Why in the News?
For the first time since India’s independence, the Shipki La pass in Himachal Pradesh has been opened to domestic tourists, marking a historic shift in India’s border tourism strategy.
About Shipki La Pass:
- It is a high-altitude mountain pass at 3,930 meters in the Kinnaur district of Himachal Pradesh, on the India–Tibet (China) border.
- It is one of only 3 official border trading points between India and Tibet, along with Nathu La (Sikkim) and Lipulekh (Uttarakhand).
- The Sutlej River (called Langqen Zangbo in Tibet) enters India near Shipki La, adding geographical importance to the area.
- The pass lies along National Highway 5 (NH5) and is considered one of the highest motorable roads in India.
- Historically, it served as a major trade route, enabling exchange of salt, wool, spices, yak tails, and tea between India and Tibet.
- Trade was stopped in 1962 after the India-China war, resumed in 1992, but was halted again during COVID-19.
- On June 9, 2025, Himachal Pradesh opened the pass to Indian tourists for the first time since Independence.
- The initiative is part of a “Border Tourism” strategy, which includes the launch of the Sarhad Van Udyan (Border Forest Park).
- It is also being considered as an alternate route for the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra.

Other Important Himalayan Passes:
- Ladakh and Jammu & Kashmir:
- Khardung La (5,359 m) – Among the highest motorable passes; connects Leh with Nubra Valley.
- Zoji La – Links Srinagar with Leh; vital for year-round Ladakh access.
- Chang La, Baralacha La, Umling La (5,798 m) – Crucial for Leh connectivity and defense.
- Rezang La – Famous for the 1962 India-China war battle.
- Karakoram Pass, Aghil Pass, Demchok Pass – Strategic India-China border passes.
- Himachal Pradesh:
- Rohtang Pass – Connects Kullu with Lahaul-Spiti; key for tourism and logistics.
- Parang La – Links Spiti Valley and Parvati Valley; used by trekkers and herders.
- Shipki La – Now open to tourists; historical Indo-Tibetan trade route.
- Uttarakhand:
- Lipulekh Pass (5,632 m) – Used for Kailash Mansarovar Yatra.
- Mana Pass – One of the highest vehicle-accessible passes; connects to Tibet.
- Niti Pass, Milam Pass, Kuthi Pass – Historical trade and pilgrimage routes.
- Sikkim:
- Nathu La – Major border trade route; part of the ancient Silk Route.
- Jelep La – Historical route linking Sikkim with Lhasa via Chumbi Valley.
- Arunachal Pradesh:
- Se La, Bum La – Connect to Tawang and Bhutan border.
- Pangsau Pass, Diphu Pass – Connect Arunachal with Myanmar; important for WWII history and connectivity.
| [UPSC 2007] Which one of the following Himalayan passes was reopened around in the middle of the year 2006 to facilitate trade between India and China?
Options: (a) Chang La (b) Jara La (c) Nathu La (d) Shipki La |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Tamil Nadu government has officially notified a Greater Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi in Ramanathapuram district.

What is a Bird Sanctuary?
- India’s bird sanctuaries are established under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (WLPA).
- Section 18 of the WLPA empowers State governments to declare wildlife or bird sanctuaries based on ecological or zoological importance.
- The law prohibits hunting of protected birds and prescribes penalties for violations, including fines and imprisonment.
|
About Greater Flamingo (Phoenicopterus roseus):
- Overview: It is the largest and most widespread flamingo species, found across Africa, southern Europe, and South and Southeast Asia, including India and Pakistan.
- Presence in India: India hosts both Greater and Lesser Flamingos. Greater Flamingo is the state bird of Gujarat.
- Behaviour and Diet: These birds form monogamous pairs and get their pink coloration from a diet rich in brine shrimp and algae. They are omnivores, feeding on invertebrates, small fish, algae, and decaying plant matter.
- Habitat: They prefer saltwater lagoons, mudflats, and saline lakes, and are important indicators of wetland health.
- Migration Pattern: Every year, 100,000–150,000 flamingos migrate from Gujarat to Mumbai, typically arriving in November and settling in the Thane Creek Flamingo Sanctuary.
- Migration Triggers: Their movement depends on food availability, water levels, and colony crowding.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern (LC) (species is widespread and abundant)
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II (protected but with lesser penalties than Schedule I)
- CMS (Convention on Migratory Species): Appendix II (species need international cooperation for conservation)
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species): Appendix II (trade is regulated to avoid overexploitation)
About the Flamingo Sanctuary at Dhanushkodi:
- Location: The sanctuary lies in the Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve, spanning 524.7 hectares in Rameshwaram taluk.
- Habitat: It includes mangroves, sand dunes, mudflats, and marshes, supporting migratory birds, marine life, and sea turtles.
- Flyway Connection: The site falls along the Central Asian Flyway, a key route for wetland migratory birds.
- Bird Census: The 2023–24 wetland bird survey recorded over 10,700 birds, including herons, egrets, sandpipers, and both flamingo species.
