Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bab al Mandab Strait

Central idea
The central idea focuses on the Houthi threat to Red Sea shipping, emphasizing the importance of navies and diplomatic efforts to maintain stability in the Indian Ocean. Historical trade warfare context and the need to address challenges like drone warfare underscore the urgency in safeguarding international trade routes. India’s proactive role and diplomatic leverage play a crucial role in ensuring regional stability.
Key Highlights:
- Houthi rebels, post the October 7 Hamas attack on Israel, pose a threat to Red Sea merchant-shipping traffic.
- Alfred Mahan’s emphasis on navies as a means to protect foreign trade and commerce for national prosperity.
- Indian Ocean’s vital role in global economy with 1,00,000 annual merchantmen, carrying 80% of the world’s oil.
- Indian Navy’s proactive role as a “preferred security partner” in maintaining good order at sea.
Key Challenges:
- Rising threat to Red Sea shipping by Houthi rebels affecting global trade.
- Historical instances of trade warfare impacting security and prosperity.
- Critical choke points in the Indian Ocean vulnerable to interdiction by states, pirates, and terrorists.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Choke points: Narrow passages in the Indian Ocean constricting shipping traffic.
- Tanker war: Strategy targeting merchant ships to impact trade, as seen in the Iran-Iraq conflict.
- Flag state: State in which a ship is registered, exercising exclusive jurisdiction over vessels.

Key Quotes:
- “The necessity of a navy… springs from the existence of peaceful shipping…”
- “The Indian Navy’s self-assigned role of ‘preferred security partner’ in the region.”
Anecdotes:
- Eight-year-long Iran-Iraq conflict saw a “tanker war” impacting merchant ships in the Persian Gulf.
- Houthi rebels launching attacks on US Navy units and merchant shipping in the Bab al Mandab Strait.
Key Statements:
- Indian Navy’s commendable alacrity in responding to emergent situations in the Red Sea.
- US launching operation “Prosperity Guardian” to safeguard Red Sea shipping.
Key Examples and References:
- Germany targeting Allied merchant shipping in 20th-century global conflicts.
- Houthi attacks in the Bab al Mandab Strait affecting merchant ships seeking safe passage.
Critical Analysis:
- Importance of maintaining good order at sea for India’s own interest and international commitment.
- Challenges posed by ongoing Yemeni civil war affecting shipping in the Red Sea.
- Complexity of the conflict involving Saudi Arabia-Iran proxy clash and multilateral dimensions.
Way Forward:
- India leveraging its good standing with Iran and Israel to urge moderation and restraint.
- Addressing the challenges posed by drone warfare and evolving effective counter-measures.
- Ensuring diplomatic efforts to prevent the west Asian conflagration from spreading to the Indian Ocean.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Chameleon Trojan
Mains level: Not Much

Central Idea
- Security researchers have identified an updated version of the ‘Chameleon Trojan’ malware, capable of disabling biometric authentication methods.
Chameleon Trojan
- The malware’s primary objective is to steal the phone’s PIN by bypassing fingerprint and face unlock security features.
- This trojan attaches itself to legitimate Android applications, such as Google Chrome, to evade detection.
- It operates in the background and is reportedly undetectable during runtime, bypassing Google Protect alerts and other security software.
- It exploits the Accessibility service on Android 12 and earlier versions, while on newer versions, it circumvents Google’s security restrictions through different methods.
Modus Operandi of Chameleon Trojan
- To bypass new restrictions, the malware displays an HTML page instructing users to enable the Accessibility service for the app, compromising device security.
- Once active, it captures on-screen content, navigates using gestures, and steals PINs and passwords, subsequently accessing more sensitive data like credit card details and login credentials.
- The malware also tracks app usage habits to time its attacks when the device is least likely to be in use.
Protection against Chameleon Trojan
- Users are advised to avoid installing Android apps from unofficial sources to reduce the risk of malware infection.
- Be wary of enabling the Accessibility service for apps that are not well-known or trusted.
- Conducting regular security scans on the device can help in identifying and mitigating threats.
- Ensuring that Google Play Protect is enabled at all times is recommended for continuous monitoring and protection against malware.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Maulana Azad National Fellowship
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- Research students have raised concerns about the disparity in scholarship amounts under the Maulana Azad National Fellowship (MANF) compared to other research fellowships.
About Maulana Azad National Fellowship
|
Details |
| Objective |
To support students from minority communities in pursuing M.Phil. and Ph.D. |
| Launch |
Launched by the Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India |
| Eligibility |
Students from minority communities (Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, Zoroastrians, Jains) who have cleared CBSE/NTA-UGC NET or CSIR NET |
| Financial Assistance |
Covers university fee, maintenance allowance, and other necessary allowances; granted for up to 5 years |
| Administration |
Managed by the Ministry of Minority Affairs; University Grants Commission (UGC) as the nodal agency |
| Selection Process |
JRF-NET (Junior Research Fellow- National Eligibility Test) examination |
| Purpose and Impact |
Encourages higher studies and research in various fields; aims at educational and socio-economic development of minority communities |
Recent Developments and Concerns
- Discontinuation of MANF: Union Minority Affairs Minister announced the discontinuation of MANF, citing overlaps with similar scholarships.
- Research Community’s Reaction: The research community, represented by the All India Research Scholars Association (AIRSA), has expressed disappointment, emphasizing the role of research in socio-economic development and the importance of MANF for financially constrained minority students.
Comparison with Other Fellowships
- Last Revision in 2019: The last increase in MANF scholarship amounts was in 2019, while other scholarships have seen recent revisions.
- Current Fellowship Amounts: UGC-approved schemes now offer ₹37,000 for junior researchers and ₹42,000 for senior researchers, a significant increase from previous amounts.
