Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2-Balancing India's interests in the light of US's strategy to contain China in the Pacific.
Context
Since 2017, the United States government has released a few reports and fact sheets on its new Indo-Pacific strategy. Buried in these documents is a much deeper agenda of the U.S. government: to use three large Asian states — Australia, India, and Japan — to isolate China. There is nothing else to it.
The scale of BRI and the US objections
- Objections to BRI: The U.S. government has made it clear that what it finds most objectionable is China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), which has signed on more than 70 countries in the world.
- What BRI aims to achieve? Adopted in 2013, the BRI is intended as a mechanism to-
- Development of new markets: BRI aims to end China’s reliance upon the markets of the West and to develop new markets in other continents.
- Building infra: It is also intended to use China’s massive surpluses to build infrastructure in key parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- Investment of $ 1.3 trillion: By 2027, according to estimates by Morgan Stanley, China will spend about $1.3 trillion on this ambitious construction project.
- Involvement of Saudi Arabia: Even Saudi Arabia, a close ally of the U.S., has made the BRI one of the cornerstones of its Saudi Vision 2030 plan.
- Involvement of Pakistan: While China has invested $68 billion to build the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor from Xinjiang to Pakistan’s Gwadar Port.
- Saudi Arabia has agreed to invest $10 billion in the port itself.
Significance of the BRI and comparison with the US spending
- Staggering scale and participation: The scale of Chinese investment, and the participation of a range of countries with different political identities in the BRI, is staggering.
- Loss of appetite in the US to spend: At the Indo-Pacific Business Forum in July 2018 the U.S. said that it has spent $2.9 billion through the Department of State and the USAID (United States Agency for International Development).
- It has lined up hundreds of millions of dollars more through its U.S. Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) and the Overseas Private Investment Corporation.
- Inadequate US spending: If one adds up all the money that the U.S. intends to spend for economic projects, it is still a fraction of the amount spent by China.
- ‘America First’ attitude: There is no appetite in Washington, D.C., with its ‘America First’ attitude, to funnel more money towards investments in the region currently being built by the BRI.
Military Claims of the US and investment
- US investment with military presence: It appears as if U.S. investments will come only with military claims.
- The case of Nepal: A few years ago, Nepal discovered a large amount of uranium in Mustang, near the Nepal-China border; this has certainly motivated U.S. interest in Nepal’s economy.
- If the U.S. money comes with U.S. military presence, this will create a serious flashpoint in the Himalayas.
Raising human right and transparency issue against China
- The argument of human rights and transparency
- Rhetorical argument: Unable to outspend the Chinese, the U.S. government is making a rhetorical argument that it has more respect for “transparency, human rights, and democratic values” than China, which “practices repression at home and abroad”.
- The argument of transparency and the debt trap
- Debt trap used by the US: It is hard to imagine the U.S. being “transparent” with its trade deals. It is equally hard to imagine the U.S. being able to argue that it would not put countries into debt.
- Debt crisis created by the US in the 1980s: The U.S. government enabled a massive Third World debt crisis in the 1980s, which was then used by the U.S.-driven International Monetary Fund’s Structural Adjustment Programs to strangle countries in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
- This history is alive, and it makes a mockery of the U.S.’s attempt to say that its own approach is superior to that of China’s.
US withdrawal from multilateralism
- Apart from that, the U.S. government has already indicated that it is uninterested in multilateral deals.
- Withdrawal from TPP: The US withdrew from the Trans-Pacific Partnership in 2017, for instance.
- Australia and Japan shrugged, and then put their energy into the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, which sidelines the U.S.
The claim of free and open Indo-Pacific
- Renaming the Pacific Command: In May 2018, the U.S. military’s Pacific Command was renamed the Indo-Pacific Command, a symbolic gesture that provides a military aspect to the Indo-Pacific Strategy.
- What free and open mean to the US? The U.S. government has made it clear that for all its talk of a “free and open Indo-Pacific”, what it actually wants is an Indo-Pacific with fewer Chinese ships and more U.S. warships.
- Just before this renaming, the U.S. National Security Strategy of 2017 noted that “China seeks to displace the United States in the Indo-Pacific region”, and so the Indo-Pacific Strategy intends for the S. to fight for its dominance in the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and in the Asian rim.
