capacity of key infrastructure such as road, rail and warehousing as well as on operational ease of logistics.
Key Highlights of the 2023 Report
- ‘Achievers’ Category: States like Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Punjab, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Sikkim, Tripura, and UTs Chandigarh, Delhi are named as ‘Achievers’.
- Category Shifts: Maharashtra moved from ‘Achievers’ to ‘Fast Movers’, while Odisha shifted from ‘Achievers’ to ‘Aspirers’.
- ‘Fast Movers’: Kerala and Maharashtra among coastal States, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand among land-locked States, and Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland among North Eastern States are ‘Fast Movers’.
- ‘Aspirers’: Goa, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and UTs like Daman & Diu/Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Jammu & Kashmir, Ladakh are categorized as ‘Aspirers’.
Policy perspectives
- Digital Initiatives: Digital reforms like PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, ULIP, and GST are driving India’s improved global ranking.
- India’s Improved LPI Rank: India’s LPI rank improved by six places to 38th position in 2023, reflecting the positive impact of these efforts.
- Vision for Logistics Sector: India’s logistics sector is set to grow from a $3.5 trillion to $35 trillion economy by 2047.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Moulding the Himalayas needs caution
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Char Dham Project
Mains level: Environment Impact Assessment (EIA)
Central idea
The Uttarkashi tunnel collapse has thrown light on the major flaws in the infrastructure development in the Indian Himalayan Region
Key Highlights:
- The Char Dham Project in the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) has raised concerns about the sustainability of the current development model.
- The focus is on the carrying capacity of the IHR, questioning the extensive road widening, hydropower projects, and tourism promotion.
- The geological sensitivity of the Himalayas, marked by earthquakes and frictional shear rocks, makes such infrastructure projects dangerous.
Challenges:
- Lack of adherence to mountain construction codes and basic safety protocols in the rush for construction projects.
- The fragmentation of the Char Dham Project into smaller sections for Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) raises questions about its comprehensive evaluation.
- The need to address the broader issue of carrying capacity in the IHR, encompassing hydropower projects, tourism, and road development.
Key Phrases:
- “Construction in this zone is dangerous” due to the sensitive geological nature of the Himalayas.
- The Supreme Court should address the issue of carrying capacity in the Himalayas, considering the impact of infrastructure on the ecosystem.
- The transformative phase in the IHR requires a reevaluation of the integration approach with new geographies.
Critical Analysis:
- The article criticizes the lack of seriousness in implementing safety measures, citing the Silkyara tunnel incident in Uttarakhand.
- Emphasis on learning from failures, international protocols, and the inclusion of local communities in monitoring structures are suggested for safer infrastructure development.
Key Examples and References:
- The Atal tunnel in Himachal Pradesh is cited as an exception with a rigorous safety protocol, contrasting it with the safety lapses in the Char Dham Project.
- The flash floods of 2013 in Uttarakhand are mentioned as the basis for initiating the Char Dham Yatra and subsequent infrastructure projects.
Key Data:
- The Char Dham Project is approximately 900 km long, broken into 53 sections for separate EIAs.
- Geological and geotechnical studies highlight the dangerous nature of construction in the Himalayas.
Key Facts:
- The carrying capacity discussion extends beyond the number of people to include infrastructure aspects like hydropower projects and roads.
- The importance of a legislative architecture that involves local communities and adheres to international protocols for safer infrastructure development.
Key Terms for value addition in your answer:
- Carrying capacity
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Geological sensitivity
- Transformative phase
- Safety protocols
Way Forward:
- Urgent dialogue on carrying capacity in the Himalayas, considering the total impact of infrastructure development.
- Adoption of international protocols and legislative architecture for safer construction, involving local communities and civil society.
- Reevaluation of the integration approach in the transformative phase of the IHR, ensuring stability and safety standards in infrastructure projects.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Setu Bandhan Scheme
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Setu Bandhan Scheme
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Recently, the Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways announced the approval of Setu Bandhan Scheme for seven bridge projects in Arunachal Pradesh, utilizing funds from the Central Road and Infrastructure Fund (CRIF).
What is Setu Bandhan Scheme?
- Setu Bandhan is an initiative under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- Its primary aim is to enhance inter-state connectivity, particularly in rural border areas that have been historically underserved by state roads.
- The scheme aims to replace railway line Level Crossings (LCs) with Road Over Bridges (ROBs) or Rail Under Bridges (RUBs) in various states.
About Central Road and Infrastructure Fund (CRIF)
- Established in 2000 through the Central Road Fund Act, 2000.
- Previously known as the Central Road Fund.
- It falls under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance.
- The fund is financed through a cess levied in conjunction with excise duty on petrol and diesel.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Financing the green transition
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Climate financing mechanism, institutions and development in news
Mains level: Issues related to climate financing
Central Idea
- The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) plays a crucial role in alleviating the challenges associated with implementing the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) and financing projects in the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP). While NaBFID has made significant strides in disbursing loans to address India’s infrastructure needs, certain areas warrant careful consideration to ensure sustainable and climate-resilient development
Relevance of the topic
Climate finance for sustainable infrastructure and low carbon economy
What is National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)?
- The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) is a specialized financial institution established by the Government of India.
- NaBFID is responsible for providing financial assistance, loans, and credit facilities to infrastructure projects across sectors such as transportation, energy, water and sanitation, urban development, and social infrastructure.
- It focuses on supporting projects that contribute to sustainable development, climate resilience, and inclusive growth.
- One of the key objectives of NaBFID is to implement the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) and finance projects outlined in the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP).
Financial risks associated with climate change
- Physical Risks: These risks are associated with the direct impact of climate change on physical assets and infrastructure. They include:
- Property Damage: Increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires can cause significant damage to properties, leading to financial losses for property owners and insurers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Climate-related events can disrupt supply chains, causing delays, shortages, and increased costs for businesses.
- Asset Devaluation: Physical assets, such as properties located in areas prone to sea-level rise or extreme weather events, may lose value due to the increased risk associated with climate change impacts.
- Transition Risks: These risks arise from the transition to a low-carbon economy and the efforts to mitigate climate change. They include:
- Policy and Regulatory Changes: Governments implementing stricter environmental regulations or imposing carbon pricing mechanisms can impact the profitability and viability of certain industries, leading to financial losses for companies.
- Technology Disruptions: Rapid advancements in clean energy technologies and shifts away from carbon-intensive industries can render certain assets, such as fossil fuel reserves or outdated infrastructure, economically obsolete.
- Market Shifts: Changing consumer preferences and investor sentiment towards sustainability can result in shifts in market demand, affecting the profitability and market value of companies operating in carbon-intensive sectors.
- Liability Risks: These risks arise from legal and financial liabilities associated with climate change impacts. They include:
- Litigation and Legal Actions: Companies, particularly those in high-emission sectors, may face lawsuits and legal actions for their contribution to climate change or for inadequate adaptation measures.
- Insurance Claims: Increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events can lead to higher insurance claims, putting pressure on insurance companies and potentially increasing premiums for policyholders.
- Investor Lawsuits: Investors may file lawsuits against companies for failing to disclose climate-related risks, misrepresenting their environmental performance, or mismanaging climate-related risks, potentially resulting in financial settlements.
What is the need for Financing the green transition?
- Mitigating Climate Change: The transition to a low-carbon and sustainable economy is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change. Green financing enables the deployment of renewable energy, energy efficiency measures, and other sustainable technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By redirecting financial resources towards green projects, we can accelerate the decarbonization of various sectors and limit global warming.
- Transitioning to a Sustainable Future: Green financing supports the development and implementation of sustainable practices across sectors. It promotes investments in clean energy, sustainable infrastructure, circular economy models, and environmentally friendly technologies. Financing the green transition is necessary to shift from resource-intensive and polluting practices towards more sustainable and resilient systems.
- Fostering Innovation and Economic Growth: Green financing stimulates innovation and drives economic growth. Investments in renewable energy, energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable infrastructure create new markets, industries, and job opportunities. It encourages research and development of cutting-edge technologies, positioning countries and businesses at the forefront of the green economy.
- Managing Environmental and Social Risks: Financing the green transition helps manage environmental and social risks associated with unsustainable practices. It supports projects that prioritize environmental stewardship, protect biodiversity, and promote social inclusivity. By integrating environmental and social considerations into financing decisions, we can mitigate negative impacts on ecosystems, communities, and vulnerable populations.
- Meeting Sustainable Development Goals: Green financing is aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It supports the achievement of goals such as affordable and clean energy, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, and biodiversity conservation. Financing projects that contribute to the SDGs is essential for creating a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
- Addressing Investor Demand and Risk Management: Increasingly, investors are demanding sustainable and responsible investment options. Green financing provides opportunities for investors to align their portfolios with environmental objectives and sustainability targets. It also helps manage financial risks associated with climate change and unsustainable practices by redirecting investments towards climate-resilient assets and projects.
- International Commitments and Agreements: Many countries have committed to international agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius. Financing the green transition is essential for countries to meet their climate commitments and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
How India is financing its green transition?
- International Climate Finance: India has been accessing international climate finance, including funds from multilateral development banks, climate funds, and bilateral partnerships. These funds support the implementation of climate mitigation and adaptation projects in India. For example, the Green Climate Fund (GCF) has provided financial assistance to India for renewable energy, sustainable urban development, and climate-resilient agriculture.
- National Clean Energy and Environmental Funds: India has established national funds to support the green transition. The National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF) was created to finance clean energy initiatives, energy efficiency projects, and research and development. Additionally, the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) supports climate adaptation and resilience projects.
- Domestic Banks and Financial Institutions: Indian banks and financial institutions are increasingly incorporating green financing into their portfolios. They provide loans, credit facilities, and investment products for renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives, and sustainable infrastructure development. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also encouraged banks to prioritize lending to the renewable energy sector.
- Green Bonds: India has witnessed a growth in green bond issuances, which enable the mobilization of capital specifically for climate-friendly projects. Indian entities, including government-backed institutions, corporations, and municipalities, have issued green bonds to finance renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure projects. The success of India’s sovereign green bond issuance has paved the way for further green bond investments in the country.
- International Cooperation and Partnerships: India collaborates with international partners to attract green investments and promote technology transfer. Collaborative initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance (ISA) aim to mobilize funding and facilitate the deployment of solar energy projects in India and other member countries.
- Renewable Energy Certificates and Incentives: The Indian government has implemented mechanisms such as Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and feed-in tariffs to incentivize renewable energy generation. RECs provide financial benefits to renewable energy producers, encouraging investment in clean energy projects.
- Energy Efficiency Financing: India has implemented various financing schemes to promote energy efficiency in industries, buildings, and the transportation sector. Initiatives like the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) scheme provide financial incentives and market-based mechanisms to encourage energy efficiency improvements.
- Collaborative Programs and Funds: India participates in collaborative programs and funds such as the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and the World Bank’s Clean Technology Fund (CTF). These platforms provide financial resources and technical assistance to support India’s green transition projects
Loopholes in National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
- Insufficient Integration of Climate Resilience: The NIP’s focus on traditional grey infrastructure and limited integration of green and blue infrastructure is a significant loophole.
- Lack of Detailed Sectoral Needs Assessment: The NIP needs a more comprehensive and detailed assessment of sectoral needs to ensure that investments are targeted in the most critical areas. Without a thorough analysis of sector-specific requirements, there is a risk of misallocation of resources and insufficient prioritization of key infrastructure projects.
- Inadequate Private Sector Engagement: While the NIP recognizes the importance of public-private partnerships (PPPs), the experience with PPPs in India has been mixed. There have been instances of cost overruns, delays, and disputes in PPP projects.
- Limited Focus on Rural Infrastructure: The NIP primarily emphasizes urban infrastructure development, potentially neglecting the critical needs of rural areas. Addressing the infrastructure deficit in rural regions, including connectivity, healthcare facilities, and education, is essential for equitable development and inclusive growth.
- Financing Challenges: While NaBFID has made progress in disbursing loans, the flow of funds to sustainable projects and addressing climate-related challenges remains a significant hurdle. There is a need to enhance expertise in evaluating climate risks, correlating them with financial risks, and quantifying them accurately.
- Limited Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency and accountability in the implementation of the NIP is vital. Clear monitoring and reporting mechanisms should be established to track project progress, expenditure, and outcomes.
Way forward
- Refine and Strengthen Mandate: NaBFID should refine its mandate to explicitly prioritize sustainable and climate-resilient infrastructure projects. This would provide a clear direction and enhance its impact on India’s green transition.
- Enhance Risk Management: NaBFID should continue to enhance its risk assessment and management capabilities. This includes integrating climate risk assessments, considering environmental and social risks, and adopting best practices for sustainable infrastructure financing.
- Foster Public-Private Partnerships: NaBFID should actively engage with the private sector and foster partnerships to attract private investments and leverage their expertise. This can be done through transparent and streamlined processes, risk-sharing mechanisms, and collaborative project planning.
- Promote Innovation and Technology: NaBFID can encourage innovation and the deployment of advanced technologies in infrastructure projects. This includes supporting research and development, promoting technology transfer, and incentivizing the adoption of clean and sustainable solutions.
- Strengthen Environmental and Social Safeguards: NaBFID should enforce robust environmental and social safeguards to ensure that infrastructure projects adhere to sustainable practices, respect community rights, and minimize negative impacts on ecosystems and vulnerable populations.
- Embrace Digitalization: NaBFID can leverage digital technologies to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve monitoring and evaluation of infrastructure projects. This can include the use of data analytics, remote monitoring, and digital platforms for project management.
Conclusion
- To achieve sustainable and climate-resilient infrastructure development, NaBFID must address the gaps in integrating climate risk, enhance transparency and mainstream sustainability, and navigate the challenges associated with financial risks. By focusing on structural measures, engaging the private sector effectively, and harnessing innovative financial products, NaBFID can play a pivotal role in driving climate-resilient investments and integrating nature into decision-making processes
Also read:
| Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM): A Flawed Approach to Climate Finance |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Financing the green transition
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Climate financing mechanism, institutions and development in news
Mains level: Issues related to climate financing
Central Idea
- The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) plays a crucial role in alleviating the challenges associated with implementing the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) and financing projects in the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP). While NaBFID has made significant strides in disbursing loans to address India’s infrastructure needs, certain areas warrant careful consideration to ensure sustainable and climate-resilient development
*Relevance of the topic*
*Climate finance for sustainable infrastructure and low carbon economy
What is National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID)?
- The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) is a specialized financial institution established by the Government of India.
- NaBFID is responsible for providing financial assistance, loans, and credit facilities to infrastructure projects across sectors such as transportation, energy, water and sanitation, urban development, and social infrastructure.
- It focuses on supporting projects that contribute to sustainable development, climate resilience, and inclusive growth.
- One of the key objectives of NaBFID is to implement the National Monetisation Pipeline (NMP) and finance projects outlined in the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP).
Financial risks associated with climate change
- Physical Risks: These risks are associated with the direct impact of climate change on physical assets and infrastructure. They include:
- Property Damage: Increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and wildfires can cause significant damage to properties, leading to financial losses for property owners and insurers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Climate-related events can disrupt supply chains, causing delays, shortages, and increased costs for businesses.
- Asset Devaluation: Physical assets, such as properties located in areas prone to sea-level rise or extreme weather events, may lose value due to the increased risk associated with climate change impacts.
- Transition Risks: These risks arise from the transition to a low-carbon economy and the efforts to mitigate climate change. They include:
- Policy and Regulatory Changes: Governments implementing stricter environmental regulations or imposing carbon pricing mechanisms can impact the profitability and viability of certain industries, leading to financial losses for companies.
- Technology Disruptions: Rapid advancements in clean energy technologies and shifts away from carbon-intensive industries can render certain assets, such as fossil fuel reserves or outdated infrastructure, economically obsolete.
- Market Shifts: Changing consumer preferences and investor sentiment towards sustainability can result in shifts in market demand, affecting the profitability and market value of companies operating in carbon-intensive sectors.
- Liability Risks: These risks arise from legal and financial liabilities associated with climate change impacts. They include:
- Litigation and Legal Actions: Companies, particularly those in high-emission sectors, may face lawsuits and legal actions for their contribution to climate change or for inadequate adaptation measures.
- Insurance Claims: Increasing frequency and severity of climate-related events can lead to higher insurance claims, putting pressure on insurance companies and potentially increasing premiums for policyholders.
- Investor Lawsuits: Investors may file lawsuits against companies for failing to disclose climate-related risks, misrepresenting their environmental performance, or mismanaging climate-related risks, potentially resulting in financial settlements.
What is the need for Financing the green transition?
- Mitigating Climate Change: The transition to a low-carbon and sustainable economy is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change. Green financing enables the deployment of renewable energy, energy efficiency measures, and other sustainable technologies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By redirecting financial resources towards green projects, we can accelerate the decarbonization of various sectors and limit global warming.
- Transitioning to a Sustainable Future: Green financing supports the development and implementation of sustainable practices across sectors. It promotes investments in clean energy, sustainable infrastructure, circular economy models, and environmentally friendly technologies. Financing the green transition is necessary to shift from resource-intensive and polluting practices towards more sustainable and resilient systems.
- Fostering Innovation and Economic Growth: Green financing stimulates innovation and drives economic growth. Investments in renewable energy, energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable infrastructure create new markets, industries, and job opportunities. It encourages research and development of cutting-edge technologies, positioning countries and businesses at the forefront of the green economy.
- Managing Environmental and Social Risks: Financing the green transition helps manage environmental and social risks associated with unsustainable practices. It supports projects that prioritize environmental stewardship, protect biodiversity, and promote social inclusivity. By integrating environmental and social considerations into financing decisions, we can mitigate negative impacts on ecosystems, communities, and vulnerable populations.
- Meeting Sustainable Development Goals: Green financing is aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It supports the achievement of goals such as affordable and clean energy, sustainable cities and communities, responsible consumption and production, climate action, and biodiversity conservation. Financing projects that contribute to the SDGs is essential for creating a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
- Addressing Investor Demand and Risk Management: Increasingly, investors are demanding sustainable and responsible investment options. Green financing provides opportunities for investors to align their portfolios with environmental objectives and sustainability targets. It also helps manage financial risks associated with climate change and unsustainable practices by redirecting investments towards climate-resilient assets and projects.
- International Commitments and Agreements: Many countries have committed to international agreements like the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius. Financing the green transition is essential for countries to meet their climate commitments and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
How India is financing its green transition?
- International Climate Finance: India has been accessing international climate finance, including funds from multilateral development banks, climate funds, and bilateral partnerships. These funds support the implementation of climate mitigation and adaptation projects in India. For example, the Green Climate Fund (GCF) has provided financial assistance to India for renewable energy, sustainable urban development, and climate-resilient agriculture.
- National Clean Energy and Environmental Funds: India has established national funds to support the green transition. The National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF) was created to finance clean energy initiatives, energy efficiency projects, and research and development. Additionally, the National Adaptation Fund for Climate Change (NAFCC) supports climate adaptation and resilience projects.
- Domestic Banks and Financial Institutions: Indian banks and financial institutions are increasingly incorporating green financing into their portfolios. They provide loans, credit facilities, and investment products for renewable energy projects, energy efficiency initiatives, and sustainable infrastructure development. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has also encouraged banks to prioritize lending to the renewable energy sector.
- Green Bonds: India has witnessed a growth in green bond issuances, which enable the mobilization of capital specifically for climate-friendly projects. Indian entities, including government-backed institutions, corporations, and municipalities, have issued green bonds to finance renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable infrastructure projects. The success of India’s sovereign green bond issuance has paved the way for further green bond investments in the country.
- International Cooperation and Partnerships: India collaborates with international partners to attract green investments and promote technology transfer. Collaborative initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance (ISA) aim to mobilize funding and facilitate the deployment of solar energy projects in India and other member countries.
- Renewable Energy Certificates and Incentives: The Indian government has implemented mechanisms such as Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and feed-in tariffs to incentivize renewable energy generation. RECs provide financial benefits to renewable energy producers, encouraging investment in clean energy projects.
- Energy Efficiency Financing: India has implemented various financing schemes to promote energy efficiency in industries, buildings, and the transportation sector. Initiatives like the Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) scheme provide financial incentives and market-based mechanisms to encourage energy efficiency improvements.
- Collaborative Programs and Funds: India participates in collaborative programs and funds such as the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and the World Bank’s Clean Technology Fund (CTF). These platforms provide financial resources and technical assistance to support India’s green transition projects
Loopholes in National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
- Insufficient Integration of Climate Resilience: The NIP’s focus on traditional grey infrastructure and limited integration of green and blue infrastructure is a significant loophole.
- Lack of Detailed Sectoral Needs Assessment: The NIP needs a more comprehensive and detailed assessment of sectoral needs to ensure that investments are targeted in the most critical areas. Without a thorough analysis of sector-specific requirements, there is a risk of misallocation of resources and insufficient prioritization of key infrastructure projects.
- Inadequate Private Sector Engagement: While the NIP recognizes the importance of public-private partnerships (PPPs), the experience with PPPs in India has been mixed. There have been instances of cost overruns, delays, and disputes in PPP projects.
- Limited Focus on Rural Infrastructure: The NIP primarily emphasizes urban infrastructure development, potentially neglecting the critical needs of rural areas. Addressing the infrastructure deficit in rural regions, including connectivity, healthcare facilities, and education, is essential for equitable development and inclusive growth.
- Financing Challenges: While NaBFID has made progress in disbursing loans, the flow of funds to sustainable projects and addressing climate-related challenges remains a significant hurdle. There is a need to enhance expertise in evaluating climate risks, correlating them with financial risks, and quantifying them accurately.
- Limited Transparency and Accountability: Ensuring transparency and accountability in the implementation of the NIP is vital. Clear monitoring and reporting mechanisms should be established to track project progress, expenditure, and outcomes.
Way forward
- Refine and Strengthen Mandate: NaBFID should refine its mandate to explicitly prioritize sustainable and climate-resilient infrastructure projects. This would provide a clear direction and enhance its impact on India’s green transition.
- Enhance Risk Management: NaBFID should continue to enhance its risk assessment and management capabilities. This includes integrating climate risk assessments, considering environmental and social risks, and adopting best practices for sustainable infrastructure financing.
- Foster Public-Private Partnerships: NaBFID should actively engage with the private sector and foster partnerships to attract private investments and leverage their expertise. This can be done through transparent and streamlined processes, risk-sharing mechanisms, and collaborative project planning.
- Promote Innovation and Technology: NaBFID can encourage innovation and the deployment of advanced technologies in infrastructure projects. This includes supporting research and development, promoting technology transfer, and incentivizing the adoption of clean and sustainable solutions.
- Strengthen Environmental and Social Safeguards: NaBFID should enforce robust environmental and social safeguards to ensure that infrastructure projects adhere to sustainable practices, respect community rights, and minimize negative impacts on ecosystems and vulnerable populations.
- Embrace Digitalization: NaBFID can leverage digital technologies to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve monitoring and evaluation of infrastructure projects. This can include the use of data analytics, remote monitoring, and digital platforms for project management.
Conclusion
- To achieve sustainable and climate-resilient infrastructure development, NaBFID must address the gaps in integrating climate risk, enhance transparency and mainstream sustainability, and navigate the challenges associated with financial risks. By focusing on structural measures, engaging the private sector effectively, and harnessing innovative financial products, NaBFID can play a pivotal role in driving climate-resilient investments and integrating nature into decision-making processes
Also read:
| Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM): A Flawed Approach to Climate Finance |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
What is Project Dantak?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project Dantak
Mains level: NA
The Prime Minister has praised the initiative by Border Roads Organisation Project Dantak to commemorate 64th Raising Day.
What is Project Dantak?
| Description | |
| Establishment | Established on April 24, 1961, as per the agreement between the third king of Bhutan and then Prime Minister of India Jawahar Lal Nehru. |
| Objective | Identify the most important aspects of connectivity and spur the socio-economic development and growth of Bhutan. |
| Responsibility | Construct and maintain roads suitable for motorised transportation in Bhutan. |
| Legal Provision | Established under the provision of the Indo-Bhutan Treaty of Peace and Friendship, 1949. |
Works and Involvement
| Description | |
| Infrastructure Development | Constructing infrastructure in adjoining Indian districts, including Sherbathang–Nathu La road, Gangtok–Sherbathang road, and Sevoke–Gangtok road. |
| Establishment of Facilities | Establishing medical and education facilities in outlying areas, which were the first in those regions. |
| Takthi Canteen | Takthi Canteen, commonly known as the DANTAK canteen, is a major stop for travelers midway between Phuentsholing and Thimphu. |
| Recruitment of Workers | Recruiting local workers from Bhutan and Indian workers from adjoining districts like Jaigaon, Alipurduar, and other parts of Eastern and North-Eastern India under a basic monthly wage. |
| Supervision of Work | Posting officials from India for the supervision of work. |
Controversies and Incidents
- The Bhutanese Government accused DANTAK of installing Indian tricolour-themed raised pavement markers or reflectors on the highway railings. DANTAK confirmed their presence, and those reflectors were immediately replaced.
- A 204 meters long bridge in Haa along the Damchu-Haa road collapsed in February 2021, leaving 3 workers dead and 6 missing. The bridge was handed over to Project DANTAK by the contractor.
- The project has faced criticisms for its approach to hiring practices and labor management.
Major projects undertaken
- Paro Airport: Built in 1968 as an airstrip for on-call helicopter services for the Indian Armed Forces. Now used as an international airport.
- Yonphula Airfield: Domestic Airport in Bhutan
- Thimphu – Trashigang Highway: Major Highway in Bhutan
- Damchu-Chukha Road: Major Road in Bhutan
- India House Estate: The Indian Embassy in Bhutan.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
India’s first underwater transport tunnel spanning the Hooghly River
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hooghly River
Mains level: Not Much

