Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Mains level: Regional languages assertiveness

Introduction
- Activists protested against non-Kannada signboards in Bengaluru, leading to vandalism across the city.
Kannada Signboards Issue
- Demand for Kannada Signboards: The issue dates back to the early 2000s when Bengaluru emerged as a global IT hub. The then Chief Minister S.M. Krishna issued a circular in 2002 for Kannada signboards, which lacked legal backing.
- Legal Challenges: Attempts to mandate Kannada signboards faced legal hurdles, with the High Court staying and striking down related rules in 2009 and 2014.
Recent Developments: Legislation and Protests
- Kannada Language Comprehensive Development Act, 2022: The Act, passed by the State Legislature in 2022, mandates that 60% of signboards be in Kannada.
- KRV’s Campaign: KRV campaigned for the implementation of this norm, leading to the protest and subsequent vandalism.
- State Government’s Ordinance: The government plans to promulgate an ordinance to clarify the 60:40 rule for signboards and set a compliance deadline of February 28.
Impact on Commercial Establishments
- Anxiety among Businesses: The new rule has caused concern among retailers, with fears of increased vigilante actions and financial burdens due to signboard changes.
- Opposition from Retailers: The Retailers Association of India and other business groups have opposed the mandate, citing its impact on Bengaluru’s cosmopolitan nature and brand image.
Political Dynamics
- Election Context: The issue has gained political significance ahead of the parliamentary polls, with both the Congress and BJP staking positions on the language issue.
- Kannada as a Political Plank: Despite political consensus on promoting Kannada, the language has not been a successful political issue in the state.
Concerns over Bengaluru’s Image
- Brand Bengaluru at Risk: The vandalism and language controversy could potentially harm Bengaluru’s reputation as a global investment destination.
- Calls for Government Action: Industry leaders and civic activists have urged the government to take measures to restore confidence and preserve the city’s inclusive culture.
Conclusion
- Need for Sensible Policy: The government faces the challenge of promoting Kannada while maintaining Bengaluru’s cosmopolitan and investor-friendly image.
- Addressing Vandalism: Strong action against vandalism and a balanced approach to language policy are essential to prevent further damage to Bengaluru’s brand and social harmony.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: NA
Mains level: Can be used as case study

Introduction
- Prof. Akeel Bilgrami, a distinguished professor from Columbia University, delivered a lecture at Madras Christian College in Tambaram.
- His talk, titled ‘Gandhi in his time and ours: Reflections on Secularism and Multiculturalism’, explored the nuances of secularism in India and Europe.
Prof Bilgrami on Secularism
He emphasized on three commitments primarily on which Secularism is based:
- Freedom of Religion: The first commitment emphasizes the freedom of religious belief and practice.
- Constitutional Principles: The second commitment involves principles unrelated to religion, such as equality and freedom of speech, enshrined in the constitution.
- Meta-Commitment: The third commitment dictates that in case of a clash between the first two, the constitutional principles must take precedence.
Gandhi’s Perspective on Secularism
- European Context: Gandhi viewed secularism as a doctrine to address the damage caused by religious majoritarianism in Europe.
- Irrelevance to India: He believed that the issues secularism aimed to address in Europe were not present in India, making it irrelevant in the Indian context.
- Nationalism and Anti-Imperialism: For Gandhi, nationalism was synonymous with anti-imperialism and inherently inclusive, contrasting with European forms of nationalism.
Distinguishing Secularisation from Secularism
- Secularisation: Prof. Bilgrami described secularisation as a social process involving the loss of religious belief and changes in religious practices.
- Secularism: In contrast, secularism is a political doctrine advocating for the separation of religion from politics.
Rejecting the Notion of ‘Indian’ Secularism
- Misconception: Prof. Bilgrami dismissed the popular notion that ‘Indian’ secularism is about the acceptance of all religions.
- Pluralism vs. Secularism: He clarified that the acceptance of all religions is more accurately described as pluralism, not secularism.
Conclusion
- Deeper Understanding: Prof. Bilgrami’s lecture provided a deeper understanding of secularism and its application in different contexts.
- Relevance to Contemporary India: His insights are particularly relevant in contemporary India, where secularism and multiculturalism continue to be subjects of intense debate and discussion.
- Future Discourse: The lecture sets the stage for further discourse on how secularism should be interpreted and implemented in India’s diverse and multi-religious society.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Deep Tech
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian government is set to approve a new ‘deep tech’ policy. Following public comments on the draft released in July 2023, the final version of the policy is ready for Cabinet approval.
Understanding ‘Deep Tech’
- Definition and Scope: ‘Deep tech’ refers to startups that develop intellectual property based on new scientific breakthroughs, aiming for significant impact. Ex. AI, ML, Blockchain, Quantum Computing etc.
- Startup India Data: As per Startup India, there are 10,298 startups in various sub-sectors of deep tech as of May 2023.
- Exclusion Criteria: Businesses based on easily replicable ideas do not qualify as deep tech startups.
Draft National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP) 2023
- Policy Goals: The NDTSP aims to address challenges in funding, talent acquisition, and scaling R&D operations for deep tech startups.
- Strategic Approach: The policy is designed to promote innovation, economic growth, and societal development in the deep tech sector.
India’s Deep Tech Ecosystem
- Global Ranking: India ranks third globally in the startup ecosystem, with over 3000 deep tech businesses.
- Sectoral Expansion: These firms are expanding into areas like agriculture, life sciences, chemistry, aerospace, and green energy.
Policy Foundations and Prospects
- Public Consultation: The draft policy was open for public feedback until September 15, after consultations with stakeholders in the deep tech ecosystem.
- Key Pillars: The policy focuses on securing India’s economic future, progressing towards a knowledge-driven economy, bolstering national capability, and encouraging ethical innovation.
Policy Elements and Recommendations
- Funding and Innovation: The policy proposes financial support through grants, loans, and venture capital, along with regulatory simplifications and academia-industry collaboration.
- Talent Development: Emphasis on STEM education, training opportunities, and attracting international talent.
- Infrastructure and Technology Access: Establishment of deep tech incubation centers, testing facilities, and shared infrastructure resources.
- Public Procurement and Market Opportunities: Encouraging government agencies to adopt deep tech solutions and facilitating international market access.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Establishing a uniform IP framework and implementing cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
- Transformative Potential: The NDTSP is poised to guide India’s deep tech landscape, fostering technological innovation and economic growth.
- Measuring Success: The policy’s effectiveness will be gauged by its impact on startups, innovation depth, and societal transformation.
- Democratizing Deep Tech: The strategy aims to make deep tech benefits accessible across society, leveraging research-driven breakthroughs for national advancement.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Paleolithic Age
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- Floods Uncover Historical Artifacts: The recent floods in Mulugu district, Telangana, have led to the discovery of Paleolithic quartzite tools, shedding new light on the region’s ancient human habitation.
- Discovery by Amateur Historians: The tools were found in a dried-up stream bed by a team led by Sriramoju Haragopal, an amateur historian.
About Paleolithic Age
|
Details |
| Timeframe |
Approximately 2.6 million years ago to about 10,000 BCE. |
| Characteristics |
Marked by the use of stone tools by early humans. Tools were mainly hand axes, cleavers, and choppers. |
| Major Sites |
- Bhimbetka in Madhya Pradesh
- Soan Valley in Punjab
- Sites in Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Maharashtra
- Narmada Valley in Central India
- Attirampakkam in Tamil Nadu
- Hunsgi in Karnataka
- Kurnool in Andhra Pradesh
- Didwana in Rajasthan
- Belan Valley in Uttar Pradesh
|
| Lifestyle |
Nomadic hunter-gatherers; relied on hunting animals and gathering plants for food. |
| Cultural Developments |
Development of basic stone tools and control of fire. |
| Art and Symbolism |
Evidence of early art found in Bhimbetka rock shelters, with paintings and engravings. |
| Climate and Environment |
Varied climatic conditions over millennia; included ice ages and warmer periods. |
| Human Species |
Mainly Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. |
Details of the Discovery
- Location of Find: The hand axes were discovered between Gurrevula and Bhupatipuram villages in Mulugu district.
- Specific Find: Researchers found a significant stone axe measuring 15.5 cm in length, 11 cm in width, and 5.5 cm in thickness.
Context and Comparison
- Global Significance: Similar hand axes have been discovered worldwide, indicating a common tool type used by early humans for various purposes.
- Historical Context in India: The first discovery of a Paleolithic site in India was in 1863 at Attirampakkam near Madras (now Chennai), with bifacial hand-axes dating back to about 15 lakh years, known as the Madras Hand-Axe Industry or Madrasian Culture.
Historical Significance
- Paleolithic Era Tools: According to paleontologists, the stone axe dates back to the Lower Paleolithic period, approximately 30 lakh years ago.
