Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Anti-defection law
Mains level: Paper 2- Paragraph 4 of Tenth Schedule
Context
The ongoing political crisis in Maharashtra, and many others before it, are grim reminders of what the Tenth Schedule can and cannot do.
About 10th Schedule
- In 1985 the Tenth Schedule, popularly known as the anti-defection law, was added to the Constitution.
- But its enactment was catalyzed by the political instability after the general elections of 1967.
- This was the time when multiple state governments were toppled after MLAs changed their political loyalties.
- The purpose of the 1985 Constitution Amendment was to bring stability to governments by deterring MPs and MLAs from changing their political parties on whose ticket they were elected.
- The penalty for shifting political loyalties is the loss of parliamentary membership and a bar on becoming a minister.
Provisions of the 10th Schedule
- Instances of floor crossing have long gone unchecked and unpunished.
- In part, this can be attributed to the exemption given to mergers between political parties which facilitate bulk defections.
- Disqualification provision: The second paragraph of the Tenth Schedule allows for disqualification of an elected member of a House if such member belonging to any political party has voluntarily given up membership of their party, or if they vote in the House against such party’s whip.
- Exceptions: Paragraph 4 creates an exception for mergers between political parties by introducing three crucial concepts — that of the “original political party”, the “legislature party”, and “deemed merger”.
- What is the legislature party? It means the group consisting of all elected members of a House for the time being belonging to one political party.
- Original political party: An “original political party” means the political party to which a member belongs (this can refer to the party generally, outside of the House).
- Paragraph 4 does not clarify whether the original political party refers to the party at the national level or the regional level.
How Paragraph 4 of the 10th Schedule deals with mergers?
- Paragraph 4 is spread across two sub-paragraphs, a conjoint reading of which suggests that a merger can take place only when an original party merges with another political party, and at least two-thirds of the members of the legislature party have agreed to this merger.
- It is only when these two conditions are satisfied that a group of elected members can claim exemption from disqualification on grounds of merger.
- The second sub-paragraph (of Paragraph 4) says that a party shall be “deemed” to have merged with another party if, and only if, not less than two-thirds of the members of the legislature party concerned have agreed to such merger.
- However, in most cases there is no factual merger of original political parties at the national (or even regional) level.
- Creation of legal fiction: Paragraph 4 seems to be creating a “legal fiction” so as to indicate that a merger of two-third members of a legislature party can be deemed to be a merger of political parties, even if there is no actual merger of the original political party with another party.
- In statutory interpretation, “deemed” has an established understanding.
- The word “deemed” may be used in a law to create a legal fiction, and give an artificial construction to a word or a phrase used in a statute.
- In other cases, it may be used to include what is obvious or what is uncertain.
- In either of these cases, the intention of the legislature in creating a deeming provision is paramount.
Merger exception and issues with it
- The merger exception was created to save instances of the principled coming together of political groups from disqualification under the anti-defection law, and to strike a compromise between the right of dissent and party discipline.
- In the absence of mergers of original political parties, the deeming fiction could, presumably, be used as a means to allow mergers of legislature parties.
- Encouraging defection: Reading Paragraph 4 in this manner would empower legislature parties to solely merge with another party, and thus, practically ease defection.
What if sub-paragraphs are read conjunctively?
- For a valid merger then, an original political party has to first merge with another political party, and then two-thirds of the legislature party must support that merger.
- Given the politics of current times, stark differences in parties’ respective ideologies, and deep-seated historical rivalries, it is unimaginable how a merger between major national or regional parties would materialise.
Way forward
- Remove Paragraph 4: In a situation where either reading of Paragraph 4 in its current form yields undesirable results, its deletion from the Tenth Schedule is a possible way forward.
- The Law Commission in 1999 and the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC) in 2002 made similar recommendations.
- Revisiting by Supreme Court: Till that happens, an academic revisiting of the Tenth Schedule by the Supreme Court, so as to guide future use of the anti-defection law, is timely and should happen soon.
Conclusion
Neither of these two interpretations of Paragraph 4complements the ‘mischief’ that the Tenth Schedule was expected to remedy — that of curbing unprincipled defections. Amending it is the need of the hour.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- India-UAE relations
Context
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit to the UAE on June 28 was his fourth, having visited the country earlier in August 2015, in February 2018 and again in August 2019.
Why do the Gulf and UAE matters to India?
- The UAE has given crucial support to India in the Islamic world, first by inviting our late External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj as a guest of honour at an OIC foreign ministers meeting in Abu Dhabi.
- The UAE stood with us on Jammu and Kashmir following the abrogation of Article 370.
- The Gulf is our third-largest trading partner.
- The Gulf region is our principal source of hydrocarbons.
- It is also a major source of foreign investment.
- The region is home to some 8 million Indians who send in over $50 billion annually in remittances.