- Ecological Importance: Mangrove species like Avicennia and Rhizophora dominate the area, offering breeding grounds and coastal protection.
| [UPSC 2015] With reference to an organization known as ‘BirdLife International’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
(1) It is a Global Partnership of Conservation Organizations. (2) The concept of ‘biodiversity hotspots’ originated from this organization. (3) It identifies the sites known/referred to as ‘Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas’.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only * (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India has added two new wetlands—Khichan in Phalodi and Menar in Udaipur, both located in Rajasthan—to the Ramsar List of Wetlands of International Importance. With these additions, India’s total number of Ramsar sites has reached 91.
Khichan and Menar Wetlands:
- Khichan (Phalodi District):
- It is internationally famous for hosting thousands of migratory Demoiselle cranes, making it a major birdwatching destination.
- The wetland supports biodiversity, acting as a crucial habitat for migratory birds and maintaining ecological balance.
- Menar (near Udaipur):
- It is known as Rajasthan’s “Bird Village”, celebrated for its community-led conservation efforts.
- It hosts rare birds like the cinereous vulture, Himalayan griffon, Dalmatian pelican, and black-tailed godwit.
|
About the Ramsar Convention:
- It is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands.
- It was established on February 2, 1971, in the city of Ramsar, Iran.
- The convention focuses on:
- Identifying and designating wetlands of global importance.
- Ensuring effective management of these wetlands.
- Promoting international cooperation for wetland protection.
- India and the Ramsar Convention:
-
- India became a signatory in 1982.
- The first Site in India was Chilika Lake in Odisha, designated in 1981.
- As of now, India has 91 Ramsar sites, covering around 13.58 lakh hectares.
- Wetlands listed under Ramsar make up about 10% of India’s total wetland area.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest number of Ramsar sites (20), followed by Uttar Pradesh (10).
9 Criteria for Declaring Ramsar Sites:
A wetland can be declared a Ramsar Site by a signatory country if it meets one or more of the following criteria:
- It has unique, rare, or representative wetland types.
- It supports vulnerable, endangered, or endemic species.
- It is a habitat for waterfowl, especially during migration.
- It holds significant ecological, botanical, zoological, limnological, or hydrological features.
- It supports scientific research and promotes biodiversity conservation.
- It provides ecosystem services like flood control, water purification, and groundwater recharge.
- It has cultural, spiritual, or recreational value.
- It supports sustainable livelihoods for local communities.
- It faces threats requiring international cooperation for conservation.
Other Key Facts:
- 171 countries are currently part of the Ramsar Convention.
- The United Kingdom has the highest number of Ramsar sites (175); Mexico follows with 142 sites.
- Bolivia has the largest wetland area under protection, covering 148,000 sq. km.
- World Wetlands Day is celebrated every year on February 2, to commemorate the signing of the Ramsar Convention and raise awareness about the importance of wetlands.
- The Montreux Record is a list of Ramsar sites that require urgent conservation attention due to human-induced threats.
|
| [UPSC 2022] Consider the following pairs:
Wetland/Lake Location
1. Hokera Wetland — Punjab
2. Renuka Wetland — Himachal Pradesh
3. Rudrasagar Lake — Tripura
4. Sasthamkotta Lake — Tamil Nadu
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
Options: (a) Only one pair (b) Only two pairs* (c) Only three pairs (d) All four pairs. |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand opened to tourists on June 1 for its annual four-month window.

About the Valley of Flowers National Park:
- Location: The park is in Chamoli district, Uttarakhand, within the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- Altitude and Size: It covers 87 square kilometres and lies at 3,352 to 3,658 metres above sea level.
- Protected Status: Declared a National Park in 1980 and became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988.
- Natural Features: Known for its colourful meadows, dense forests, waterfalls, and snow-capped mountains.
- Mountain Range: Lies in the transition zone between the Zanskar and Great Himalaya ranges.
- River System: The Pushpawati River, from the Tipra Glacier, flows through the valley into the Alaknanda River.
- Ecosystem: It is part of the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, which was named a UNESCO Man and Biosphere (MAB) Reserve in 2004.
Flora and Fauna of the Valley:
- Plant Diversity: The valley has over 520–650 species of flowers like orchids, primulas, poppies, daisies, and the sacred brahmakamal.
- Flora by Altitude Zones:
-
- Sub-alpine (3,200–3,500 m): Trees like maple, fir, birch, and rhododendron.
- Lower alpine (3,500–3,700 m): Shrubs like junipers, willows, and geraniums.
- Higher alpine (above 3,700 m): Mosses, lichens, and the blue Himalayan poppy.
- Animal Life: Includes rare species like the Asiatic black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, brown bear, red fox, and the Himalayan monal bird.
| [UPSC 2019] Which one of the following National Parks lies completely in the temperate alpine zone?
Options: (a) Manas National Park (b) Namdapha National Park (c) Neora Valley National Park (d) Valley of Flowers National Park* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Jharkhand government has announced to establish its first tiger safari in the fringe area of the Barwadih Western Forest Range in Latehar district, which is part of the Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR).
What is a Tiger Safari?
- About: A tiger safari is a tourist activity where visitors observe tigers in natural-like habitats, usually around tiger reserves.
- Legal Status: The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 does NOT define tiger safaris but restricts construction in protected areas unless approved by the National Board for Wildlife.
- Policy Origin: The idea was formally introduced in 2012 by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under its tourism guidelines.