Also read:
Scholarship Schemes for Religious Minorities: Reality Check
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Core Sector
Mains level: Read the attached story
Central Idea
- India’s eight core sectors experienced a significant slowdown, growing by 7.8% in November, down from 12% in October.
About Core Industries in India
- The main or key industries constitute the core sectors of an economy.
- In India, eight sectors are considered the core sectors.
- These sectors are in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
About Index of Eight Core Industries
- The monthly Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) is a production volume index.
- ICI measures the collective and individual performance of production in selected eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement and Electricity.
- Before the 2004-05 series six core industries namely Coal, Cement, Finished Steel, Electricity, Crude petroleum and Refinery products constituted the index basket.
- Two more industries i.e. Fertilizer and Natural Gas were added to the index basket in the 2004-05 series. The ICI series with base 2011-12 will continue to have eight core industries.
The components covered in these eight industries for compilation of the index are as follows:
- Coal – Coal Production excluding Coking coal.
- Crude Oil – Total Crude Oil Production.
- Natural Gas – Total Natural Gas Production.
- Refinery Products – Total Refinery Production (in terms of Crude Throughput).
- Fertilizer – Urea, Ammonium Sulphate (A/S), Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN), Ammonium chloride (A/C), Diammonium Phosphate (DAP), Complex Grade Fertilizer and Single superphosphate (SSP).
- Steel – Production of Alloy and Non-Alloy Steel only.
- Cement – Production of Large Plants and Mini Plants.
- Electricity – Actual Electricity Generation of Thermal, Nuclear, Hydro, imports from Bhutan.
Recent data: Sector-Wise Growth Details
- Decline in ICI: The ICI witnessed a 3.34% drop from October, marking its lowest since March 2023.
- Sector-Specific Trends: Notably, only refinery products and coal showed month-on-month growth, with significant year-on-year increases.
- Steel Production: Growth in steel production hit a 13-month low at 9.1%.
- Crude Oil and Fertilizer: Crude oil saw a contraction, while fertilizer production growth decelerated.
- Natural Gas and Electricity: Both natural gas output and electricity generation growth slowed down considerably in November.
Comparative Analysis with Previous Year
- Year-on-Year Comparison: The core sectors had a 5.7% growth in November 2022.
- Influence of Base Effects: Last year’s high growth in certain sectors like cement significantly influenced this year’s comparative figures.
Economic Insights and Projections
- Bank of Baroda’s Perspective: The slowdown in fertilizer growth aligns with the end of the rabi sowing season, as per the bank’s chief economist.
- IIP Forecast: The core sectors are expected to contribute to an IIP growth of 7%-8%.
- Economists’ View: Experts predict a continued slowdown in core sector growth due to strong base effects from the previous fiscal year.
Future Expectations and Challenges
- India Ratings and Research Predictions: A slowdown in core sector growth is anticipated in the coming months, influenced by the strong base effect.
- Broader Economic Impact: This slowdown is indicative of larger economic challenges, potentially affecting future policy and market expectations.
Conclusion
- Economic Resilience Test: The trends in India’s core sectors underscore the challenges in sustaining growth amid diverse economic conditions.
- Need for Strategic Economic Planning: Addressing these slowdowns will require astute economic planning and possibly new strategies to boost growth in these key sectors.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: desperate and perilous journeys of Indian migrants seeking illegal routes to the U.S. and Canada
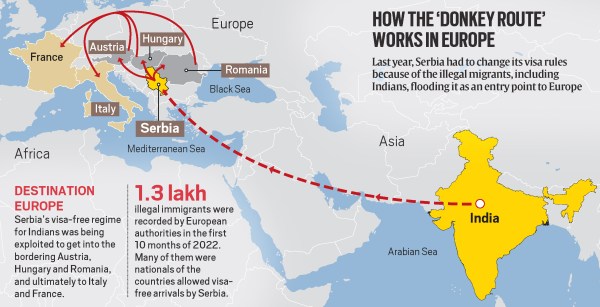
Central idea
The grounding of a chartered plane in France reveals the desperate and perilous journeys of Indian migrants seeking illegal routes to the U.S. and Canada. It emphasizes the role of agents, tragic incidents, and the necessity for international collaboration to address the root causes and dismantle illegal immigration networks, highlighting the human cost of such endeavors.
Key Highlights:
- A chartered plane from the UAE to Nicaragua, carrying 303 Indians, was grounded in France for a human trafficking probe.
- The flight was hired by a non-European client, and passengers were possibly trafficked, leading to a French investigation.
- The passengers claimed they boarded willingly, and the flight was eventually forced to return to Mumbai.
- Gujarat and Punjab have high numbers of illegal Indian migrants to the U.S. and Canada, often taking risky “donkey routes.”
Key Challenges:
- Lack of opportunities in Gujarat pushes people to seek better prospects abroad, leading to illegal migration.
- Human trafficking networks operate, exploiting the desperation of individuals seeking a better life.
- The dangers of “donkey routes” involve traversing various countries with lenient visa policies, risking lives in harsh conditions.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Donkey routes: Illegal migration paths involving multiple countries with lenient visa policies.
- Human trafficking: Exploitative practices involving illegal transportation of individuals.
- Chartered flight: Private aircraft hired for specific travel purposes.
- Asylum seekers: Individuals seeking protection and refuge in a foreign country.

Key Quotes:
- “The French authorities had received a tip-off and took it very seriously.”
- “The episode has once again called attention to the staggering number of Indians who migrate illegally to the U.S. or Canada.”
- “People don’t find any opportunities here. There are no well-paying jobs and sometimes no jobs at all.”
Anecdotes:
- Two passengers seeking asylum in France carried multiple passports and a substantial amount of money.
- Families taking extreme risks, like freezing to death near the U.S. border or drowning in attempts to cross rivers.
Key Statements:
- French authorities stopped exploring human trafficking angle after passengers claimed they boarded willingly.