Deepening bilateral ties
- CEPA: In a virtual summit with Sheikh Mohamed in February 2022, both sides signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- CEPA is a significant milestone that was negotiated and finalised in just 88 days and promises to increase bilateral trade from $60 billion to $ 100 billion in five years.
- It is expected to help Indian exports in areas ranging from gems and jewellery and textiles to footwear and pharmaceuticals, apart from enhanced access for Indian service providers to 11 specific sectors.
- Vision statement: An ambitious, forward-looking Joint Vision Statement titled, “Advancing the India and UAE Comprehensive Strategic Partnership: New Frontiers, New Milestones” was also issued.
- The Dubai-based DP World and India’s National Skills Development Council signed an agreement to set up a Skill India Centre in Varanasi to train local youth in logistics, port operations and allied areas so that they can pursue overseas employment.
New avenues for multilateral cooperation
- The rapid normalisation of ties between the UAE and Israel following the Abraham Accords of August 2020 has also opened new avenues of trilateral and multilateral cooperation.
- Technology, capital and scale: Some Israeli tech companies are already establishing a base in Dubai and seeking to marry niche technologies with Emirati capital and Indian scale.
- 2I2U: The US has announced that President Joe Biden’s forthcoming visit to West Asia will see a virtual summit of what it calls the 2I2U, a new grouping that brings together India, Israel, the US and UAE.
Conclusion
The UAE today is India’s closest partner in the Arab world. Both countries need to expand the areas of cooperation and deepen their engagement.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Back2Basics: Abraham Accords
- The Israel–UAE normalization agreement is officially called the Abraham Accords Peace Agreement.
- It was initially agreed to in a joint statement by the United States, Israel and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) on August 13, 2020.
- The UAE thus became the third Arab country, after Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994, to agree to formally normalize its relationship with Israel as well as the first Persian Gulf country to do so.
- Concurrently, Israel agreed to suspend plans for annexing parts of the West Bank.
- The agreement normalized what had long been informal but robust foreign relations between the two countries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Office of the VP
Mains level: Read the attached story
The Election Commission has announced that the election to the post of the Vice-President (VP) will be held on August 6, as M. Venkaiah Naidu’s term was coming to an end on August 10.
About Vice President of India
- The VP is the deputy to the head of state of the Republic of India, the President of India.
- His/her office is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the order of precedence and first in the line of succession to the presidency.
- The vice president is also a member of the Parliament as the ex officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Qualifications
- As in the case of the president, to be qualified to be elected as vice president, a person must:
- Be a citizen of India
- Be at least 35 years of age
- Not hold any office of profit
- Unlike in the case of the president, where a person must be qualified for election as a member of the Lok Sabha, the vice president must be qualified for election as a member of the Rajya Sabha.
- This difference is because the vice president is to act as the ex officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Roles and responsibilities
- When a bill is introduced in the Rajya Sabha, the vice president decides whether it is a money bill or not.
- If he is of the opinion that a bill introduced in the Rajya Sabha is a money bill, he shall refer it to the Speaker of the Lok Sabha.
- The vice president also acts as the chancellor of the central universities of India.
Election procedure
- Article 66 of the Constitution of India states the manner of election of the vice president.
- The vice president is elected indirectly by members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament and NOT the members of state legislative assembly.
- The election is held as per the system of proportional representation using single transferable votes.
- The voting is conducted by Election Commission of India via secret ballot.
- The Electoral College for the poll will comprise 233 Rajya Sabha members, 12 nominated Rajya Sabha members and 543 Lok Sabha members.
- The Lok Sabha Secretary-General would be appointed the Returning Officer.
- Political parties CANNOT issue any whip to their MPs in the matter of voting in the Vice-Presidential election.
Removal
- The Constitution states that the vice president can be removed by a resolution of the Rajya Sabha passed by an Effective majority (majority of all the then members) and agreed by the Lok Sabha with a simple majority( Article 67(b)).
- But no such resolution may be moved unless at least 14 days’ notice in advance has been given.
- Notably, the Constitution does not list grounds for removal.
- No Vice President has ever faced removal or the deputy chairman in the Rajya Sabha cannot be challenged in any court of law per Article 122.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PACS
Mains level: Rural banking in India
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has approved a proposal to digitise around 63,000 primary agricultural credit societies (PACS).
What are the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS)?
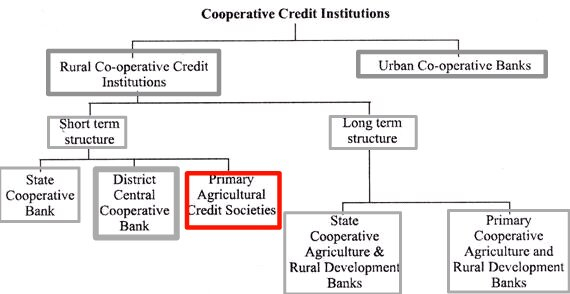
- PACS is a basic unit and smallest co-operative credit institutions in India.
