Why in the News?
Recently astronomers using the ATLAS telescope in Chile discovered 3I/ATLAS, the third known interstellar object and possibly the oldest comet ever detected, estimated to be over 7 billion years old.

About 3I/ATLAS:
- Discovery: It was detected on July 1, 2025, by the ATLAS telescope in Río Hurtado, Chile; confirmed interstellar due to its hyperbolic orbit and high speed (57–68 km/s).
- Significance: It is likely the oldest comet ever observed — possibly 7.6–14 billion years old, older than our 4.5-billion-year-old solar system.
- Nature: It appeared like an interstellar comet, showing signs of activity including a coma (cloud of dust/ice) and likely a tail as it nears the Sun.
- Composition: Rich in water ice and complex organic compounds; has a reddish hue indicating ancient, primordial material.
- Size: Estimated nucleus diameter is 10–30 km — larger than previous interstellar objects like 1I/ʻOumuamua and 2I/Borisov.
- Trajectory:
- Closest to Earth: ~270 million km (no threat).
- Closest to Sun: ~210 million km (Oct 29–30, 2025).
- Will exit the solar system permanently after perihelion.
- Scientific Importance:
- It offers rare opportunity to study materials from another star system.
- It can reveal clues about the formation of the Milky Way, other solar systems, and early star formation processes.
Back2Basics: ATLAS Telescope
- ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System) is a NASA-funded early warning project for detecting small near-Earth objects (NEOs).
- It is developed and operated by the University of Hawaii’s Institute for Astronomy.
- As of 2025, ATLAS operates five telescopes in Hawaii, South Africa, Chile, and the Canary Islands.
- Each telescope has a 0.5-meter Wright-Schmidt design, a 1-meter focal length, and a 110 MP CCD detector with a 7.4° field of view.
- The system scans 20,000 square degrees of sky three times per night and provides 1–3 week warnings for asteroids 45–120 meters wide.
- In addition to asteroids, ATLAS also discovers supernovae, comets, dwarf planets, and variable stars.
|
What are Interstellar Objects?
- Overview: Celestial bodies that originate outside the solar system and travel through it on open-ended (hyperbolic) orbits.
- Key Characteristics:
- Not gravitationally bound to the Sun.
- Travel at very high speeds, often unaffected by solar gravity.
- Do not return once they pass through the inner solar system.
- Known Interstellar Visitors:
-
- 1I/ʻOumuamua (2017) – Asteroid-like, no coma or tail.
- 2I/Borisov (2019) – Active comet with typical cometary features.
- 3I/ATLAS (2025) – Discussed above.
- How are they Identified:
- Hyperbolic trajectory confirmed via orbital calculations.
- Speed at great distances exceeds gravitational escape velocity.
- Scientific Value:
- Provide direct clues about planetary formation beyond our solar system.
- Can reveal chemical signatures from other star systems.
- Allow us to study primordial matter from distant parts of the galaxy.
- Act as natural probes from unknown regions of the Milky Way.
| [UPSC 2011] What is the difference between asteroids and comets?
1. Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are formed of frozen gases held together by rocky and metallic material. 2. Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and mercury. 3. Comets show a perceptible glowing tail, while asteroids do not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 3 only* (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India’s flagship freight rail infrastructure project — the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) — is nearing full commissioning.
About the Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) Project:
- Overview: It is a flagship railway initiative by the Ministry of Railways to modernise and streamline freight movement in India.
- Launch: The foundation stone was laid in 2006 by PM Dr. Manmohan Singh.
- Implementing Agency: It is implemented by the Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Ltd. (DFCCIL), a Special Purpose Vehicle established in October 2006.
- Objective: The main aim is to develop high-capacity, high-speed freight-only rail corridors to decongest passenger routes and improve logistics efficiency.
- Investment Size: With a total estimated cost of ₹1.25 lakh crore, the DFC is among India’s largest rail infrastructure investments.
- Corridor Coverage:
-
- Eastern DFC (EDFC): Spans 1,337 km from Sonnagar (Bihar) to Sahnewal (Punjab) — fully operational.
- Western DFC (WDFC): Stretches 1,506 km from JNPT (Mumbai) to Dadri (UP) — 93% complete, to be commissioned by Dec 2025.
- Need for DFCs: The project was necessitated by overuse of the Golden Quadrilateral, which carries over 50% of freight on just 16% of India’s rail routes.