Central idea: The East-West Metro corridor, the second line of Kolkata’s Metro network that is currently under construction, will connect Kolkata and Howrah, and one of its highlights is India’s first underwater transport tunnel spanning the Hooghly river.
Hooghly River: Some facts
| Description | |
| Name | Bhagirathi Hooghly River (Anglicized alternatively spelled Hoogli or Hugli) |
| Source | Close to Giria, north of Baharampur and Palashi, in Murshidabad |
| Length | 260 km |
| Flows through | West Bengal |
| Endpoint | Bay of Bengal |
| Importance | Lifeline for Kolkata, transportation route for goods and people, historical trade route, cultural and ecological resource |
| Challenges | Changing course, frequent floods, pollution from industrial effluents and sewage |
| Additional Information | A man-made canal called the Farakka Feeder Canal connects the Ganges to the Bhagirathi to bring the abundant waters of the Himalayan river to the narrow river that rises in West Bengal.
The main course of the Ganges then flows into Bangladesh as the Padma. The Bhagirathi Hooghly River is also called the Ganga or the Kati-Ganga in the Puranas. |
About the East-West Corridor
- The East-West Corridor is expected to significantly ease congestion in the city.
- The line connects Kolkata’s IT hub of Salt Lake Sector V to the western suburb of Howrah.
- The eastern part of the East-West line is operational while the western portion of the corridor is underground.
- There are 12 stations on the entire route, including the country’s deepest, Howrah, at a depth of 33 meters.
Key feature: Underwater Tunnel
- The tunnels under the Hooghly River are 520 meters long and more than 30 meters below the river surface at its deepest point.
- The trains will have an operational speed of 80 km/h and will cover the half-kilometre stretch under the Hooghly in about 45 seconds.
- The underwater tunnels have an internal diameter of 5.55 meters and an external diameter of 6.1 meters.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Zojila Tunnel to revolutionise connectivity to Ladakh
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zojila Pass
Mains level: Not Much

