Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NDSAP
Mains level: Paper 2-Sharing of public data
Open access to public data is essential for policy analysis and evidence-based policymaking. Policy framework for sharing of public data by the government is also looked into in this article.
How Open Data Charter came about
- Open-source software enthusiasts and civil society activists in the U.S. and U.K. came with a demand to unlock the data gathered by governments for unfettered access and reuse by citizens.
- Data collected at public expense must belong to the people. This is the principle for the Open Data Charter adopted by 22 countries since 2015.
- It calls upon governments to disseminate public data in open digital formats.
- In return, the Charter argues, governments can expect “innovative, evidence-based policy solutions”.
Steps toward making data accessible-NDSAP
- The National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP) was adopted in 2012.
- It was a step towards making non-sensitive government data accessible online.
- The main thrust of the policy is to “promote data sharing and enable access to Government of India owned data for national planning, development and awareness”.
- The implementation guidelines for NDSAP include ideals such as “openness, flexibility, transparency, quality” of data.
- It aims to facilitate “access to Government of India shareable data in machine-readable form”.
- The guidelines prescribe open digital formats suitable for analysis and dissemination.
- Opaque formats such as the portable document format and the image format are discouraged.
- As part of the Open Government Data (OGD) initiative, data.gov.in was launched in 2012.
- However, the implementation has lagged far behind its stated objectives.
How data could have helped policy making in Covid pandemic
- The district-wise, demographic-wise case statistics and anonymous contact traces released in the public domain would have proved useful.
- Reliable model forecasts of disease spread and targeted regional lockdown protocols could have been generated.
- Model forecasts have limitations, but models without inputs from empirical data are even more unreliable.
Violation of OGD in data shared for pandemic
- Principles of OGD notwithstanding, sufficiently granular infection data are not available.
- Violating the data format guidelines, OGD portal provides COVID-19 data only as a graphic image unsuitable for any analysis.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research and mygov.in fare no better.
- They too do not publish district-wise statistics, and the available data are not in usable formats.
Examples from other countries
- The data portals of Canada, the U.K. and the U.S. present district-wise COVID-19 cases data.
- These countries also provide data about the emergent effects on mental health, jobs and education.
- According to the latest report of the Open Data Barometer, an independent group measuring the impact of open data, these nations lead the pack.
- India is a contender to reach the top bracket and not a laggard.
Way forward
- The government must provide the impetus and incentive to exploit this voluminous data by invigorating the dated national data portal.
- Every department must be mandated to share substantive data respecting privacy concerns.
- The government should look within for examples of creative outcomes of opening up the database.
- Start-ups have built novel applications using Indian Railways data to provide ticket confirmation prediction and real-time train status.
Consider the question “Examine the provisions for data sharing and accessibility in India. Also, elaborate how the sharing of public data could help in policymaking.”
Conclusion
Sharing public data is a way to create beneficial social impact. So, the government must ensure the implementation of policy measures and encourage the analysis of public data to come at the informed policy decision.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Aggregate demand, components of India's growth
Mains level: Paper 3- Importance of spending of infrastructure
Spending on infrastructure can help kickstart the economy. This article highlights the importance of spending on infrastructure and suggests ways to find resources.
Gloomy prospects for Indian economy
- The IMF estimates the global economy to contract by -4.9 per cent this year.
- It could still contract should the virus not recede in the latter half of 2020.
- As for the Indian economy, growth has been decelerating for the past eight quarters.
- Indications by the RBI suggest that growth is contracting for the first time in four decades.
- We must address the elephant in the room — the need to further aid a demand recovery as the economy begins to reopen.
Components of Indias growth
- Growth in the Indian economy has been dominated by the following components respectively-
- 1) Consumption.
- 2) It is followed by investments.
- 3) Government expenditure.
- 4) Net exports.
- However, consumption and investment demand have been subdued for the past few quarters, dragging down overall growth.
- Keynesian theory suggests that for aggregate demand to increase, at least one of the components of GDP needs to expand.
