Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3-Climate change and adoption of clean and sustainable energy to tackle with it.
Context
Significance of electricity in our life
- Interconnecting economic prosperity: Electrical energy is a juncture that inter-connects economic prosperity.
- Amplifies social equity.
- Ushers in a liveable environment for us.
- No development in its true sense is possible if we leave aside energy and specifically sustainable energy.
- It is almost indispensable for holistic and sustainable progress of any kind.
Burning of fossil fuel and climate change
- Singular reliance on fossil fuel: Ever since the industrial revolution, development has almost singularly relied on the burning of fossil fuels, emitting huge volumes of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- 41% of electricity from coal: As per data by the World Coal Association, a little over 41% of all electricity generated is produced from coal.
- Problems with coal: Burning coal for electricity production leads to-
- High level of hazardous carbon emissions.
- Rising levels of pollution: water and air pollution during mining and air pollution during burning.
- Working condition of miners: Added to the disastrous working conditions of miners, coal cannot be regarded as a sustainable source of energy.
- Global warming and climate change: Despite increasing awareness, not much is being done to mitigate climate change.
- Rise over 1.5oC and Consequences: IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) has reiterated that unless global temperature rise is not kept within 1.5 degrees Celsius, natural and human systems will be irreparably damaged.
- Rise over 2o C and Consequences: Even a slight increase in atmospheric temperature by 2 degrees Celsius will result in a substantial rise in sea levels.
- Consequences for human life: The rise in sea level would, in turn, translate into a whopping 10 million more people going homeless and another 50% people facing severe water scarcity.
- The aim of becoming carbon neutral: To join the efforts, many global public and private stakeholders have pledged their allegiance into becoming net-zero carbon emitters.
- But we are still far from achieving our objectives, as the IEA (International Energy Agency) recently reported that the Earth’s temperature rise will range between 1.8 degrees Celsius and 2.7 degrees Celsius soon.
Sustainable energy as a necessity
- Energy efficiency and energy management: As the world is evolving into an interconnected form of world-of work, life and more-energy efficiency and energy management have slowly come to be a central driving force.
- Sustainable energy a necessity: In order to power smart homes, industries, hospitals and other mission-critical operations, sustainable energy is no more a matter of choice, but of necessity.
- IoT to help achieve energy efficiency: Technology adoptions like IoT and connected services can greatly enhance energy efficiencies and many global behemoths are coming to terms with this reality.
- Demand for an alternative source of energy: Environmental factors, coupled with rising costs and stringent regulatory guidelines, are adding to the demand for alternative sources of energy.
- Alternate as well as sustainable: The alternate sources are expected not only to satiate the growing consumption needs but are proven to be a sustainable option in the long run.
Electricity 4.0
- Electricity 4.0: That is, sustainable methods of energy generation and efficient and cost-effective usage of produced energy.
- The sustainable energy need of the sustainable future: To lay the foundation stone for a sustainable future, there is a critical need to investigate how we create and consume energy.
- The answer lies in renewables becoming the dominant source of power, globally.
- A new form of energy mix: There is a growing need to build a new form of energy mix under Electricity 4.0, with renewable ways of electricity creation, at its very core. A new order where-
- Electrical internet of things (EIOT).
- Cloud computing.
- Artificial intelligence.
- And the tools of today’s digital era are fully leveraged to maximise energy efficiency.
Way forward
- Given that the major cause of global warming is Carbon Dioxide, so the first step to combat it would be-
- Electrifying the planet: The augmented proliferation of energy-efficient, electricity-based equipments that are prevalent now, such as e-mobility, electrical heating, innovative applications such as electric aviation fleets can be one way to do that.
- Scale up the production of renewable energy: The immediate need is to scale up the production of renewable electricity and build conducive public-policy frameworks to further this goal.
- Adoption of digital technology: It is imperative to adopt digital technology in order to optimise the efficiency of our energy consumption and electrical networks. Digital connectivity, software and artificial intelligence can well be dubbed as the fulcrum that will support our transition toward Industry 4.0.
- Concerted efforts from all stakeholders: To reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions or to promote energy decarbonisation, concerted efforts are required from all stakeholders – the community, regions, government and the private sector.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Need to define the natural forests and effects of climate change on forests.