- Gujarat Police cracking down on agents facilitating illegal immigration through donkey routes.
Key Examples and References:
- Shashi Kiran Reddy, a Hyderabad-based agent, behind the chartered flight facilitating illegal immigration.
- Instances of families freezing to death near the U.S. border or drowning while attempting to cross rivers.
Critical Analysis:
- Lack of opportunities and frustration in Gujarat and Punjab contribute to the high number of illegal migrants.
- The existence of human trafficking networks highlights the exploitation of individuals seeking better prospects.
Way Forward:
- Address root causes like lack of opportunities and corruption to discourage illegal migration.
- Strengthen efforts to dismantle human trafficking networks, collaborating with international agencies.
- Enhance awareness about legal migration pathways and associated risks to deter individuals from choosing illegal routes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: na
Mains level: neuropsychiatric disorders

Central idea
Dr. Ennapadam S. Krishnamoorthy advocates for prioritizing rehabilitation services globally, emphasizing their crucial role in treating neuropsychiatric disorders across the lifespan. He highlights the need for awareness, collaboration, and innovative solutions to address the significant burden of disabilities and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
Key Highlights:
- Dr. Ennapadam S. Krishnamoorthy emphasizes the importance of transformative solutions for persons with neuropsychiatric disorders, spanning childhood to old age.
- The focus is on enhancing activities of daily life and quality of life for individuals affected by various neuropsychiatric conditions.
- Rehabilitation services are crucial, with 2.41 billion individuals globally requiring rehabilitation according to the WHO’s Global Burden of Disease study.
Key Challenges:
- Rehabilitation is often seen as a disability-specific service, leading to under-prioritization despite its significant societal benefits.
- Lack of awareness in the community that disablement can be treated and, in some cases, reversed.
- The need for a shift in perception among medical professionals to recognize rehabilitation as an essential service.
Key Terms:
- Neuropsychiatric disorders
- Transformative solutions
- Rehabilitation
- Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS)
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)
- Functional Magnetic Stimulation (FMS)
- Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES)
- Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tA-VNS)
Key Phrases:
- “Rehabilitation needs are plentiful with a global burden of 2.41 billion individuals.”
- “Neurology and psychiatry are closely linked, requiring a continuum of care.”
- “Scientific advances, such as NIBS procedures, offer promising avenues for treatment.”
Key Quotes:
- “Disablement does not need to be endured; it can be treated, even reversed, in a proportion of cases.”
- “Rehabilitation services need to be multidisciplinary, multicomponent, and holistic.”
Key Statements:
- “Rehabilitation services are traditionally under-resourced despite individual and societal benefits.”
- “There is a need to build awareness that disablement can be treated.”
Key Examples and References:
- Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) as a mainstream treatment for depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- Functional Magnetic Stimulation (FMS) for pain, spasticity, and other neurological symptoms.
- Transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) showing success in improving memory, cognition, mood, and various neurological conditions.
- Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (tA-VNS) being investigated for depression, migraine, and dysautonomia.
Key Facts:
- 2.41 billion individuals globally had conditions benefiting from rehabilitation in 2019.
- The number of individuals requiring rehabilitation increased by 63% from 1990 to 2019.
Key Data:
- 317 million individuals affected by neuropsychiatric disorders in childhood.
- 167 million adolescents and 970 million people affected globally by mental health conditions.
Critical Analysis:
- Lack of prioritization and resources for rehabilitation despite a significant global burden.
- The necessity for a paradigm shift in perceiving rehabilitation as essential for a broad spectrum of neurological and mental health problems.
Way Forward:
- Increase awareness about the treatability of disabilities.
- Promote collaboration between governments, public and private sectors to find innovative solutions for persons with disabilities.
- Enhance training and development opportunities for rehabilitation professionals.
- Advocate for a multidisciplinary, holistic approach to rehabilitation services.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill, 2023
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill, 2023, faced opposition uproar but was passed in the Rajya Sabha on August 3. Subsequently, it was approved in the Lok Sabha on December 21, marking its legislative passage.
Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill: Purpose and Objectives
- Repealing the 1867 Act: The Bill aims to repeal the Press and Registration of Books Act, 1867, modernizing the regulatory framework for periodicals.
- Key Provisions: It includes a notable clause preventing individuals convicted of terrorism or acting against state security from publishing periodicals.
- Rationale for Introduction: The Bill focuses on easing business processes for publishers, removing procedural hurdles, and reducing the administrative burden of declarations and filings.
Comparison with the 1867 Act
- Exclusion of Books: Unlike the 1867 Act, the 2023 Bill excludes books from its purview, as they fall under the HRD Ministry’s jurisdiction.
- Penalty Structure: The new Bill replaces imprisonment with fines for certain violations and introduces an appellate mechanism led by the Press Council of India Chairman.
- Shift in Administrative Power: Power is transferred from the District Magistrate to the newly established Press Registrar General, centralizing the registration and regulation process.
Declaration and Registration Process
- Simplification of Procedures: The Bill simplifies the declaration process, eliminating the need for DM involvement and allowing online intimations for printing presses.
- Simultaneous Processing: It enables concurrent processing of title allotment and registration applications, streamlining the procedure.
- Time-Bound Responses: The specified authority must provide feedback within 60 days, expediting the registration process.
UAPA Provision in the Bill
- Restriction on Convicted Individuals: The Bill bars individuals convicted of terrorist acts or unlawful activities, as defined under the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967, from publishing periodicals.
- Security Concerns: This provision addresses concerns about the misuse of periodicals for activities threatening national security or sovereignty.
Conclusion
- Modernizing Media Regulation: The Press and Registration of Periodicals Bill, 2023, represents a significant overhaul of India’s media regulatory framework, aligning it with contemporary needs.