- Tool Identification: The tools were identified based on their chipping style, material, and size, typical of Paleolithic hunter-gatherers who used heavy quartzite for large tools.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully tested a 100 W class Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell based Power System (FCPS) in space.
- The FCPS was part of the POEM3 orbital platform, launched onboard PSLV-C58 on January 1, 2024.
About FCPS Experiment
- Primary Goal: The experiment aimed to assess the operation of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel cells in space and gather data for future mission designs.
- Power Generation: During the test, 180 W power was generated using Hydrogen and Oxygen gases, providing valuable data on the performance of the power system.
About Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells
|
Details |
| Basic Principle |
Converts chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy, producing water and heat as byproducts. |
| Key Components |
Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA)
Platinum-based catalyst
Gas Diffusion Layers (GDLs)
Bipolar Plates |
| Operation |
Hydrogen Oxidation: At the anode, hydrogen molecules (H2) are split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-).
Proton Conduction: The PEM allows only protons to pass through to the cathode, blocking electrons.
Electron Flow: Electrons travel through an external circuit to the cathode, creating an electric current.
Oxygen Reduction: At the cathode, oxygen molecules (O2) from the air combine with the protons and electrons to form water (H2O).
Heat Production: The reaction generates heat, which can be used for heating purposes in some applications. |
| Types of Membranes |
Perfluorosulfonic acid (PFSA) membranes (common)
Hydrocarbon-based membranes (alternative) |
| Advantages |
High power density
Low operating temperatures (60-80°C)
Zero emissions with pure hydrogen |
Applications in Space and Society
- Multipurpose Space Use: Fuel cells are particularly suitable for human space missions, providing essential power, water, and heat from a single system.
- Societal Benefits: They have significant potential for societal applications, including as replacements for conventional vehicle engines and in standby power systems.
- Advantages over Batteries: Fuel cells offer range and refuelling times comparable to conventional engines and are expected to enable emission-free transportation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Union Cabinet, led by Prime Minister, has sanctioned the “Prithvi Vigyan (Prithvi)” scheme, a significant project of the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- With a budget of Rs 4,797 crore, the scheme is planned for the period from 2021 to 2026.
About Prithvi Vigyan Scheme
- Consolidation of Programs: The Prithvi scheme unifies five existing sub-schemes:
- Atmosphere & Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services (ACROSS),
- Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology (O-SMART),
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER),
- Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE),
- Research, Education, Training and Outreach (REACHOUT).
- Aim: This integration is designed to enhance our understanding of Earth’s systems and apply scientific knowledge for societal, environmental, and economic benefits.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Comprehensive Observations: The scheme emphasizes long-term monitoring across the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere, and solid earth to track Earth System’s vital signs and changes.
- Development of Predictive Models: It focuses on creating models for weather, ocean, and climate hazards and advancing climate change science.
- Exploration Initiatives: Exploration of Polar Regions and high seas is a key aspect, aiming to discover new phenomena and resources.
- Technological Advancements: The scheme also stresses the development of technology for the sustainable exploitation of oceanic resources for societal applications.
Role of the Ministry of Earth Sciences
- Provision of Critical Services: The Ministry is responsible for delivering crucial services related to weather, climate, ocean and coastal states, hydrology, seismology, and natural hazards.
- Support in Disaster Management: These services are essential for issuing forecasts and warnings for natural disasters, thereby aiding in disaster preparedness and risk mitigation.
Holistic Approach to Earth System Sciences
- Broad Scope of Study: Earth System Sciences involve studying the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere, and their complex interactions.
- Integrated Research Efforts: The Prithvi scheme aims to address these components comprehensively, enhancing understanding and providing reliable services for India.
Impact and Future Prospects
- Addressing Major Challenges: The scheme’s integrated research and development efforts will tackle significant challenges in various fields like weather, climate, oceanography, cryospheric studies, and seismology.