Union Transport Minister recently visited the Zojila Tunnel In Jammu & Kashmir which is Asia’s longest as well as highest.
About Zojila Tunnel
- The Zojila tunnel is an upcoming 14.15 km road tunnel that will connect Srinagar and Leh in the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- It is being constructed as part of a project to improve connectivity in the region, with a connecting tunnel from Z-Morh to the Zojila tunnel also being built.
- The tunnel is being built at a cost of more than Rs 4,600 crore and is expected to be completed by December 2023.
Need for the tunnel
- All weather connectivity: The Zojila Pass is closed during harsh winters due to fears of avalanches, landslides, and slippery roads, cutting off areas beyond the pass from the rest of the country for at least five months.
- Military mobilization: The upcoming Zojila tunnel will provide perennial connectivity between Ladakh and the rest of the country and benefit both civilians and the military.
- Time and effort saving: The distance from Baltal to Minamarg, currently 40 km, will come down to 13 km, with travel time expected to be cut by an hour and a half.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
In news: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
Mains level: Road infrastructure

Photos of the soon-to-be-inaugurated Delhi-Mumbai Expressway have gone viral, receiving widespread appreciation online.
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
- The Delhi-Mumbai Expressway is a proposed 1380 km expressway that will link the capital city of Delhi to Mumbai, India.
- The expressway is being planned as a six-lane expressway and will pass through the states of Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- Started in 2018, the project is set to be completed by the end of 2023.
- The expressway is expected to reduce the travel time between Delhi and Mumbai by up to 12 hours.
- The expressway will also have several rest stops and will be equipped with advanced technology such as electronic toll collection, smart traffic management and surveillance systems.
- The expressway will be built in a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
Some basic details
- The expressway is being constructed with an initial budget of INR 98,000 crore.
- According to claims by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, it will reduce the distance between Delhi and Mumbai by 180 km (from 1424 km to 1242 km).
- Depending on the volume of traffic the expressway sees, there are plans in place to expand it to a 12-lane expressway in the future.
- The reduction in distance and travel time is set to result in annual fuel savings of more than 320 million litres and reduce CO2 emissions by 850 million kg.
Some unique features
- Importantly, the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway is set to introduce certain features seldom seen in road construction in India.
- According to claims from the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, the expressway will boast of a state-of-art traffic management system.
- There will also be a dedicated three metre wide corridor for laying utility lines including fibre optic cables, pipelines as well as solar power generation.
- The expressway will also have provisions for rain water harvesting at intervals of 500 m, with over 2000+ water recharge points.
Provisions for wildlife conservation
- A crucial feature of the project will be its provisions for “wildlife conservation”.
- The expressway is the first in Asia and only the second in the world to feature animal overpasses and underpasses to facilitate unrestricted movement of wildlife.
- Furthermore, the expressway has been aligned in a way to minimize the destruction of protected forests.
- Two iconic 8-lane tunnels will also be built, one through Mukundra sanctuary without disturbing the endangered fauna in the region and the second through the Matheran eco-sensitive zone.
- A 3 ft tall boundary wall and sound barriers will also be constructed in sections prone to wildlife.
Crack Prelims 2023! Talk to our Rankers
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
National Logistics Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NLP
Mains level: Read the attached story

The government will announce the National Logistics Policy (NLP) this week, aiming to bring down logistics costs and address challenges plaguing importers and exporters.
What is Logistics?
- Logistics refers to the overall process of managing how resources are acquired, stored, and transported to their final destination.
- It involves identifying prospective distributors and suppliers and determining their effectiveness and accessibility.
Why need a logistics policy?

- Organizing and consolidating the sector: India’s logistics sector is largely unorganized and fragmented.
- Reducing logistics cost: This is why the country’s logistics costs are as high as 14-15% of the GDP, against 7-8% in developed nations such as the Singapore and the US, who leverage it to boost exports. The NLP aims to bring down India’s logistics cost to 8% in the next five years.
- Preventing waste of perishable items: As per some estimates in India, about 16% of agri-production is wasted at different stages of the supply chain.
- Warehousing development: Moreover, due to factors such as limited capacity and availability of warehouses, the cost of transaction increases.
- Multi-modal integration: The new policy is going about simplification, technology and will have a multimodal approach that will combine rail, water, and air — all modes of transport.
What role will technology play?
- Advanced analytics: The NLP will aim to harness technologies such as AI and blockchain. It aims to create a data analytics centre for driving greater transparency and continuous monitoring of key logistics metrics.
- Single window portal: Under NLP, a portal will be created, where service providers such as warehousing providers, shipping experts, transporters, customs brokers, and various governmental agencies will be unified.
Will it boost cooperation between ministries?
- Unifying multiple departments: Currently, the logistics value chain is managed by several ministries—road transport and highways, shipping, railways, and civil aviation.
- Single-point clearances: Agencies like the Central Drug Standard Control Organization and the Food Safety and Standard Authority of India provide clearances.
- Nationwide integration: The NLP could enhance their integration at the central level.
What about reducing the carbon footprint?
- Energy-efficient transportation: The draft logistics policy lays emphasis on the shift to more energy-efficient means of transportation, as well as the use of greener fuels which could reduce the supply chain’s carbon footprint.
- Vehicular emission reduction: Moreover, the draft policy, released earlier, emphasized creating regulations for controlling vehicular noise, emissions, and wastage.
- Green warehousing principles: The new logistics policy also aims to incorporate green principles in the functioning of warehouses which contribute to nearly 10% of the logistics costs.
Will it change India’s commodity transport?
- Transport of crucial commodities: The proposed policy aims to focus on the transport of crucial commodities such as coal, steel, iron ore, food grains, steel, cement, fruits and vegetables.
- Creating nationwide clusters: The current logistical network for transporting them is mainly confined to regional clusters.
- Integrating national supply-chains: The NLP could help establish a link between the place of origin, and destination place and integrate the supply on a national level.
- Optimum logistics identification: The draft also proposes identification of the right mode of transport for each of these commodities to minimise losses during transport.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
GPS-based toll system to replace FASTag
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: FASTags, GPS
Mains level: Read the attached story

The government plans to start a GPS-based toll system in place of FASTag to ensure seamless payment and vehicle movement on national highways.
Why in news?
- The move would end the role of toll plazas across the country.
How will a GPS-based tolling system work?
- Vehicles will be fitted with an electronic device that can track their movement.
- Highways will be geo-fenced, creating virtual boundaries. The system will use GPS or radio frequency identification technologies.
- The software will recognize when a mobile device enters or leaves a particular area, and toll will be charged based on the distance travelled at the highway’s exit point.
- As the system is based on sensors, there will be no need to stop at toll plazas.
- Vehicles and users must be registered with the GPS toll system, linked to bank accounts that will be used to transfer toll payments.
What are FASTags?
- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- RFID uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
Issues with FASTags
- Since the card is affixed to the windscreen, it can be easily misplaced, damaged or stolen.
- The existing FASTag system, though faster than cash payments, still requires vehicles to stop at toll booths to enable reading of tags.
- Also, the vehicle must wait till the gate is opened.
- It has been observed that sometimes the toll fee is deducted twice from user account. Mostly, this happens due to a technical glitch.
- Some card readers take longer time to read and register. Hence the purpose of saving time is itself defied.
- Still, the wait time at toll booths is much more than the 30 seconds that was promised earlier.
- Also, it has not helped reduce the number of toll booths.
Hence the benefits of using FASTag far outweigh the challenges.
Is FASTags a total failure?
- Usage has increased since FASTag was made mandatory in 2021 after its launch in 2015.
- Penetration has grown from nearly 16% in FY18 to 96.3% in FY22.
- Total toll collection in FY18 was ₹21,948 crore, including ₹3,532 crore collected through FASTags.
- In FY22, toll collection through FASTags increased sharply to ₹33,274 crore out of total toll collection of ₹34,535 crore.
How will GPS benefit highway users?
- GPS tolling uses satellite-based navigation and requires no halting.
- Also, vehicles can be charged only for their actual travel on a highway stretch.
- Currently, toll is paid at toll booths which is fixed between two points of tolling and a user does not get any concession even if he/she exits before completing the full run between two toll plazas.
- The new system should reduce the toll amount charged for travel on highways.
What is the progress so far on GPS tolling?
- The Union road ministry has amended the National Highways Fee (Determination of Rates and Collection) Rules, 2008, allowing for the collection of toll based on distance travelled on national highways.
- This will facilitate the introduction of GPS tolling.
- First trials may be done on the under-construction Mumbai-Delhi expressway which will be geo-fenced.
- Also the cost of GPS devices needs to be considered at very beginning.
Way forward
- The system needs a proper legislative framework, and a full launch is still years away. The government intends to introduce it in phases.
- The road ministry is expected to amend the Motor Vehicles Act and create rules to facilitate GPS tolling as well as to penalize offenders.
- Moreover, GPS will come with its own set of complications on calculating differential tolls.
- Regulations and framework for these need to be developed first.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
‘Kerala Savari’: India’s first online taxi service as a public option
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kerala Savari
Mains level: Cab aggregators malpractices and their regulation in India