- Balancing Ease of Business and Security: While the Bill aims to facilitate easier operations for publishers, it also incorporates measures to safeguard against security threats.
- Potential for Debate and Discussion: The Bill’s passage, amidst opposition concerns, suggests ongoing debates about media freedom, security, and regulatory oversight in India’s evolving democratic landscape.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Factors shaping India's foreign policy

Central Idea
- Contradiction in Global Aspirations: Despite calls for peace, 2023 witnessed the continuation and emergence of significant conflicts, notably between Russia and Ukraine, and in the Gaza Strip.
- China’s Stance: Amidst its economic challenges, China’s aggressive posture remains a concern for the West and India, adding to the global tension.
2023: Strategic Realities and Challenges
Crisis in the Middle East: The Hamas attack disrupted efforts to normalize Israel-Arab relations, leading to a devastating response from Israel and derailing the reconciliation process.
- Stress in India-US Ties: Allegations of an Indian official’s involvement in an assassination plot have strained relations, with India promising to investigate if provided with information.
- Russia-Ukraine War Fatigue: The prolonged conflict sees the West grappling with funding challenges, while Russia, despite sanctions, maintains resilience, partly due to its closeness with China.
- India’s Maldives Challenge: The new government’s request for India to withdraw military personnel and terminate agreements reflects its proximity to China, complicating India’s strategic position.
- China, the Biggest Worry: The ongoing border standoff and China’s influence in the region, including its ties with Russia and the Maldives, continue to be India’s primary strategic concerns.
- G20 and Global South Positioning: India’s leadership in the G20 and its role in uniting the Global South reflect its aspiration to continue the legacy of Non-Alignment adapted to modern realities.
- Engagement in Kabul: India’s cautious engagement with the Taliban and coordination for consular services indicate a nuanced approach to Afghanistan, balancing security and diplomatic needs.
2024: Anticipating Challenges and Opportunities
- Impact of Lok Sabha Elections: The election outcome will significantly influence India’s foreign policy, with a stronger mandate potentially leading to more assertive stances, while a weaker mandate might reflect coalition compulsions.
- US & Canada Relationships: Navigating the complexities arising from the assassination plot allegations and maintaining robust ties with both nations will be crucial for India.
- New Government in Pakistan: The post-election scenario in Pakistan might offer a window for re-engagement, depending on the political dynamics and India’s strategic choices.
- Outcome in Bangladesh: India’s interest in the continuation of Sheikh Hasina’s government reflects security and connectivity priorities, with the opposition viewed with caution.
- Continuing Deadlock with China: The border standoff and its potential escalation will be a critical factor in India’s security and diplomatic strategy, especially in an election year.
- West Asia Dynamics: India’s evolving stance in the Israel-Hamas conflict and its implications for its position in the Global South will be closely watched, with a focus on balancing relations and principles.
- Future of the War in Ukraine: India’s balancing act between its economic interests and international pressures, especially in its relationship with Russia, will continue to be a delicate matter.
- Trade Pacts and Tech Partnerships: Finalizing trade agreements and enhancing tech partnerships with the West will be key areas of focus, with potential major developments expected in 2024.
Conclusion
- Balancing Act: India’s foreign policy in the coming years will involve navigating a complex array of global conflicts, bilateral tensions, and internal political dynamics.
- Strategic Posture: The outcomes of various global and regional conflicts, along with India’s own electoral politics, will shape its strategic and foreign policy posture, reflecting a blend of continuity and change.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polygraph Test
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- In the ongoing investigation of the Parliament security breach, Delhi Police sought court permission for polygraph tests on six accused to uncover their motives.
- A polygraph test, commonly known as a lie detector test, measures physiological responses believed to differ when a person lies.
Mechanics of a Polygraph Test
- Physiological Monitoring: The test involves attaching instruments like cardio-cuffs or sensitive electrodes to monitor blood pressure, pulse, and other variables.
- Response Analysis: As questions are asked, responses are numerically evaluated to determine truthfulness, deception, or uncertainty.
- Historical Origin: First conducted in the 19th century by Cesare Lombroso, an Italian criminologist, to measure blood pressure changes in suspects during interrogation.
Constitutional and Legal Provisions
- Article 20(3) of the Indian Constitution: This article protects against self-incrimination, stating that no accused shall be compelled to be a witness against themselves.
- Infringement Concerns: Forcing an accused to undergo polygraph or narcoanalysis tests is seen as a violation of Article 20(3), making consent essential.
- Article 21 and Human Rights: Polygraph tests are criticized for mental torture, potentially violating the right to life and privacy under Article 21.
Limitations and Challenges
- Scientific Reliability: Neither polygraph nor narco tests are scientifically proven to be 100% accurate, raising questions about their reliability.
- Impact on Vulnerable Individuals: These tests can adversely affect those unaware of their rights or unable to access legal advice, leading to potential abuse and media exploitation.
Legal and Constitutional Rulings
- Selvi vs State of Karnataka & Anr (2010): The Supreme Court ruled that lie detector tests should be voluntary, with legal implications explained to the accused.
- D.K. Basu vs. State of West Bengal (1997): The Court deemed involuntary administration of these tests as potentially violating the Right to Life and Liberty and the Right to Privacy.
- Indian Evidence Act, 1871: The results of these tests are not admissible as evidence in court.
- National Human Rights Commission Guidelines (1999): Established consent and procedural guidelines for administering polygraph tests.
Way Forward
- Role as Investigative Tools: While not reliable for conclusive evidence, polygraph tests can aid in complex investigations.
- Balancing Scientific Techniques and Rights: The government should promote scientific methods in investigations while ensuring strict adherence to ethical and legal standards.
- Consent and Decency: The administration of these tests must be consensual, respecting the dignity and rights of the individuals involved.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Pervasiveness of Plastic: Plastic, with its beneficial properties like durability, has become a ubiquitous part of modern life.
