Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 2- India-US relations.
Context
President Trump’s visit had the right optics. Attention must now turn to India-US priority areas.
What were the mutual gains and highlights of the visit?
- Security: Homeland Security is an American expression. For us to own it shows our concerns on cross-border sponsored terrorism.
- Nuclear technology: Our nuclear VVER power plant technologies are state of the art and of Russian and French design.
- Fast breeder: Good, but one more is better. We are well on the way to the fast breeder on the thorium route and these nuclear turbines are an essential step.
- Unlimited thorium: We don’t have much uranium but unlimited thorium, so in the long run, apart from solar, this is the energy future.
- Insurance obstacle resolved: Obviously, the insurance obstacle, as to who will bear the cost of insurance against disaster damage, which the Americans were raising earlier, has been resolved.
- We have to build nuclear power to provide the initial feedstock for the thorium-based reactors.
- No progress on trade pact: There are obviously differences between the two nations on the trade pact.
- There is “progress”, but otherwise, we don’t know the way forward. Since the event was Ahmedabad-based, Amul is invading America and dairying is real politics.
- US concerns over Kashmir issue: The US concern on Kashmir and minority rights is real.
- If the largest foreign office establishment in the world is raising issues through their chief, let’s not bury our head in the sand.
- Our defence minister expressing sadness at former chief ministers of Jammu and Kashmir being in detention was a gesture to the US President’s stand on pursuing solutions.
- The bipartisan foreign policy of India shifting: The Americans generally rally behind the President on foreign policy.
- We are more advanced now and have kicked a bipartisan approach to foreign affairs.
- Seven decades of a bipartisan policy are thrown away without a word in explanation.
Challenges to the rights in India
- Every right is tampered with. Your religion, your identity in a country that never questioned it, you name it, it’s in question.
- Multiple identity cards not accepted: The Aadhaar card, passport, ration card, election card are not enough. One office doesn’t accept another’s card, even if they carry the same information.
- A study on a ration card and election cards: A study funded by the Canadian IDRC showed the poor only keep under lock and key the ration and election cards. One saves them from starvation, the other gives them dignity. At least once every five years, the mightiest knock at their door. We must not destroy, we must build.
Conclusion
There are obviously differences between the two nations on the trade pact. But apart from trade, there are many areas the cooperation on which can benefit both the countries.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3- Dealing with the trinity of social disharmony, economic slowdown and and global health epidemic.
Context
India faces imminent danger from the trinity of social disharmony, economic slowdown and a global health epidemic.
Social disharmony
- Violence in Capital: Delhi has been subjected to extreme violence over the past few weeks. We have lost nearly 50 of our fellow Indians for no reason. Several hundred people have suffered injuries.
- Communal tensions have been stoked and flames of religious intolerance fanned by unruly sections of our society, including the political class.
- University campuses, public places and private homes are bearing the brunt of communal outbursts of violence.
- Institutions of law and order have abandoned their dharma to protect citizens. Institutions of justice and the fourth pillar of democracy, the media, have also failed us.
Impact of social disharmony on the economy
- Exacerbating the economy: At a time when our economy is floundering, the impact of such social unrest will only exacerbate the economic slowdown.
- Lack of investment by the private sector: It is now well accepted that the scourge of India’s economy currently is the lack of new investment by the private sector.
- Investors, industrialists and entrepreneurs are unwilling to undertake new projects and have lost their risk appetite.
- Increase in fears and risk aversion: Social disruptions and communal tensions only compound investors’ fears and risk aversion.
- Social harmony, the bedrock of economic development, is now under peril.
- When policy tweaks stop to matter: No amount of tweaking of tax rates, showering of corporate incentives or goading will propel Indian or foreign businesses to invest, when the risk of eruption of sudden violence in one’s neighbourhood looms large.
- How the vicious cycle works: Lack of investment means a lack of jobs and incomes, which, in turn, means a lack of consumption and demand in the economy.
- A lack of demand will only further suppress private investments. This is the vicious cycle that our economy is stuck in.
Impact of COVID-19 on the economy
- Global reactions: Nations across the world have sprung into action to contain the impact of this epidemic. China is walling off major cities and public places. Italy is shutting down schools. America has embarked aggressively both to quarantine people as well as hasten research efforts to find a cure.
- Many other nations have announced various measures to address this issue.
- What India can learn? India too must act swiftly and announce a mission-critical team that will be tasked with addressing the issue. There could be some best practices we can adopt from other nations.