- Freight Transport Target: The goal is to increase the rail share of freight to 45% by 2030 as part of the National Rail Plan.
Key Features of the DFC:
- Dedicated Infrastructure: The DFCs feature electrified double-line tracks, exclusively for freight, separating them from passenger traffic.
- Load and Speed Capacity: Built to handle 32.5-tonne axle loads and support freight train speeds of up to 100 km/h.
- Cargo Type by Corridor:
-
- Eastern DFC: Focused on coal and raw materials.
- Western DFC: Transports containers, cement, fertilisers, and other industrial goods.
- Train Speed: Trains currently operate at 50–60 km/h, with further speed gains expected through modern rolling stock.
- Capacity Utilization: Already operating at over 85% capacity, with projections of 480 daily trains (240 each direction) by mid-2026.
- Future Expansion Plans:
-
- East Coast Corridor: Paradip to Vijayawada
- East–West Corridor: Kharagpur to Mumbai
- North–South Corridor: Delhi to Chennai
- Estimated Expansion Cost: The combined cost of these three new corridors is around ₹4 lakh crore, with the East Coast Corridor prioritized first.
| [UPSC 2000] Which one of the following ports of India handles the highest tonnage of import cargo?
Options: (a) Calcutta (b) Kandla (c) Mumbai* (d) Visakhapatnam |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Ahead of the 16th Census of India, experts have stated that counting the six main indigenous tribes of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, including the Jarawa, is feasible.

About Jarawa Tribe:
- Location: They live in the Middle and South Andaman Islands of India.
- Official Status: They are classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) by the GoI.
- Population Growth: Their population has risen from 260 (1998) to around 647 (2025) due to better healthcare and low external interference.
- First Contact: Voluntary contact with outsiders began in 1997, allowing limited medical aid, schooling, and trade.
- Key Features:
- Lifestyle: They are hunter-gatherers and fisherfolk, moving in nomadic groups of 40–50 individuals.
- Ancestry: Believed to be descendants of the extinct Jangil tribe and among the earliest human migrants from Africa.
- Health Profile: They maintain strong physical health with low incidence of lifestyle diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
- Lifespan: Natural childbirth is common, and the average lifespan now exceeds 50 years.
Note:
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to 5 PVTGs, which are among the most isolated and distinct indigenous communities in India. They are- Great Andamanese, Jarawas, Onges, Sentinelese, Shompens. |
Back2Basics: Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
- Overview: They are a subgroup within Scheduled Tribes considered most backward and vulnerable.
- Habitat: They generally inhabit remote localities having poor infrastructure and administrative support.
- Distribution: There are 75 such groups identified and categorized PVTGs.
- Origin of the concept:
-
- The Dhebar Commission (1960-1961) stated that within Scheduled Tribes there existed an inequality in the rate of development.
- During the 4th Five Year Plan (1969-74) a sub-category was created within Scheduled Tribes to identify groups that were considered to be at a lower level of development.
- This sub-category was named “Primitive tribal group”.
- In 2006 the government of India proposed to rename PVTGs.
- Features of PVTGs: Groups that satisfied any one of the criteria are considered PVTGs:
-
- Pre-agricultural system of existence
- The practice of hunting and gathering
- Zero or negative population growth
- Extremely low level of literacy in comparison with other tribal groups.
|
| [UPSC 2019] Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India:
1. PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
2. A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
3. There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
4. Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Options: (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 2, 3 and 4 (c) 1, 2 and 4* (d) 1, 3 and 4 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
India is taking part in Talisman Sabre 2025, the 11th and largest edition of the Australia-U.S.-led multinational military exercise, involving over 35,000 personnel from 19 countries.
About Exercise Talisman Sabre:
- Overview: It is a biennial multinational joint military exercise, co-led by Australia and the United States.
- Inception: It began in 2005 and has been conducted every 2 years, typically during odd-numbered years.
- Objective: The primary aim is to enhance combat readiness, improve interoperability, and strengthen the joint operations capability of participating armed forces.
- Scope of Operations: It focuses on high-end warfighting, including:
- Crisis-action planning
- Contingency response
- Multi-domain operations across land, air, sea, cyber, and space
- Strategic Importance: It plays a key role in promoting regional security cooperation and supports the vision of a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific.
Key Features of the 2025 Edition:
- Scale: The 2025 edition involves over 35,000 military personnel from 19 participating countries, making it the largest and most complex iteration of the exercise so far.