Context
Global warming, drought and El Niño may lead to increased forest fires.
The success story of India
- Reduced deforestation: India has succeeded in reducing deforestation to some extent through an effective Forest Conservation Act and large-scale afforestation programme.
- Comparison with other countries: India performed better when compared with other forest-rich tropical countries such as Brazil, Indonesia and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Without the Forest Conservation Act and its reasonably effective implementation, India would have lost significant extent of forest area.
- Increased afforestation: India has also been implementing significant scale afforestation, though the rates of afforestation have declined recently.
- Agro-forestry, involving raising fruit tree plantations contribute to some extent.
- Commercial plantations of eucalyptus, casuarina, teak, poplar, etc., have been raised by farmers for commercial purposes.
- The above steps have resulted in potentially reducing the pressure on natural forests.
Need to measure ‘natural forest’
- Increase in an area under forest: According to the latest biennial State of Forest Report (SFR) of the Forest Survey of India (FSI), an area under forests has been increasing.
- Natural forests not specifically measured: It is not clear what percentage of increase in forest area is due to changes in natural forests which are generally rich in biodiversity.
- The report doesn’t specify what percentage of change in area is due to commercial plantation and what percentage is contributed by horticulture or urban parks.
- Need to define ‘natural forest’: What will be of most concern to forest and biodiversity conservation is to understand the status of natural forest and biodiversity.
- India can use the same definition of forests but must estimate and report the area under natural forests and other forest plantation categories.
- India needs to define ‘natural forests’ first, further, this would involve additional staff time and resources.
- The resilience of natural forests to forest fires: Tropical forests rich in biodiversity are likely to be more resilient than monoculture dominated plantations or exotics.
- Vulnerability to forest fires varies from forests to forests: Studies by the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have shown that degraded forests, fragmented forests and biodiversity-poor forests are more vulnerable to climate change.
Climate change and its impacts
- IPCC reports on large scale loss: The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports have repeatedly concluded that climate change will lead to large-scale loss of biodiversity, before the end of the current century or even earlier.
- Modelling studies by IISc.: Preliminary modelling studies by Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have shown that about 20% of forests will be impacted by climate change.
- No change to adapt: The modelling studies means that existing forest biodiversity and its structure and composition will not be able to adapt to the new climate and there could be mortality or forest dieback.
- The threat of forest fires: Further, warming, drought and El Niño will lead to increased forest fires, and may even be favourable to forest pests.
- Unfortunately, the models currently in use for assessing the impact of climate change are not suitable for the complex and highly diverse forest types that exist in India.
Conclusions
- Given that global warming will continue, India will have to brace itself to adapt to the impending impacts. In India, there is very limited research on climate change and its impacts on forests, putting our famed biodiversity-rich country status under threat.
- India needs to realistically assess, monitor and model climate change and its impacts and be prepared to adapt to impending climate change.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2-Foreign relations with Pakistan, Issues and need to resume the talks.
Context
Pakistan is changing significantly, which is good for itself and its neighbour as well.
Changing Pakistan
- Major stakeholders in favour of peace: The civil society, the political parties, and even the military establishment of Pakistan have come to favour peaceful and cooperative relations with India.
- Both the power-centre on the same page: Both Islamabad and Rawalpindi, Pakistan’s two centres of power, are now on the same page in seeking “honourable peace” with New Delhi on the basis of “sovereign equality”.
- Heavy price paid by Pakistan: There is a broad consensus in Pakistani society and polity that their country has paid a very heavy price by supporting the forces of Islamist extremism and terrorism.
- The futility of using terrorism as foreign policy: There is also consensus that using terrorism for achieving mistaken foreign policy ends in Afghanistan and India.
Conducive conditions for dialogues
- Four factors have influenced the welcome winds of change in Pakistan.
- First-Realisation that Pakistan has suffered a lot:
- Harm at home and to the global image: There is the across-the-board realisation that Pakistan has suffered a lot, both domestically and in terms of damage to its global image, by supporting religious extremism and terrorism.
- A large number of casualties: Terrorists have killed a shockingly large number of civilians -certainly far many more than in India. Several thousand soldiers have lost their lives in the army’s “war on terror”-more than the number of casualties in all the wars with India.