Bringing in reforms to address the problems
- The government must quickly embark on a three-point plan.
- First, it should focus all energies and efforts on containing the COVID-19 threat and prepare adequately.
- Two, it should withdraw or amend the Citizenship Act, end the toxic social climate and foster national unity.
- Three, it should put together a detailed and meticulous fiscal stimulus plan to boost consumption demand and revive the economy.
Turning a moment of deep crisis into a moment of great opportunity
- The past instance of turning crisis into an opportunity: In 1991, India and the world faced a similar grave economic crisis, with a balance of payments crisis in India and a global recession caused by rising oil prices due to the Gulf War.
- But India was able to successfully turn this into an opportunity to reinvigorate the economy through drastic reforms.
- Turning the present crisis into an opportunity: Similarly, the virus contagion and the slowing down of China can potentially open up an opportunity for India to unleash second-generation reforms to become a larger player in the global economy and vastly improve prosperity levels for hundreds of millions of Indians.
- To achieve that, we must first rise above divisive ideology, petty politics and respect institutional salience.
Conclusion
The India that we know and cherish is slipping away fast. Wilfully stoked communal tensions, gross economic mismanagement and an external health shock are threatening to derail India’s progress and standing. It is time to confront the harsh reality of the grave risks we face as a nation and address them squarely and sufficiently.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not much.
Mains level: Paper 3-Ensuring fair competition and dealing with the problem of predatory pricing.
Context
Any intervention to “correct” pricing essentially involves placing a higher weightage on the assumed losses of competitors/producers than on the consumer’s apparent gains. This is not a straightforward exercise.
Duopolies and scrutiny by the CCI
- Duopolies in the most segment: The online marketplace or the platform/intermediation service market is now largely characterised by duopolies in most segments:
- Amazon and Flipkart in e-commerce, Uber and Ola in transport, Zomato and Swiggy in food service, MakeMyTrip and Yatra in travel bookings.
- Some niche players do exist in these segments, but by and large, the market has been carved up by large players.
- Why CCI is scrutinising these companies? Several of these companies have come under the scrutiny of the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
- What are the issues involved? The issues involved here have far-reaching ramifications for both online and offline market places. Some of the more contentious issues are:
- Do such market structures restrict online competition?
- Are the players engaging in predatory pricing?
- If so, is it driving out both online and offline competition and does this adversely impact consumer welfare?
- Is there a need for policy intervention, and, if so, what should be the underlying framework?
Lower barrier to entry not translating into greater competition
- Market not working as per theory: In theory, the online market structure should facilitate greater competition given the lower barriers to entry. But this may not be the case.
- Take-over: Most other firms in the segments mentioned above have either been taken over or have folded up.
- What is the reason for the emergence of such marker structures
- Positive feedback loop: One explanation for the emergence of these market structures is that as companies grow, with more users coming on board these platforms, they benefit from what CCI calls positive feedback loop.
- This leads to market concentration.
- Difficulties for new players: Given the network effects, which are common in digital spaces, it becomes difficult for new players to enter these spaces, and gain market share as there isn’t much space for many such networks.
- Capital intensive market: Another possible explanation is that, contrary to perception, the online space is highly capital intensive.
- Deep pockets are required to fund the discounts to get customers on board initially.
- Such market structures are more likely in capital deficit countries like India.
- Incumbents restricting new entrant: Incumbents, as in other sectors, may also engage in various strategies to restrict entry and thus competition.
- Even small actions by these platforms coupled with the network effects can adversely impact competition.
Predatory pricing-issues involved in it
- Allegations of predatory pricing driving out the competition: Many allege that these two-sided online platforms engage in predatory pricing or below-cost pricing either by funding it themselves (deep pockets) or by squeezing producers.
- This drives out the competition — both online as well as offline.
- Predatory pricing is anti-competition, to begin with.
- How it is harmful to the customers? While consumers do benefit in the short run, once the competition is driven out, the platform starts raising prices to recoup previous losses.
- But is it that straightforward?
- What are the issues involved in predatory pricing?
- First- Assessing whether a platform is engaged in predatory pricing.
- In India, it is defined as price falling below average variable cost — may not be a straightforward exercise.
- Why it is not a straight forward exercise? The dynamics of online pricing (prices change over time), their unique cost structures — in such two-sided platforms, prices/costs on both sides should be seen in conjunction — as well as the impact of economies of scale and organisational efficiency in lowering costs, all need to be factored in.