- Participating Nations:
- Full participants: Australia, the United States, India, Canada, Fiji, France, Germany, Indonesia, Japan, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, South Korea, Singapore, Thailand, Tonga, and the United Kingdom.
- Observer nations: Malaysia and Vietnam.
- Geographical Expansion: For the first time, parts of the exercise will be conducted outside Australia, with training also planned in Papua New Guinea.
- New Defence Capabilities: The 2025 edition will showcase:
- UH-60M Black Hawk helicopters
- Precision Strike Missile (PrSM) system introduced by the Australian Defence Force
- Multi-Domain Focus: Operations will span across land, sea, air, space, and cyberspace, reflecting the modern, multi-domain nature of warfare.
- Strategic Outcome: It aims to improve regional response capabilities, strengthen defence partnerships, and promote peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific region.
| [UPSC 2008] ‘Hand-in-Hand 2007’, a joint anti-terrorism military training was held by the officers of the Indian Army and officers of the Army of which one of the following countries?
Options: (a) China *(b) Japan (c) Russia (d) USA |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Tamil Nadu CM stressed the need to declare the Thirukkural as a national book and to set up a major organisation in Delhi to promote Thiruvalluvar’s ideas.

About Thirukkural:
- Overview: Thirukkural is a classical Tamil literary work consisting of 1,330 couplets (kurals), each containing seven words.
- Form and Message: Composed in the Kural Venba poetic form, it is renowned for its universal values, secular ethics, and moral guidance that transcend time, religion, and culture.
- Authored by: The text is traditionally attributed to Thiruvalluvar, also known simply as Valluvar.
- How old is it: Scholars date the text between 300 BCE and 500 CE, though its exact period remains debated.
- Components: The Thirukkural is divided into 3 major sections:
-
- Aram (Virtue / Dharma): Deals with personal morality, non-violence, and ethical conduct—emphasizing values such as truth, charity, self-control, and compassion.
- Porul (Wealth / Artha): Focuses on social, political, and economic life, including governance, justice, taxation, warfare, diplomacy, and administration.
- Inbam (Love / Kama): Explores human emotions, love, and personal relationships, especially themes of romance, domestic life, and emotional well-being.
Key Features of Thirukkural:
- Ethical Emphasis: Promotes timeless values like non-violence (ahimsa), truth, self-restraint, gratitude, and hospitality.
- Societal Themes: Highlights issues such as education, friendship, agriculture, social justice, and temperance.
- Cultural Reverence: Referred to by honorifics such as “Tamil Veda” and “Divine Book”, symbolizing its moral and spiritual stature.
- Literary Qualities: Celebrated for its brevity, clarity, and philosophical depth, making it accessible and universally admired.
Back2Basics: Sangam Literature
- Overview: It refers to the ancient body of Tamil texts composed during the Sangam period, traditionally dated from 3rd century BCE to 3rd century CE.
- Meaning: The word Sangam means “assembly” or “academy”, referring to gatherings of Tamil poets under the patronage of Pandya kings.
- Historical Context: According to Tamil tradition, there were three Sangams:
-
- First Sangam (Madurai): No known literary works have survived.
- Second Sangam (Kapadapuram): Only Tolkappiyam (grammar and poetics) survives.
- Third Sangam (Madurai): Source of most surviving Sangam literature.
- Nature and Content:
- Literary Form: Written in classical Tamil poetry, the texts reflect secular themes like love, war, charity, governance, agriculture, and trade.
- Societal Insight: Offers a detailed glimpse into the social, political, and economic life of ancient Tamil society.
- Key Texts:
-
- Tolkappiyam: The earliest Tamil grammar and work on poetic theory.
- Ettuthogai (Eight Anthologies): Collections of short poems.
- Pattupattu (Ten Idylls): Longer narrative poems.
- Padinenkilkanakku (Eighteen Minor Works): Didactic works focused on ethics and morality.
- Three Epics: Silappatikaram, Manimekalai, Sivaga Sindamani/. These were compiled later but are deeply influenced by Sangam themes.
|
| [UPSC 2023] Which one of the following explains the practice of Vattakirutal’ as mentioned in Sangam poems?