- The threat of FATF blacklisting: Furthermore, Islamabad is under relentless pressure from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) to act decisively and irreversibly against terrorist organisations.
- Second-Decrease in religious radicalisation in Pakistan
- The decrease in the financial support to radicalism: What has contributed to the diminished importance of religious radicalism is also the shrinking inflow of petrodollars from Saudi Arabia and Gulf countries that promoted this agenda.
- The ideological influence of religious radicalisation on Pakistan’s civil society is clearly declining.
- Change in Saudi Government Policy: Export of Wahhabism is no longer a foreign policy priority of the Saudi Arabian government.
- Changing policies in UAE: The United Arab Emirates has gone a step further, under the leadership of Abu Dhabi’s Crown Prince Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, it is pursuing inter-religious tolerance with a zeal that has surprised Muslims and non-Muslims alike.
- Third-Interest of China
- Rise of China as an economic and security partner: The third factor is China, which has emerged as Pakistan’s most important economic and security partner.
- The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and BRI: The flagship projects under Beijing’s BRI has begun to modernise Pakistan’s infrastructure spectacularly, but its security is which could be threatened by terrorism is also the concern for China.
- Connection with China’s Xinjiang Province: China has urged Pakistan’s ruling establishment to take firm steps to curb the activities of Islamist groups because they can easily foment trouble in China’s Muslim-majority Xinjiang province.
- India-China relation factor: Beijing is also engaged in a steady effort to improve relations with New Delhi, in recognition of India’s rising economic and geopolitical stature in Asia and globally.
- Possibility of India-China-Pakistan cooperation: China’s President Xi Jinping even mooted cooperation among China, India and Pakistan at Mamallapuram summit.
- Fourth-Military establishment in favour of peace.
- The military establishment seems to be fully convinced of the need for normalisation of India-Pakistan
- Opening of Kartarpur Sahib Corridor: The opening of the Kartarpur Sahib Corridor, perhaps the greatest confidence-building measure between the two countries since 1947, is almost entirely due to Gen. Bajwa’s personal commitment to the project.
- The economic crisis in Pakistan: Bajwa’s is also said to be convinced of the need to open the doors for economic and trade cooperation between the two countries given a serious economic crisis Pakistan is going through.
- Discussion on the Kashmir issue: The Pakistan Army may also be ready to discuss a solution to the Kashmir issue on the basis of a formula Gen. Pervez Musharraf had discussed with PMs Atal Bihari Vajpayee and Dr Manmohan Singh.
Conclusion
India needs to seize the opportunity to resume the talks with Pakistan on all the contentious issues and try to resolve the disputes so that the improved relations could help both the countries and the neighbouring countries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TMT, Mauna Kea
Mains level: India's abroad space missions
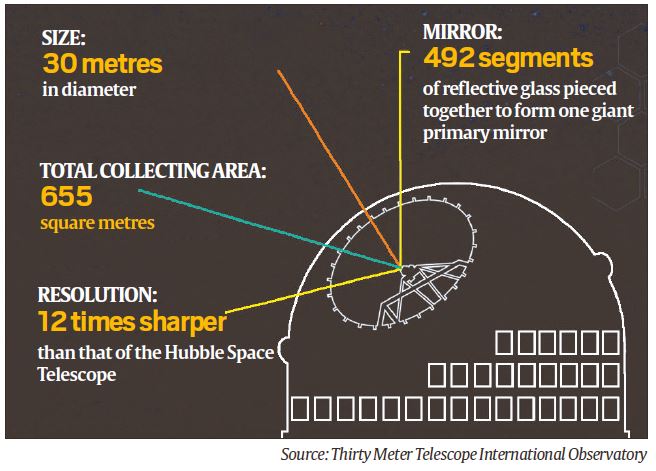
India, a partner in the construction of one of the largest telescopes in the world, TMT, has said it wants the project to be moved out of the proposed site at Mauna Kea, a dormant volcano in Hawaii.
Thirty Metre Telescope
- The TMT is a proposed astronomical observatory with an extremely large telescope (ELT) that has become the source of controversy over its planned location on Mauna Kea on the island of Hawaii in the US state of Hawaii.
- It is being built by an international collaboration of government organisations and educational institutions, at a cost of $1.4 billion.
- “Thirty Metre” refers to the 30-metre diameter of the mirror, with 492 segments of glass pieced together, which makes it three times as wide as the world’s largest existing visible-light telescope.
- The larger the mirror, the more light a telescope can collect, which means, in turn, that it can “see” farther, fainter objects.
- It would be more than 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes and would be able to resolve objects 12 times better than the Hubble Space Telescope.
Utility of the telescope
- One of its key uses will be the study of exoplanets, many of which have been detected in the last few years, and whether their atmospheres contain water vapour or methane — the signatures of possible life.
- For the first time in history, this telescope will be capable of detecting extraterrestrial life.
- The study of black holes is another objective.
- While these have been observed in detail within the Milky Way, the next galaxy is 100 times farther away; the TMT will help bring them closer.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: InvITs and REITs
Mains level: Not Much

Markets regulator SEBI has put in place a framework for the rights issue of units by listed REIT and InvITs.
What are InvITs and REITs?
Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvIT)
- An Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvITs) is like a mutual fund, which enables direct investment of small amounts of money from possible individual/institutional investors in infrastructure to earn a small portion of the income as return.
- InvITs work like mutual funds or real estate investment trusts (REITs) in features.
- InvITs can be treated as the modified version of REITs designed to suit the specific circumstances of the infrastructure sector.
- They are similar to REIT but invest in infrastructure projects such as roads or highways which take some time to generate steady cash flows.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REIT)
- A REIT is roughly like a mutual fund that invests in real estate although the similarity doesn’t go much further.
- The basic deal on REITs is that you own a share of property, and so an appropriate share of the income from it will come to you, after deducting an appropriate share of expenses.
- Essentially, it’s like a group of people pooling their money together and buying real estate except that it’s on a large scale and is regulated.
- The obvious pitch for a REIT is that it enables individuals to generate income and capital appreciation with money that is a small fraction of what would be required to buy an entire property.
- However, the resemblance to either mutual funds or to owning property ends there.
- According to Indian regulation on REITs, these are meant to primarily own finished and rented out commercial properties –– 80 per cent of the investments must be in such assets. That excludes a real estate that is under development.
Why need InvITs and REITs?
- Infrastructure and real estate are the two most critical sectors in any developing economy.
- A well-developed infrastructural set-up propels the overall development of a country.
- It also facilitates a steady inflow of private and foreign investments, and thereby augments the capital base available for the growth of key sectors in an economy, as well as its own growth, in a sustained manner.
- Given the importance of these two sectors in the country, and the paucity of public funds available to stimulate their growth, it is imperative that additional channels of financing are put in place.
What did SEBI rule?
- SEBI said the issuer will have to disclose objects of the issue, related-party transactions, valuation, financial details, review of credit rating and grievance redressal mechanism in the placement document.
- The SEBI had first notified REITs and InvIT Regulations in 2014, allowing setting up and listing of such trusts which are popular in some advanced markets.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Various committees mentioned in the newscard
Mains level: Three capitals concept
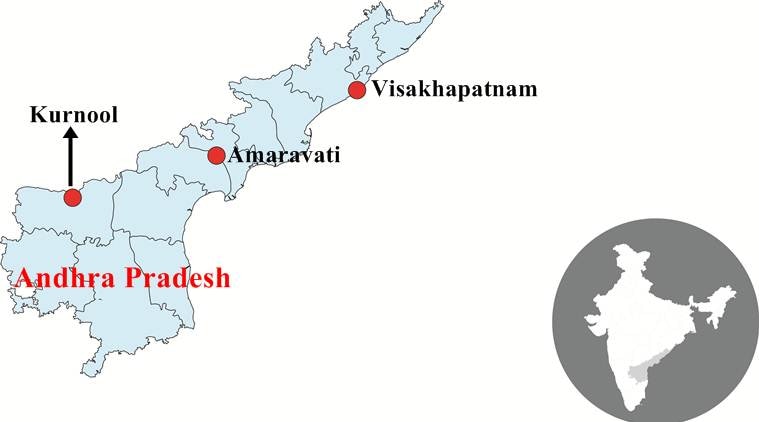
The Andhra Pradesh Assembly passed The Andhra Pradesh Decentralisation and Equal Development of All Regions Bill, 2020, paving the way for three capitals for the state.