- Environmental Impact: Approximately 50% of plastic is used only once before being discarded, contributing to significant environmental issues, including ocean pollution.
Psychological Aspects of Plastic Use
- Consumer Behavior Influence: The omnipresence of plastic shapes consumer choices and behaviors, influenced by marketing strategies, packaging design, and product aesthetics.
- Packaging and Brand Perception: Packaging plays a crucial role in plastic use, with visual appeal and brand image significantly impacting consumer preferences.
- Color Psychology in Packaging: The use of color in packaging design evokes specific emotions and expectations, influencing purchasing decisions.
Convenience Factor and Limited Alternatives
- Role of Convenience: Plastic packaging’s ability to keep products fresh and hygienic has been a key driver of its market dominance.
- Lack of Economical Alternatives: The absence of affordable alternatives for food packaging often leaves consumers with no choice but to opt for plastic-wrapped items.
Pro-Environmental Behavior (PEB) and Plastic Use
- Understanding PEB: Limiting plastic use and purchase is an example of pro-environmental behavior, influenced by awareness, knowledge, and values.
- Factors Influencing PEB: Concern about plastic, knowledge of its effects, and the perceived commitment of others to address its impact play roles in shaping PEB.
Market Trends and Social Influences
- Impulsive Buying and Social Media: The growth of social media and peer pressure have been linked to increased compulsive buying behaviors, often leading to increased plastic consumption.
- Influence of Social Norms: Social norms promoting consumption have led to an increase in plastic use, despite its environmental costs.
Stages of Behavioral Readiness in Plastic Consumption
Five Stages of Readiness include-
- Pre-contemplation,
- Contemplation,
- Preparation,
- Action, and
- Maintenance.
Role of Storytelling and Marketing in Plastic Awareness
- Emotional Engagement: Storytelling in marketing can emotionally engage customers with the lifecycle of plastic items, enhancing environmental awareness.
- Positive and Negative Impacts: Marketing power can influence consumer behavior both positively and negatively in the context of plastic use.
- Objective vs. Subjective Knowledge: Understanding the specifics of an issue (objective knowledge) versus personal belief or awareness (subjective knowledge) influences behavior.
- Barriers to Action: Lack of personal connection, gradual environmental impact, moral disengagement, and immediacy issues are barriers to taking action against plastic pollution.
Way forward
- Role of Education and Design: Knowledge is crucial, but behavioural change also depends on product design that encourages environmentally friendly choices.
- Supplier and Retailer Responsibility: Minimizing packaging, using recyclable materials, and clear recycling instructions are key steps.
- Policy Initiatives: Policies raising awareness of plastic pollution’s effects can facilitate a sustainability-focused behavioural shift.
- Emergence of Sustainable Brands: As consumers increasingly look to brands for sustainable options, there is a growing market for environmentally conscious products.
Conclusion
- Critical Role of Habit Change: Altering consumer habits is essential for environmental protection, requiring a multifaceted approach involving education, policy, and market innovation.
- Sources: Insights drawn from the Sustainability and Consumer Behaviour Report 2022 by Deloitte United Kingdom and research by Mittali Tyagi, PhD Scholar at Manav Rachna International Institute of Research and Studies.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Medical Negligence and its impact on the marginalized people

Central Idea
- A women recently died from septic shock after a surgery in Jamshedpur, leading her brother to allege medical negligence due to unauthorized surgeon substitution and lack of postoperative care.
- The case has ignited discussions on the legal and ethical aspects of medical negligence in India, amidst proposed changes to exempt doctors from criminal prosecution.
Understanding Medical Negligence
- Definition and Impact: Medical negligence involves a breach of duty by healthcare professionals, leading to patient harm or death.
- Legal Framework: Currently, under Section 106(1) of the Bharatiya Nyaya (Second) Sanhita (BNSS), doctors face potential imprisonment and fines if convicted of negligence, though proposed changes might alter this.
Recent Developments and Legal Provisions
- Recent Announcement: MHA proposed exempting doctors from criminal prosecution in negligence cases, sparking debate and concern among various stakeholders.
- Constitutional Rights: The proposed changes have to be balanced against constitutional protections like Article 20(3) and Article 21, which safeguard against self-incrimination and ensure the right to life and liberty.
Role of the Indian Medical Association (IMA)
- IMA’s Stance: The IMA has advocated for exempting doctors from criminal prosecution for negligence, citing the increasing harassment and detrimental impact on patient care.
- Concerns Raised: The IMA also highlighted the high number of medical negligence cases filed against doctors and the economic losses due to violence against healthcare professionals.
Ethical and Societal Implications
- Power Dynamics: Critics argue that exempting doctors from criminal prosecution might exacerbate power imbalances in the doctor-patient relationship and lead to increased medical malpractice.
- Marginalized Populations at Risk: There’s concern that such exemptions could disproportionately affect vulnerable groups, including women, queer, transgender individuals, and rural residents.
Legal and Ethical Conundrums
- Good Faith Clause: BNSS clauses provide some protection for acts done in good faith, but the distinction between negligence and accident remains unclear.
- Bioethicists’ Perspective: Experts emphasize the need for a balanced approach that considers both healthcare professionals’ challenges and patients’ rights and safety.
Way Forward
- Nationwide Dialogue: The IMA plans to engage in discussions with the government and public to advocate for their position.
- Need for Comprehensive Data: Critics like Geet suggest conducting a nationwide survey to understand the scope of medical negligence and inform policy decisions.
- Legal Recourse for Patients: Ensuring that patients have access to legal recourse and justice is crucial to maintaining trust in the healthcare system and preventing violence against doctors.
Conclusion
- Complex Decision-Making: Exempting doctors from criminal prosecution for medical negligence is a multifaceted issue requiring careful consideration of legal, ethical, and societal factors.