- Discount for clearing inventories: Besides, one would also have to take into account that even offline firms engage in deep discounting to clear inventories.
- As do both online and offline firms to acquire customers in the early stages of their business.
- Second-The impact of such pricing strategies on competition and on consumer welfare must be carefully assessed.
- Driving out competitors is not equal to driving out the competition: It is quite likely that once the competition is eliminated and the platform starts to raise prices, new players will enter the market, attracted by higher prices.
- Driving out competitors may not be the same as driving out the competition — though the extent to which new firms are able to enter the market will depend on the degree to which barriers to entry exist.
- Concerns of recovering the losses: Platforms will be mindful that losses will be hard to recover, and may not engage in below-cost pricing to drive out competitors for extended periods.
- Consumers are unlikely to lose out as prices are likely to remain low.
- Third- Possibility of collusion
- There is also an argument for closer examination of such market structures because of the possibility of collusion.
- Customers moving towards cheaper options: In most such markets, as the consumer has little to differentiate between the two platforms, it is the price that sets them apart.
- Consumers tend to gravitate towards the cheaper option. This ensures continuous competition between the major players to offer low prices.
- Possibility of customer left with no option: It is possible that at some point, the players will find it in their interest to venture into some sort of agreement that allows both of them to survive, rather than be engaged in a race to the bottom — as has seemingly happened in the telecom sector.
- Fourth- Linking predatory pricing with abuse of dominant market position must be reexamined.
- The dominant position is not always linked with predatory pricing: As the experience of the telecom sector shows, a dominant position may not be a prerequisite for predatory pricing.
- Accepting this argument would imply that if regulatory intervention is required to check predatory pricing, it could kick in before market power or dominance is established.
- Taking into account deep pockets: Alternatively, the definition of market dominance could be expanded to take into account deep pockets.
Conclusion
- Set of guidelines instead of the fixed framework: Any intervention to “correct” pricing essentially involves placing a higher weightage on the assumed losses of competitors/producers than on the consumer’s apparent gains. This is not a straightforward exercise. Having a fixed predetermined framework is unlikely to be helpful. Instead, it would be more useful to have a set of guiding principles based on which regulatory intervention, if required, can be undertaken.
- Safeguarding competition not competitors: Competition policy should be driven by safeguarding competition, not competitors. It should seek to bring about greater transparency in pricing and reduce information asymmetry.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Not Much
Mains level: Ethnic turmoil in North East
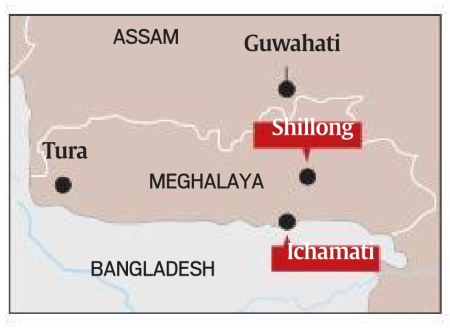
Last week, ethnic violence left three dead in Meghalaya. The violence underlined the ethnic complexities of Meghalaya, with tensions coming back to the fore following the passage of the Citizenship (Amendment) Act.
Multi-ethnic Meghalaya
- Meghalaya became a state in 1972 when it was carved out of Assam. Before that, Shillong, now Meghalaya’s capital, used to be the capital of Assam.
- Sharing a 443-km border with Bangladesh, Meghalaya has seen decades of migration from areas that are now in Bangladesh, as well as from various Indian states via Assam.
- Besides the indigenous groups, Meghalaya’s residents include Bengalis, Nepalis, Marwaris, Biharis and members of various other communities.
- Meghalaya is a tribal majority state, and the indigenous Khasis, Jaintias and Garos are entitled to 80% reservation in government jobs.
- Various groups have continuously expressed concerns that illegal migration from Bangladesh and the growth of “outsiders” from other states would overwhelm the indigenous communities.
Meghalaya violence: The CAA context
- The CAA relaxes the norms for Hindus from Bangladesh (among six religious groups from three countries) for eligibility to apply for Indian citizenship.
- Long before that, the legislation was already facing protests in the Northeast, including Meghalaya. Eventually, the Centre decided the CAA will not apply in Sixth Schedule areas.
- The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution has special provisions for administration of certain areas in the Northeast, including almost the whole of Meghalaya.