- Rules on Tiger Inclusion (2016): Initially, safaris were allowed only in buffer or fringe zones and could host rescued or conflict tigers, not zoo-bred ones.
- Amended Rules (2019): The NTCA later allowed even zoo-bred tigers, with Central Zoo Authority (CZA) in charge of animal welfare.
- Supreme Court Ruling (2024): The court ordered that safaris must be built outside core and buffer zones to protect wild habitats.
About Jharkhand’s Tiger Safari Project:
- Location: Planned in the Barwadih Western Range, outside core and buffer zones of Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), in line with the Supreme Court’s order.
- Animal Inclusion: Will house only rescued, injured, or orphaned tigers from various reserves and zoos — not wild tigers from PTR.
- Tourism and Employment: The project aims to boost tourism and create jobs for around 200 locals as guides and staff.
- Approval Process: The plan is still in early stages. After state Forest Department approval, a Detailed Project Report (DPR) will go to NTCA and CZA.
Back2Basics: Palamu Tiger Reserve
- It is located in Jharkhand’s Latehar and Garhwa districts, is one of India’s oldest tiger reserves, established under Project Tiger in 1973.
- Spanning over 1,014 sq. km, it features a diverse landscape of valleys, hills, plains and is nourished by rivers like the North Koel, Auranga, and Burha.
- The reserve is rich in moist and dry deciduous forests, dominated by Sal and bamboo.
- It is home to key wildlife species, including tigers, Asiatic elephants, leopards, and sloth bears.
|
| [UPSC 2020] Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”?
Options: (a) Corbett (b) Ranthambore (c) Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam* (d) Sunderbans |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Donald Trump plans to announce that the US will officially refer to the Persian Gulf as the “Arabian Gulf” or “Gulf of Arabia”, aligning with the preferences of Arab nations.

About Persian Gulf
- The Persian Gulf is a marginal sea of the Indian Ocean, located in Western Asia.
- It is connected to the Arabian Sea through the Strait of Hormuz, a critical maritime chokepoint for global oil shipments.
- The gulf spans an area of approximately 251,000 km².
- Its average depth is around 50 meters, with a maximum depth of about 90 meters.
- The total coastline is roughly 5,117 km, with Iran possessing the longest share (~1,536 km).
- The gulf is bordered by:
- North: Iran
- Southwest: Saudi Arabia, Qatar, UAE
- Northwest: Iraq, Kuwait, Bahrain
- Key islands:
- Qeshm Island (Iran) — the largest island in the Persian Gulf (~1,491 km²), nearly 2.5 times the size of Bahrain.
- Bahrain — a sovereign archipelago state with over 50 islands, and home to a major US naval base.
- It is recognized officially by the International Hydrographic Organisation (IHO) as the “Persian Gulf”.
| [UPSC 2024] Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Sumed pipeline is a strategic route for Persian Gulf oil and natural gas shipments to Europe.
Statement-II: Sumed pipeline connects the Red Sea with the Mediterranean Sea.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Options: (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I* (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I (c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The recent Pahalgam terror attack has revived debates on India’s 1966 decision to surrender the Haji Pir Pass to Pakistan during Tashkent Agreement of 1966.
This move is compared to the Soviet Union’s 1954 transfer of Crimea, which created lasting security challenges.
About Haji Pir Pass:
- The Haji Pir Pass is located in the Pir Panjal Range of Jammu and Kashmir, at an altitude of 2,637 meters (8,652 feet).
- It connects Poonch in India to Rawalakot in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
- Historically, it was a vital route for connecting Jammu to the Kashmir Valley before 1947, making it an essential part of India’s transportation network.
- Post-partition, it became part of PoK and, during the 1965 Indo-Pak War, India recaptured it under Operation Bakshi.
- However, it was returned to Pakistan following the Tashkent Agreement in 1966, a decision criticized by many experts.
How Haji Pir Pass is a Chokepoint?
- Strategic Military Route: The pass provides Pakistan with the ability to control and monitor the Kashmir Valley from a high-altitude position, serving as a key route for military logistics and infiltration.
- Gateway for Infiltration: Historically, it has been used for militant infiltration into India, fuelling insurgency and instability in Kashmir.
- Shortened Military Access: Retaining the pass would have reduced the distance between Poonch and Uri from 282 km to 56 km, improving India’s military logistics and rapid deployment.
- Control over Key Terrain: Controlling the pass enables domination of the surrounding hills, limiting Pakistan’s ability to sustain military pressure and infiltration.
| [UPSC 2007] Which one of the following Himalayan passes was reopened around in the middle of the year 2006 to facilitate trade between India and China?
(a) Chang La (b) Jara La (c) Nathu La* (d) Shipki La |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH) of Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR) in Rajasthan is set to expand by approximately 4,500 hectares.

What is Critical Tiger Habitat (CTH)?
- CTHs are designated under the Wildlife Protection Act (WLPA), 1972, to conserve tiger populations, keeping areas inviolate for tiger conservation.
- The core areas of tiger reserves, where human activities are prohibited, serve as Critical Tiger Habitats.
- Surrounding buffer zones allow sustainable human activities like eco-tourism and regulated resource use, supporting conservation efforts.
- These areas are scientifically identified based on studies of tiger movement, breeding patterns, and environmental needs, ensuring long-term survival and ecological balance.