Kerala has soft launched ‘Kerala Savari’, the country’s first online taxi service owned by a State government, to ensure fair and decent service to passengers along with fair remuneration to auto-taxi workers.
What is Kerala Savari?
- Operated by the Motor Workers Welfare Board under the aegis of the Labour Department, the Kerala Savari ensures safe travel for the public at ‘government approved fares’ without any ‘surge pricing’.
- The ‘Kerala Savari’ app would be made available to the public on online platforms shortly as it is under the scrutiny of Google now.
Why such initiative?
- The alleged unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights by private app-based cab aggregators have come as a major concern for governments.
- Recently, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) had issued notices to cab aggregators Ola and Uber for unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights which include:
- Charging exorbitant fares during peak hours
- Unprofessional behaviour from the part of drivers
- Lack of proper response from customer support, and
- Undue levy of cancellation charges despite the cab driver refusing to accept the ride booked by the passenger etc.
- It is against this backdrop that the Kerala government has decided to come up with an app-based platform to offer auto-taxi service for the public.
What are the main attractions of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- There will be no fluctuation in fares on Kerala Savari irrespective of day or night or rain.
- But Kerala Savari only 8% service charge in addition to the rate set by the government, whereas the private cab aggregators charge up to 20 to 30% service charge.
What are the security-related features of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- Kerala Savari is claimed as a safe and reliable online service for women, children, and senior citizens.
- This consideration has been given importance in app designing and driver registration.
- A police clearance certificate is mandatory for drivers joining the scheme apart from the required proper training.
- A panic button system has been introduced in the app.
- It has also been decided to install GPS in vehicles at a subsidised rate.
Will the new government initiative end the monopoly of private cab aggregators?
- Kerala has over five lakh autorickshaws and one lakh cabs.
- The State government plans to bring all auto-taxi workers engaged in the sector under the new platform.
- Since smartphone literacy is high in Kerala, the State is hopeful of bringing them under the scheme in a short span of time.
- In addition, the Kerala government has also decided to provide fuel, insurance, and tyre subsidies for vehicle owners in the future and has already initiated talks with major companies in this regard.
- After the evaluation of the first phase of the project in Thiruvananthapuram, it will be extended to the entire State in a phased manner.
- Kerala Savari is expected to reach Kollam, Ernakulam, Thrissur, Kozhikode, and Kannur municipal limits within a month.
Regulation of Cab Aggregators in India
|
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Places in news: Sela Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Sela Pass
Mains level: Strategic border infrastructure

The strategically-significant Sela Tunnel project in Arunachal Pradesh is nearing completion well before the deadline.
What is Sela Tunnel Project?
- The Sela Tunnel is the longest bi-lane road tunnel in the world.
- The total length of the project, including the tunnels, the approach and the link roads, will be around 12 km.
- The tunnel is being constructed by the Border Roads Organisation at an altitude of 13,800ft near the Indo-China border.
- It is being built on the 317km long Balipara-Charduar-Tawang (BCT) road which connects West Kameng, East Kameng and Tawang districts of Arunachal Pradesh to the rest of the country.
Why is the project important?
- All-weather connectivity to Tawang and other forward areas in the sector will be the most important advantage that the project promises.
- At the moment, Sela pass stays closed for a few winter months.
- The project will provide a new alignment on the axis towards the LAC, and allow movement of military and civil vehicles all through the year.
Significance of the tunnel
- China is undertaking massive infrastructure development and troop build-up in the Rest of Arunachal Pradesh (RALP) area.
- In military parlance, the RALP is an area in Arunachal Pradesh other than the Kameng area.
- Other than the Kameng area consisting of East and West Kameng districts, the rest of the State is referred to by the Army as the RALP.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
Mains level: NA
National Logistics Portal (NLP) is set to be integrated with Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) to make the multi-modal logistics ecosystem more efficient.
Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP)
- ULIP is designed to enhance efficiency and reduce the cost of logistics in India by creating a transparent, one window platform that can provide real-time information to all stakeholders.
- It was also emphasized that the solution should have the visibility of multi-modal transport, and all the existing systems of various ministries, governing bodies, and private stakeholders should be integrated with the ULIP system.
- This will create a National Single Window Logistics Portal which will help in reducing the logistics cost.
- ULIP will provide real-time monitoring of cargo movement while ensuring data confidentiality with end-to-end encryption, comprehensive reduction in logistic cost resulting in competitive costing.
There are three key components which are defining the ULIP platform:
- Integration with existing data sources of ministries: As authorization, compliance and clearance are some of the critical activities of Logistics; the integration with data points of ministries shall enable a holistic view and interlink the handshaking points.
- Data exchange with private players: To enable the private players, logistics service providers, and industries to utilize the data available with ULIP and at the same time share their data (transportation, dispatch, delivery, etc.) with ULIP, thereby streamlining the processes to bring better efficiency through data exchange.
- Unified document reference in the supply chain: To enable a single digitized document reference number for all the documentation processes in a single platform.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Chisumle- Demchok: Worlds’ Highest Motorable Road
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chisumle- Demchok Road
Mains level: Critical border infrastructures

Ladakh’s Chisumle-Demchok Road, when it crosses the Umling Pass, is now the world’s highest motorable road.
Chisumle- Demchok Road
- The project to build the road through the pass — a part of Border Roads Organization (BRO) Project Himank — had been completed in 2017, after which vehicles had started playing on the route.
- The road is in south Ladakh. It passes through Umling La Pass, which is at a height of over 19,000 feet.
- The height of the pass makes it the highest motorable road in the world, and was recently recognized as such by Guinness World Records.
- The 52-km road ‘black-top’ tarmac road from Chisumle to Demchok betters the previous record of a road in Bolivia, which connects the volcano Uturuncu at 18,953 feet.
- The road was built under extremely challenging conditions, as temperatures in the region can fall to below minus 40 degrees Celsius, and oxygen levels go down to 50 per cent below normal.
Top of the world
- At the pass, the road is higher than both the base camps for the climb to Mount Everest, the world’s highest mountain.
- The South Base Camp in Nepal is at a height of 17,598 ft, while North Base Camp in Tibet is at 16,900 ft.
- The Chisumle-Demchok road is also higher than the Siachen Glacier, which is situated at 17,700 feet.
- Khardung La in Leh, which at one time was among the highest roads in the world, is at an altitude of 17,582 feet.
Military significance of the road
- This road provides a direct route from Chisumle, which lies on the major road coming from Leh, Karu and Nyoma.
- All of these stations have important military stations which are close to the Line of Actual Control.
- Demchok has been an India-China flashpoint earlier, the site of a standoff between the two armies in 2016.
- In the current standoff in eastern Ladakh, which began in May 2020, Demchok has come up as a point of contention.
Other benefits offered
- The new axis will be helpful for the armed forces, making it easier to mobilize troops and equipment, including rations.
- The road will not only enable faster movement of armed forces to the region but will also boost tourism and improve the socio-economic condition of the local people in the region.
Certain limitations
- Since the road goes through such a high pass, road transport will be unfeasible during the winter, when the armed forces rely on air support.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
How the new Warehousing Policy will transform India’s logistics
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Logistcs and Supply chain management in India
In order to reduce transportation and logistic cost, the union government along with the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) is working on warehouse policy.
What are Warehouses?
- A warehouse is a building for storing goods.
- Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc.
- They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities, towns, or villages.
Objectives of the New Warehousing Policy
- Logistics boost: The new policy is aimed at improving logistics throughout the country.
- Supply chain management: The modern warehouses will house cold-storage chains and will be able to store all kinds of cargo—wet and dry.
- De-congesting cities: These facilities are expected to come up outside city centres so that large trucks carrying the cargo do not need to enter the city to unload their goods.
- Fuel efficiency: This will also help boost bulk carrying capacity and save fuel.
- Curbing air pollution: The idea is to minimize pollution and traffic congestion in major cities.
Who will frame and implement the policy?
- NHAI: The policy will be framed by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI). It will also be the implementing agency.
How?
- Through Land Banks: There are land banks along the highways and expressways of the country with the NHAI.
- PPP mode: Tenders will be floated for such land parcels, inviting private players to develop warehousing zones in PPP mode on a revenue-sharing basis or for a fixed fee.
What will be the impact on logistic costs?

- Logistics cost-saving: Warehousing zones will help cut India’s logistics cost, which is 14%-16% of gross domestic product (GDP), compared to 8%-10% of GDP in China and 12%-13% in the US.
- Establishment of MMLPs: The warehousing zones and multi-modal logistics parks (MMLPs) are being set up by the NHAI.
- FMCG sector boost: This will help Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) firms, steel and cement makers stock inventory near major hubs.
How will MMLPs aid warehousing policies?
- Integration of multi-modal transport includes the development of 35 MMLPs.
- The MMLPs are aimed at fostering inter-modal connectivity through dedicated railway lines and access from highways to provide connectivity to an airport or a seaport or an inland waterway terminal.
- The aim is to:
- Remove deficiencies related to logistics
- Draw the associated costs down, and
- Strategically integrate highway projects and other connectivity initiatives
Why such move?
Ans. E-commerce boom
- The e-commerce sector has been driving the demand for logistics and warehousing across global markets.
- It has emerged as the most prominent driver of Indian warehousing market volumes along with the third party logistics sector.
- This sector’s share in transactions has grown from 18% in FY17 to 31% in FY21.
- The Indian market is on the verge of its next phase of growth with domestic groups such as Tatas and Reliance entering the business.
- Thus far, Amazon.com Inc. and Walmart Inc. have driven the market.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Char Dham Road Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Char Dham Project
Mains level: Environmental issues with the project
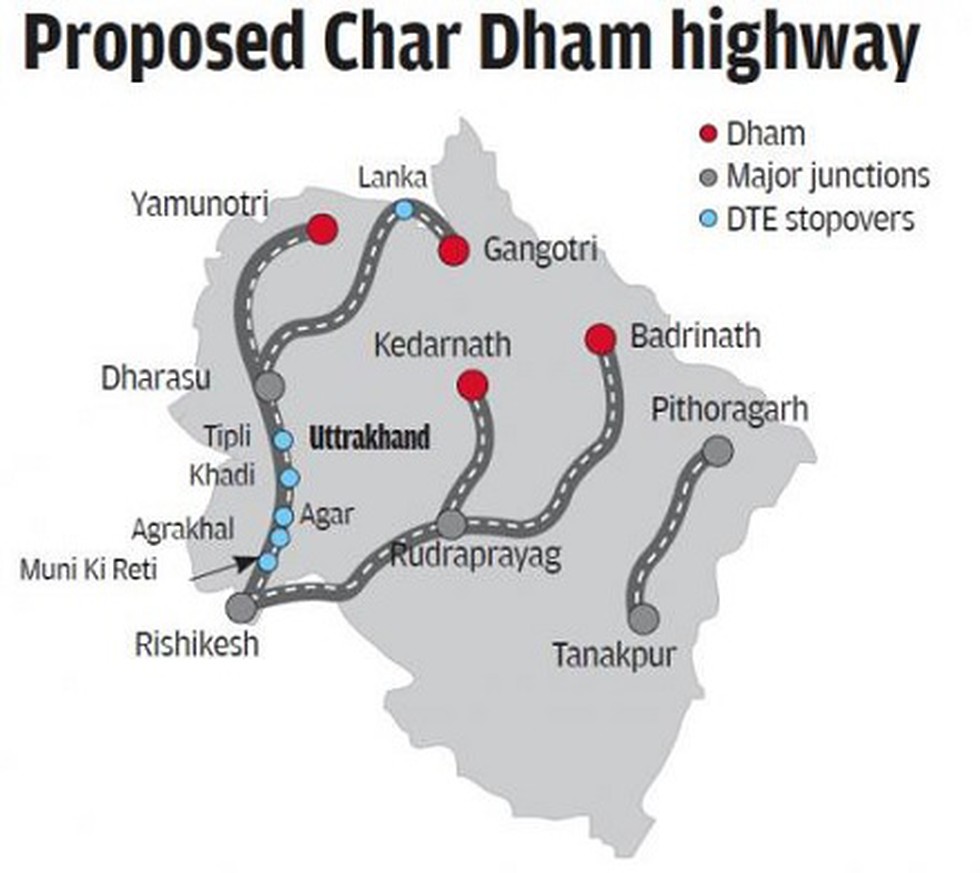
The needs of defence and environment have to be balanced and a “nuanced” approach is required, said the Supreme Court while hearing an appeal against the widening of roads in Uttarakhand hills for the “Char Dham project”.
What is Char Dham?
- The Char Dham is a set of four pilgrimage sites in India.
- It is believed that visiting these sites helps achieve moksha (salvation).
- The four Dhams are, Badrinath, Dwaraka, Puri and Rameswaram.
The highway project
- The Char Dham highway project connects the four himalayan shrines of Gangotri, Yamunotri, Kedarnath and Badrinath in Garhwal Himalayas.
- It has 899-km road which the Centre wants to broaden near Dehradun.
What is the controversy?
The Supreme Court formed a high-powered committee (HPC) to examine the issues. In July 2020, the HPC submitted two reports after members disagreed on the ideal width for hill roads.
- Deforestation: In 2018, the road-expansion project was challenged by an NGO for its potential impact on the Himalayan ecology due to felling trees, cutting hills and dumping muck (excavated material).
- Terrain damage: It was observed that a wider road requires additional slope cutting, blasting, tunnelling, dumping and deforestation.
- Increasing vulnerability: All of this will further destabilise the Himalayan terrain, and increase vulnerability to landslides and flash floods.
Criticism of the Project
- Work without clearance: Project work and felling of trees on different stretches, adding up to over 250 km, has been continuing illegally since 2017-18.
- Misusing old clearance: Work started on stretches adding up to over 200 km on the basis of old forest clearances issued to the Border Roads Organisation during 2002-2012.
- False declaration: The work began by falsely declaring that these stretches did not fall in the Eco Sensitive Zones of Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary, Rajaji National Park, Valley of Flowers National Park etc.
The defence angle
- Even as the project grappled to come clean, it garnered support from the MoD seeking a double-lane road to meet the requirement of the Army.
- The project always had a strategic angle to it as the highways would facilitate troop movement to areas closer to the China border.
- Suddenly, this became the sole justification for building wider roads.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Report, 2021
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: LEADS Index
Mains level: Not Much

The Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2021 Index Rankings has been recently released.
About LEADS
- The LEADS index was launched in 2018 by the Commerce and Industry Ministry and Deloitte.
- It ranks states on the score of their logistics services and efficiency that are indicative of economic growth.
- States are ranked based on quality and capacity of key infrastructure such as road, rail and warehousing as well as on operational ease of logistics.
Highlights of the 2021 report
- India’s logistics costs account for 13-14 per cent of GDP, compared to 7-8 per cent in developed countries.
- Gujarat, Haryana and Punjab have emerged as the top performers in the LEADS 2021 index respectively.
- West Bengal, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh and Assam were ranked 15th, 16th, 17th, 18th, 19th, 20th and 21st respectively.
- North Eastern States, and J&K and Ladakh have been considered a separate group for LEADS rankings.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
PM GatiShakti — National Master Plan
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gati Shakti Master Plan
Mains level: Infrastructure development measures
The PM has inaugurated the GatiShakti — National Master Plan for infrastructure development aimed at boosting multimodal connectivity and driving down logistics costs.
GatiShakti — National Master Plan
- PM GatiShakti is a digital platform that connects 16 ministries — including Roads and Highways, Railways, Shipping, Petroleum and Gas, Power, Telecom, Shipping, and Aviation.
- It aims to ensure holistic planning and execution of infrastructure projects.
- The objective is to ensure that every department now has visibility of each other’s activities providing critical data while planning and execution of projects.
- Through this, different departments will be able to prioritize their projects through cross-sectoral interactions.
Notable features
- Geospatial data: The portal will offer 200 layers of geospatial data, including on existing infrastructure such as roads, highways, railways, and toll plazas.
- Protected areas management: It would also geographic information about forests, rivers, and district boundaries to aid in planning and obtaining clearances.
- Realtime monitoring: The portal will also allow various government departments to track, in real-time and at one centralized place, the progress of various projects.
Monitoring mechanism
- The National Master Plan has set targets for all infrastructure ministries.
- A project monitoring group under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) will monitor the progress of key projects in real-time.
- It would report any inter-ministerial issues to an empowered group of ministers, who will then aim to resolve these.
Need for such Project
- Avoiding poor infrastructure planning: Examples of poor infrastructure planning included newly-built roads being dug up by the water department to lay pipes.
- Creating a multi-modal network: The government expects the platform to enable various government departments to synchronize their efforts into a multi-modal network.
- Timely completion of infra projects: It is also expected to help state governments give commitments to investors regarding timeframes for the creation of infrastructure.
- Inefficient connectivity: Currently, a number of economic zones and industrial parks are not able to reach their full productive potential due to inefficient multi-modal connectivity.
- Easy clearance: The portal allows stakeholders to apply for these clearances from the relevant authority directly.
Logistics costs in India
- Studies estimate that logistics costs in India are about 13-14% of GDP as against about 7-8% of GDP in developed economies.
- High logistics costs impact cost structures within the economy by making it more expensive for exporters to ship merchandise to buyers.
Benefits offered by PM-GatiShakti
- Collaborative planning: It would incorporate infrastructure schemes under various ministries and state governments, including the Bharatmala and inland waterways schemes, and economic zones.
- Logistics boost: It would boost last-mile connectivity and thus bring down logistics costs with integrated planning and reducing implementation overlaps.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Places in news: Zojila Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zoji La Pass and other himalayan passes
Mains level: Critical border infrastructures

Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways has inspected the work on Zojila and Z Morh tunnels.
Zojila Tunnel
- The Zojila is set to be Asia’s longest bi-directional tunnel.
- It will connect Srinagar, Dras, Kargil and Leh via a tunnel through the famous Zojila Pass.
- Located at more than 11,500 feet above sea level, the all-weather Zojila tunnel will be 14.15 km long and ensure road connectivity even during winters.
- It will make the travel on the 434-km Srinagar-Kargil-Leh Section of NH-1 free from avalanches, enhance safety and reduce the travel time from more than 3 hours to just 15 minutes.
- The speed limit inside the tunnel is likely to be the same as in the Atal tunnel – 80 kmph.
Z-Morh tunnel
- The Z-Morh tunnel — being developed at Sonmarg — will provide it all-weather connectivity with Srinagar allowing it to remain open to tourists all year round.
- It is likely to be ready by December 2023 and is being developed at a cost of ₹2,378 crore.
Significance of these tunnels
- The project holds strategic significance as Zojila Pass is situated at an altitude of 11,578 feet on the Srinagar-Kargil-Leh National Highway and remains closed during winters due to heavy snowfall.
- At present, it is one of the most dangerous stretches in the world to drive a vehicle and this project is also geo-strategically sensitive.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Back2Basics: Major Passes in India

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway: World’s longest
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
Mains level: NA

The Minister for Road Transport and Highways Union Minister Nitin Gadkari concluded the review of the work progress on the Delhi-Mumbai Expressway.
Delhi-Mumbai Expressway
- The ambitious infra project started in the year 2018 is being constructed at a cost of Rs 98,000 crore and is scheduled for completion by March 2023.
- States: Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra
- Once ready, the expressway will feature a spur to Noida International Airport and Jawaharlal Nehru Port to Mumbai through a spur in the financial capital.
- It will reduce travel time between certain cities to 12-12.5 hours from 24 hours.
- The project is expected to improve connectivity to economic hubs of India like Jaipur, Ajmer, Kishangarh, Chittorgarh, Kota, Udaipur, Ujjain, Bhopal, Indore, Vadodara, Ahmedabad, and Surat.
Key features of the expressway
- The expressway which is eight-lane access-controlled can be expanded to a 12-lane expressway depending on the traffic volume
- It will boast wayside amenities such as resorts, food courts, restaurants, fuel stations, logistics parks, facilities for truckers
- For accident victims, it will offer a helicopter ambulance service as well as a heliport, which will use drone services for business
- Along the highway, over two million trees and shrubs are planned to be planted
- The highway project is Asia’s first and the world’s second to include animal overpasses in order to facilitate unrestricted wildlife movement
- Besides, it will also involve two iconic eight-lane tunnels
- The project will result in annual savings of more than 320 million litres of fuel as well as reduce Carbon dioxide emissions by 850 million kg
- Over 12 lakh tonnes of steel will be consumed in the project’s construction, which is equivalent to constructing 50 Howrah bridges
- For the project, 80 lakh tonnes of cement will be consumed, which is around 2 percent of the country’s annual cement production capacity
- The ambitious Delhi-Mumbai Expressway project has also created job opportunities for thousands of trained civil engineers apart from generating over 50 lakh man-days of work
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Bharat Series (BH-series) for Vehicles
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bharat series (BH-series)
Mains level: Not Much

The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has rolled out a new series for vehicles registration ‘BH’ to avoid re-registration of vehicles while moving to another state.
Bharat series (BH-series)
- There was a procedure of re-registration of a vehicle while moving to another state.
- A vehicle bearing BH registration mark shall not require assignment of a new registration mark when the owner of the vehicle shifts from one State to another.
- Format of Bharat series (BH-series) Registration Mark –
Registration Mark Format:
- YY BH #### XX
- YY – Year of first registration
- BH- Code for Bharat Series
- ####- 0000 to 9999 (randomized)
- XX- Alphabets (AA to ZZ)
Why such move?
- Station relocation occurs with both Government and private sector employees.
- Such movements create a sense of unease in the minds of such employees with regard to transfer of registration from the parent state to another state.
- Under section 47 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, a person is allowed to keep the vehicle for not more than 12 months in any state other than the state where the vehicle is registered.
Who can get this BH series?
- BH-series will be available on voluntary basis to Defense personnel, employees of Central Government/ State Government/ Central/ State PSUs and private sector companies/organizations.
- The motor vehicle tax will be levied for two years or in multiple of two.
- This scheme will facilitate free movement of personal vehicles across States/UTs of India upon relocation to a new State/UT.
- After completion of the fourteenth year, the motor vehicle tax shall be levied annually which shall be half of the amount which was charged earlier for that vehicle.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy, 2021
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Voluntary Vehicle-Fleet Modernization Programme (VVMP)
Mains level: Vehicle scrappage
The launch of India’s vehicle scrapping policy or the Voluntary Vehicle-Fleet Modernization Programme (VVMP) seeks to usher in a new age of what it means to own and use an automobile in India.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy: Key Features
- Fitness testing: The government plans to set up between 450-500 automated vehicle fitness testing stations across India on a PPP basis. Private vehicles – which are over 20 years old – will have to undergo fitness tests, at an estimated cost of Rs 300-400 per test.
- Scrappage: A total of 60-70 vehicle scrapping centers will also be built, situated no further than 150-200 kilometers away from any location in India.
- Green Tax: Vehicles that pass the automated tests will be subjected to a ‘green tax’, which will see owners shell out an additional 10 percent to 25 percent of road tax at the time of the renewal of the vehicle’s fitness certificate, along with re-registration fees.
- Penalties: Those who choose to drive a vehicle that has failed the automated test will face substantial penalties, and such vehicles could also be impounded.
- Choice of owners: The scrappage policy leaves the choice of scrapping to the owner of the vehicle, with Gadkari saying the automated tests will place emphasis on vehicle fitness, and not its age.
Implementation plan
- The implementation of the vehicle scrappage policy in India is still some time away.
- Initially, it will be heavy commercial vehicles that will need to undergo fitness tests starting 1 April, 2023.
- Fitness tests will be made mandatory for all other types of vehicles from 1 June, 2024, in a phased manner.
Why need such policy?
- Clean mobility: More than one crore vehicles on India’s roads contribute greatly to rising pollution levels, as well as their tendency to be less fuel-efficient towards the end of their life.
- Reducing oil import: The promotion of clean mobility necessitates a reduction in the country’s fuel import bills, and a reduction in emissions is a pressing need at this time.
- Road safety: Such vehicles are also inherently unsafe and can be a threat to their occupants as well as other road users.
- Consumer benefits: Scrapping an old vehicle and replacing it with a new one will bring substantial monetary benefits for motorists, in addition to reducing emissions and enhancing fuel efficiency.
Benefits for a vehicle owner