- Harnessing Resources Sustainably: It explores sustainable methods to utilize both living and non-living resources, contributing to national development and environmental conservation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Jan Vishwas Bill 2023
Mains level: The impact of voice votes, the Anti-Defection Law, and the dismissal of division calls on legislative transparency and accountability
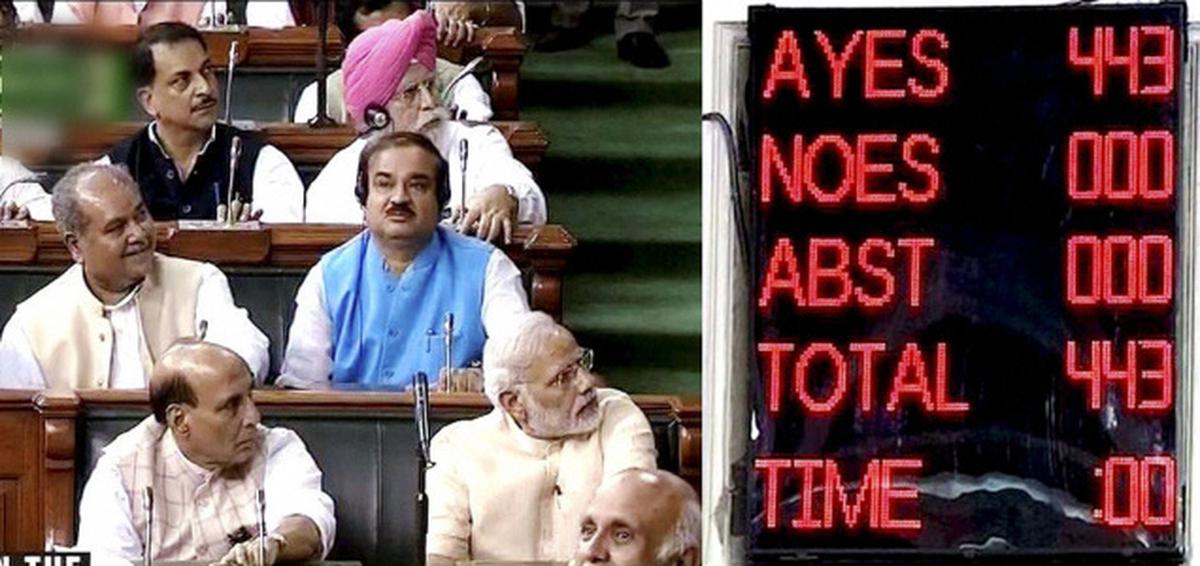
Central Idea:
The article discusses the absence of voting records during the recent Parliament session, highlighting the significance of recorded votes in representing legislators’ stances and fostering transparency in the legislative process. It also explores the impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent and the increasing use of voice votes, leading to a lack of accountability.
Key Highlights:
- 19 bills were passed in the recent Parliament session, but voting records were not made available.
- The use of voice votes, lacking individual records, is a preferred method for passing legislative motions.
- The Anti-Defection Law has limited MPs’ ability to dissent, reducing the significance of debates and votes.
- The scarcity of voting records hampers Opposition parties in communicating their positions to the electorate.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of transparency due to the absence of voting records.
- The impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ freedom to dissent.
- Dismissal of division calls during crucial legislative moments.
Key Terms:
- Voice vote
- Anti-Defection Law
- Division call
- Legislative transparency
- Accountability
- Dissent
Key Phrases:
- “A shadow of opacity has fallen over our legislative processes.”
- “The scarcity of voting records can be a symptom of a deeper problem.”
- “The impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent is a matter of concern.”
Key Quotes:
- “Transparency defines the measure to which our parliamentarians’ political decisions are traceable, which begets accountability.”
- “The right to a division, meant to be readily available, has become shrouded in subjective judgement.”
Key Examples and References:
- The passage of the Jan Vishwas Bill 2023 and the farm bills through voice votes.
- Asaduddin Owaisi’s dissent on various bills, illustrating the importance of voting records.
- Dismissal of division calls during the passage of the Weapons of Mass Destruction Bill and the Electricity Amendment Bill.
Key Facts:
- In Modi I, 40 divisions were raised for 180 bills, while in Modi II, only 20 divisions were allowed for 209 bills.
- Only 15.4% of bills in the BJP’s 10-year tenure have voting records.
Critical Analysis:
The article critically examines the impact of voice votes, the Anti-Defection Law, and the dismissal of division calls on legislative transparency and accountability. It emphasizes the need for voting records to ensure a clear representation of MPs’ stances.
Way Forward:
- Reevaluate the impact of the Anti-Defection Law on MPs’ dissent.
- Ensure the availability of voting records to enhance legislative transparency.
- Address the dismissal of division calls to uphold the right to record votes.
- Promote a more accountable and transparent legislative process through recorded votes.