- Scheduled Tribes and other forest dwellers’ rights are respected within the legal framework, making conservation inclusive.
- The largest critical tiger habitat in India is the Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR) spanning 5937 square kilometers.
About Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR):
- STR is located in Alwar district, Rajasthan, about 107 km from Jaipur, and is one of India’s most important tiger reserves.
- Initially a royal hunting preserve, it became a sanctuary in 1955 and upgraded to a national park in 1979.
- STR was one of the first tiger reserves under the Project Tiger initiative.
- In 2008, after the tiger population was wiped out due to poaching and human encroachment, tigers were successfully relocated to the reserve, marking a world-first for tiger reintroduction.
- Flora: STR has semi-deciduous forests, grasslands, rocky landscapes, and cliffs. The park is primarily dominated by dhok trees, covering around 90% of the area, alongside other species like salar, kadaya, and gol trees.
- Fauna: The reserve is home to species like tigers, leopards, sambhar deer, nilgai, wild boars, rhesus macaques, and hyenas.
- Ruparel River flows through STR, contributing to its ecological richness by supporting wildlife and plant species.
| [UPSC 2020] Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”?
Options: (a) Corbett (b) Ranthambore (c) Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam* (d) Sunderbans |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Odisha government has notified Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR) as a national park, covering 845.70 sq/km. It is the 107th national park and the second in eastern Odisha, following Bhitarkanika.

About Similipal National Park:
- Situated in the Mayurbhanj district of northern Odisha, Similipal is surrounded by high plateaus and hills.
- It includes the Khairiburu and Meghashini peaks, rising to 1,515 meters above sea level.
- The park has a diverse terrain with hills, open grasslands, and wooded areas, supporting various species.
- Flora: The park is home to 1,078 plant species, including 94 species of orchids, with Sal trees dominating the forests.
- Fauna: It boasts diverse wildlife, including leopards, gaurs, elephants, sloth bears, and pangolins. Similipal also supports migratory birds like Bar-headed geese and Brahmini ducks.
- Several indigenous tribes inhabit the region, such as Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, and Khadia.
- Similipal was declared a Tiger Reserve in 1956, included under Project Tiger in 1973, and became a Biosphere Reserve in 2009.
Melanistic Tigers of Similipal:
- Similipal is home to the world’s only wild population of pseudo-melanistic tigers, with 13 known to inhabit the area.
- These tigers have a distinct appearance due to higher melanin levels, causing a unique, black-striped coat.
- The mutation in the Taqpep gene makes these tigers pseudo-melanistic.
| [UPSC 2012] Consider the following protected areas; 1. Bandipur 2. Bhitarkanika 3. Manas 4. Sundarbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
Options: (a) 1 and 2 Only (b) 1, 3 and 4 Only* (c) 2, 3 and 4 only (d) 1,2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Naini Lake
Why in the News?
Naini Lake, one of Nainital’s key attractions, has recorded a water level of 4.7 feet, marking a 5-year low, sparking concerns about drinking water scarcity as the summer season approaches.
About Naini Lake
- Naini Lake is situated in the heart of Nainital, a hill station in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is surrounded by seven hills.
- The lake is natural kidney-shaped and is one of the main attractions of Nainital.
- It was discovered by P. Barron, an English businessman, in the mid-19th century, which led to the development of Nainital as a hill station.
- The deepest point of Naini Lake is 89 feet.
- The normal gauge level of the lake is 12 feet, and its water level has recently dropped to 4.7 feet, marking a five-year low.
Why is the Water Level declining?
- The Uttarakhand Jal Sansthan extracts 10 million litres of water daily from Naini Lake for drinking water supply to the city of Nainital.
- 76% of the city’s water demand was met by the lake in 2024, but increasing population, tourist activity, and commercialisation have intensified pressure on the lake’s water resources.
- The lake faces numerous threats, including:
- Decreased snowfall and rainfall, especially in the winter months.
- Unplanned construction and encroachments around the lake, leading to the reduction of its catchment area.
- Pollution due to the discharge of untreated wastewater and improper disposal of solid waste.
- Siltation caused by debris dumping in Sukhatal Lake, a major aquifer recharge area for Naini Lake, has contributed to the shrinking of the lake’s size.
- Climate change is affecting the region’s weather patterns, with annual temperatures rising by nearly 1.5 degrees Celsius between 1970 and 2022.
|
Other Important Lakes in India (Artificial and Manmade):
| Type |
Lake Name |
Location |
Details |
| Natural |
Dal Lake |
Jammu & Kashmir |
Famous for houseboats and scenic beauty, located in Srinagar. |
| Vembanad Lake |
Kerala |
The longest lake in India, central to Kerala’s backwaters and tourism. |
| Sambhar Lake |
Rajasthan |
Largest inland saltwater lake, important for bird migration, especially flamingos. |
| Manmade |
Kolleru Lake |
Andhra Pradesh |
A large freshwater lake, critical for bird habitats and a wetland. |
| Hussain Sagar Lake |
Telangana |
Constructed in 1562, famous for its Buddha statue and as a water source. |
| Upper Lake |
Madhya Pradesh |
Artificial lake in Bhopal, important for water supply and recreational activities. |
| Indira Sagar Lake |
Madhya Pradesh |
A large reservoir created by the Indira Sagar Dam for power generation and irrigation. |
| [UPSC 2018] Which one of the following is an ‘Artificial Lake‘?