- This is a very dangerous war that the U.S. seeks to impose on Asia.
India adopting the US project of Indo-Pacific
- Australia and Japan moving away: As the military aspect of the Strategy increased, both Australia and Japan edged away from full-scale adoption of the U.S. project.
- Japan has begun to use the term “Indo-Pacific” without the word “Strategy”.
- Australia has signed onto a “comprehensive strategic partnership” with China.
- Only India adopting the project: Only India remains loyal to the agenda set by U.S. President Donald Trump.
- No US strategy to contain China: In all the documents released by the U.S. government and in all the speeches by officials, there is no discussion of the strategy to contain China.
- There is only rhetoric that skates into the belligerent territory.
Conclusion
India would be advised to study the U.S. project rather than jump into it eagerly. Room for an independent foreign policy for India is already narrowed, and room for independent trade policy is equally suffocated. To remain the subordinate ally of the U.S. suggests that India will miss an opportunity to be part of a reshaped Asia.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- Data localisation and issues involved.
Context
The contentious clauses on local data storage in the revised Personal Data Protection Bill need re-examination.
What Personal Data Protection Bill contains?
- Greater control to an individual: The draft law is a comprehensive piece of legislation that seeks to give individuals greater control over how their personal data is collected, stored and used.
- The promise of improvement over the current privacy law: Once passed, the law promises a huge improvement on current Indian privacy law, which is both inadequate and improperly enforced.
- Criticism of the bill: The proposed bill has attracted criticism on various grounds such as-
- The exceptions created for the state.
- The limited checks imposed on state surveillance, and-
- Regarding various deficiencies in the structures and processes of the proposed Data Protection Authority.
The issue over the “data localisation”
- Data within the country: The phrase, which can refer to any restrictions on cross-border transfer of data, has largely come to refer to the need to physically locate data within the country.
- Provisions for the transfer of personal data outside India: The PDP Bill enables the transfer of personal data outside India, with the sub-category of sensitive personal data have to be mirrored in the country (e. a copy will have to be kept in the country).
- Ban on transfer of critical data outside the country: Data processing/collecting entities will, however, be barred from transferring critical personal data (a category that the government can notify at a subsequent stage) outside the country.
- Different from Justice Srikrishna committee report: These above provisions have been changed from the earlier version of the draft Bill, released by the Justice Srikrishna Committee in 2018.
- The 2018 draft imposed more stringent measures that required both personal and sensitive personal data to be mirrored in the country (subject to different conditions).
- Welcome move: The move to liberalise the provisions in the 2019 version of the Bill is undoubtedly welcome, particularly for businesses and users.
How removing the restriction matters?
- Reduction in cost to business: Liberalised requirements will limit costs to business and ensure users have greater flexibility in choosing where to store their data.
- More proportionate approach: The changes in the 2019 draft reflect a more proportionate approach to the issue as they implement a tiered system for cross-border data transfer, ostensibly based on the sensitivity/vulnerability of the data.
- Move-in accordance with the right to privacy: This seems in accord with the Supreme Court’s dicta in the 2017 Puttaswamy case.
- Conditions for interference in privacy: The Court had made it clear that interference in the fundamental right to privacy would only be permissible if inter alia deemed necessary and proportionate.
Test of proportionality in the bill
- On closer examination, it appears that even the revised law may not actually stand the test of proportionality.
- The three-argument for imposing norms: There are broadly three sets of arguments advanced in favour of imposing stringent data localisation norms:
- Sovereignty and government functions. Referring to the need to recognise Indian data as a resource to be used to further national interest (economically and strategically), and-
- To enable enforcement of Indian law and state functions.
- Accruing benefits to the local industry: The second claim is that economic benefits will accrue to local industry in terms of creating local infrastructure, employment and contributions to the AI ecosystem.
- Protection of civil liberties: Regarding the protection of civil liberties, the argument is that local hosting of data will enhance its privacy and security by ensuring Indian law applies to the data and users can access local remedies.
- Contradiction in the claim of protection? If data protection was required for the above purposes, it would make sense to ensure that local copies were retained of all the categories of personal data provided for in the Bill (as was the case with the previous draft of the law).
- Sectoral obligations: In the alternative, sectoral obligations would also suffice as is currently the case with sectors such as digital payments data, certain types of telecom data, government data, etc.