- Once the vehicle has been scrapped, the owner will receive anywhere between four to six percent of their old vehicle’s ex-showroom price, and a scrappage certificate.
- This will make the individual eligible for a road tax rebate of 25 percent, a registration fee waiver and a discount of five percent of a new vehicle’s ex-showroom cost, offered by the vehicle manufacturer.
- This will essentially make a new vehicle cheaper for someone who has scrapped their old vehicle, with potential discounts in the range of Rs 30,000 (for a car costing Rs 6 lakh) to Rs 50,000 (for a car costing Rs 10 lakh).
What are the other positives?
- Investment and Employment: The policy will attract investment of over Rs 10,000 crore, and generate 50,000 jobs in the country.
- Recycling: Proper recycling of raw materials obtained from the scrapping will help reduce the import of materials such as aluminium, copper, steel and more.
- Vehicle price control: With the potential to recycle up to 99 percent of materials used in a vehicle, raw material costs are estimated to drop by as much as 40 percent.
- Transition to EVs: There’s also a possibility to derive materials needed for local production of lithium-ion batteries from scrapping older vehicles, which could help drive the growth of the EV business.
- Circular Economy: A circular economy depends on reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing and recycling of resources to create a closed-loop system, minimizing the use of resources, generation of waste, pollution and carbon emissions.
- Demand boost: Globally, a scrappage policy has been followed by a boost in demand in the auto manufacturing sector, especially in Europe and the US.
UPSC 2022 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Haldibari- Chilahati Rail Link
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Haldibari- Chilahati Rail Link
Mains level: Not Much

The freight trains have started commuting via the restored Haldibari (India) – Chilahati (Bangladesh) rail link.
Haldibari- Chilahati Rail Link
- The Haldibari – Chilahati rail link between India and then East Pakistan was operational till 1965.
- The distance between Haldibari Railway Station till the international border is 4.5 km, while that of Chilahati is around 7.5 km till the ‘zero points’.
- This was part of the Broad-Gauge main route from Kolkata to Siliguri during the partition.
- Trains traveling to Assam and North Bengal continued to travel through the then East Pakistan territory even after partition.
- However, the war of 1965 effectively cut off all the railway links between India and then East Pakistan.
- The link was reopened in 2020 for the movement of passenger and goods traffic.
Other railway links between India and Bangladesh
As of now, five links connecting India with Bangladesh have been made operational which include:
- Petrapole (India) – Benapole (Bangladesh)
- Gede (India) – Darshana (Bangladesh)
- Singhabad (India) – Rohanpur (Bangladesh)
- Radhikapur (India) – Birol (Bangladesh)
- Haldibari (India) – Chilahati (Bangladesh)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Kuthiran Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kuthiran tunnel
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways has inaugurated the Kuthiran Tunnel in Kerala
Kuthiran Tunnel
- Kuthiran Tunnel is a Twin-tube tunnel at Kuthiran in Thrissur District of Kerala.
- It is located on National Highway 544, owned and operated by the National Highways Authority of India.
- It is Kerala’s first-ever tunnel for road transport and South India’s Longest 6-lane road tunnel.
- Kuthiran gradient is situated in the Kuthiran Hills, situated in the western part of Anaimalai Hills. The hills are a notified Peechi- Vazahani wildlife sanctuary.
- It will drastically improve connectivity to Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- The road will improve connectivity to important ports and towns in North-South Corridor without endangering wildlife.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Fast Tracking Freight in India
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Freight transport in India
Mains level: NA

NITI Aayog, RMI and RMI India’s new report, Fast Tracking Freight in India: A Roadmap for Clean and Cost-Effective Goods Transport, presents key opportunities for India to reduce its logistics costs.
Freight transport in India
- Freight transportation is a critical backbone of India’s growing economy, and now more than ever, it’s important to make this transport system more cost-effective, efficient, and cleaner.
- Due to the rising demand for goods and services, freight transport demand is expected to grow rapidly in the future.
- While freight transport is essential to economic development, it is plagued by high logistics costs and contributes to rising CO2 emissions and air pollution in cities.
Highlights of the Roadmap
- According to the report, India has the potential to:
- Reduce its logistics cost by 4% of GDP
- Achieve 10 gigatonnes of cumulative CO2 emissions savings between 2020 and 2050
- Reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions by 35% and 28%, respectively, until 2050
- The report outlines solutions for the freight sector related to policy, technology, market, business models, and infrastructure development.
Various recommendations
- The recommendations include increasing the rail network’s capacity, promoting intermodal transport, improving warehousing and trucking practices, policy measures and pilot projects for clean technology adoption, and stricter fuel economy standards.
- When successfully deployed at scale, the proposed solutions can help India establish itself as a leader in logistics innovation and efficiency in the Asia–Pacific region and beyond.
Transforming the system
- As India’s freight activity grows five-fold by 2050 and about 400 million citizens move to cities, a whole system transformation can help uplift the freight sector.
- This transformation will be defined by tapping into opportunities such as efficient rail-based transport, the optimization of logistics and supply chains, and a shift to electric and other clean-fuel vehicles.
- These solutions can help India save ₹311 lakh crore cumulatively over the next three decades.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
New Vehicle Scrappage Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Vehicle Scrappage Policy

Auto majors have welcomed the new vehicle scrappage policy rolled out by Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways, saying it would encourage people to replace old vehicles while boosting the sector.
Under the policy, those choosing to voluntarily scrap their old vehicles will get financial incentives from the government and the automaker.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy: Key Highlights
- Personal vehicles older than 20 years and commercial vehicles older than 15 years will have to undergo a fitness test at the government registered ‘Automated Fitness Centres’.
- Vehicles that fail to pass the test will be declared as ‘end-of-life vehicles’, which would mean that the vehicle would have to be recycled.
- This will pave the way for older vehicles to be scrapped.
- In case, the vehicles pass the test, owners will have to pay a hefty fee for re-registration.
- According to the new policy, the re-registration fee would be hiked around eight times for personal vehicles, and around 20 times for commercial vehicles.
What Are Automated Fitness Centres?
- Every vehicle will have to go under a mandatory fitness test at the automated fitness centres.
- The government aims to have at least 718 centres across the country.
- These centres will test the vehicle’s emission, and braking and other safety components as prescribed by Central Motor Vehicle Rules, 1989.
- Appointments to these centres will have to be booked online and the fitness report will be electronically generated.
Change in Fee Structure
- The government has increased the fee for renewal and grant of fitness certificate of older vehicles up to 20 times.
- Here is the new fee structure for personal vehicles older than 15 years:
- Two-wheelers – Rs 1,000
- Three-wheeler/quadricycles – Rs 3,500
- Cars – Rs 7,500
(Do not worry about the data. It is the state PSCs which may ask such information)
For commercial vehicles:
- Passenger motor vehicles – Rs 10,000
- Heavy goods/large motor vehicles – Rs 12,500
Benefits for buyers
- In case you decide to scrap your old vehicle at the registered scrapping centres, you will get approximately 4-6 per cent of the value of the vehicle’s ex-showroom price.
- The ex-showroom price is the cost of the vehicle, excluding the charges paid for registering the vehicle at RTO and insurance.
- Moreover, if you buy a new vehicle you will be given a flat 5 per cent discount on presenting a scrapping certificate.
- Registration fees will also be waived on the purchase of a new vehicle.
Obtaining a Scrapping Certificate
- Old vehicle owners will be able to formally scrap their registered vehicles at the automated scrapping centres.
- These centres will be linked with the Vahan database of the transport ministry.
- After you scrap your vehicle with the government registered agency, you will be provided with the scrapping certificate.
- You will then be eligible for the benefits proposed under the scheme.
Implementation
Tentative timeline for the new rules:
- Rules for fitness tests and government scrapping centres to come into effect – 1 October 2021
- The scrapping of government and PSU vehicles above 15 years of age to start – 1 April 2022
- Fitness testing for heavy commercial vehicles – 1 April 2023
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] FASTag declared mandatory
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fastag
Mains level: Fastag and its benefits for speedy transport
Ministry of Road Transport & Highways has decided that all lanes in the fee plazas on National Highways shall be declared as “FASTag lane of the fee plaza”.
Fastag went unnoticed this year. The RFID technology deployed in this holds an intuition for its relevance in CS prelims and many forthcoming exams.
What is ‘FASTag’?
- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
How does it work?
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- RFID technology is similar to that used in transport access-control systems, like Metro smart card.
- If the tag is linked to a prepaid account like a wallet or a debit/credit card, then owners need to recharge/top up the tag.
- If it is linked to a savings account, then money will get deducted automatically after the balance goes below a pre-defined threshold.
- Once a vehicle crosses the toll, the owner will get an SMS alert on the deduction. In that, it is like a prepaid e-wallet.
Must read:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
What are Fastags?
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Fastag
Mains level: RFID technology
From January 1, all lanes of National Highways will accept only electronic payments through FASTag.
Fastags work on a unique technology called RFID (Radio Frequency Identification). This has gone unnoticed in several competitive exams. Hence it is still relevant for the aspirants.
Also read
Fastags
- As per Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, since 1st December 2017, the FASTag had been made mandatory for all registered new four-wheelers and is being supplied by the Vehicle Manufacturer or their dealers.
- It has been mandated that the renewal of fitness certificate will be done only after the fitment of FASTag.
- For National Permit Vehicles, the fitment of FASTag was mandated since 1st October 2019.
What is ‘FASTag’?

- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
How does it work?
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- RFID technology is similar to that used in transport access-control systems, like Metro smart card.
- If the tag is linked to a prepaid account like a wallet or a debit/credit card, then owners need to recharge/top up the tag.
- If it is linked to a savings account, then money will get deducted automatically after the balance goes below a pre-defined threshold.
- Once a vehicle crosses the toll, the owner will get an SMS alert on the deduction. In that, it is like a prepaid e-wallet.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Places in news: Zojila Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Zojila Pass
Mains level: Road infrastructure in Himalayas
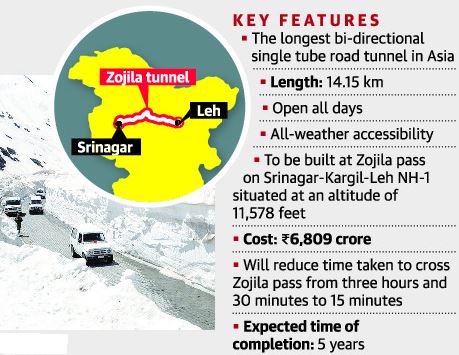
Union Transport Ministry has launched the first blasting for construction-related work at the Zojila tunnel that will provide all-year connectivity between Srinagar valley and Leh.
These days various Himalayan passes and tunnels are overwhelmingly seen in news. Open your Atlas and try to spot all of them for now and once before the exam.
Zojila Tunnel
- The Zojila is set to be Asia’s longest bi-directional tunnel.
- It will connect Srinagar, Dras, Kargil and Leh via a tunnel through the famous Zojila Pass.
- Located at more than 11,500 feet above sea level, the all-weather Zojila tunnel will be 14.15 km long and ensure road connectivity even during winters.
- It will make the travel on the 434-km Srinagar-Kargil-Leh Section of NH-1 free from avalanches, enhance safety and reduce the travel time from more than 3 hours to just 15 minutes.
- The speed limit inside the tunnel is likely to be the same as in the Atal tunnel – 80 kmph.
Its significance
- The project holds strategic significance as Zojila Pass is situated at an altitude of 11,578 feet on the Srinagar-Kargil-Leh National Highway and remains closed during winters due to heavy snowfall.
- At present, it is one of the most dangerous stretches in the world to drive a vehicle and this project is also geo-strategically sensitive.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Kozhikode-Wayanad Tunnel Project
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: About the Tunnel, EIA
Mains level: NA