(a) Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu) (b) Kolleru (Andhra Pradesh) (c) Nainital (Uttarakhand) (d) Renuka (Himachal Pradesh) |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Anchar Lake
Why in the News?
Anchar Lake, a vital water body in Kashmir, is renowned for producing Nadru (lotus stem), an aquatic delicacy that holds cultural, culinary, and economic significance in the region.

About Anchar Lake
- Anchar Lake is situated in Soura, Srinagar near Ganderbal.
- It is connected to Dal Lake via Amir Khan Nallah, which passes through Gilsar and Khushal Sar Lakes.
- The lake is a part of the Sindh River Delta and plays a crucial role in supporting local aquatic ecosystems.
- It is an integral part of the Shallabugh Wetland, which covers 1,675 hectares and serves as a designated bird sanctuary.
-
- It provides an essential habitat for migratory birds and various native aquatic species.
- It functions as a flood-control reservoir, receiving excess water from Dal Lake during heavy rainfall.
- It is home to the Hanji community, whose livelihood traditionally depended on fishing and other lake-based activities.
PYQ:
[2018] Which one of the following is an artificial lake?
(a) Kodaikanal (Tamil Nadu)
(b) Kolleru (Andhra Pradesh)
(c) Nainital (Uttarakhand)
(d) Renuka (Himachal Pradesh) |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bangus Valley
Why in the News?
The Jammu and Kashmir government has announced new ecotourism policies for Bangus Valley, a scenic yet lesser-known destination near the Line of Control (LoC) in North Kashmir.

About Bangus Valley
- It is situated in Kupwara district, Jammu & Kashmir, about 100 km from Srinagar in the Pir Panjal range, close to the Line of Control (LoC).
- It consists of 2 valleys:
- Boud Bangus (Big Bangus): ~300 sq km, surrounded by Rajwar, Mawar, and Shamasbury ranges.
- Lokut Bangus (Small Bangus): A smaller valley northeast of Big Bangus, known for trekking routes.
- Its name is derived from Sanskrit words “Van” (forest) and “Gus” (grass), meaning “Forest of Grass.”
- Connectivity:
- Handwara via Reshwari Mawer (shortest and most preferred route).
- Handwara via Rajwar (trekking route).
- Kupwara via Chowkibal (under development, expected completion by 2025).
- Road connectivity via Handwara is complete (June 2022).
Ecological Importance of Bangus Valley:
- Biodiversity: Home to 50+ animal species and 10+ bird species.
- Key Mammals: Musk deer, antelope, snow leopard, brown bear, black bear, red fox, monkeys.
- Bird Species: Tragopan, monal pheasant, black partridge, bush quail, wild fowl.
- Flora: Rich in medicinal plants and wildflowers, supporting traditional herbal medicine.
- Water Conservation: 14 tributaries, including Roshan Kul, Tillwan Kul, Douda Kul, feed the Pohru River.
- Climate Sensitivity: Threatened by glacial melt and changing precipitation patterns.
PYQ:
[2019] Siachen Glacier is situated to the:
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Similipal Tiger Reserve
Why in the News?
The Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha has witnessed a significant reduction in poaching incidents following the installation of TrailGuard AI, an AI-powered early alert system that detects intruders in the forest.
About Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR)
- Located in Mayurbhanj District, Northern Odisha, characterized by hilly and undulating terrain with open grasslands and dense forests.
- Twin peaks: Khairiburu and Meghashini, reaching 1,515 meters above sea level.
- Inhabited by tribal communities such as Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- Declared a Tiger Reserve in 1956 and brought under Project Tiger in 1973.
- Recognized as part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 2009.
- Flora:
- 1,078 species of plants, including 94 species of orchids.
- Sal (Shorea robusta) is the dominant tree species.
- Fauna:
- Rich in wildlife, including Leopards, Elephants, Gaurs, Langurs, Barking Deer, Sloth Bears, Sambar, Pythons, Pangolins, and Flying Squirrels.
- Diverse birdlife, including migratory species like Bar-Headed Geese and Brahmini Ducks.
- Home to freshwater snails (Radix genus) in its water bodies.
Melanistic Tigers of Similipal:
- Similipal is the only place in the world where pseudo-melanistic tigers are found in the wild.
- 27 of Odisha’s 30 tigers (AOTE-2023-24) live in Similipal, including 13 pseudo-melanistic tigers.
- The unique black-striped pattern in these tigers is due to a mutation in the Taqpep gene.
|
PYQ:
[2011] Two important rivers – one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha – merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of Bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area.
Which one of the following could be this?
(a) Bhitarkanika
(b) Chandipur-on-sea
(c) Gopalpur-on-sea
(d) Simlipal |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gulf of Eilat
Why in the News?
Researchers have discovered a significant pause in coral reef growth in the Gulf of Eilat/Aqaba during the late Holocene period.
Key Highlights of the Study:
- The study identified a 4,400 – 1,000-year hiatus in coral growth, similar to events observed in Mexico, Brazil, and Australia.
- Scientists attribute this temporary halt to a sea-level drop caused by tectonic activity and cooling events, which exposed coral reefs and disrupted their development.