- Despite the large exemption, the concerns have persisted in Meghalaya, and demands for an Inner Line Permit (ILP) regime have gathered fresh momentum.
- If the ILP system is introduced, every Indian citizen from any other state would require a time-bound permit to visit Meghalaya.
Signals simmering tensions
- The last four decades have seen numerous incidents of violence in Meghalaya targeted at non-tribals, including from Bengal and Nepal.
- The latest bout follows a sustained campaign over the implementation of the Inner Line Permit and unrest in the Northeast over the CAA that led to six deaths in Assam two months ago.
- The violence last week has an immediate context in the anti-CAA campaign and ILP demand.
Shillong, then and now
- Shillong has seen violence against “outsiders” several times in the last four decades.
- The targets were Bengalis in 1979, Nepalis in 1987, and Biharis in 1992.
- In 2018, Shillong saw clashes between Khasis and Punjab-origin Dalit Sikhs whose ancestors had settled there over 100 years ago.
- All that began collapsing after Independence, Constitutional institutions set up to safeguard the interest of the tribes came to be popularly perceived as opportunities to convert these tribal areas into exclusive zones of tribal hegemony.
- The issue of ‘foreigners’ illegally residing in the state of Meghalaya was one of the most important issues which dominated state politics in the 1970s and 1980s.
- In 1979, the state was plunged into a crisis for the first time since it was created.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Read the attached story
Mains level: Dignity of the Parliament
Seven MPs of a political party were suspended for unruly behaviour in the Lok Sabha. The motion was passed by a voice vote.
What is the reason for suspending an MP?
- The general principle is that it is the role and duty of the Speaker of Lok Sabha to maintain order so that the House can function smoothly.
- This is a daunting task even at the best of times.
- In order to ensure that proceedings are conducted in the proper manner, the Speaker is empowered to force a Member to withdraw from the House (for the remaining part of the day), or to place him/her under suspension.
What are the rules under which the Speaker acts?
Rule Number 373 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business says:
- The Speaker, if is of the opinion that the conduct of any Member is grossly disorderly, may direct such Member to withdraw immediately from the House, and any Member so ordered to withdraw shall do so forthwith and shall remain absent during the remainder of the day’s sitting.
To deal with more recalcitrant Members, the Speaker may take recourse to Rules 374 and 374A. Rule 374 says:
- The Speaker may, it deems it necessary, name a Member who disregards the authority of the Chair or abuses the rules of the House by persistently and wilfully obstructing the business thereof.
- If a Member is so named by the Speaker, the Speaker shall, on a motion being made forthwith put the question that the Member (naming such Member) be suspended from the service of the House for a period not exceeding the remainder of the session: Provided that the House may, at any time, on a motion being made, resolve that such suspension be terminated.
- A member suspended under this rule shall forthwith withdraw from the precincts of the House.
What is the procedure for revocation of a Member’s suspension?
- While the Speaker is empowered to place a Member under suspension, the authority for revocation of this order is not vested in her.
- It is for the House, if it so desires, to resolve on a motion to revoke the suspension.
What happens in Rajya Sabha?
- Like the Speaker in Lok Sabha, the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha is empowered under Rule Number 255 of its Rule Book to “direct any Member whose conduct is in his opinion grossly disorderly to withdraw immediately” from the House.
- Any Member so ordered to withdraw shall do so forthwith and shall absent himself during the remainder of the day’s meeting.
- The Chairman may name a Member who disregards the authority of the Chair or abuses the rules of the Council by persistently and wilfully obstructing business.
- In such a situation, the House may adopt a motion suspending the Member from the service of the House for a period not exceeding the remainder of the session.
- The House may, however, by another motion, terminate the suspension.
- Unlike the Speaker, however, the Rajya Sabha Chairman does not have the power to suspend a Member.
Way Forward: Striking a balance
- There can be no question that the enforcement of the supreme authority of the Speaker is essential for smooth conduct of proceedings. A balance has to be struck.
- However, it must be remembered that her job is to run the House, not to lord over it.
- The solution to unruly behaviour has to be long-term and consistent with democratic values.
- A step in that same direction could be to discontinue the practice of herding people out of the visitors’ gallery when the House witnesses chaos.