In essence, the article advocates for the restoration of transparency in the legislative process through the provision of voting records and a reconsideration of the Anti-Defection Law’s impact on MPs’ dissent.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR)
Mains level: Complexity of human-wildlife conflicts

Central Idea:
The article highlights the success of Corbett Tiger Reserve (CTR) in India in managing and conserving its tiger population, emphasizing the importance of a balanced approach involving wildlife protection, community engagement, and ecological sustainability.
Key Highlights:
- CTR, spanning 1288.31 sq.km, has shown significant progress in tiger conservation, recording the highest density of wild tigers globally, from 231 to 260 in four years.
- The richly-forested, highly-biodiverse landscape attracts various enthusiasts and researchers.
- The article acknowledges the unsung heroes among the forest staff and local communities who contribute to the reserve’s ecosystem.
- Grassland and water management practices, strategic wildlife corridors, and addressing human-wildlife conflicts are vital aspects of CTR’s holistic approach.
Key Challenges:
- Human-wildlife conflicts, particularly with tigers and elephants, pose a formidable challenge.
- Ensuring the safety and security of the forest staff, who face risks while patrolling the reserve.
- Balancing the economic dependence of local communities on tiger-related tourism with the risks posed by wild animals.
Key Terms:
- Tiger Conservation Plan
- Core and buffer zones
- Biodiversity
- Grassland management
- Wildlife corridors
- Human-wildlife conflict
- Eco Development Committees (EDCs)
Key Phrases:
- “An unforgettable sight: the dread and danger lurking in the treacherous gaze of a stalking tiger.”
- “A delicate balance of forest flora and fauna is crucial for a healthy forest ecology.”
- “The rising incidence of human-elephant and tiger-human conflict poses a formidable challenge.”
- “Living with Tigers initiative aims at creating awareness and behavioral changes among local communities.”
Key Quotes:
- “A glimpse of the peerless king of the jungle in all his majesty is truly captivating.”
- “The only way ahead is by enjoining forest conservation upon all local stakeholders.”
- “The revival of the tiger since 1973 has meant a cultural renaissance and revival of our conservation ethics and values.”
Key Examples and References:
- The success of the beehive-fencing project to guard crops against wild elephants.
- The “Living with Tigers” initiative promoting awareness and behavioral changes among school children and villagers.
- The economic dependence of Ramnagar district on tiger-related tourism.
Key Facts:
- CTR covers 1288.31 sq.km and recorded 260 tigers in 2022.
- 27 different kinds of grasslands are present at CTR.
- The beehive-fencing project resulted in the creation of “Corbee Honey,” managed by local Eco Development Committees.
Critical Analysis:
The article acknowledges the complexity of human-wildlife conflicts as “wicked problems,” requiring unique solutions. It emphasizes the need for a collaborative, engaging, and socio-culturally-sensitive approach in addressing conservation challenges.
Way Forward:
- Continue efforts to balance economic benefits of tiger-related tourism with wildlife conservation.
- Scale up successful initiatives like the beehive-fencing project and “Living with Tigers” awareness program.
- Strengthen community engagement for long-term conservation efforts.
- Promote sustainable practices for wildlife protection, grassland management, and water conservation.
In essence, the article underscores the success of CTR in tiger conservation and the imperative of a comprehensive approach involving ecological sustainability, community engagement, and innovative solutions to address ongoing challenges.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: DigiYatra
Mains level: Read the attached story

Central Idea
- Travellers at Indian airports have raised privacy concerns over the Digi Yatra initiative, which involves collecting facial biometrics without explicit consent.
About DigiYatra
- DigiYatra offers paperless airport entry using facial recognition technology.
- It aims for paperless, contactless airport checkpoints, identifying travelers by facial features linked to boarding passes.
- This system automates passenger entry at various points like airport entry, security checks, and boarding using facial recognition.
- Passengers no longer need to present ID cards and boarding passes.
- The DigiYatra Foundation, a joint venture with stakeholders including the Airports Authority of India and major Indian airports, is implementing the project.
- The Airports Authority of India holds a 26% stake, while five major airports equally share the remaining 74%.
How to Use DigiYatra?
- Passengers register on the DigiYatra app with Aadhaar validation and a self-captured image.
- Next, they scan their boarding pass, sharing credentials with airport authorities.
- At the airport e-gate, passengers scan their boarding pass; the facial recognition system validates their identity and travel documents.
- After validation, passengers can enter through the e-gate.
- Normal security clearance and boarding procedures still apply.
Need for DigiYatra
- Facial recognition technology streamlines flying and reduces airport congestion.