Declining consumption demand
- These two components were perhaps casualties of a sharp deceleration in credit supply.
- The IL&FS debacle in September 2018 only made matters worse.
- The NBFC sector, suffered from funding crunches leading to a further squeeze in credit supply.
- Freeze in credit supply impacted consumption demand.
- This deceleration is likely to exacerbate going forward.
Declining rate of investment
- Broad-based utilisation levels, as represented by the RBI, dropped to 68.6 per cent in Q3FY20.
- This is well below the 75 per cent benchmark for new capacity addition, implying suboptimal levels of fresh investments.
- A higher rate of investments is essential for sustainable economic growth.
- The deteriorating economic scenario and increasing levels of debt with rating downgrades for industries are likely to aggravate existing problems.
Importance of expenditure on spending on infrastructure
- Government expenditure is the only exogenously determined element in a Keynesian framework.
- The positive push required to aid a demand recovery has to come through the government.
- However, with sparse resources that India has, we must deploy funds that yield a higher return.
- One key area that can provide the necessary support is infrastructure investment.
- A study by S&P Global estimates 1 per cent of GDP spend on infrastructure can boost real growth by 2 per cent while creating 1.3 million direct jobs.
- Historically, countries have used infrastructure to provide counter-cyclical support to the economy.
- Notably, infrastructure has strong links to growth and with both supply and demand-side features that help generate employment and long-term assets.
- India already has an upper hand here.
- Front-loading key projects with greater visibility from the recently announced National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) could aid in a quicker recovery.
Special infrastructure bond
- India already has several institutions for infrastructure development purposes from the likes of IIFCL, IRFC to more recently NIIF.
- Taking a cue from China, floating special infrastructure bonds through this organisation to accelerate the funding of the NIP could aid a speedier recovery.
- Further, taking a page from the New Deal and its Reconstruction Finance Corporation, this institution’s ability for greater leverage can be used to make amends to our credit channels.
- This ability could also be used for the development of state government and urban local body bond markets.
- This could help businesses and bankers overcome risk aversion and bring back trust in the system while financing new paths for growth.
Consider the question “Highlight the role of consumption and investment as the two largest contributors to India’s growth and explain how spending on the infrastructure could help revive the economy hit hard by the pandemic”
Conclusion
The exogenous component in the form of spending by the government could step-in in a greater way, perhaps because, it is the only one that can.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- India-China standoff
How India overcomes the challenge posed by China would have far-reaching effects. Role of Russia and the U.S. is important for India. This article discusses these factors and the significance of the outcome of the conflict started at Galwan.
Two takes on India’s China policy
- Following Galwan encounter, there are two views about the future of India’s China policy.
- Some say that structural constraints would limit dramatic changes in policy once the heat of the moment dissipates.
- While others say that the Galwan clash comes amidst the deepening crisis in bilateral relations over the last decade.
- Stalled boundary talks, a widening trade deficit, the clash of national interests in the region, and Chinese opposition to India’s global aspirations have together strained Sino-Indian relations.
- Galwan is the last straw, the argument goes, that broke the camel’s back.
So, what will be the outcome
- The relationship is likely to depend on how the current military confrontation in Ladakh is resolved.
- If it ends with a quick return to the status quo that prevailed in April, inertia is likely to limit radical policy departures.
- If the Ladakh crisis ends in a setback for India, the pressure on Delhi to radically reorient its China policy will mount.
What if the standoff continues?
- In that case strengthening India’s military and political hand against China is the immediate objective of Delhi’s post-Galwan diplomacy.
- The long term steps suggested include the construction of a military alliance with the US and other Western partner.
- As as well as economic decoupling and diversification.
- Short term steps are about being able to stare down the Chinese in the current military confrontation and hold its ground.
Role of Russia
- Three decades after the collapse of the Soviet Union, India’s dependence on Russian arms remains substantive.
- Rajnath Singh’s visit to Moscow amidst the crisis with China underlines the weight of the past in India’s security policy.