- So, the ruling party of the day invariably insists on the maintenance of discipline, just as the Opposition insists on its right to protest. And their positions change when their roles flip.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Freedom in the World Report
Mains level: Read the attached story
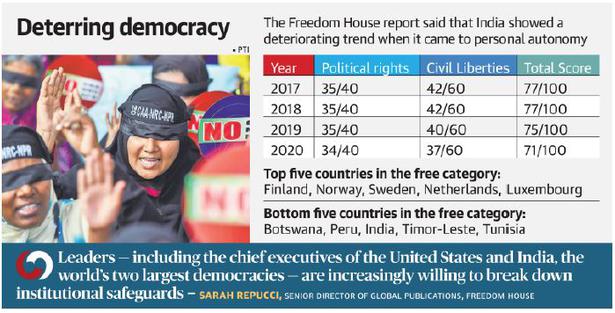
India has become one of the world’s least free democracies, according to a global survey.
Freedom in the World Report
- It is a yearly survey and report by the U.S. based non-governmental organization Freedom House.
- It measures the degree of civil liberties and political rights in every nation and significant related and disputed territories around the world.
- The report derives its methodology from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1948.
- It covers 195 countries, awarding scores based on political rights indicators such as the electoral process, political pluralism and participation and government functioning, as well as civil liberties indicators related to freedom of expression and belief associational and organisational rights, the rule of law and personal autonomy and individual rights.
Highlights of the report

Deteriorating freedom in India
- The report ranks India at the 83rd position, along with Timor-Leste and Senegal.
- This is near the bottom of the pile among the countries categorised as “Free”.
- India’s score fell by four points to 71, the worst decline among the world’s 25 largest democracies this year.
- India scored 34 out of 40 points in the political rights category, but only 37 out of 60 in the civil liberties category, for a total score of 71, a drop from last year’s score of 75.
- The report treats “Indian Kashmir” as a separate territory, which saw its total score drop precipitously from 49 to 28 this year, moving it from a status of “Partly Free” to “Not Free”.
Reason for the downfall
- The annulment of autonomy and the subsequent shutdown of Kashmir, the NRC and the CAA, as well as the crackdown on mass protests, have been listed as the main signs of declining freedom in the report.
- These three actions have shaken the rule of law in India and threatened the secular and inclusive nature of its political system said the report.
- The report slammed the internet blackout in Kashmir terming it the longest shutdown ever imposed by democracy.
- It said freedom of expression was under threat in India, with journalists, academics and others facing harassment and intimidation when addressing politically sensitive topics.
- It warned that the Indian government’s alarming departures from democratic norms under present govt. could blur the values-based distinction between Beijing and New Delhi.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gairsain
Mains level: Two/Three capitals concept

Uttarakhand govt names Gairsain as the new summer capital of the state.
Gairsain
- Gairsain is situated at the eastern edge of the vast Dudhatoli mountain range, located almost at the centre of the state, at a distance of approximately 250 kilometres from Dehradun.
- It is easily accessible from both the Garhwal and the Kumaon divisions, and in a way, acts as the bridge between the two regions.
- Uttarakhand was carved out as a separate state from Uttar Pradesh in 1998.
- Gairsain was best suited to be the capital of the mountainous state as it was a hilly region falling on the border of Kumaon and Garhwal regions.
- But it was Dehradun, located in the plains that served as the temporary capital.
- With the fresh announcement, there is no clarity on either the city’s current status or a new winter capital.
- The state Assembly is located in Dehradun, but sessions are held in Gairsain as well.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Highlights of the report
Mains level: State of higher education in India
.png)
Indian higher-education institutes have improved their performance on the global stage, with a greater number getting ranked in the top-100 programs, according to the latest edition of the Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings by Subject 2020.
Major findings of the report
- IIT Bombay (44), IIT Delhi (47), IIT Kharagpur (86), IIT Madras (88) and IIT Kanpur (96) found place in top 100 of this category.
- In the Natural Sciences category, three Indian institutions made it to the top 200: IIT-Bombay at 108th rank closely followed by the IISc, Bangalore at the 111th position, while IIT-Madras scraped in at the 195th rank.
- Jawaharlal Nehru University remained the country’s top institution in the Arts and Humanities category, with a global ranking of 162, followed at a distance by Delhi University at 231.
- Delhi University topped the Social Sciences and Management category, with a global ranking of 160, followed by IIT-Delhi at 183.
- There are no Indian institutions in the world’s top 200 when it comes to Life Sciences and Medicine.
- The top institution in the country is the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, which had a global ranking of 231.
- Other top subjects included physics & astronomy with 18 Indian institutes, biological sciences (16), electrical engineering (15), chemical engineering (14) and mechanical engineering (14).