- This technology, already in use at airports like Dubai, Singapore, Atlanta, and Narita (Japan), enhances efficiency.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
- Data Usage and Deletion: Passenger data will be used only for defined purposes and deleted 24 hours after flight departure.
- Compliance and Concerns: The FRT system will adhere to India’s data privacy and protection practices. However, concerns have been raised about the adequacy of the Personal Data Protection Bill (PDPB), 2019, which falls short of the standards set by the Justice Srikrishna Committee and does not fully align with the Justice K.S. Puttaswamy vs Union of India judgment on the right of privacy.
Concerns Over Biometric Scanning at Airports
- Privacy and Consent: Issues of data storage, access, and the option to opt-out raise privacy concerns among passengers.
- Biometric Data Misuse: Without clear regulations, there’s a risk of personal data being accessed or misused by unauthorized entities.
Issues with Biometric Scanning Technologies
- Inherent Bias: Research indicates that FRT and AI can be biased, with higher misidentification rates for non-white individuals.
- Algorithmic Discrimination: Studies have shown that machine learning algorithms can discriminate based on race and gender.
Conclusion
- Advancements in Air Travel: The implementation of FRT in Indian airports marks a significant technological advancement in air travel.
- Addressing Privacy Concerns: Ensuring robust data privacy measures and addressing inherent biases in technology are crucial for the successful and ethical implementation of FRT systems.
- Future of Air Travel Security: As FRT becomes more prevalent, continuous evaluation and improvement of these systems will be essential to safeguard passenger privacy and enhance travel efficiency.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2022:
Consider the following (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- Digi Locker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Na
Mains level: critical examination of the challenges in the current education system

Central Idea:
The article discusses the challenges and inadequacies in the current examination systems of educational institutions in India. It emphasizes the need for transparency, oversight, and credibility in assessments to ensure that degrees and certificates truly reflect students’ learning achievements.
Key Highlights:
- Credibility of the examination system is crucial for maintaining educational standards.
- Decentralized systems in India with numerous universities and boards face challenges in maintaining transparency and standardization.
- The article criticizes the focus on memory-based testing, inflation of marks, and a lack of emphasis on higher-order thinking skills.
- Employers often rely on their own assessments rather than institutional certifications.
- The article suggests the use of technology, external audits, and adherence to minimum standards to improve assessment processes.
Key Challenges:
- Lack of transparency and oversight in examination processes.
- Inconsistency and inadequacies in syllabi and teaching methods.
- Confidentiality leading to malpractices and scandals in examinations.
- The need for balancing autonomy with proper oversight in educational institutions.
- Negligence, fraud, and quality issues in assessment processes.
Key Terms:
- Decentralized system
- Transparency
- Oversight
- Standardization
- Higher-order thinking
- Autonomy
- External audit
- Credibility
- Minimum standards
- Technology in assessment
Key Phrases:
- “Credibility of assessment and standard of education can be ensured only through transparency in teaching and assessment.”
- “Inconsistency of the examination system is cause for concern.”
- “Confidentiality is also a cause for scandals in examinations.”
- “Transparency and proper oversight take lead roles in the examination systems.”
Key Quotes:
- “A credible examination system is one of the key ways to improve the standard of education.”
- “The employability of a graduate depends on higher order learning, while examination boards do not certify students on those skills.”
- “The higher education regulator truly believes in decentralization through autonomous institutions without oversight.”
Key Examples and References:
- Instances of question papers with language errors, conceptualization issues, and irrelevant questions.
- Employers disregarding institutional certifications in favor of their own assessments.
- The coaching market for competitive examinations and skilling due to a lack of faith in institutional certifications.
Key Facts:
- India has over 1,100 universities, 50,000 affiliated colleges, and 60 school boards.
- Total enrollment in higher education is 40.15 million students.
- Employers conduct rigorous assessments of candidates’ academic achievements and suitability for employment.
Critical Analysis:
The article provides a critical examination of the challenges in the current education system, emphasizing the need for transparency, oversight, and credibility. It highlights the disconnect between institutional certifications and actual learning outcomes, calling for a shift towards higher-order thinking skills.
Way Forward:
- Emphasize transparency in teaching and assessment processes.
- Implement external audits of assessment systems to ensure reliability and consistency.
- Balance autonomy with proper oversight in educational institutions.
- Use technology to standardize question paper setting and evaluation processes.
- Codify and address issues of negligence, fraud, and academic inadequacies in assessments.
- Release audit reports regularly to assess examination boards in terms of transparency, reliability, and consistency.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