- India is also pressing other major defence suppliers, including France and Israel, to accelerate deliveries on contracted defence equipment.
- There have been reports from Russia, that China is pressing Moscow not to sell the new fighter aircraft to India.
- Russia and China are strong strategic partners today.
- While the past suggests India has a special claim to Russian affections, there is a Sino-Russian strategic cohabitation today in opposition to America
- How Russia responds to India’s request will have a major bearing on the future evolution of Delhi’s ties with Moscow.
Role of the U.S.
- Unlike Russia’s public stance of neutrality between India and China, Washington has come out in favour of Delhi.
- There was vocal public support of the US defence and foreign policy establishment against Chinese aggression at Galwan.
- Media reports from Delhi say the US is already supplying valuable real-time military intelligence of value to the Indian armed forces.
- Washington is apparently willing to do more but is letting Delhi decide the pace and intensity of that cooperation.
Challenges in the U.S. cooperation
- The uncertain political moment in the US amidst the general election scheduled for early November can’t be underestimated.
- A change of guard in Washington will certainly slow things down as the new administration settles down and reviews its priorities.
- America’s stakes in China are far higher than Russia’s.
- Profound economic interdependence of the U.S. and China is a significant political constraint on the US’s options.
- On deeper military cooperation with Washington, Delhi would want to move with care rather than rush into it as it did in 1962.
How will outcomes of the crisis matter for India
- If Delhi comes out of this crisis wounded, its troubles at home and the world will mount significantly.
- A weakened India will find recasting its China policy even harder.
- But victorious India will find its international political stock rising and its options on China expanding.
- Successful Indian resistance to China’s expansionism would be a definitive moment in the geopolitical evolution of Asia.
- The stakes for India and the world, then, are far higher today than in 1962.
Consider the question “Examine the issues that introduce friction in India-China relations. Also, elaborate on the scope of India’s alliance with the U.S to counter the challenges posed by China.”
Conclusion
Outcomes of the resistance will have a profound impact on India’s standing and India’s destiny.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: STARS Project
Mains level: Read the attached story
The World Bank has approved a $500 million Strengthening Teaching-Learning and Results for States Program (STARS) to improve the quality and governance of school education in six Indian states.
Try this question:
Q. The STARS Project recently seen in news is an initiative of:
World Bank/ Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation / UNECOSOC/ UNICEF
STARS Project
- The STARS project will be implemented through the Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, the flagship central scheme.
- The six states include- Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha and Rajasthan.
- It will help improve learning assessment systems, strengthen classroom instruction and remediation, facilitate school-to-work transition, and strengthen governance and decentralized management,
- Some 250 million students (between the age of 6 and 17) in 1.5 million schools and over 10 million teachers will benefit from the STARS program.
- STARS will support India’s renewed focus on addressing the ‘learning outcome’ challenge and help students better prepare for the jobs of the future – through a series of reform initiatives.
Reform initiatives under STARS
- Focusing more directly on the delivery of education services at the state, district and sub-district levels by providing customized local-level solutions towards school improvement.
- Addressing demands from stakeholders, especially parents, for greater accountability and inclusion by producing better data to assess the quality of learning.
- Equipping teachers to manage this transformation by recognizing that teachers are central to achieving better learning outcomes. The program will support individualized, needs-based training for teachers that will give them an opportunity to have a say in shaping training programs and making them relevant to their teaching needs.
- Investing more in developing India’s human capital needs by strengthening foundational learning for children in classes 1 to 3 and preparing them with the cognitive, socio-behavioural and language skills to meet future labour market needs.
Issues with the project
- First, it fails to address the basic capacity issues: major vacancies across the education system from District Institutes of Education and Training (DIETs), district and block education offices, to teachers in schools, remain unaddressed.
- Without capable and motivated faculty, teacher education and training cannot be expected to improve.
- Second, the Bank ignores that decentralizing decision-making requires the devolution of funds and real decision-making power.
- Greater decentralisation can allow accountability to flow to the people rather than to supervising officers.