- MIT, Stanford University and the University of Cambridge has secured top three positions in the Engineering and Technology category.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC)
Mains level: Read the attached story
Scientists at International Advanced Research for Powder Metallurgy & New Materials (ARCI), Hyderabad have developed Polymer Electrolyte Membrane fuel cells (PEMFC).
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells

- Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells (PEMFC) are a type of fuel cell being developed mainly for transport applications, as well as for stationary fuel-cell applications and portable fuel-cell applications.
- Their distinguishing features include lower temperature/pressure ranges (50 to 100 °C) and a special proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membrane.
- PEMFCs generate electricity and operate on the opposite principle to PEM electrolysis, which consumes electricity.
- They are a leading candidate to replace the aging alkaline fuel-cell technology, which was used in the Space Shuttle.
Working

- The PEMFC uses a water-based, acidic polymer membrane as its electrolyte, with platinum-based electrodes.
- The protons pass through the membrane to the cathode side of the cell while the electrons travel in an external circuit, generating the electrical output of the cell.
Applications in disaster management
- Emergency Operation Centres (EOC) backed with 10 kW systems is being planned as a natural disaster management measure.
- Tamil Nadu is generally affected by five to six cyclones every year, of which two to three are severe and is followed by frequent power cuts.
- ARCI is now planning to set up a PEMFC system for Tamil Nadu to operate the systems like early warning systems, VHF set, IP phone, BSNL Ethernet and office equipment like scanner, computers, printers, phone, FAX and normal requirements like lighting and fan.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Law for Rain Water Harvesting
Mains level: Rooftop water conservation strategy

The Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs has issued the Model Building Bye Laws, 2016 for guidance of the States/UTs and has a chapter on ‘Rainwater Harvesting’.
Why such move?
- These laws aim to regulate the over-exploitation and consequent depletion of ground water.
- It would enable States/UTs to enact suitable ground water legislation for regulation of its development, which includes provision of rain water harvesting.
About the Bye Laws
- 33 States/UTs have adopted the rainwater harvesting provisions.
- The provisions of this chapter are applicable to all the buildings.
Various provisions
- As per Model Building Bye Laws- 2016, provision of rainwater harvesting is applicable to all residential plots above 100 sq.m.
- Water being a State subject, initiatives on water management including conservation and water harvesting in the Country is primarily States’ responsibility.
- So the implementation of the rainwater harvesting policy comes within the purview of the State Government/Urban Local Body / Urban Development Authority.
Back2Basics
Groundwater governance in India
- Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) has been constituted under Section 3(3) of the ‘Environment (Protection) Act, 1986’ for the purpose of regulation and control of groundwater development and management in the Country.
- CGWA is regulating ground water withdrawal by industries/infrastructure/ mining projects in the country for which guidelines/ criteria have been framed which includes rainwater harvesting as one of the provisions while issuing No Objection Certificate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Perseverance rover
Mains level: Not Much

NASA has named its next Mars rover ‘Perseverence’.
About Perseverance
- The Perseverance rover weighs less than 2,300 pounds and is managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab.
- The rover’s mission will be to search for signs of past microbial life. It will also collect samples of Martian rocks and dust, according to the release.
- The rover will also be tasked with studying the red planet’s geology and climate.
- All of NASA’s previous Mars rovers — including the Sojourner (1997), Spirit and Opportunity (2004) and Curiosity (exploring Mars since 2012) — were named in this way.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Bank Mergers
Mains level: Read the attached story
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister has approved the mega consolidation of ten PSBs into four which include the –
- Amalgamation of Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank of India into Punjab National Bank
- Amalgamation of Syndicate Bank into Canara Bank
- Amalgamation of Andhra Bank and Corporation Bank into Union Bank of India
- Amalgamation of Allahabad Bank into Indian Bank
About the merger
- The amalgamation would be effective from 1.4.2020 and would result in creation of seven large PSBs with scale and national reach with each amalgamated entity having a business of over Rupees Eight lakh crore.
- The Mega consolidation would help create banks with scale comparable to global banks and capable of competing effectively in India and globally.
- Greater scale and synergy through consolidation would lead to cost benefits which should enable the PSBs enhance their competitiveness and positively impact the Indian banking system.
Must read
Bank Mergers
[Burning Issue] Merger of Public Sector Bank
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now




.png)