Kerala CM has launched a tunnel road project that would connect Kozhikode with Wayanad.
Try this PYQ:
Q.From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats?
(a) Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
(b) Nallamala Forest
(c) Nagarhole National Park
(d) Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve
Kozhikode-Wayanad Tunnel Project
- The 7-km tunnel, being described as the third-longest in the country, is part of an 8-km road cutting through sensitive forests and hills of the Western Ghats.
- Its endpoints are at Maripuzha in Thiruvambady village panchayat (Kozhikode) and Kalladi in Meppadi panchayat (Wayanad).
- The tunnel is an outcome of a decades-long campaign for an alternative road as the Thamarassery Ghat Road is congested and gets blocked by landslides during heavy monsoon.
How will the road impact the ecology?
- The Forest Department has identified the proposed route as a highly sensitive patch comprising evergreen and semi-evergreen forests, marshlands and shola tracts.
- This region is part of an elephant corridor spread between Wayanad and Nilgiri Hills in Tamil Nadu.
- Two major rivers, Chaliyar and Kabani that flows to Karnataka, originate from these hills in Wayanad.
- Eruvazhanjipuzha, a tributary of Chaliyar and the lifeline of settlements in Malappuram and Kozhikode, begins in the other side of the hills.
- The region, known for torrential rain during the monsoon, has witnessed several landslides, including in 2019 at Kavalappura near Nilambur and at Puthumala, Meppadi in Wayanad.
Environmental clearance issues
- Proponents of the project have been stressing that the tunnel will not destroy forest (trees).
- The MoEFCC guidelines state that the Forest Act would apply not only to surface area but the entire underground area beneath the trees.
- For tunnel projects, conditions relating to underground mining would be applicable.
- As the proposed tunnel is 7 km long, it will require emergency exit points and air ventilation wells among other measures, which would impact the forest further.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
ATAL: World’s Longest Highway Tunnel
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Atal Tunnel
Mains level: Significance of the Border Infrastructure

PM Modi has inaugurated the Atal Tunnel at Rohtang at an altitude of above 3,000 metres in Himachal Pradesh.
Refer this link to read more about Himalayan passes and rivers
https://www.civilsdaily.com/the-northern-and-northeastern-mountains-part-1/
Atal Tunnel
- The 9.02 km-long-tunnel, built by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO), is the world’s longest highway tunnel and connects Manali to Lahaul-Spiti valley.
- It provides all-weather connectivity to the landlocked valley of Lahaul-Spiti, which remains cut-off for nearly six months in a year as the Rohtang Pass is usually snow-bound between November and April.
- Before the tunnel construction, the Lahaul Valley used to remain closed for vehicular movement due to bad weather conditions.
- It reduces the distance by 46 km between Manali and Leh and the travel time by about 4 to 5 hours. It is expected to boost tourism and winter sports in the region.
- The tunnel, also significant from the military logistics viewpoint, will provide better connectivity to the armed forces in reaching Ladakh.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Atal Tunnel at Rohtang
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Atal Tunnel, Pir Panjal Range
Mains level: Not Much

The Atal Tunnel at Rohtang, near Manali, is almost complete in all respects and will be inaugurated very soon in September.
Tap to read more about Himalayas at:
https://www.civilsdaily.com/the-northern-and-northeastern-mountains-part-1/
Atal Tunnel
- The 9-km-long tunnel is constructed under the Pir Panjal range.
- It has been named after former PM Atal Bihari Vajpayee and will be the world’s longest highway tunnel above the altitude of 10,000 feet (3000 metres).
- It was scheduled to be completed by May 2020, in a revised estimate, but the Covid-19 pandemic pushed back the completion by a few months due to lockdown conditions.
- Vehicles can travel at a maximum speed of 80 km per hour. Up to 1,500 trucks and 3,000 cars are expected to use it per day when the situation gets to normal.
What is its strategic advantage?
- Cutting through the Pir Panjal range, the tunnel will reduce the distance between Manali and Leh by 46 km.
- The tunnel will provide almost all-weather connectivity to the troops stationed in Ladakh.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
River Ropeway over Brahmaputra
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brahmaputra Ropeway
Mains level: Not Much
 India’s ‘longest’ river ropeway across the Brahmaputra River was unveiled in Guwahati.
India’s ‘longest’ river ropeway across the Brahmaputra River was unveiled in Guwahati.
Navigate to this page for more readings on Brahmaputra River systems:
Brahmaputra River System
Brahmaputra Ropeway

- The 1.82 km bi-cable jig-back ropeway connects the southern bank of the Brahmaputra and a hillock behind the Doul Govinda temple in North Guwahati on the other.
- It passes over the mid-river Peacock Island that houses Umananda, a medieval Shiva temple.
- It thus cuts travel time between the two banks to 8 minutes.
- The current travel options between the two banks are by ferry (30 minutes or more, depending on current and season) or by road through a bridge that usually takes over an hour in the traffic.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Kailash – Mansarovar Yatra Route from Dharchula to Lipulekh
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various passes in news, BRO
Mains level: India's border connectivity and the role of BRO

The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has completed the construction of road from Dharchula to Lipulekh along the China Border, famously known as Kailash-Mansarovar Yatra Route.
We can expect a prelims question asking to arrange few passes from West to East or vice versa. Click here to get through all such Himalayan Passes.
Darchula – Lipulekh road
- The road is an extension of Pithoragarh-Tawaghat-Ghatiabagarh road. In this 80 Km road, the altitude rises from 6000 feet to 17,060 feet.
- It originates from Ghatiabagarh in Uttarakhand and terminates at Lipulekh Pass, the gateway to Kailash Mansarovar.
- With the completion of this project, the arduous trek through treacherous high-altitude terrain can now be avoided by the Pilgrims of Kailash Mansarovar Yatra and the period of journey will be reduced by many days.
(Note: The Lipulekh Pass links Uttarakhand with China’s Tibetan Autonomous Region.)
Significance
- At present, the travel to Kailash Mansarovar takes around two to three weeks through Sikkim or Nepal routes.
- Lipulekh route had a trek of 90 Km through high altitude terrain and the elderly yartris faced lot of difficulties.
- Now, this yatra will get completed by vehicles.
Also read:
Back2Basics: Border Roads Organisation (BRO)
- The BRO develops and maintains road networks in India’s border areas and friendly neighboring countries and functions under the Ministry of Defence.
- It is entrusted for construction of Roads, Bridges, Tunnels, Causeways, Helipads and Airfields along the borders.
- Officers from the Border Roads Engineering Service (BRES) and personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF) form the parent cadre of the Border Roads Organisation.
- It is also staffed by officers and troops drawn from the Indian Army’s Corps of Engineers on extra regimental employment.
- The BRO operates and maintains over 32,885 kilometers of roads and about 12,200 meters of permanent bridges in the country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
Mains level: Read the attached story

- To augment infrastructure and create jobs in the country, the government task force on National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), which in its report projected total investment of Rs 111 lakh crore in infra projects over five years.
- It said that 18 per cent of the targeted investment is expected to be made in the road sector.
It is estimated that India would need to spend $4.5 trillion on infrastructure by 2030 to sustain its growth rate. The endeavour of the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), is to make this happen in an efficient manner.
What is the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)?
- NIP includes economic and social infrastructure projects.
- During the fiscals 2020 to 2025, sectors such as Energy (24%), Roads (19%), Urban (16%), and Railways (13%) amount to around 70% of the projected capital expenditure in infrastructure in India.
- It has outlined plans to invest more than ₹102 lakh crore on infrastructure projects by 2024-25, with the Centre, States and the private sector to share the capital expenditure in a 39:39:22 formula.
Key benefits of NIP
- Economic: Well-planned NIP will enable more infra projects, grow businesses, create jobs, improve ease of living, and provide equitable access to infrastructure for all, making growth more inclusive.
- Government: Well-developed infrastructure enhances the level of economic activity, creates additional fiscal space by improving the revenue base of the government, and ensures the quality of expenditure focused in productive areas.
- Developers: Provides a better view of project supply, provides time to be better prepared for project bidding, reduces aggressive bids/ failure in project delivery, ensures enhanced access to sources of finance as a result of increased investor confidence.
- Banks/financial institutions (F1s)/investors: Builds investor confidence as identified projects are likely to be better prepared, exposures less likely to suffer stress given active project monitoring, thereby less likelihood of NPAs.
Projects include
- The report contains recommendations on general and sector reforms relating to key infrastructure sectors for implementation by the Centre and states.
- These projects will be implemented under the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), a first of its kind exercise, by consulting states, relevant ministries and departments.
- Three committees will be set up to monitor project progress, eliminate delays, and find ways to raise resources, along with a steering committee in each of the infrastructure ministries.
- Sectors such as energy (24%), roads (18%), urban (17%) and railways (12%) amount to around 71% of the projected investments.
- The projects will also be spread across sectors such as irrigation, mobility, education, health, water and the digital sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Rohtang Pass and its location
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various passes in news, BRO
Mains level: NA
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has opened the Rohtang Pass, three weeks in advance, for transporting essential supplies and relief materials to Lahaul and Spiti districts of Himachal Pradesh.
Rohtang Pass
- It is a high mountain pass (elevation 3,980 m) on the eastern Pir Panjal Range of the Himalayas around 51 km from Manali.
- It connects the Kullu Valley with the Lahaul and Spiti Valleys of Himachal Pradesh, India.
- The pass lies on the watershed between the Chenab and Beas basins.
- On the southern side of this pass, the Beas River emerges from underground and flows southward and on its northern side, the Chandra River, a source stream of the river Chenab, flows westward.
Another pass in new:
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
Agartala-Akhaura Railway Link
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Agartala-Akhaura Link
Mains level: Railway connectivity in NE states

The landmark Agartala-Akhaura railway line to connect the northeastern region with Bangladesh is expected to be ready by the end of 2021.
About Agartala-Akhaura Link
- MoU for Indo-Bangla Railway connectivity project viz. Agartala-Akhaura new Broad Gauge line (15.06 Km) was signed on 16.02.2013 between India and Bangladesh.
- The link will connect Gangasagar in Bangladesh to Nischintapur in India and from there to Agartala.
- The Project was at standstill because of the sharp increase in the cost of land for the sections in India.
- The Railway Ministry would bear the cost of laying the 5.46-km track on the Indian side and the cost of the 10.6-km track on the Bangladesh side was being borne by the Ministry of External Affairs.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
[pib] Draft National Logistics Policy
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Logistics Policy
Mains level: Logistics sector of India

The Union Minister of Commerce and Industry reviewed the draft National Logistics Policy and the proposed action plan for implementation of the policy prepared by the Department of Logistics, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
The key feature of the draft policy
- The draft National Logistics Policy has been prepared in consultation with the Ministries of Railways, Road Transport and Highways, Shipping and Civil Aviation.
- Forty-six Partnering Government Agencies (PGAs)
- Inputs were analysed in detail for consideration in the Policy.
- Vision and Objectives for Logistics in India: To drive economic growth and trade competitiveness of the country through a truly integrated, seamless, efficient, reliable and cost-effective logistics network, leveraging best in class technology, processes and skilled manpower.
- Key objectives of the national logistics policy: Given the pivotal role of the logistics sector in the development of the economy and the need to incorporate learnings from global best practices, the policy outlines an ambitious set of objectives.