Options: (a) Kings employing women bodyguards
(b) Learned persons assembling in royal courts to discuss religious and philosophical matters
(c) Young girls keeping watch over agricultural fields and driving away birds and animals
(d) A king defeated in a battle committing ritual suicide by starving himself to death* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The President of India has nominated Harsh Vardhan Shringla, Ujjwal Nikam, C. Sadanandan Master, and Meenakshi Jain to the Rajya Sabha.

About Nominated Members to the Rajya Sabha:
- Number and Tenure: The President of India nominates 12 members to the Rajya Sabha for a six-year term.
- Purpose of Nomination: This provision is meant to honor individuals with exceptional contributions in the fields of arts, literature, science, and social service.
- Constitutional Basis: This right is granted to the President under the Fourth Schedule, in accordance with Articles 4(1) and 80(2) of the Constitution of India.
- Constitutional Provisions for Nominated Members:
- Article 80(1)(a): Provides for nomination of 12 members to the Rajya Sabha by the President.
- Article 80(3): Specifies that the nominees must have special knowledge or practical experience in one or more of the following fields: Literature; Science; Art; Social service.
Composition of the Rajya Sabha:
- Total Strength: The current strength of the Rajya Sabha is 245 members, comprising:
- 233 elected members representing States and Union Territories
- 12 nominated members by the President
- Permanent Nature: The Rajya Sabha is a permanent body and is not subject to dissolution.
- Biennial Retirement: One-third members retire every two years, and elections are held to fill the vacant seats.
|
Powers and Privileges of Nominated Members:
- Equal Rights in House Proceedings: Nominated members enjoy all powers, privileges, and immunities of an elected Member of Parliament.
- Participation in Proceedings: They can take part in all debates, discussions, and committees in the House.
- Voting Rights Exceptions:
- They cannot vote in the election of the President of India.
- They can vote in the election of the Vice President.
- Political Affiliation Provision: According to Article 99, a nominated member is given six months to join a political party after being nominated.
| [UPSC 2014] Consider the following statements:
1. The Chairman and the Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha are not the members of that House. 2. While the nominated members of the two Houses of the Parliament have no voting right in the presidential election, they have the right to vote in the election of the Vice President.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only* (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) has granted approval for diverting 142.76 hectares of forest land in Sharavathi Valley Lion-Tailed Macaque Wildlife Sanctuary, Karnataka.

About Lion-Tailed Macaque:
- Scientific Classification: The Lion-Tailed Macaque (Macaca silenus), also known as the Wanderoo or Bearded Monkey, is an primate species endemic to the Western Ghats of India.
- Distribution: It is found primarily in the states of Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu.
- Physical Characteristics: Recognized by a silver-white mane surrounding a black face and a lion-like tuft at the end of its tail, the body is covered in glossy black fur, and both sexes look similar.
- Habitat and Behaviour
- Preferences: The species inhabits tropical evergreen rainforests, and is also found in monsoon forests and shola-grassland ecosystems.
- Habitat: It is arboreal (tree-dwelling) and diurnal (active during the day).
- Elevation Range: Typically lives at altitudes between 600 and 1,800 metres above sea level.
- Human Avoidance: Known for being shy, it tends to avoid human contact, staying high in the forest canopy.
- Social Structure: Lives in social groups of 8 to 20 individuals, usually led by a dominant male.
- Behaviour:
- Dietary Habits: Primarily frugivorous, eating fruits, but also consumes leaves, stems, flowers, buds, fungi, and occasionally insects and small animals.
- Communication System: Possesses a rich vocal communication system with over 17 distinct vocalizations.
- Territorial Behavior: Males use loud calls to mark territory and warn intruders.
- Conservation Status:
-
- IUCN Status: Classified as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- Legal Protection: Appendix I of CITES; Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Population and Conservation Efforts:
-
- Population: It is estimated at around only 2,500 individuals.
- Key Protected Area: The Sharavathi Valley Lion-Tailed Macaque Wildlife Sanctuary in Karnataka hosts the largest known population in any protected area, with around 700 individuals.
- Ecological Importance:
- Serves as an indicator species for rainforest health.
- Plays a vital role in seed dispersal, contributing to forest regeneration.
| [UPSC 2023] Consider the following fauna:
1. Lion-tailed Macaque 2. Malabar Civet 3. Sambar Deer
How many of the above are generally nocturnal or most active after sunset?
Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two* (c) All three (d) None |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (SC-NBWL) has decided to review and revise the 2011 guidelines on the declaration of Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) around wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
What are Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs)?
- Overview: ESZs, also called Ecologically Fragile Areas (EFAs), are areas notified by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) around Protected Areas (PAs) like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
- Purpose:
- Act as “shock absorbers” to protect areas by regulating potentially harmful activities.
- Serve as transition zones from highly protected to less protected ecosystems.
- Help conserve biodiversity, maintain landscape connectivity, and prevent fragmentation of habitats.
- Legal Basis:
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, particularly Section 3(2)(v).
- Rule 5(1) of Environment (Protection) Rules, 1986.
- Wildlife Conservation Strategy, 2002: Recommended declaring 10 km radius around PAs as default ESZ.
- Demarcation Process:
- ESZ boundaries vary in width based on ecological sensitivity and ground realities.
- Factors considered: species presence, migration routes, landscape linkage, human settlements, etc.
- Activity Zonation:
- Prohibited: Commercial mining, polluting industries, major hydro projects, wood logging.
- Regulated: Tree felling, large-scale agriculture change, road widening, tourism infrastructure.
- Permitted: Rainwater harvesting, organic farming, green energy use.
- Present Status:
- 347 final notifications issued.
- Where no ESZ is notified, a default 10-km ESZ is applicable (SC 2022 ruling).
2011 Guidelines on ESZs:
- Issued by MoEFCC to standardize and guide the process of ESZ declaration.
- Key Features:
-
- Emphasized flexibility and site-specific demarcation.
- Classified activities into permitted, regulated, prohibited.
- Directed preparation of a Zonal Master Plan (ZMP) within 2 years of ESZ notification.
- Called for community involvement, scientific input, and buffer management.
|
Recent Context:
- Reasons Behind: Revision One-size-fits-all (10-km blanket rule) is not effective:
- Urban examples: Sanjay Gandhi National Park (Mumbai), Asola Bhatti Sanctuary (Delhi).
- In Himachal Pradesh, ~65% area already under forest cover.
- Kerala: Fear of new sanctuary leading to more restrictions.
- Over-generalized: Existing guidelines unsuitable for marine sanctuaries, need ecosystem-specific norms.
| [UPSC 2014] With reference to ‘Eco-Sensitive Zones’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Eco-Sensitive Zones are the areas that are declared under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
2. The purpose of the declaration of Eco-Sensitive Zones is to prohibit all kinds of human activities in those zones except agriculture.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 * |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