- Despite this, the reef recovered by recolonizing from deeper coral communities, showcasing its natural resilience.
|

About Gulf of Eilat
- Also known as the Gulf of Aqaba, it is a narrow extension of the Red Sea, located between the Sinai Peninsula (Egypt) and the Arabian Peninsula.
- It connects to the Red Sea through the Strait of Tiran and borders Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.
- The city of Eilat (Israel) and Aqaba (Jordan) lie along its shores, making it a strategic trade and tourism hub.
Geographical and Political Significance:
- Strategic Trade Route: Provides access to the Indian Ocean via the Red Sea, critical for Israel and Jordan’s maritime trade.
- Bordering Multiple Nations: Shares coastlines with Egypt, Israel, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia, making it a key area for regional diplomacy and security.
- Tourism & Marine Biodiversity: Known for coral reefs and marine life, attracting divers and boosting the economies of Eilat and Aqaba.
- Geopolitical Sensitivity: The Strait of Tiran has been historically significant in Arab-Israeli conflicts, especially during the Six-Day War (1967) when Egypt blocked Israeli access.
- Energy & Trade Importance: It is an alternative route for oil shipments and goods trade, reducing reliance on the Suez Canal.
PYQ:
[2014] Which of the following have coral reefs?
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands
2. Gulf of Kachchh
3. Gulf of Mannar
4. Sunderbans
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in the News?
The Karnataka government’s move to build a tribal village in Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary’s buffer zone has sparked debates on environmental conservation, tribal rights, and human-wildlife conflict.
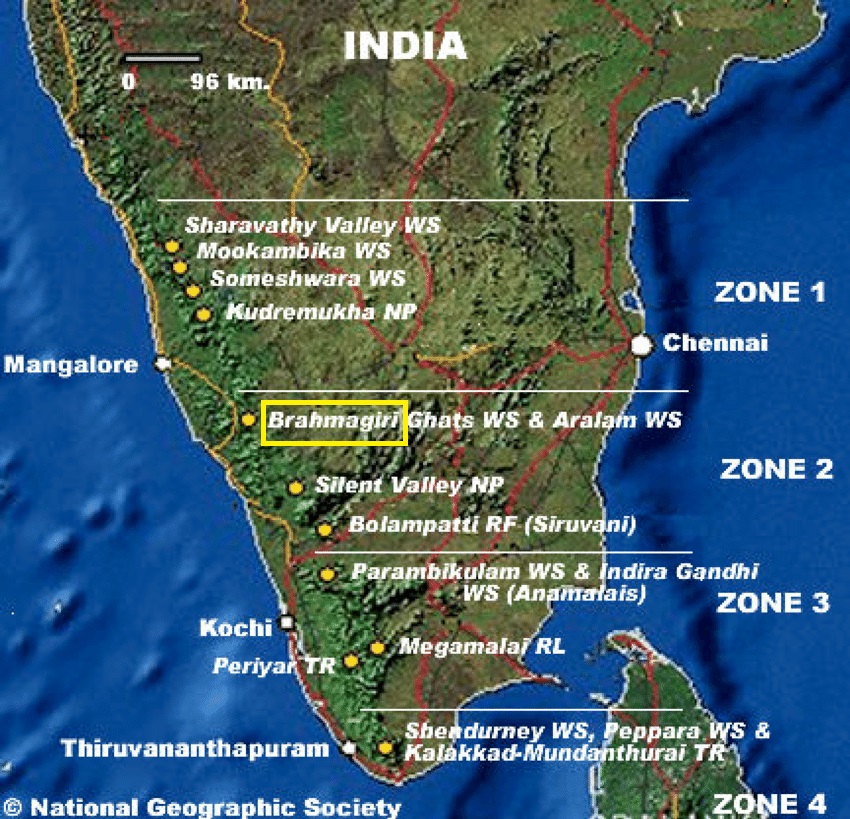
About Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary:
- The Brahmagiri WLS is located in Kodagu District, Karnataka, within the Western Ghats.
- It serves as a crucial ecological corridor, facilitating wildlife movement between Nagarhole National Park and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Geographical Location and Features
-
- It is situated approximately 250 km from Bengaluru and derives its name from the Brahmagiri Peak, the highest point in the region.
- The sanctuary was declared a protected area on June 5, 1974, to conserve its unique flora and fauna.
- The terrain consists of evergreen and semi-evergreen forests, grasslands, and shola forests, which provide a habitat for various species.
-
- Bamboo species are widely spread across the region, providing food for herbivores like elephants and deer.
- The diverse vegetation supports a wide range of faunal species by offering food, shelter, and nesting sites.
-
- Carnivores: Tigers, jungle cats, leopard cats, wild dogs, and sloth bears.
- Herbivores: Indian elephants, gaurs, sambars, spotted deer, barking deer, mouse deer, and wild pigs.
- Primates: Lion-tailed macaques, Nilgiri langurs, slender loris, bonnet macaques, and common langurs.
- Small Mammals & Rodents: Malabar giant squirrels, giant flying squirrels, Nilgiri martens, common otters, brown mongooses, civets, porcupines, and pangolins.
- Reptiles: King cobras, Indian cobras, pythons, Malabar pit vipers.