The following are some of the key objectives for logistics in India, to be achieved in the next five years:
1. Creating a single point of reference for all logistics and trade facilitation matters in the country which will also function as a knowledge and information sharing platform
2. Driving logistics cost as a % of GDP down from estimated current levels of 13-14% to 10% in line with best-in-class global standards and incentivize the sector to become more efficient by promoting integrated development of logistics
Objectives of the Logistics Policy
- Creating a National Logistics e-marketplace as a one-stop marketplace. It will involve simplification of documentation for exports/imports and drive transparency through digitization of processes involving Customs, PGAs etc in regulatory, certification and compliance services
- Creating a data and analytics centre to drive transparency and continuous monitoring of key logistics metrics
- Encouraging industry, academia and government to come together to create a logistics Center of Excellence, and drive innovation in the logistics sector
- Creating and managing on an ongoing basis, an Integrated National Logistics Action Plan which will serve as a master plan for all logistics-related development.
- Providing an impetus to trade and hence economic growth by driving competitiveness in exports
- Doubling employment in the logistics sector by generating additional 10-15 million jobs and focus on enhancing skills in the sector and encouraging gender diversity
- Improve India’s ranking in the Logistics Performance Index to between 25 to 30
- Strengthening the warehousing sector in India by improving the quality of storage infrastructure including specialized warehouses across the country
- Reducing losses due to agri-wastage to less than 5% through effective agri-logistics
- Providing impetus to the MSME sector in the country through a cost-effective logistics network
- Promoting cross-regional trade on e-commerce platforms by enabling a seamless flow of goods
- Encouraging the adoption of green logistics in the country
Policy thrust areas
This policy defines the key thrust areas for logistics in India, which will be the focus of the relevant ministries as well as act as guidance to the state governments. The prioritized focus areas for logistics are detailed below:
- Focusing on critical projects to drive an optimal modal mix and to enable first mile and last-mile connectivity
- Driving the development of Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLPs)
- Driving interventions to reduce logistics cost and promote logistics efficiency for movement of key commodities
- Creating a single-window Logistics e-marketplace
- Setting up a Logistics Data and Analytics Center
- Creating a Center of Trade facilitation and Logistics excellence (CTFL) and leveraging the expertise of multilateral agencies
- Creating an Integrated National Logistics Action Plan and align with respective state development plans
- Support strengthening of the warehousing sector
- Enhancing transport and rolling stock infrastructure
- Streamlining EXIM processes to promote trade competitiveness
- Reducing dwell time for interstate cargo movement by road
- Promoting standardization in the logistics sector
- Ensuring seamless movement of goods at Land Customs Stations (LCS) and Integrated Check Points (ICP)
- Generating employment, enhancing skilling and encouraging gender diversity in the logistics sector
- Setting up a Startup acceleration fund
Funding for logistics initiatives

A non-lapsable Logistics fund will be created, to drive progress against the key thrust areas. The Logistics fund can be deployed for the following
- Providing viability gap funding for select MMLP projects, first and last-mile projects and projects for poorly-serviced remote areas.
- Incentivizing select logistics skilling programs and training institutes
- Setting up a start-up acceleration fund to incentivize the development of new technology in logistics particularly the farm to plate space
- Creating the Center for Trade Facilitation and Logistics Excellence (CTFL) Setting up a big data-enabled logistics data hub and analytics centre
- Creating a single-window logistics e-marketplace
Institutional Framework & Governance for Logistics

For this purpose, four committees/councils will be constituted:
- National Council for Logistics, chaired by the Prime Minister
- Apex inter-ministerial Committee, chaired by the Minister of Commerce and Industry
- India Logistics Forum chaired by the Commerce Secretary with representation from key industry/business stakeholders and academia.
- Empowered task force on logistics will be created, as a standing committee chaired by the head of the Logistics Wing.

Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Roads, Highways, Cargo, Air-Cargo and Logistics infrastructure – Bharatmala, LEEP, SetuBharatam, etc.
National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Infrastructure Pipeline
Mains level: $5 trillion economy: Prospects and Challenges
Union Finance Minister has unveiled Rs 102 lakh crore of infrastructure projects, under National Infrastructure Pipeline. It will be implemented in the next five years as part of the government’s spending push in the infrastructure sector.
What is the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP)?
- NIP includes economic and social infrastructure projects.
- During the fiscals 2020 to 2025, sectors such as Energy (24%), Roads (19%), Urban (16%), and Railways (13%) amount to around 70% of the projected capital expenditure in infrastructure in India.
- It has outlined plans to invest more than ₹102 lakh crore on infrastructure projects by 2024-25, with the Centre, States and the private sector to share the capital expenditure in a 39:39:22 formula.
Key benefits of NIP
- Economic: Well-planned NIP will enable more infra projects, grow businesses, create jobs, improve ease of living, and provide equitable access to infrastructure for all, making growth more inclusive.
- Government: Well-developed infrastructure enhances the level of economic activity, creates additional fiscal space by improving the revenue base of the government, and ensures the quality of expenditure focused in productive areas.
- Developers: Provides a better view of project supply, provides time to be better prepared for project bidding, reduces aggressive bids/ failure in project delivery, ensures enhanced access to sources of finance as a result of increased investor confidence.
- Banks/financial institutions (F1s)/investors: Builds investor confidence as identified projects are likely to be better prepared, exposures less likely to suffer stress given active project monitoring, thereby less likelihood of NPAs.
Is NIP a road to $5 trillion economy?
- Finance minister said that the Rs 102 lakh crore National Infrastructure Projects will help make India a $5 trillion economy by 2025.
- These projects are on top of Rs 51 lakh crore spent by the Centre and the states during the last six years.
- The new pipeline consists of 39 per cent projects each by the Centre and states and the balance by 22 per cent by private sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Challenges, opportunities & criticism of the Real Estate Regulatory Bill 2016
The Real Estate Regulatory Bill, 2016 is being hailed as a much-needed step to reform the real estate sector. It will help regulate the sector and bring in clarity for both buyers and developers.
What was the need for regulation in the real estate?
- The real estate sector has some issues such as a lengthy process for project approvals, lack of clear land titles, and prevalence of black money
- There wasn’t complete transparency as far as govt approvals were concerned
- There were also instances when projects were sold without adequate clearances
- The delayed projects, sometimes by up to 6 years and arbitrary changes in layout plans are rampant in the sector
How does the Bill seeks to regulate the sector?
The basic thrust of this Bill is to regulate the delivery of projects to home buyers. It provides them a legal safeguard for their investment, and seeks to address timely delivery of houses. It seeks to enforce the contract between the developer and buyer and act as a fast track mechanism to settle disputes
- It establishes state level regulatory authorities called Real Estate Regulatory Authorities (RERA)
- The Bill establishes state level tribunals called Real Estate Appellate Tribunals. Decisions of RERAs can be appealed in these tribunals
- It makes mandatory the disclosure of all information for registered projects like details of promoters, layout plan, land status, schedule of execution and status of various approvals
- The Bill prohibits a developer from changing the plan in a project unless two-thirds of the allottees have agreed for such a change
- It says that builders must specify the time-frame for completion of projects and stick to it, or be ready to pay penalties
- The Bill mandates that 70% of the amount collected from buyers of a project be used only for construction of that project < This provision will effectively allow developers to continue their practice of diverting funds collected for a project towards land acquisition or other projects, and will work in their favour by also allowing them to grow their land and/or project portfolio>
How will the Real Estate Regulatory Authorities help improve the sector?
- Residential real estate projects need to be registered with RERAs, except few
- Promoters cannot book or offer these projects for sale without registering them
- Real estate agents dealing in these projects also need to register with RERAs
- On registration, the promoter need to provide details of the project to the RERA
Challenges ahead
- The Bill will make life difficult for builders, as they would face more red-tapeism now, especially in procuring relevant approvals.
- This Bill does not address the developers demand of a single-window clearance from the govt
- The implementation of the Bill is up to the states, it leaves builders with greater chances of being harassed
Impact
- Timely completion of projects would lead to a steady increase in supply of homes
- It is expected that these measures will eventually bring down home prices and increase demand
- It will be good for the overall economy too, as the housing sector has strong backward (cement, steel and other building material industries) and forward (furniture and furnishings, interior decoration, electrical and electronics) linkages with other industries
- More number of job creation in the economy
Criticism
- The builder lobbies argued that the bill should have a time-frame for municipal and other authorities to give timely approvals, because the delay in approvals lead to delays in handing over possession of apartments
- In terms of pricing, which is governed by circle rates, it will be difficult to monitor
Future
- The states’ support for faster clearances to projects will be required to make this Bill successful
- Govt is also trying to bring in a National Urban Rental Housing Policy, which would take into account the requirements of tenancy hassles in modern days
Published with inputs from Pushpendra
Sagarmala Project: Smart ports for Blue Revolution in India
The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister Modi, on March,2015 gave its ‘in-principle’ approval for the concept and institutional framework of Sagarmala Project. Let’s take a glance on it.
What’s the prime objective of Sagarmala?
The prime objective of the Sagarmala project is to promote port-led direct and indirect development and to provide infrastructure to transport goods to and from ports quickly, efficiently and cost-effectively.
What’s the current issue and background of ports in India?
- At present there are around 200 ports (small and big) in the country, of these, only 12 are major ports which are government owned ports, which handle about 58% of sea-borne traffic.
- These major ports operate as Trusts under the Major Ports Trust Act, 1963, except for the Port of Ennore, which is a company under the Companies Act.
- There are legacy issues with these govt owned major ports, they do not keep pace with emerging technology, requirements of international trade, emerging trends in containerisation, flexible rules, size of ships etc.
Which are the 12 Major Ports ?
These are Kolkata (including Dock Complex at Haldia), Visakhapatnam, Chennai, V.O. Chidambaranar (Tuticorin), Cochin, New Mangalore, Mormugao, Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT), Mumbai, Kandla and Ennore.
Just, Look back into the history?
In 2003, then PM Vajpayee proposed Project Sagarmala with following features:
- Setup Sagarmala Development Authority (Similar to National highway authority of India).
- It will get money via Maritime development cess. (5 paise per kg on cargo).
- It will improve ports, shipping industry, inland water transport, coastal shipping.
- PPP and FDI to gather more investment.
Then, which are the Key pillars to achieve Smart-development ?
- Supporting and enabling Port-led Development through appropriate policy and institutional interventions.
- Providing for an institutional framework for ensuring inter-agency and states’ collaboration for integrated development.
- Port Infrastructure Enhancement, including modernization and setting up of new ports.
- Efficient Evacuation to and from hinterland.
What are some of the measures to make Smart Ports?
- Ports should be registered as Companies under Companies Act.
- The port administration should only look after the provisions of infrastructure and safety and not day-to-day running of the port
- There is still no regulation to control the trade practices.
- Hence, there is a dire need to introduce a regulatory architecture that takes care of ex-ante declaration of rates of services.
Then, what’s the plan to implement such a vast initiative?
- For a comprehensive and integrated planning for “Sagarmala”, a National Perspective Plan (NPP) for the entire coastline shall be prepared within six months.
- It will identify potential geographical regions to be called Coastal Economic Zones (CEZ).
- While preparing the NPP, synergy and integration with planned Industrial Corridors, Dedicated Freight Corridors, National Highway Development Programme, Industrial Clusters and SEZs would be ensured.
What are the suggestions for effective mechanism at state level?
- Set up State Sagarmala Committee to be headed by CM / Minister in Charge of Ports.
- Sagarmala Coordination and Steering Committee (SCSC) shall be constituted under the chairmanship of the Cabinet Secretary and others.
- This Committee will provide coordination between ministries, state governments and agencies connected with implementation and review the progress of implementation of the National Perspective Plan.
How does it ensure the sustainable development in CEZ?
- This would be done by synergising and coordinating with State Governments and line Ministries of Central Government through their existing programmes.
- Such as those related to community and rural development, tribal development and employment generation, fisheries, skill development, tourism promotion etc.
- In order to provide funding for such projects and activities that may be covered by departmental schemes a separate fund by the name ‘Community Development Fund’ would be created.
What’s the role of Institutional Framework ?
- It has to provide for a coordinating role for the Central Government.
- It should provide a platform for central, state governments and local authorities to work in tandem and coordination under the established principles of cooperative federalism.
What’s the role of NSAC?
A National Sagarmala Apex Committee (NSAC) is envisaged for overall policy guidance and high level coordination, and to review various aspects of planning and implementation of the plan and projects.
So, Is it Good to have smart ports on the line of Smart Cities?
Can you answer some questions?
#1. Can you examine the bottlenecks in Indian port infrastructure and list the initiative taken in recent times to address this issue?
#Q.2 Indian port infrastructure can be revamped by Sagarmala project by effective management? critically comment.
Published with inputs from Arun




