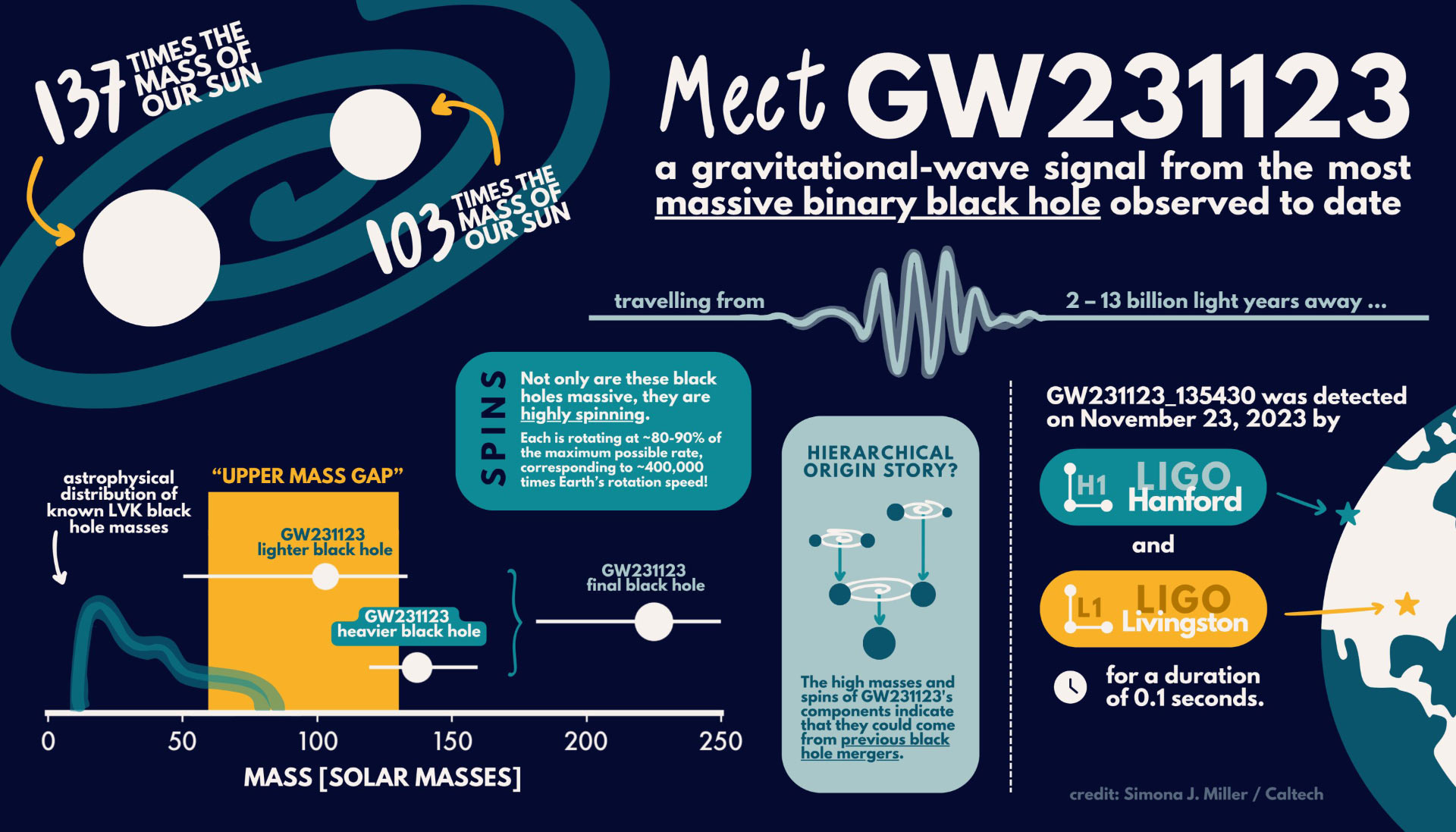
Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDDKY), aimed at enhancing agricultural productivity, promoting sustainable practices, and improving rural livelihoods.
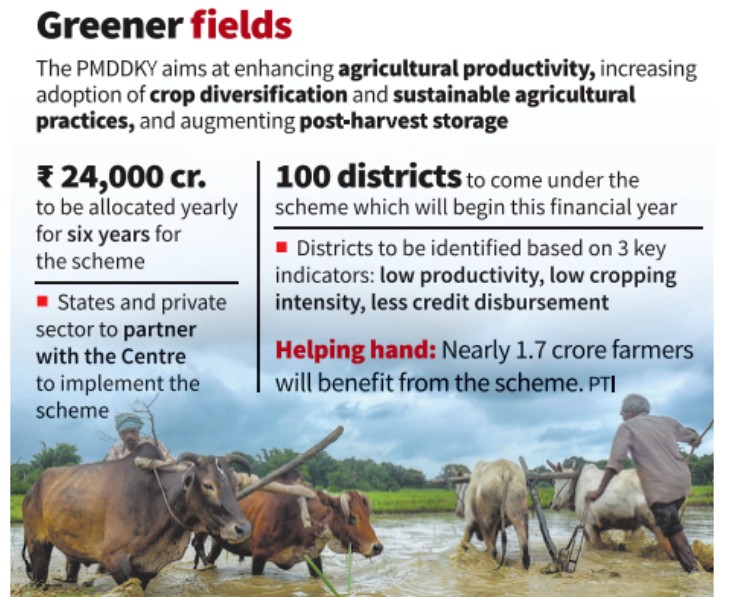
About Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDDKY)
- Objective: Aims to transform agriculture in 100 low-performing districts by addressing productivity gaps.
- Inspiration: Modelled on NITI Aayog’s Aspirational Districts Programme; first scheme focused solely on agriculture and allied sectors.
- Launch: Announced in Union Budget 2025–26 and approved by the Union Cabinet chaired by PM Narendra Modi.
- Approach: Driven by convergence of schemes, collaboration across stakeholders, and healthy competition among districts.
Key Features:
- Scheme Integration: Merges 36 schemes from 11 ministries into one unified framework.
- Budget & Duration: ₹24,000 crore annual outlay for six years (starting 2025–26).
- District Selection:
- 100 districts with low productivity, cropping intensity, and credit access
- At least one district from each state/UT
- Focus Areas:
- Boosting productivity
- Promoting crop diversification and sustainability
- Improving irrigation and water efficiency
- Expanding post-harvest storage
- Enhancing credit access
- Performance Monitoring: Monthly ranking on 117 Key Performance Indicators (KPI) via centralized dashboard.
- Support Mechanism: NITI Aayog to provide capacity-building and reviews.
- Expert Note: Credit-based selection criteria may require refinement.
Implementation:
- District Planning: Each district to prepare an Agriculture and Allied Activities Plan.
- Plan Approval: Handled by District Dhan Dhaanya Samiti, chaired by the Collector and including progressive farmers.
- National Alignment:
- Agricultural self-sufficiency
- Soil and water conservation
- Promotion of organic/natural farming
- Governance: Committees at district, state, and national levels to guide execution.
- Monitoring: Central Nodal Officers (CNOs) to conduct field visits and track progress.
- Technical Support: Agricultural universities to serve as knowledge partners.
- Expected Outcomes: Boost farm income, create local livelihoods, and support Atmanirbhar Bharat through enhanced agri-productivity.
| [UPSC 2020] Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes?
1. Working capital for maintenance of farm assets 2. Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini truck 3. Consumption requirements of farm households 4. Post-harvest expenses 5. Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 5 only (b) 1, 3 and 4 only* (c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |