- In an austerity move, the Union government has decided to reduce wasteful expenditure on items such as travel and food by 20 percent, it is learnt.
- A decision of this effect was taken at a recent meeting of the Cabinet Committee on Investment and Growth (CCIG) chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- All ministries have been directed to reduce wasteful expenditure on travel, food and conferences by 20 percent.
- Note: The CCIG was recently created in June 2019.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3-Potentials of UPI in increasing digital payments.
Context
UPI has brought digital payments to the common man and it has immense scope for growth.
Zero MDR rate
- Recently the finance minister made the announcement of the zero merchant discount rate (MDR) policy for payments through RuPay debit cards and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) instruments.
- What does it mean? This policy dictates that when a consumer pays a merchant using RuPay or UPI, the bank may not charge the merchant a commission on the sale value that it usually charges a merchant.
- Criticism of the move: Critics of this policy lament that it would begin to reverse the progress India has made in recent years to expand the digital payments network.
Some facts and figures
- Setting up of NPCI: In 2008 the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) was set up as an umbrella organization for operating retail payments and settlements in India.
- UPI: In 2016, NPCI introduced UPI.
- UPI has since registered 100 million users.
- UPI now clocks more than 1 billion transactions every month.
- Growth prospects for mobile payments: According to the NITI Aayog, mobile payments in India are expected to grow nearly 20-fold to $190 billion in the next three years.
- Digital payment for the common man: There are 1 billion mobile phone users in India.
- 420 million users have a feature phone, these users can use the *99# USSD service to dial into 13 different languages.
- Which would connect them to UPI and brings digital payments to the common man.
Need for innovation
- We are far behind: India is far behind china, where 55% of spending is done digitally, compared to only 11% in India.
- The outlook for future growth is mind-boggling.
- There is a need for innovation at three levels.
- First level-Adoption
- A better understanding of human behaviour, technology, use cases and dis-use cases will facilitate the 10x growth necessary in adoption rates to cover the entire population.
- Second level-Policy
- The government has the rare opportunity to develop a data-centric understanding of how the economy conducts itself and uses money, and can set taxes accordingly.
- Third level-Technology
- Voice for authentication: At the technology level, there is an opportunity to use voice as a means for authentication and conduct transactions across multiple local languages.
- Data analysis: Copious amounts of data from payment transactions can be analysed to understand user needs and develop personalized loans and financial solutions at scale.
Taking UPI to Global Level
- UPI in Singapore and UAE: The NCPI is gearing up to take UPI to other countries, beginning with Singapore and the United Arab Emirates.
- NCPI is working with its counterpart in Singapore, the Network for Electronic Transfers for Singapore, to bring UPI live in Singapore.
- The low hanging fruit is to provide payment solutions to Indians travelling abroad.
- Competition with global peers: The bigger and tougher game is to increase its usage among local people in countries outside India.
- This would put UPI in competition with the likes of PayPal and Skrill.
Conclusion
We have seen just the tip, albeit a very substantial tip, of the digital payments iceberg. In the coming years, young business leaders of today must learn to uncover the iceberg itself.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Reforms in banking sector and financial stability, Deposit Insurance and its significance.
Context
The amendments to the FRDI Bill, 2017—now renamed the Financial Sector Development and Regulation (Resolution) Bill, 2019—are being worked out.
Three crucial issues
- Specifics are being worked out in the bill on three crucial issues.
- First issue: The first issue is regarding the increase in the deposit insurance cover of customers.
- Second issue: To iron out the contentious issues related to the bail-in clause
- Third issue: To decide whether this resolution framework should apply to the public sector banks.
- Advantages of the move: At a time when the public sector banks have come under the stress of bad loans, increasing the deposit insurance coverage limit would be a welcome approach.
- Increasing the depositor’s confidence: The move will reinforce depositors’ confidence in the banking system in general, and the public sector banks in particular.
The issue of the government “ownership” of the banks and financial stability
- Ownership of government: The role of the “ownership” of banks towards financial stability is a much-debated issue in the country.
- RBI is positive about govt. ownership: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has attributed a positive role to the government ownership of banks in attaining financial stability.
- The issue of competitive neutrality: Committee to Draft Code on the Resolution of Financial Firms has blamed govt. ownership for causing a “lack of competitive neutrality” in the financial sector.
- Need of level playing field: Committee argued for the need of a “level playing field” for both the public and private sector financial firms for the sake of competitive neutrality.
- The concept of an overarching resolution framework for all financial firms gained traction.
Would the all-encompassing Resolution Corporation be efficacious?
- The FRDI Bill, 2017 sought to amend as many as 20 legislations for the diverse financial sector in this country, which is regulated by various institutions, like-
- RBI for the banks and the non-banking financial corporations.
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) for the insurance markets,
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) for securities markets and mutual funds.
- The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority for pension funds.
- The pertinent question
- The pertinent question is whether an all-encompassing resolution corporation can be really efficacious for the much-discussed financial stability of this country.
Fundamental issues
- Neutrality of ownership
- Different motives behind operations: While private financial institutions are predominantly governed by profit motives, for the public sector agencies, various social obligations, such as “financial inclusion,” assume primacy.
- Reason for commoner’s confidence: It is the sense of the government’s involvement (or ownership) that has forged commoners’ confidence to park their financial savings with them.
- The move may end up destabilising the financial sector: If the sovereign guarantee and resolving power are taken away from the government domain to some resolution corporation, it may destabilise the financial system.
- The Bail-in clause
- Deposit over 1 lakh included in bail-in mechanism: The FRDI Bill 2017 suggests that deposit amounts over and above the cover limit (which currently is at one lakh) will be included in the bail-in mechanism.
- Further, despite the RBI’s caution against financial instability, short-term debts and uncategorised client assets are also currently under this mechanism.
- The falling growth rate of deposits: These provisions and the bill per se came against the backdrop of the Financial Stability Report, 2017 that revealed a 3.3% drop in the year-on-year growth rate of deposits for all scheduled banks in the country.
Conclusion
In the context of decelerating financial stability, the government needs to undertake these resolution reforms with caution that the reforms do not end-up eroding depositors’ faith in the domestic financial institutions.
.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much
Mains level: Paper 2- Relations with Pakistan and need to resume the talks to resolve the issues.
Context
India announced that it will invite all heads of government of Shanghai Co-operation Organisation member countries, including Pakistan.
Significance of the invitation
- First since 2014: The summit will assume significance should Pakistan Prime Minister accept the invitation.
- As it will be the first by a head of government or state of that country to India since former Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif attended the swearing-in ceremony of Prime Minister in 2014.
- Hopes belied: Nothing came from that meeting and hopes created by the invitation were belied.
- Failed attempts to engage: Attempts to engage after that failed, including at a previous SCO summit at Ufa in 2015.
Latest events that further reduced the engagement
- Pulwama attack: First, there was the February 2019 Pulwama attack, India’s Balakot response, and Pakistan’s counter-response.
- Article 370: After India did away with Jammu & Kashmir’s special status, India and Pakistan have downgraded even their diplomatic presence in each other’s countries.
- Both the countries withdrew their high commissioners after the Article 370 issue.
- Trade stopped completely: Bilateral trade, which had managed to survive earlier shocks to relations, has stopped completely.
Opportunities presented by SCO summit
- “Inputs of all stakeholders”: In deciding whether to accept the invitation, the Pakistan PM will have to take into consideration “inputs of all stakeholders”.
- A polite way of saying that the final yes or no will rest with the Pakistan Army.
- A chance for a high-level meeting: Even if Imran Khan stays away and sends a minister instead, it would still be a chance for a high-level bilateral meeting.
- The world wants India and Pakistan to engage: The world wants India and Pakistan to engage, and this was evident in the way the UNSC refused to take up the Kashmir issue, saying it was not the forum for it.
- Opportunity for India to make a start: India has declared several times recently that it wants to peel away from historical foreign policy baggage.
- India should make a start with Pakistan by making it possible for such a meeting to take place.
- Making acceptance of invitation easier: India can make it easier for the Pakistan Prime Minister to accept the invitation.
- Resuming trade: A start could be made by resuming trade, which has ground to a dead halt
- Sending High Commissioner back: India can start by sending India’s High Commissioner back to his office in Islamabad.
Conclusion
The SCO summit presents an opportunity for both the countries to end the long hiatus in the relations which is essential for both the countries to resolve the long-standing issues and progress of both the countries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Monsoon: Its onset and retreat
Mains level: Various factors causing uncertainty in monsoon predictions
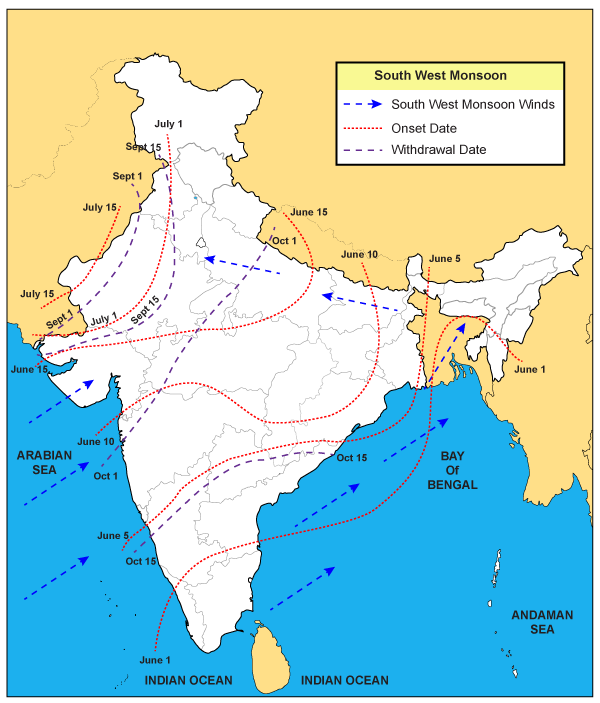
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) had decided to revise the normal onset and withdrawal dates for the monsoon in some parts of the country from this year.
Onset of Monsoon
- The four-month southwest monsoon season, which brings as much as 70 per cent of the country’s annual rainfall, officially begins on June 1, with the onset over Kerala, and ends on September 30.
- It takes about a month and half after onset on the Kerala coast to cover the entire country; and about a month, beginning from the northwestern parts of the country on Sept. 1 to withdraw completely.
- Although the June 1 date for the onset of the monsoon on the Kerala coast is unlikely to be changed, the dates for onset in many other parts of the country are expected to be revised.
- Mumbai, for example, expects to start getting rain from June 10 the revision is likely to push this date back by a few days.
- Effectively, the monsoon is now expected to have later arrival and withdrawal dates in most parts of the country.
Why was this revision needed?
- The main reason for the revision in the normal dates is the changes in precipitation patterns that have been taking place over the last many years.
- In the last 13 years, for example, only once has the onset over the Kerala coast happened on June 1.
- While two or three days of earlier or later onset falls within the yearly variability in several years the onset happened five to seven days late.
- Similarly, the commencement of withdrawal has happened in the first week of September only twice during this period, and last year, the withdrawal started as late as October 9 — and was completed in around just a week.
Recent peculiarity with the exam
- One of the significant changes being noticed is that rainfall is getting increasingly concentrated within a narrow band of days within the monsoon season.
- So, there are extremely wet days followed by prolonged periods of dry days.
- IMD data show that over several previous years, nearly 95 per cent of monsoon precipitation in 22 major cities of the country had happened over a period of just three to 27 days.
- Delhi, for example, had received almost 95 per cent of its monsoon rainfall over just 99 hours. And half of Mumbai’s monsoon rain had fallen over just 134 hours, or five and a half days, on average.
Regional variations
- Patterns of regional variations in rainfall are also changing
- Areas that have traditionally received plenty of rainfall are often remaining dry, while places that are not expected to get a lot of monsoon rain have sometimes been getting flooded.
- Climate change could be one of the factors driving these changes, but there could be other reasons as well.
What will be the impact of IMD’s move?
For Farmers
- The revisions are meant to reflect the changes in precipitation patterns in recent years.
- New dates will likely nudge farmers in some parts of the country to make slight adjustments in the time of sowing their crops.
- It would definitely have an impact on our agriculture practices — when to start sowing, when to harvest.
- So, even if there is a delay in the arrival of monsoon by three to four days over a region, it would not matter much if there is a fairly good rainfall distribution thereafter.
- The change in dates would affect water management practices as well.
For Industries
- The planning that goes to beat the heat — several cities execute heat action plans — just ahead of the monsoon would have to factor in the need to be prepared for longer periods of heat.
- Rajeevan said many other activities including industrial operations, the power sector, or those using cooling systems, would also need to change their behaviour.
- The power grid can, for example, have more realistic planning for peak periods of electricity consumption in certain months.
Way Forward
- The changed dates are expected to be announced in April, when the IMD makes its first forecast for the monsoon.
- Agro-meteorologists, however, agree that more than the onset, it is the information about the spatio-temporal distribution of rainfall that will be more helpful for farmers.
- Ultimately, the change in normal dates of the onset and withdrawal of the monsoon would help people understand when to expect rains, and to plan their activities accordingly.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Project 39A
Mains level: Capital Punishment and its justification
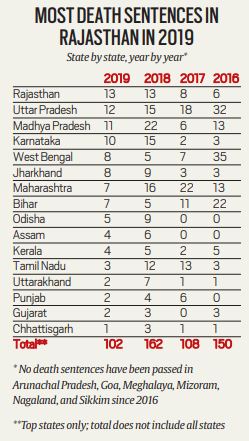
Trial courts in India delivered 102 death sentences in 2019, over 60% fewer than the 162 death sentences passed in 2018.
Highlights of the Report
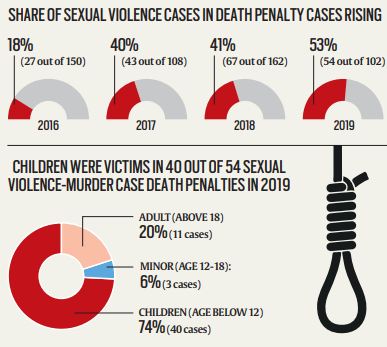
- In 2019, fewer death sentences overall were delivered.
- 1 out of 2 sentences for sexual violence-murder; in 3 out of 4 sexual violence-murder death sentences, children were the killer’s victims.
- The courts were, however, especially unforgiving of murders that involved sexual violence — the proportion of death sentences imposed for murders involving sexual offences was at a four-year high in 2019 at 52.94%.
- 2019 also saw the highest number of confirmations by High Courts in four years; 17 out of the 26 confirmations (65.38%) were in offences of murder involving sexual violence.
- The Supreme Court, primarily during the tenure of the previous CJI Gogoi, listed and heard 27 capital cases, the most in a year since 2001.
Project 39A
- These are the headline findings in the fourth edition of The Death Penalty in India: Annual Statistics, published by Project 39A at the National Law University (NLU), Delhi.
- Project 39A is a research and litigation initiative focussed on the criminal justice system, and especially issues of legal aid, torture, death penalty, and mental health in prisons.
- The report tracked news of death sentences awarded by trial courts published online by news organisations in English and Hindi.
- It checked these numbers against judgments uploaded to websites of High Court and district courts.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National E-Mobility Mission Plan, 2020
Mains level: FAME Scheme and its progress

The Supreme Court has sought the response of the government on a petition that alleges the non-implementation of the National E-Mobility Mission Plan, 2020 (NEMMP), which came out in 2012.
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020
- The plan was launched by the Government of India in 2013 with the objective of achieving national fuel security by promoting electric and hybrid vehicles.
- It had set a target of achieving a sale of seven million EVs by 2020 and thereby aimed to cut total carbon dioxide emissions by three per cent from the ‘do nothing’ scenario.
- The government would provide fiscal and monetary incentives for this industry.
- The plan had made several recommendations for the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), including electric-powered government fleets and public transportation and subsidies for those who opt for EVs.
What was the petition about?
- The petition contended that the governmental apathy has violated the fundamental rights of citizens to health and clean environment guaranteed under Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution.
- The government had failed in its obligation to mitigate the impact of climate change and air pollution partly attributable to emissions from vehicles that burn fossil fuels.
- Government’s failure to suitably implement these recommendations is the direct cause of air pollution levels that have turned our cities into virtual ‘gas chambers’.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: nCoV
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has been closely monitoring the situation after the reports of 41 confirmed cases of novel Corona virus (nCoV) including one death from Wuhan, China, 2020.
About Novel Corona Virus
- Corona viruses are large family of viruses, which cause illnesses to people and also circulate in animals including camels, cats and bats.
- They cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome.
- 2019-nCoV is a new strain that has not been previously identified in humans.
- Much remains to be understood about the new coronavirus, which was first identified in China earlier this month.
- Not enough is known about 2019-nCoV to draw definitive conclusions about how it is transmitted, clinical features of disease, or the extent to which it has spread. The source also remains unknown.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: APNA UREA - SonaUgle
Mains level: Not Much

APNA UREA – SonaUgle
- The Union Minister for Chemicals and Fertilizers launched the “APNA UREA – SonaUgle” brand of Hindustan Urvarak & Rasayan Limited (HURL).
- HURL is Joint Venture Company promoted by the three Maharatna Companies i.e. Coal India Limited (CIL), NTPC Limited (NTPC) and Indian Oil Corporation Limited (IOCL) as the lead promoters with FCIL and HFCL as other two partners.
- The commissioning of the HURL’s three Units in the states of UP, Bihar and Jharkhand will open forward and backward linkages for business activity in the Eastern part of India.
- It will be instrumental in opening new avenues for the generation of income and employment in the Eastern part of our country.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TrueNat
Mains level: Menace of TB and its elimination measures

The WHO has endorsed TrueNat, an Indian indigenous molecular diagnostic tool for tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis.
TrueNat
- The TrueNat TB test is a new molecular test that can diagnosis TB in one hour as well as testing for resistance to the drug rifampicin.
- The TrueNat MTB and MTB Plus assays also show comparable accuracy to the TB-LAMP assay as replacement tests for sputum smear microscopy.
- The data for TrueNat MTB-Rif shows similar accuracy to WHO-approved commercial line probe assays.
- It is developed by the Goa-based Molbio Diagnostics.
- The company was provided with technical assistance and resources by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) to help commercialise Truenat.
- ICMR had assessed and validated the diagnostic tool. It has high diagnostic accuracy as initial test to diagnose TB.
- It will be used as an initial test thus replacing sputum smear microscopy.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: TCEPF, TRAI
Mains level: Telecom regulation in India
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has informed that telecom service providers will need to deposit all unclaimed money of consumers, including excess charges and security deposit, in the Telecommunication Consumers Education and Protection Fund (TCEPF).
Telecommunication Consumers Education and Protection Fund (TCEPF)
- The TCEPF Regulations, 2007 have been amended to provide the basic framework for depositing unclaimed money of consumers by service providers, maintenance of the TCEPF and other related aspects.
- Any unclaimed / unrefundable amount belonging to consumers in the TCEP fund will be utilized for the welfare measures of the consumers.
- With this amendment, service providers will deposit any unclaimed consumer money of any form such as excess charges, security deposit, plan charges of failed activations, or any amount belonging to a consumer, which service providers are unable to refund to consumers.
Why such move?
- The TRAI observed that there is a need to bring clarity among service providers in depositing money which they are unable to refund to the consumers.
- While some service providers were depositing money only on account of excess billing revealed in the audit, others were depositing unclaimed money such as security deposits and plan charges of failed activations.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yada Yada
Mains level: NA
A new virus detected in Australian mosquitoes has been provisionally named the Yada Yada virus (YYV).
Yada Yada
- It is an alphavirus, a group of viruses that the researchers described as small, single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses.
- It includes species important to human and animal health, such as Chikungunya virus and Eastern equine encephalitis virus.
- They are transmitted primarily by mosquitoes and (are) pathogenic in their vertebrate hosts.
- Unlike some other alphaviruses, Yada Yada does not pose a threat to human beings.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now