- Will data localisation lead to privacy protection? We note that the security of data is determined more by the technical measures, skills, cybersecurity protocols, etc. put in place rather than its mere location.
- Localisation may make it easier for domestic surveillance over citizens.
- Enabler of better exercise of privacy by citizens: It may also enable the better exercise of privacy rights by Indian citizens against any form of unauthorised access to data, including by foreign intelligence.
- Effectiveness matters: The degree of protection afforded to data will depend on the effectiveness of the applicable data protection regime.
- Protecting privacy through less intrusive measures: Insofar as privacy is concerned, this could be equally protected through less intrusive, suitable and equally effective measures such as requirements for contractual conditions and using adequacy tests for the jurisdiction of the transfer.
- Such conditions are already provided for in the PDP Bill as a set of secondary conditions.
- The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation too uses a similar framework.
- Extra-territorial operation: The extraterritorial application of the PDP Bill also ensures that the data protection obligations under the law continue to exist even if the data is transferred outside the country.
- Giving an individual a choice: If privacy protection is the real consideration, individuals ought to be able to choose to store their data in any location which afford them the strongest privacy protections.
- It is arguable that data of Indians will continue to be more secure if stored and processed in the European Union or California.
- These two jurisdictions have strong data protection laws and advanced technical ecosystems.
Way forward
- Identification of the issues: The joint parliamentary committee ought to, ideally, identify the need, purpose and practicality of putting in place even the (relatively liberal) measures contained in the PDP Bill.
- Broader thinking at policy level: Further, in order for localisation-related norms to bear fruit, either in terms of protecting citizen rights, enabling law enforcement access to data or enabling the development of the local economy, there has to be broader thinking at the policy level.
- This may include for instance-
- Reforming surveillance-related laws.
- Entering into more detailed and up-to-date mutual legal assistance treaties.
- Enabling the development of sufficient digital infrastructure, and
- Creating appropriate data-sharing policies that preserve privacy and other third party rights, while enabling data to be used for socially useful purposes.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Location of Idlib Province
Mains level: Usual turmoil in Syria
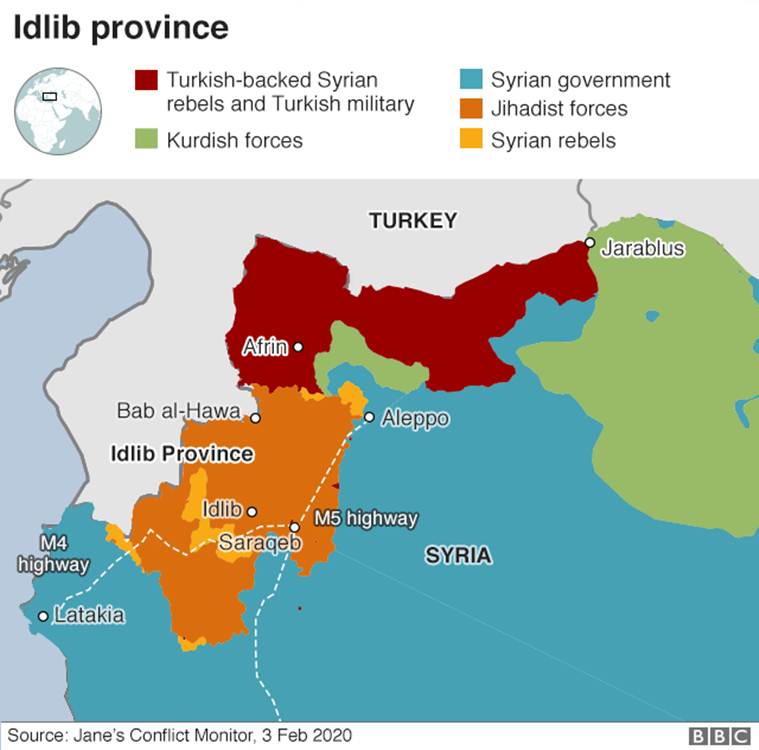
The nine-year-old war in Syria is currently raging in the northwestern province of Idlib, with rapidly escalating tensions between government forces of President Bashar al-Assad and the Turkish military.
Background
- President’s Assad’s forces are backed by Russia, who are clashing with thousands of Turkish troops south of its border with Syria.