- Ensuring Justice and Quality Care: Any policy changes must strive to protect patients’ rights while also considering the challenges faced by medical professionals, ensuring that the healthcare system remains just, accountable, and focused on delivering high-quality care. Top of Form
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: INC, Important Sessions
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- On December 28, 1885, the Indian National Congress (INC) was established, marking the beginning of a significant journey in Indian politics.
- The INC’s journey from influencing British policy to leading India’s nationalist movement, dominating post-independence politics, and its current decline offers a rich political narrative.
Indian National Congress: Inception in 1885
- Founding by AO Hume: Allan Octavian Hume, an English bureaucrat, founded the INC to advocate for greater self-governance in India.
- First Session: The inaugural session in Bombay saw 72 reformers, journalists, and lawyers unite, aiming not for independence but to influence British policies favorably for Indians.
- Safety Valve Theory: The INC initially served as a platform for Indians to express grievances, seeking to unify diverse population segments and regenerate the nation across various dimensions.
Politics of Petitions
- Early Challenges: The Congress faced criticism from both the British and Indians; the former for disrupting the status quo and the latter for its passive resistance approach.
- Composition and Critique: Dominated by educated, upper-class individuals, the INC was often seen as too moderate and not sufficiently representative of all Indians.
- Internal Divisions: By 1906, ideological differences led to a split between the moderates (Gopal Krishna Gokhale, Surendranath Banerjea) and the extremists (Bal Gangadhar Tilak), particularly over responses to the Bengal Partition.
Leadership under Mahatma Gandhi
- Reunification and Transformation: The INC, under Gandhi’s influence from 1915, transformed into a mass movement, focusing on social issues like caste discrimination and poverty.
- Diverse Membership: Despite its Hindu upper-caste dominance, the party included members from various ethnic and religious backgrounds.
- Purna Swaraj Declaration: At the 1929 Lahore session, the INC, under Jawaharlal Nehru’s presidency, committed to complete independence, a goal achieved in 1947 but marred by Partition.
Dominance in Post-Independence India
- Electoral Success: The INC’s legacy and organizational strength led to victories in the first six general elections.
- Policy Direction: Under Nehru, the party promoted secularism, socialist economics, and non-aligned foreign policy.
- Internal Power Struggles: Post-Nehru, internal conflicts emerged, notably between Indira Gandhi and the party’s old guard, leading to a split into Congress (R) and Congress (O).
Onset of Decline
- Electoral Setbacks: The Emergency period (1975-77) led to the INC’s first national electoral defeat in 1977.
- Fluctuating Fortunes: While it regained power, the 1989 loss marked the end of its dominance, with the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) emerging as a strong alternative.
- Recent Struggles: The INC’s significant reduction in parliamentary strength in the 2014 and 2016 elections underscores its ongoing decline.
Back2Basics: Important Sessions of INC
- 1896, Calcutta: Presided over by Rahimtulla M. Sayani, where the national song “Vande Mataram” was sung for the first time.
- 1906, Calcutta: Presided over by Dadabhai Naoroji, where the goal of Swaraj (self-rule) was formally adopted.
- 1917, Calcutta: Annie Besant became the first woman president of the INC.
- 1924, Belgaum: The only session presided over by Mahatma Gandhi.
- 1937, Faizpur: The first session held in a rural area, reflecting the INC’s commitment to rural issues and agrarian reform.
- 1938, Haripura: Subhas Chandra Bose elected as President, which marked a shift towards a more radical approach in the freedom struggle.
- 1940, Ramgarh: Last session presided over by Mahatma Gandhi; emphasized on individual Satyagraha.
- 1955, Avadi (Madras): Adoption of the ‘Avadi Resolution’ which called for a socialist pattern of society.
- 1964, Bhubaneswar: First session after the death of Jawaharlal Nehru, marking a new era in the party’s leadership.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Three Gorges project
Mains level: India’s stationary course in the shipping value chain

Central idea
The article explores the contrasting trajectories of China and India in the maritime industry, emphasizing China’s dominance in shipbuilding and India’s focus on seafaring labor and ship management. It underscores the missed opportunities for India in shipbuilding, leading to a decline in its global maritime standing. The absence of a strategic focus on shipbuilding and the decline of state-owned enterprises pose challenges for India’s maritime growth.
Key Highlights:
- The Yangtze River, deeply embedded in China’s history, serves as a blend of tradition, culture, and modern commerce, symbolized by the Three Gorges project.
- China’s maritime success, highlighted by its dominance in shipbuilding, stands in contrast to India’s focus on seafaring labor and ship management.
- India, once ahead in maritime endeavors, faces challenges as its shipbuilding capabilities lag, impacting the overall growth of the shipping industry.
Key Challenges:
- India’s maritime industry confronts limitations in shipbuilding, ownership, and financing, contributing to a decline in its global standing.
- The absence of a strategic focus on shipbuilding, coupled with the decline of the state-owned Shipping Corporation of India, has hindered India’s maritime progress.
Key Terms:
- Three Gorges project: A monumental hydropower initiative on the Yangtze River, symbolizing China’s modern engineering achievements.
- Seafarer: An individual engaged in maritime activities, such as navigation, on vessels like ships and boats.

Key Quotes:
- “China, by 2020, was making half of all ships in the world,” a stark contrast to India’s negligible share in shipbuilding.
- “Indian seafarers and their management companies contribute an estimated $6 billion in foreign exchange annually.“
- “India’s Maritime India Vision 2030 lacks a clear plan for shipbuilding and owning,” hindering its growth in the maritime industry.
Key Statements:
- The article underscores the transformative significance of the Three Gorges project, symbolizing China’s advancement in modern engineering.
- India’s historical lead in maritime activities has been overshadowed by its limited involvement in shipbuilding and related sectors.