- It requires not just investment in the capacity of the front-line bureaucracy but also in increasing their discretionary powers while fostering social accountability.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PM-FME scheme
Mains level: Food processing industry and the required reforms
The Ministry for Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) has launched the PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PM FME) as a part of “Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan”.
Practice question for mains:
Q.What is the PM FME Scheme? Discuss its potential to neutralize various challenges faced by India’s unorganized food industries.
PM FME Scheme
- It aims to provide financial, technical and business support for upgradation of existing micro food processing enterprises.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme to be implemented over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25 with an outlay of Rs 10,000 crore.
- The expenditure under the scheme would to be shared in 60:40 ratios between Central and State Governments, in 90:10 ratios with NE and the Himalayan States, 60:40 ratio with UTs with the legislature and 100% by Centre for other UTs.
Features of the scheme
- The Scheme adopts One District One Product (ODODP) approach to reap the benefit of scale in terms of procurement of inputs, availing common services and marketing of products.
- The States would identify food product for a district keeping in view the existing clusters and availability of raw material.
- The ODOP product could be a perishable produce based product or cereal-based products or a food product widely produced in a district and their allied sectors.
- An illustrative list of such products includes mango, potato, litchi, tomato, tapioca, kinnu, bhujia, petha, papad, pickle, millet-based products, fisheries, poultry, meat as well as animal feed among others.
- The Scheme also place focus on waste to wealth products, minor forest products and Aspirational Districts.
Credit facility provided
- Existing Individual micro food processing units desirous of upgradation of their unit can avail credit-linked capital subsidy @35% of the eligible project cost with a maximum ceiling of Rs.10 lakh per unit.
- Seed capital @ Rs. 40,000/- per SHG member would be provided for working capital and purchase of small tools.
- FPOs/ SHGs/ producer cooperatives would be provided a credit-linked grant of 35% for capital investment along the value chain.
- Support for marketing & branding would be provided to develop brands for micro-units and groups with 50% grant at State or regional level which could benefit a large number of micro-units in clusters.
Why need such a scheme?
- The unorganized food processing sector comprising nearly 25 lakh units contribute to 74% of employment in the food processing sector.
- Nearly 66% of these units are located in rural areas and about 80% of them are family-based enterprises supporting livelihood rural household and minimizing their migration to urban areas.
Challenges faced
- The unorganised food processing sector faces a number of challenges which limit their performance and their growth.
- These challenges include lack of access to modern technology & equipment, training, access institutional credit, lack of basic awareness on quality control of products; and lack of branding & marketing skills etc.
- Owing to these challenges; the unorganised food processing sector contributes much less in terms of value addition and output despite its huge potential.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gold Nanoparticles
Mains level: Applications of nanomaterials

Indian researchers have successfully synthesized gold nanoparticles (GNPs) using psychrotolerant Antarctic bacteria through a non-toxic, low-cost, and eco-friendly way.
Nanotechnology is a pathbreaking technology which can create many new materials and devices with a wide range of applications, such as in nanomedicine, nanoelectronics etc. GNPs are another distinct development.
What are Gold Nanoparticles?
- Metallic NPs have been efficiently exploited for biomedical applications and among them, GNPs are found to be effective in biomedical research.
- And NPs are those materials that are at least one dimension smaller than 100 nanometers.
- NPs have a high surface-to-volume ratio and they can provide the tremendous driving force for diffusion, especially at elevated temperatures.
- GNPs are melted at much lower temperatures (300 °C) than bulk gold (1064 °C).
- NPs have been found to impart various desirable properties to different day-to-day products.
- For example, GNPs are found to have greater solar radiation absorbing ability than the conventional bulk gold, which makes them a better candidate for use in the photovoltaic cell manufacturing industry.
Properties of GNP
1) Biomedical
- Genotoxicity describes the property of a chemical agent that is capable of damaging the genetic information of DNA and thus causing the mutation of the cell, which can lead to cancer.
- The study revealed the genotoxic effect of GNPs on a sulphate reducing bacteria (SRB).