Three capitals concept in Andhra Pradesh
- Three cities serve as capitals of the country– Pretoria (executive), Cape Town (legislative), and Bloemfontein (judicial).
- This arrangement was a result of the Second Boer War (1899-1902) in which Britain annexed the two Afrikaner speaking states -– the Orange Free State and the South African Republic (also called Transvaal Republic).
- Cape of Good Hope then remained in the British Empire, becoming self-governing in 1872, and uniting with three other colonies to form the Union of South Africa in 1910.
What are the other examples of multiple capital cities?
- Several countries in the world have implemented the concept.
- In Sri Lanka, Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is the official capital and seat of national legislature, while Colombo is the de facto seat of national executive and judicial bodies.
- Malaysia has its official and royal capital and seat of national legislature at Kuala Lumpur, and Putrajaya is the administrative centre and seat of national judiciary.
- Among Indian states, Maharashtra has two capitals– Mumbai and Nagpur (which holds the winter session of the state assembly).
- Himachal Pradesh has capitals at Shimla and Dharamshala (winter).
- The former state of Jammu & Kashmir had Srinagar and Jammu (winter) as capitals.
Reasons behind such considerations
- According to the government, decentralisation was the central theme in recommendations of all major committees that were set up to suggest a suitable location for the capital of Andhra Pradesh.
- It had been agreed in the November 16, 1937 Sri Bagh Pact (between leaders of coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema) that two university centres should be established in Waltair (Visakhapatnam) and Anantapur in Rayalaseema, and that the High Court and Metropolis should be in the coastal districts and Rayalaseema respectively.
- In December 2010, the Justice B N Srikrishna Committee, set up to look into the demand for a Telangana state, said Rayalaseema and North Coastal Andhra were economically the most backward, and the “concentration of development efforts in Hyderabad is the key reason for demand of separate states”.
- In August 2014, the K Sivaramakrishnan Committee appointed to identify locations for the new capital of AP said the state should see decentralised development, and that one mega capital city was not desirable.
Major practical problems
- The government argues that the Assembly meets only after gaps of several months, and government Ministers, officers, and staff can simply go to Amaravati when required.
- However, coordinating between seats of legislature and executive in separate cities will be easier said than done, and with the government offering no specifics of a plan, officers and common people alike fear a logistics nightmare.
- The distances in Andhra Pradesh are not inconsiderable. Executive capital Visakhapatnam is 700 km from judicial capital Kurnool, and 400 km from legislative capital Amaravati.
- The Amaravati-Kurnool distance is 370 km. The time and costs of travel will be significant.
- The AP Police are headquartered in Mangalagiri, 14 km from Vijayawada, and senior IPS officers who may be required to visit the Secretariat will have to travel 400 km to Visakhapatnam.
- Likewise, government officers who may have to appear in the High Court will have to travel 700 km to Kurnool, which does not have an airport.
- All officers and Ministerial staff who may have to be at hand to brief Ministers when the Assembly is in session, will probably have to stay put in Amaravati, leaving behind their other responsibilities in Visakhapatnam.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Warren Hastings
Mains level: Read the attached story
Donald Trump’s impeachment trial started in the US Senate. A precedent being discussed is that of the Warren Hastings case — the famous failed attempt by the British Parliament to impeach India’s first governor-general.
Warren Hastings
- Warren Hastings, the first governor-general of Bengal (and the first de facto Governor-General of India), is considered among the most significant colonial administrators to have ruled India.
- First as the governor of Bengal (1772-1774) and then as Governor-General (1774-1785), Hastings strengthened British rule in India and made profound changes in administration.
- Hastings’s conduct while in office was called into question after he returned to Britain in 1785, most prominently by Edmund Burke, the noted British parliamentarian and philosopher.
What was his impeachment case?
- In 1786, impeachment proceedings were initiated against Hastings, probing his alleged mismanagement, mistreatment of natives, and personal corruption while in India.
- William Pitt, the then British Prime Minister, first defended Hastings, but then joined the chorus against him.
- Hastings’s argued that ‘Western’ standards of legality could not be applied in the East.
- But Burke insisted that under the Law of Nature, people in India were entitled to the same protection as those in Britain.
