Why in the News?
This newscard is an excerpt from a photo published in ‘The Hindu’.
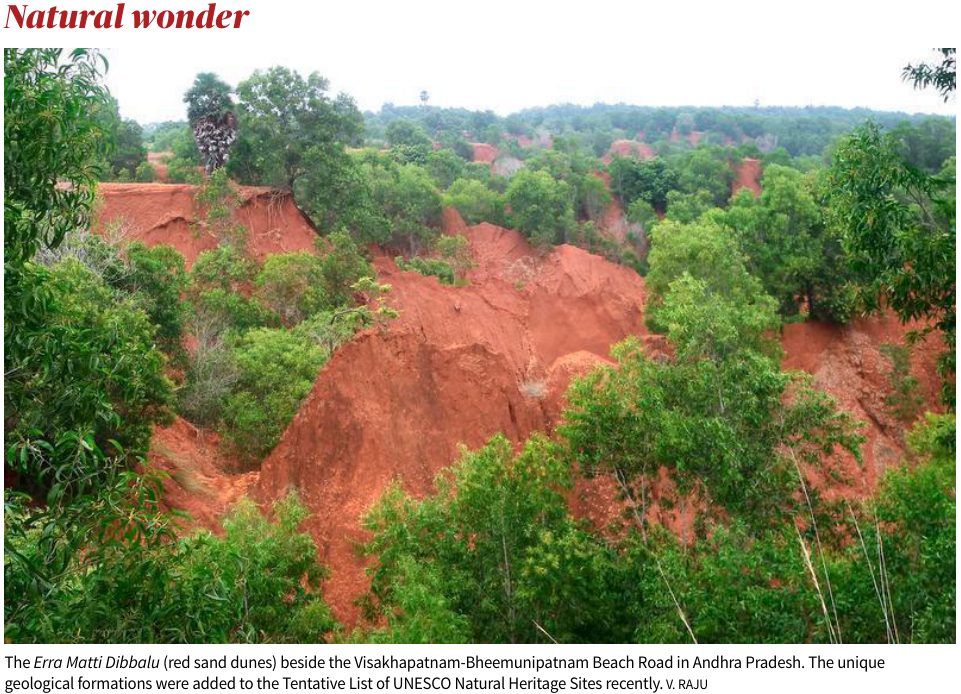

About Erra Matti Dibbalu:
- Location: Found between Visakhapatnam and Bheemunipatnam in Andhra Pradesh, stretching 5 km along the coast, with widths ranging from 200 m to 2 km.
- Meaning: In Telugu, “Erra Matti” means red soil and “Dibbalu” means mounds, describing the reddish sand dunes.
- Geological Heritage: Listed among the 34 National Geological Heritage Monument Sites of India by the Geological Survey of India (GSI).
- Formation: Created around 12,000–18,500 years ago through the combined effect of tectonic activity (2.5 million–11,000 years ago), sea-level changes, monsoonal variability, and global climatic shifts.
- Composition: Derived mainly from Khondalite rocks of the Eastern Ghats hinterland, with the red colour due to oxidation of iron-rich sediments.
Significance:
- Geological Value: Acts as a paleo-environment indicator, providing evidence of climate change, sea-level fluctuations, and coastal evolution during the late Quaternary period.
- Archaeological Importance: Artefacts from Mesolithic and Neolithic periods and sediment layers dating back to the Late Pleistocene epoch have been found here.
- Conservation Status: Declared a National Geo-heritage Monument (2016) and included in UNESCO’s Tentative List of World Heritage Sites (2025) for global recognition and protection.
- Unique Landscape: Features badland topography with sand dunes, buried channels, gullies, and dendritic drainage patterns.
- Rare Formation: Only two other similar red sand dune systems exist globally—the Teri dunes in Tamil Nadu and one site in Sri Lanka.
| [UPSC 2014] When you travel in Himalayas, you will see the following:
1. Deep gorges 2. U-turn river courses 3. Parallel mountain ranges 4. Steep gradients causing land sliding Which of the above can be said to be the evidence for Himalayas being young fold mountains? Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1, 2 and 4 only (c) 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4* |