- These GNPs can be used as composite therapeutic agent clinical trials, especially in anti-cancer, anti-viral, anti-diabetic, and cholesterol-lowering drugs.
2) Optical
- GNPs have unique optical properties too. For example, particles above 100 nm show blue or violet colour in the water, while the colour becomes wine red in 100 nm gold colloidal particles.
- They can thus be used for therapeutic imaging.
3) Electronics
- GNPs are also found to be useful in the electronics industry.
- Scientists have constructed a transistor known as NOMFET (Nanoparticles Organic Memory Field-Effect Transistor) by embedding GNPs in a porous manganese oxide.
- NOMFETs can mimic the feature of the human synapse known as plasticity or the variation of the speed and strength of the signal going from neuron to neuron.
- These novel transistors can now facilitate better recreation of certain types of human cognitive processes, such as recognition and image processing and have their application in AI.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kholongchhu Hydel Project
Mains level: Not Much
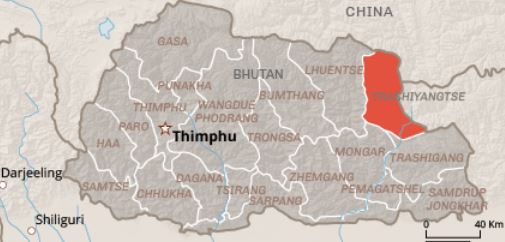
India and Bhutan took a major step forward for the construction of the 600 MW Kholongchhu project.
Try this question from CSP 2019:
What is common to the places known as Aliyar, Isapur and Kangsabati?
(a) Recently discovered uranium deposits
(b) Tropical rain forests
(c) Underground cave systems
(d) Water reservoirs
Kholongchhu Hydel Project
- The Kholongchhu project is regarded as a “milestone” in the India-Bhutan partnership, under which four hydropower projects have been built in the last 30 years totalling a capacity of 2,100 MW.
- It is one of four additional projects agreed to in 2008, as a part of India’s commitment to helping Bhutan create a total 10,000 MW of installed capacity by 2020.
- The project is located at the lower course of Kholongchhu just before its confluence with Drangmechu (Gongrichu) in Trashiyangtse District of Bhutan.
- The GoI will provide, as a grant, the equity share of the Bhutanese DGPC in the JV Company.
- Once the project is commissioned, the JV partners will run it for 30 years, called the concession period, after which the full ownership will transfer to the Bhutan government.
Whats’ so special with the project?
- It is the first hydropower joint venture project in Bhutan’s less developed eastern region of Trashiyangtse.
- It is the first time an India-Bhutan hydropower project will be constructed as a 50:50 joint venture and not as a government-to-government agreement.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gynandromorphism
Mains level: NA
Recently, a rare biological phenomenon called Gynandromorphism was observed in dragonflies at Kole wetlands of Kerala.
Gynandromorphism is a core biology concept. We can expect a prelims question in a rare scenario.
Try this question from CSP 2013:
Q.Improper handling and storage of cereal grains and oilseeds result in the production of toxins known as aflatoxins which are not generally destroyed by normal cooking process. Aflatoxins are produced by
(a) Bacteria (b) Protozoa (c) Moulds (d) Viruses
Gynandromorphism
- Gynandromorphs are individual animals that have both genetically male and female tissues and often have observable male and female characteristics.
- They may be bilateral, appearing to divide down the middle into male and female sides, or they may be mosaic, with patches characteristic of one sex appearing in a body part characteristic of the other sex.
- Gynandromorphs occur in insects, spiders, crustaceans, and other arthropods as well as in birds, but they are extremely rare, and discovering one in the field or in the laboratory is a major event.
- Estimating how frequently they occur is difficult because they usually go unnoticed in species where sexual dimorphism is less pronounced.
- Gynandromorphs have been reported in mosquitoes, fruit flies, and in other insects, but they are most dramatic in those butterfly species in which the male and female wing colours and patterns are dramatically different.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now