- Turkey has closed the border and is trying to seal itself from waves of displaced refugees as Assad presses forth with a brutal campaign to take back Idlib.
Why is Idlib important?
- Assad has been pushing to recapture Idlib, which, along with parts of neighbouring Hama, Latakia and Aleppo, are the last remaining strongholds of the rebel opposition and other groups that have been attempting to overthrow Assad since 2011.
- At one point, the opposition held large parts of Syria under its control, but that changed after Assad, with Russian military support, slowly regained control over most of the country.
- In 2015, Idlib province was overtaken by opposition forces.
- Now, Syrian government forces are attempting to capture the strategic M4 and M5 national highways that connect Idlib, Aleppo and Damascus, the capital of the country.
- Idlib skirts the two national highways and lies between Aleppo in the north and Damascus in the south.
- It’s proximity to the Turkish border makes Idlib strategically important to the Syrian government.
Who controls Idlib now?
- Since the province fell to opposition forces, there is no one group that controls Idlib, but rather, several separate factions.
- International watchdogs say that the dominant faction in Idlib is the Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), a UN-designated terrorist organization set up in 2017, with links to al-Qaeda.
- Also operating in Idlib is the Turkey-backed Syrian National Army, an armed opposition group. Included in the mix are the remnants of the Islamic State.
- Watch groups say that other factions in Idlib strongly oppose the presence of IS fighters in the province.
Why is Idlib important for Turkey?
- Idlib’s proximity to the Turkish border makes it not only important for the Syrian government, but also a cause of concern for Turkey.
- Since the war started in Syria, thousands of displaced Syrians have sought refuge in Turkey over the years.
- According to the latest known figures, Turkey presently hosts some 3.6 million refugees and is feeling the socio-economic and political strain of their presence in the country.
- More conflict in Idlib would only serve to displace more people, pushing them towards the Turkish border.
- Turkey has been witnessing a surge in hostility among its citizens towards refugees and a fresh wave of refugees will only exacerbate the situation.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yongle Blue Hole (YBH)
Mains level: Signifcance of Blue Holes

Carbon more than 8,000 years old has been found inside the world’s deepest blue hole — the Yongle Blue Hole (YBH).
Yongle Blue Hole (YBH)
- The deepest known marine cavern is the Yongle blue hole, which measures roughly 300 metres from top to bottom.
- Blue holes are marine caverns filled with water and are formed following dissolution of carbonate rocks, usually under the influence of global sea level rise or fall.
- Its waters are mostly isolated from the surrounding ocean and receive little fresh water from rainfall, making it a rare spot to study the chemistry of oxygen-deprived marine ecosystems.
- What distinguishes them from other aquatic caverns is that they are isolated from the ocean and don’t receive fresh rainwater.
- They are generally circular, steep-walled and open to surface.
Significance of YBH
- YBH has a depth of 300 metres, far deeper than the previously recorded deepest blue hole, Dean’s Blue Hole in Bahamas, which had a depth of 202 metres.
- However, like most blue holes, it is anoxic i.e. depleted of dissolved oxygen below a certain depth. This anaerobic environment is unfavorable for most sea life.
- Such anoxic ecosystems are considered a critical environmental and ecological issue as they have led to several mass extinctions.
- Concentrations of carbon, usually found in deep marine holes like YBH, provide a natural laboratory to study carbon cycling and potential mechanisms controlling it in the marine ecosystem.
- The transition from aerobic to anaerobic environment adversely affects the biogeo-chemistry of the ocean.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Taj Mahal
Mains level: Conservation of historical monuments
The Taj Mahal complex has been spruced up for the visit of US President Donald Trump and First Lady Melania Trump.
About Taj
- The Taj Mahal is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the south bank of the Yamuna river in the city of Agra.
- It was commissioned in 1632 by Shah Jahan (reigned from 1628 to 1658) to house the tomb of his favourite wife, Mumtaz Mahal; it also houses the tomb of Shah Jahan himself.
- The tomb is the centrepiece of a 17-hectare (42-acre) complex, which includes a mosque and a guest house, and is set in formal gardens bounded on three sides by a crenellated wall.
- The Taj Mahal complex is believed to have been completed in its entirety in 1653 at a cost estimated at the time to be around 32 million rupees, which in 2015 would be approximately 52.8 billion rupees (U.S. $827 million).