- Birds: Emerald doves, square-tailed bulbuls, and Malabar trogons.
PYQ:
[2020] Which one of the following protected areas is well-known for the conservation of a sub-species of the Indian swamp deer (Barasingha) that thrives well on hard ground and is exclusively graminivorous?
(a) Kanha National Park
(b) Manas National Park
(c) Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary
(d) Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Darien Gap
Why in the News?
The illegal journey into the US often involves dangerous crossings through multiple countries, including the treacherous Darien Gap – a vast, roadless jungle that connects Colombia and Panama.

What is the Darien Gap?
- The Darien Gap is a 97-km stretch of dense rainforest, swamps, and mountains that forms the only break in the Pan-American Highway, which otherwise runs from Alaska to Argentina.
- Due to its extreme terrain, harsh climate, and lack of infrastructure, the region has remained largely impenetrable.
- However, in recent years, it has become a major migration route, as thousands of people attempt to cross it in hopes of reaching North America.
- Geographical Features:
- Location: Forms the border between Panama and Colombia.
- Terrain: Consists of steep mountains, muddy swamps, fast-flowing rivers, and dense rainforests, making travel extremely difficult.
- Climate: Has a hot, humid, and rainy environment with limited access to food and water.
Geo-Political Significance:
- Migration Crisis: Over 520,000 migrants crossed in 2023, with over 300,000 crossings in early 2024.
- ‘Donkey Route’: Many migrants, including Indians, Venezuelans, Haitians, and Pakistanis, travel through Central American nations like Panama, Costa Rica, and Guatemala before reaching Mexico.
- Criminal Activity: The region is controlled by smuggling networks, drug cartels, and armed groups, who demand money, rob migrants, or subject them to violence.
- Humanitarian Concerns: Reports of sexual assaults, deaths, and disappearances are increasing, with overcrowded shelters and severe shortages of food, water, and medical aid.
PYQ:
[2015] The area known as ‘Golan Heights’ sometimes appears in the news in the context of the events is related to:
(a) Central Asia
(b) Middle East
(c) South-East Asia
(d) Central Africa |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Hollongapar Gibbon WLS
Why in the News?
Exploratory drilling for oil and gas has been approved within the eco-sensitive zone surrounding the Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary.
About the Hollongapar Gibbon WLS
- Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary was initially established as Hollongapar Reserve Forest in 1997 and renamed in 2004.
- It is the only habitat for hollock gibbons in India.
- Located in Assam, with the Bhogdoi River along its northern boundary.
- Biome classified as plains alluvial semi-evergreen forests with patches of wet evergreen forests.
- Flora:
- Upper canopy: Dominated by Hollong trees (Dipterocarpus macrocarpus), Sam, Amari, Sopas, Bhelu, Udal, and Hingori.
- Middle canopy: Features Nahar trees.
- Lower canopy: Composed of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
- Fauna:
- Primates: Includes Hoolock Gibbons, Bengal Slow Loris (only nocturnal primate in Northeast India), stump-tailed macaques, northern pig-tailed macaques, eastern Assamese macaques, rhesus macaques, and capped langurs.
- Other mammals: Indian elephants, tigers, leopards, jungle cats, wild boars, civets, squirrels, and more.
About the Hoolock Gibbons:
- Gibbons are the smallest and fastest apes, and they inhabit tropical and subtropical forests across Southeast Asia.
- It is the only ape specie found in India.
- They possess high intelligence, exhibit distinct personalities, and have strong familial bonds, reflecting characteristics similar to other ape species.
- The current population of hoolock gibbons is estimated at around 12,000, found primarily in Northeast India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and southern China.
- Two distinct species, the eastern hoolock gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys) and the western hoolock gibbon (Hoolock hoolock), were previously reported in India.
- Conservation Status
- IUCN Red List: the western hoolock gibbon is classified as Endangered, and the eastern hoolock gibbon is classified as Vulnerable.
- Both gibbon species in India are placed under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
|
PYQ:
[2010] Consider the following pairs:
Protected Area:: Well-known for
1. Bhitarkanika, Orissa :: Salt Water Crocodile
2. Desert National Park, Rajasthan :: Great Indian Bustard
3. Eravikulam, Kerala :: Hoolock Gibbon
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Inland Mangrove of Guneri
Why in the News?
The Gujarat government has declared the Guneri Inland Mangrove in Kutch as the state’s first Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) under The Biological Diversity Act, 2002.

Quick Facts about Mangroves in India:
- “Red List of Mangrove Ecosystems” report released on May 22 (International Day for Biodiversity), 2024.
- India holds 3% of South Asia’s total mangrove cover.
- Mangrove cover increased by 54 sq km (1.10%), reaching 4,975 sq km (0.15% of India’s total area).
- West Bengal leads (42.45%), followed by Gujarat (23.66%) and Andaman & Nicobar Islands (12.39%).
- South 24 Parganas, West Bengal, alone contributes 41.85% of India’s mangrove cover, including Sundarbans National Park.
- Gujarat recorded the highest increase, adding 37 sq km of mangrove cover.
|
About Guneri Inland Mangroves:
- Guneri Inland Mangroves (32.78 hectares) are a rare and unique mangrove ecosystem located in Kutch district, Gujarat.
- It is India’s last remaining inland mangrove site and one of only eight such sites globally.
- Unlike coastal mangroves, which thrive in tidal zones, Guneri mangroves exist inland without direct seawater contact.
- These mangroves have historical and ecological significance, possibly originating after the Miocene marine transgression or forming along the banks of the ancient Saraswati River in the Great Rann of Kutch.
Geographical Features:
- It is located about 45 km from the Arabian Sea and 4 km from Kori Creek.
- Terrain:
- Flat land, unlike coastal mangroves that grow in muddy, tidal zones.
- Devoid of sludge, making it resemble a forest rather than a typical mangrove swamp.
- Water Source:
- Thrives on limestone deposits, which help retain groundwater to sustain the mangroves.
- No direct tidal water influx, relying entirely on underground water connectivity.
- Biodiversity:
- Home to 20 migratory bird species and 25 resident migratory avifaunal species.
- Functions as a vital habitat for local and seasonal wildlife.
PYQ:
[2015] Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest?
(a) North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
(b) South-West Bengal
(c) Southern Saurashtra
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ramsar Wetland sites in India
Why in the News?
Ahead of World Wetlands Day (February 2nd), the Environment Ministry announced the inclusion of four new Ramsar sites, bringing India’s total to 89.
The newly designated sites are Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary and Therthangal Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu, Khecheopalri Wetland in Sikkim, and Udhwa Lake Bird Sanctuary in Jharkhand. With this, Tamil Nadu now has 20 Ramsar sites, the highest in the country, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10 sites.
About the Newly Added Ramsar Sites:
|
Description |
| Sakkarakottai Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu |
- Location: Ramanathapuram District, Tamil Nadu.
- Originally an irrigation tank, now a designated bird sanctuary.
- Recharged by northeast monsoon (Oct-Jan).
- Supports 42+ bird species, including Spot-billed Pelican, Grey Heron, Little Cormorant, and Black Kite.
|
| Therthangal Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu |
- Location: Theerthangal Village, Ramanathapuram District, Tamil Nadu.
- A freshwater ecosystem and an important breeding ground for waterbirds.
- Recorded 96 bird species across 18 orders and 44 families.
- Notable species include Oriental Darter, Black-headed Ibis, Asian Woolly-necked Stork, and Spot-billed Pelican.
|
| Khecheopalri Wetland, Sikkim |
- Location: West Sikkim, near Khecheopalri Village.
- A sacred lake revered by Buddhists and Hindus.
- Part of a temperate Himalayan peatland ecosystem, surrounded by broad-leaved mixed temperate forests.
- Flora: Rich in macrophytes, phytoplankton, and zooplankton.
- Fauna: Supports fish species like Cyprinus carpio, Danio aequipinnatus, and various migratory birds (Common Merganser, Tufted Duck).
|
| Udhwa Lake Bird Sanctuary, Jharkhand |
- Location: Sahebganj District, Jharkhand.
- Comprises two interconnected lakes: Pataura (155 ha) and Berhale (410 ha).
- Connected to the Ganga River via the Udhuwa Nala (25 km stretch).
- Pataura Lake depth: ~2 meters; Berhale Lake depth: ~70 cm, covered with aquatic vegetation.
- Flora: Home to 42 algae species and 36 aquatic macrophytes.
- Fauna: Habitat for 83 bird species, including the Near Threatened Black-necked Stork and 22 commercially valuable fish species.
|
PYQ:
[2019] Consider the following statements:
- Under Ramsar Convention, it is mandatory on the part of the Government of India to protect and conserve all the wetlands in the territory of India.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 were framed by the Government of India based on the recommendations of Ramsar Convention.
- The Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 also encompass the drainage area or catchment regions of the wetlands as determined by the authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kurdistan Region
Why in the News?
India has dispatched a humanitarian aid consignment to the Kurdistan region of Iraq.

What is the Kurdistan Region?
- The Kurdistan Region refers to areas inhabited by ethnic Kurds, primarily in Iraq, Iran, Syria, and Turkey.
- The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) administers Iraqi Kurdistan, an autonomous region in northern Iraq.
- The Kurds, a distinct ethnic and linguistic group, have long sought independence and greater autonomy.
- Geographical Significance:
- Spans across Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria, covering the Zagros Mountains and fertile plains.
- Rich in oil and natural gas, particularly in Iraqi Kurdistan, making it geopolitically significant.
- Controls key border regions and trade routes, influencing regional stability.
- Political Implications:
- The Kurdish struggle for autonomy has led to tensions with central governments, particularly in Iraq and Turkey.
- Kurdish forces (Peshmerga) have played a key role in fighting ISIS and maintaining security in northern Iraq.
- The KRG has diplomatic ties with Western countries but lacks full sovereignty.
Ongoing Dispute:
- The Kurdish independence movement faces opposition from Iraq, Turkey, Iran, and Syria, fearing territorial fragmentation.
- Iraq rejected the 2017 Kurdistan independence referendum, leading to military and economic retaliation.
- Turkey continues military operations against Kurdish groups, considering them a security threat.
- The Turkey-ISIS-Kurd relationship remains controversial, with allegations that Turkey indirectly enabled ISIS against the Kurds.
|
PYQ:
[2018] The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of:
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now