- In 1904 the first Primary Agricultural Credit Society (PACS) was established.
- It works on the grassroots level (gram panchayat and village level).
- PACS is the final link between the ultimate borrowers, i.e., rural people, on the one hand, and the higher agencies, i.e., Central cooperative bank, state cooperative bank, and Reserve Bank of India, on the other.
Who regulates PACS?
- PACS are registered under the Co-operative Societies Act and also regulated by the RBI.
- They are governed by the “Banking regulation Act-1949” and Banking Laws (Co-operative societies) Act 1965.
Various objectives of PACS
- To raise capital for the purpose of making loans and supporting members’ essential activities.
- To collect deposits from members with the goal of improving their savings habit.
- To supply agricultural inputs and services to members at reasonable prices,
- To arrange for the supply and development of improved breeds of livestock for members.
- To make all necessary arrangements for improving irrigation on land owned by members.
- To encourage various income-generating activities through supply of necessary inputs and services.
Functions of PACS
- As registered cooperative societies, PACS have been providing credit and other services to their members.
- PACS typically offer the following services to their members:
- Input facilities in the form of a monetary or in-kind component
- Agriculture implements for hire
- Storage space
Who can form PACS?
- A primary agricultural credit society can be formed by a group of ten or more people from a village. The society’s management is overseen by an elected body.
- The membership fee is low enough that even the poorest agriculturist can join.
- Members of the society have unlimited liability, which means that each member assumes full responsibility for the society’s entire loss in the event of its failure.
What capitalizes PACS?
- The primary credit societies’ working capital is derived from their own funds, deposits, borrowings, and other sources.
- Share capital, membership fees, and reserve funds are all part of the company’s own funds.
- Deposits are made by both members and non-members.
- Borrowings are primarily made from central cooperative banks.
Why need digitization?
- PACS account for 41 % (3.01 Cr. farmers) of the KCC loans given by all entities in the country and 95 % of these KCC loans (2.95 Cr. farmers) through PACS are to the small and marginal farmers.
- The other two tiers viz. State Cooperative Banks (StCBs) and District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) have already been automated by the NABARD and brought on Common Banking Software (CBS).
- Majority of PACS have so far been not computerized and still functioning manually resulting in inefficiency and trust deficit.
Significance of digitization
- Computerization of PACS will increase their transparency, reliability and efficiency, and will also facilitate the accounting of multipurpose PACS.
- Along with this, it will also help PACS to become a nodal centre for providing services such as direct benefit transfer (DBT), Interest subvention scheme (ISS), crop insurance scheme (PMFBY), and inputs like fertilizers and seeds.
Try this PYQ from CSP 1999:
Q.The farmers are provided credit from a number of sources for their short and long term needs. The main sources of credit to the farmers include-
(a) the Primary Agricultural Cooperative Societies, commercial banks, RRBs and private money lenders
(b) the NABARD, RBI, commercial banks and private money lenders
(c) the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCB), the lead banks, IRDP and JRY
(d) the Large Scale Multi-purpose Adivasis Programme, DCCB, IFFCO and commercial banks
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: New GST slabs
Mains level: Rationalization of GST
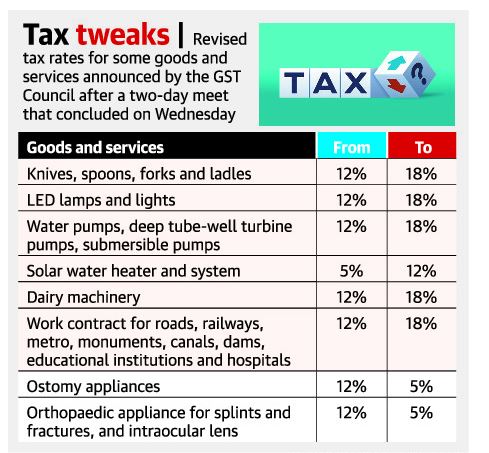
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council has decided to hike and lower GST on certain commodities.
What is the news?
- From July 18, tax hikes will kick in for over two dozen goods and services, ranging from unbranded food items, curd and buttermilk to low-cost hotels, cheques and maps.
- Tax rates will be lowered for about half-a-dozen goods and services, including ropeways and truck rentals where fuel costs are included.
- It scrapped GST for items imported by private vendors for use by defence forces.
What is GST?
- GST launched in India on 1 July 2017 is a comprehensive indirect tax for the entire country.
- It is charged at the time of supply and depends on the destination of consumption.
- For instance, if a good is manufactured in state A but consumed in state B, then the revenue generated through GST collection is credited to the state of consumption (state B) and not to the state of production (state A).