- In 1795, however, the House of Lords acquitted Hastings, and the impeachment failed.
- Burke warned that such a verdict would live in “perpetual infamy”, and the trial gave rise to a wider debate on the role of the East India Company in India.
Back2Basics
Warren Hastings and his major works
From 1772, Warren Hastings served as Governor-General of Fort Williams and the regulating act was passed after his arrival.
Important events under his rule :
- Hastings abolished the Dual System that had been established by Robert Clive. In the Dual System, the company had Diwani rights (rights to collect revenue) and the Nizam or Indian chiefs had the administrative authority.
- The judicial powers of the Zamindars were abolished. Civil and criminal courts were established. Two appellate courts were established at Calcutta, one for civil (Sadar Diwani Adalat) and one for criminal (Sadar Nizamat Adalat) cases.
- Hastings abolished the system of dastaks which were misused by company officials and traders earlier.
- He implemented several reforms in all walks of administration. The Regulating Act 1773 and Pitts India Act, 1784 were important acts passed during his tenure.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Coronavirus, Pneumonia
Mains level: Underlying threats and India's preparedness against the virus
Chinese scientists have confirmed can spread between human beings.
Corona Virus
- Corona viruses are large family of viruses, which cause illnesses to people and also circulate in animals including camels, cats and bats.
- They cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
- 2019-nCoV is a new strain that has not been previously identified in humans.
- Much remains to be understood about the new coronavirus, which was first identified in China earlier this month.
- Not enough is known about 2019-nCoV to draw definitive conclusions about how it is transmitted, clinical features of disease, or the extent to which it has spread. The source also remains unknown.
Why is it called the Wuhan Virus?
- The first cases emerged in Wuhan in central China’s Hubei province.
- On December 31 last year, authorities confirmed that a large number of patients with unexplained pneumonia were admitted in hospitals in the city.
Symptoms of infection
- According to the WHO, common signs include fever, cough, and shortness of breath. Serious infections can lead to pneumonia, kidney failure, and death.
- Although human-to-human transmission has now been confirmed, the WHO says animals are the outbreak’s likely primary source. It is not known yet which animals are responsible.
- To prevent the spread of all respiratory infections, the WHO in general asks people to cover their mouths and noses when coughing or sneezing, and to frequently wash their hands.
- Direct contact with farm or wild animals should be avoided — similar outbreaks in the past, like the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) emerged from markets where people were in contact with live animals.
Why is there concern around the world?
- People see a similarity with the SARS outbreak that infected over 8,000 people and killed around 775 in more than 35 countries worldwide in 2002-03.
- SARS too, was caused by a mystery coronavirus, and started in China.
- The source of the virus remained unknown for 15 years, until Chinese scientists in 2017 traced it back to a colony of horseshoe bats living in remote cave in Yunnan province.
- The virus was carried by civet cats which are sold in markets in China.
- Fears that SARS could reappear and memories of China misleading the rest of the world on the extent and seriousness of the outbreak have not gone away.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Startup Advisory Council
Mains level: Mechanisms to promote startup in India
The Union Government has notified the structure of the National Startup Advisory Council to advice on measures needed to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups in the country.
National Startup Advisory Council
- The Council will be chaired by Minster for Commerce & Industry.
- It will consist of the non-official members, to be nominated by Central Government, from various categories like founders of successful startups, veterans and persons capable of representing interests of incubators and accelerators etc.
- The term of the non-official members of the Startup Advisory Council will be for a period of two years.
- The nominees of the concerned Ministries/Departments/Organisations, not below the rank of Joint Secretary to the Government of India, will be ex-officio members of the Council.
- Joint Secretary, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade will be the Convener of the Council.
Various functions
- The Council will suggest measures to foster a culture of innovation amongst citizens and students in particular, promote innovation in all sectors of economy across the country
- It will also suggest measures to facilitate public organizations to assimilate innovation with a view to improving public service delivery, promote creation, protection and commercialization of intellectual property rights.
- It would suggest making it easier to start, operate, grow and exit businesses by reducing regulatory compliances and costs, promote ease of access to capital for startups, and incentivize domestic capital for investments into startups.
- It would also mobilize global capital for investments in Indian startups, keep control of startups with original promoters and provide access to global markets for Indian startups.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