- The construction project employed some 20,000 artisans under the guidance of a board of architects led by the court architect to the emperor, Ustad Ahmad Lahauri.
- The Taj Mahal was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1983 for being “the jewel of Muslim art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world’s heritage”.
Various threats to Taj
- The Supreme Court had earlier expressed concern over the marble of the Taj changing colour, and asked how the white marble, which had first become yellowish, was now turning brownish and greenish.
- Firstly, the polluting industries and the vehicular emissions in the Taj Trapezium Zone (TTZ) area are a major source of pollution.
- The second reason is that the Yamuna River, which flows behind the Taj, has become highly polluted.
- There is no aquatic life in it, and has caused insect and algae infestation on the Taj Mahal and other monuments situated on its banks.
Use of mud packs
- Increasing pollution in the air over the Gangetic Valley affecting the Taj has been a reason for concern for archaeologists and conservationists for long now.
- Mud packs were applied on the surface of the monument first in 1994, and then again in 2001, 2008, and, most recently, beginning 2014.
- Mud packs have been one of the ASI’s favoured ways to remove the yellow stains that have appeared over the years on the Taj Mahal’s white marble facade.
- The clay is applied in the form of a thick paste that absorbs the grime, grease and bird droppings on the marble, before being washed off using distilled water.
- The process is slow and tortuous, but is believed to leave the marble cleaner and shinier.
- The intricate parts are applied with special “multani mitti’ (Fuller’s clay) treatment.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pakke Tiger Reserve
Mains level: Not Much

The government in Arunachal Pradesh is planning to build a 692.7 km highway through the 862 sq km Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR). Named the East-West Industrial Corridor, the highway aims to connect Bhairabhunda in West Kameng district and Manmao in Changlang district along Arunachal Pradesh’s border with Assam.
About Pakke Tiger Reserve (PTR)
- Pakke Tiger Reserve, also known as Pakhui Tiger Reserve, is a Project Tiger reserve in the East Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The 862 km2 reserve is protected by the Department of Environment and Forest of Arunachal Pradesh.
- This Tiger Reserve has won India Biodiversity Award 2016 in the category of ‘Conservation of threatened species’ for its Hornbill Nest Adoption Programme.
- It falls within the Eastern Himalaya Biodiversity Hotspot.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: SPICe+
Mains level: Not Much

The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has launched SPICe+ web form.
SPICe+
- It would offer 10 services by 3 Central Govt Ministries & Departments (Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Ministry of Labour & Department of Revenue in the Ministry of Finance) and One State Government (Maharashtra).
- It saves as many procedures, time and cost for Starting a Business in India and would be applicable for all new company incorporations.
Following are the features of the new Spice+ web form:
- SPICe+ would be an integrated Web Form.
- SPICe+ would have two parts viz.: Part A-for Name reservation for new companies and Part B offering a bouquet of services viz.
- Registration for Profession Tax shall also be mandatory for all new companies to be incorporated in the State of Maharashtra through SPICe+.
- All new companies incorporated through SPICe+ would also be mandatorily required to apply for opening the company’s Bank account through the AGILE-PRO linked web form.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: International Judicial Conference
Mains level: Highlights of the conference
The President of India delivered the valedictory address at the International Judicial Conference being organised by the Supreme Court of India, in New Delhi.
About the Conference
- The Conference was organized by the Supreme Court of India.
- The theme of the Conference was ‘Judiciary and the Changing World’.
Important Topics of discussion at the Conference included :
- Gender Justice,
- Contemporary Perspectives on Protection of Constitutional Values,
- Dynamic Interpretations of the Constitution in a Changing World,
- Harmonization of Environment Protection vis-à-vis Sustainable Development and
- Protection of Right to Privacy in the Internet Age
Other excerpts:
“Just-World” Hypothesis
- The “Just World” fallacy is associated with the actions of bringing fair actions towards education, health, gender equality and other social issues.
- The Conference introduced the “Just World” concept in the Judicial System of India.
- By this it aims to take the judicial system of the country to every citizen irrespective of their gender.
- Also, it aimed to bring upon gender equality in other crucial areas where women have still not earned their recognition, especially the areas of mining and military.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