Key Examples and References:
- The Three Gorges project exemplifies China’s commitment to modern infrastructure and technological prowess.
- The decline of the state-owned Shipping Corporation of India serves as a reference point for India’s challenges in sustaining its maritime industry.
Key Facts and Data:
- China, contributing to 50% of global ship production by 2020, reflects its dominance in the shipbuilding sector.
- Indian seafarers and their management companies collectively contribute an estimated $6 billion in foreign exchange annually.
Critical Analysis:
- The critical analysis emphasizes the missed opportunities for India in the shipbuilding sector and the resultant impact on its overall maritime growth.
- The decline of the state-owned Shipping Corporation of India is presented as a significant factor influencing India’s maritime capabilities.
Way Forward:
- The article suggests that India should strategically prioritize shipbuilding to enhance its global maritime presence, emphasizing economic and strategic benefits.
- An integrated approach to shipbuilding would not only contribute to economic growth but also strengthen India’s naval capabilities, enhancing its geopolitical standing.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Amrita's legacy
Mains level: profound impact of supportive relationships
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: large language models
Mains level: greater socialization of AI policy
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Participatory Notes
Mains level: NA
Central Idea
- Indian capital markets witnessed a significant increase in investments through participatory notes (P-notes), reaching ₹1.31 lakh crore by the end of November.
What are Participatory Notes?
|
Details |
| Nature of Instrument |
Offshore derivative instruments with Indian shares as underlying assets. |
| Issuers |
Issued by registered Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) to overseas investors. |
| Purpose |
To allow foreign investors to invest in Indian stock markets without direct registration. |
| Anonymity |
Provide anonymity for foreign investors; beneficiary details are not disclosed to Indian regulators. |
| Regulatory Oversight |
Governed by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). |
| Compliance |
FIIs issuing P-Notes are required to adhere to KYC norms and other regulatory standards. |
| Controversies |
Associated with risks of money laundering and contributing to market volatility. |
| Regulatory Reforms |
SEBI has tightened norms over time, including enhanced KYC and disclosure requirements. |
| Economic Impact |
Significant source of foreign portfolio investment; influences market sentiment and foreign investor behavior. |
| Impact of Regulatory Changes |
Changes in regulations have affected the flow of investments through P-Notes. |
Correlation with FPI Flows
- P-Notes and FPI Trends: The investment through P-notes typically mirrors the trends in foreign portfolio investor (FPI) flows.
- Global Risk Influence: In times of global risk, investment through P-notes tends to increase, and the opposite occurs when the risk subsides.
Factors Influencing the Recent Increase
- U.S. Treasury Bond Yields: The decline in U.S. treasury bond yields is believed to have redirected FPIs’ attention to the Indian market for potentially higher returns.
- IPO Attraction: The listing of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in India has also been a factor in attracting foreign investors back to the market.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Huntington's Disease
Mains level: Not Much
Central Idea
- The Nizam’s Institute of Medical Sciences in Hyderabad reports three to four cases of Huntington’s disease monthly, with each case impacting entire families.
Understanding Huntington’s Disease
|
Details |
| Nature of Disorder |
Genetic, progressive brain disorder |
| Genetic Cause |
Mutation in the huntingtin gene on chromosome 4 |
| Inheritance Pattern |
Autosomal dominant disorder (only one copy of the defective gene, from either parent, is enough for disease onset) |
| Symptoms |
Movement Disorders: Involuntary movements (chorea), muscle problems (dystonia), abnormal eye movements.
Cognitive Disorders: Difficulty in organizing and focusing, lack of flexibility, impulse control issues.
Psychiatric Disorders: Depression, mood swings, changes in personality |
| Age of Onset |
Typically between 30 and 50 years of age, but can vary widely
Gradual onset, worsening over 10-25 years, leading to severe disabilities |
| Diagnosis |
Genetic testing to detect the presence of the defective gene |
| Treatment |
No cure; treatment focuses on managing symptoms, including medication for movement and psychiatric disorders, and therapy |
| Impact on Life Expectancy |
Can shorten life expectancy, particularly if onset is at a younger age |
Role of the HTT Gene and Glutamine Repeats
- Genetic Mutation: Huntington’s disease is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene, leading to abnormal huntingtin (Htt) proteins that damage neurons.
- Polyglutamine Tracts: The severity of the disease correlates with the length of glutamine repeats in the Htt protein; longer repeats result in earlier and more severe symptoms.
- Inheritance Pattern: The disease manifests even if only one copy of the HTT gene is mutated, demonstrating its dominant nature.
- Similar Proteins and Diseases: Other proteins with polyglutamine tracts, when mutated, can also cause neuronal degeneration, leading to disorders like spinocerebellar ataxia.
Fruit Fly Study: A Model for Understanding Huntington’s
- Genetic Engineering in Flies: Researchers engineered fruit flies to express the human HTT gene with extended polyglutamine tracts in their neurons.
- Gal4/UAS System: Utilizing the Gal4 gene from baker’s yeast, the study induced expression of mutated HTT in fly neurons.
- Symptoms in Flies: Flies with longer glutamine tracts exhibited symptoms similar to Huntington’s disease, unlike those with shorter, normal tracts.
Yod1 Gene Discovery
- Gene Expression Experiment: The study explored the effects of altering the expression of 32 genes on disease-like symptoms in fruit flies.
- Yod1’s Protective Role: Overexpression of the Yod1 gene eliminated neurodegeneration and other disease-like effects in flies with longer glutamine tracts.
Broader Implications and Future Research
- Potential in Human Treatment: If overexpression of the human version of Yod1 shows similar benefits in fruit flies, it could be a promising avenue for treating Huntington’s in humans.
- Value of Model Organisms: Studies in fruit flies and yeasts are pivotal for understanding molecular mechanisms of diseases like Huntington’s.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Global Innovation Index, Rule of Law Index, Poverty Index
Mains level: Viksit Bharat

Central idea
The article calls for a reimagining of India’s development strategy, shifting from an economic-centric model to prioritizing happiness and well-being. It critiques the current focus on GDP, highlighting the need for comprehensive social indicators in the development narrative. The central idea is to envision a “Happy India-Developed India” by 2047, where happiness becomes the central pursuit, transcending conventional economic measures.
Key Highlights:
- Viksit Bharat Launch: The launch of Viksit Bharat aims to make India a developed nation by its 100th Independence year in 2047.
- Economic Overemphasis: Critics argue that Viksit Bharat places excessive emphasis on economic development, overlooking other crucial aspects.
- Happiness as Central Pursuit: The author suggests reimagining the theme as ‘Happy India-Developed India,’ focusing on happiness as a central pursuit for meaningful development.
- Happiness Metrics: The World Happiness Report measures happiness through variables like GDP per capita, life expectancy, generosity, social support, freedom, and perception of corruption.
- Social Connections and Well-being: Countries like Finland and Denmark, ranked highest in happiness, emphasize social connections and support systems, contributing to well-being.
Key Challenges:
- Economic-Centric Development: The challenge lies in shifting the development narrative from an economic-centric model to one that prioritizes happiness and well-being.
- Social Disruption: The current economic-focused development model may lead to social disruption, imbalances, and contradictions.
- Disregard for Social Indicators: The conventional focus on GDP fails to consider crucial social indicators, neglecting human and social aspects of development.
Key Terms and Phrases:
- Viksit Bharat: The development initiative launched with the goal of making India a developed nation by 2047.
- World Happiness Report: An annual report measuring happiness using multiple variables and indicators.
- Human Development Index (HDI): An index considering life expectancy, educational attainment, and income level.
- Green Index: A World Bank-developed index measuring a nation’s wealth based on produced assets, natural resources, and human resources.
- Social Development Index: Introduced by the UN Research Institute for Social Development, it includes 16 core indicators.
- Global Innovation Index, Rule of Law Index, Poverty Index, Corruption Perceptions Index, Gender Equality Index, and World Press Freedom Index: Various indices significant for comprehensive national development.
Key Quotes:
- “Without achieving happiness, development has no meaning.”
- “Happiness ought to be the central pursuit in this journey.”
- “The nations have developed, but people are not happy.”
Critical Analysis: The article critically examines the conventional economic-focused development model and advocates for a paradigm shift towards happiness-centric development. It emphasizes the inadequacy of GDP-centric measures and highlights the importance of considering social indicators for a more inclusive and balanced development approach.
Way Forward: The way forward involves reimagining the development narrative, giving importance to happiness metrics, and incorporating a broader set of indicators such as the Human Development Index, Green Index, and others. Prioritizing social connections, well-being, and happiness in development strategies will contribute to a more holistic and sustainable vision for Viksit Bharat@2047.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Dark web
Mains level: cybersecurity

Central idea
The increasing frequency of data breaches in India, exemplified by the recent dark web sale of sensitive personal information of 815 million citizens, underscores a pressing cybersecurity challenge. India’s inadequate incident response strategies, lack of transparency, and failure to prioritize cybersecurity pose risks to individuals and national security. A comprehensive approach, focusing on prevention, detection, and transparency, is imperative for building a resilient and secure digital infrastructure in India.
Key Highlights:
- Resecurity, a US company, revealed the sale of sensitive personal data of around 815 million Indians on the dark web.
- The data included Aadhaar numbers, passport information, and addresses, posing a significant threat to individuals.
- Previous instances of data leaks in India, such as the CoWin website breach and AIIMS ransomware attack, highlight a recurring issue.
Key Challenges:
- India faces a rising trend of data breaches, with the potential for severe consequences like identity theft and financial scams.
- Lack of effective incident response strategies in India compared to countries like the US, where cybersecurity standards are being strengthened.
Key Terms:
- Dark web, Aadhaar, Passport number, Ransomware, Cybersecurity, Data breach, Incident response.
Key Phrases:
- “Leaking of sensitive information poses a severe threat to individuals’ financial well-being.”
- “India’s mobile phone usage, enhanced banking access, and growing market size make it an attractive target for bad actors.”
Key Quotes:
- “The constant flow of news about data breaches is normalizing massive losses of personal data.”
- “India’s response to data breaches is criticized for its lack of transparency, accountability, and effective incident response.”
Key Statements:
- “Data breaches are at an all-time high globally, and India is particularly vulnerable due to its economic growth and large population.”
- “Incident response strategies in India are characterized by denials and lack of transparent communication with affected citizens.”
Key Examples and References:
- Resecurity’s revelation of the sale of Indians’ personal data on the dark web.
- Previous data breaches in India, including the CoWin website leak and the AIIMS ransomware attack.
Key Facts:
- The data set on the dark web contained personally identifiable information of approximately 815 million Indian citizens.
- India lacks a long-term cybersecurity strategy, leading to inadequate handling of data breaches.
Key Data:
- The sensitive personal data of 815 million Indians was available on the dark web for a price of $80,000.
Critical Analysis:
- India’s response to data breaches is criticized for its lack of transparency, accountability, and effective incident response.
- The Data Protection Act in India is deemed insufficient, especially in addressing sensitive health information.
Way Forward:
- Prioritize the prevention, detection, assessment, and remediation of cyber incidents in India.
- Establish a cybersecurity board with government and private sector participation for concrete recommendations.
- Adopt a zero-trust architecture and mandate a standardized playbook for responding to cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- Inform and empower citizens immediately, taking responsibility for their protection and remediation in the aftermath of cyber incidents.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Make in India (MII)
Mains level: National Industrial Policy (NIP)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now