- GST, being a consumption-based tax, resulted in loss of revenue for manufacturing-heavy states.
What are GST Slabs?
- In India, almost 500+ services and over 1300 products fall under the 4 major GST slabs.
- There are five broad tax rates of zero, 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%, plus a cess levied over and above the 28% on some ‘sin’ goods.
- The GST Council periodically revises the items under each slab rate to adjust them according to industry demands and market trends.
- The updated structure ensures that the essential items fall under lower tax brackets, while luxury products and services entail higher GST rates.
- The 28% rate is levied on demerit goods such as tobacco products, automobiles, and aerated drinks, along with an additional GST compensation cess.
Why rationalize GST slabs?
- From businesses’ viewpoint, there are just too many tax rate slabs, compounded by aberrations in the duty structure through their supply chains with some inputs are taxed more than the final product.
- These are far too many rates and do not necessarily constitute a Good and Simple Tax.
- Multiple rate changes since the introduction of the GST regime in July 2017 have brought the effective GST rate to 11.6% from the original revenue-neutral rate of 15.5%.
- Merging the 12% and 18% GST rates into any tax rate lower than 18% may result in revenue loss.
Haven’t GST revenues been hitting new records?
- Yes, they have – GST revenues have scaled fresh highs in three of the first four months of 2022, going past ₹1.67 lakh crore in April.
- But there is another key factor — the runaway pace of inflation.
- Wholesale price inflation, which captures producers’ costs, has been over 10% for over a year and peaked at 15.1% in April.
- Inflation faced by consumers on the ground has spiked to a near-eight year high of 7.8% in April.
- The rise in prices was the single most important factor for higher tax inflows along with higher imports.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: G7, G12, G20
Mains level: Not Much

India is expected to host the G-20 summit in Delhi, while a number of States, including Jammu and Kashmir and north-eastern States, have been asked to suggest venues for about 100 “preparatory” meetings.
Why in news?
- The clarifications came in response to questions being raised over reports in the media about the possibility of holding the summit itself in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Pakistan had issued a strong protest last week, sent formal demarches to Foreign Ministries in G-20 member-states, asking them not to attend such meetings.
- Pakistan (alone) believes J&K is internationally recognised disputed territory.
Why such move?
- The participation of the delegates from G-20 countries will be a major boost to the efforts of the Centre to project the situation in J&K as normal.
- This is especially after J&K’s special constitutional position was ended in 2019.
What is G-20?
- Formed in 1999, the G20 is an international forum of the governments and central bank governors from 20 major economies.
- Collectively, the G20 economies account for around 85 percent of the Gross World Product (GWP), 80 percent of world trade.
- To tackle the problems or address issues that plague the world, the heads of governments of the G20 nations periodically participate in summits.
- In addition to it, the group also hosts separate meetings of the finance ministers and foreign ministers.
- The G20 has no permanent staff of its own and its chairmanship rotates annually between nations divided into regional groupings.
Aims and objectives
- The Group was formed with the aim of studying, reviewing, and promoting high-level discussion of policy issues pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability.
- The forum aims to pre-empt the balance of payments problems and turmoil on financial markets by improved coordination of monetary, fiscal, and financial policies.
- It seeks to address issues that go beyond the responsibilities of any one organization.
Members of G20
The members of the G20 consist of 19 individual countries plus the European Union (EU).
- The 19 member countries of the forum are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom and the United States.
- The European Union is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank.
Its significance
- G20 is a major international grouping that brings together 19 of the world’s major economies and the European Union.
- Its members account for more than 80% of global GDP, 75% of trade and 60% of population.
India and G20
- India has been a member of the G20 since its inception in 1999.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: CAPSTONE satellite
Mains level: Not Much

NASA has launched CAPSTONE, a microwave oven-sized CubeSat weighing just 55 pounds (25 kg).
What is CAPSTONE?
- CAPSTONE, short for Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment, is designed to test a unique, elliptical lunar orbit.
- It aims to help reduce risk for future spacecraft by validating innovative navigation technologies, and by verifying the dynamics of the halo-shaped orbit.
Its launch
- It is heading toward an orbit intended in the future for Gateway, a Moon-orbiting outpost that is part of NASA’s Artemis program.
- The orbit is known as a near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO).
- It is significantly elongated, and is located at a precise balance point in the gravities of Earth and the Moon.
- This offers stability for long-term missions like Gateway, NASA said on its website.
Mission details
- CAPSTONE will enter NRHO, where it will fly within 1,600 km of the Moon’s North Pole on its near pass and 70,000 km from the South Pole at its farthest.
- The spacecraft will repeat the cycle every six-and-a-half days and maintain this orbit for at least six months to study dynamics.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