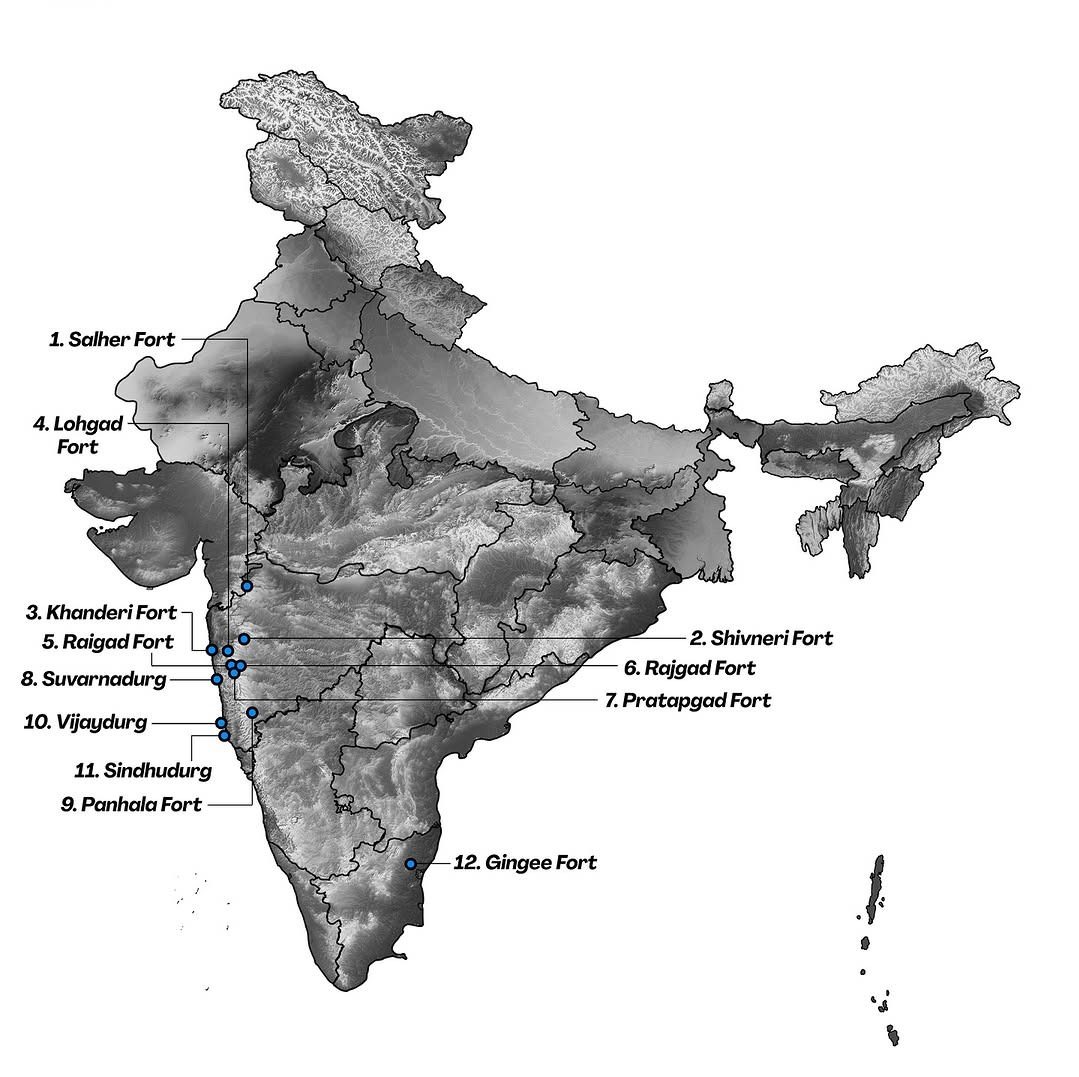
Why in the News?
The ‘Maratha Military Landscapes’ of India have been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List under the cultural category during the 47th session of the World Heritage Committee held in Paris.

About Maratha Military Landscapes:
- Overview: A network of 12 forts showcasing the Maratha Empire’s military architecture and strategic fortification from the 17th to 19th centuries.
- Time Period: Developed between 1670 CE (Shivaji’s era) and 1818 CE (end of Peshwa rule).
- Geographical Spread: 11 forts in Maharashtra and 1 in Tamil Nadu (Gingee Fort), covering hill, coastal, forest, plateau, and island terrains.
- Key Forts: Salher, Shivneri, Lohgad, Raigad, Rajgad, Pratapgad, Khanderi, Suvarnadurg, Panhala, Vijaydurg, Sindhudurg (Maharashtra); Gingee (Tamil Nadu).
- Types:
- Hill forts: Rajgad, Raigad
- Hill-forest: Shivneri
- Coastal: Suvarnadurg, Vijaydurg
- Island: Khanderi, Sindhudurg
- Protection:
- 8 forts by Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
- 4 forts by Maharashtra’s Directorate of Archaeology & Museums
- Ideology: Reflects Shivaji’s military decentralization, terrain-based defense, and self-sustaining fort systems.
- Tagged under cultural criteria:
- (iii) Exceptional testimony to a cultural tradition
- (iv) Outstanding example of military architecture
- (vi) Association with historic events and traditions
What are UNESCO World Heritage Sites?
- A WHS is a landmark or area recognized for its cultural, historical, natural, or scientific value to humanity.
- It is governed by the UNESCO World Heritage Convention (1972).
- India formally signed the Convention on November 14, 1977.
- Sites are selected by the World Heritage Committee, comprising 21 elected state parties.
- Categories include:
- Cultural (e.g., forts, temples, cities)
- Natural (e.g., forests, parks, biodiversity sites)
- Mixed (having both cultural and natural value)
- Selection is based on 10 criteria (6 cultural + 4 natural); at least one must be met.
- Once inscribed, sites are eligible for global recognition, protection, and funding.
|
| [UPSC 2024] Consider the following properties included in the World Heritage List released by UNESCO:
1. Shantiniketan 2. Rani-ki-Vav 3. Sacred Ensembles of the Hoysalas 4. Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodhgaya
How many of the above properties were included in 2023?
Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two* (c) Only three (d) All four |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has launched an expanded Sanchar Mitra Scheme to engage engineering students as digital ambassadors for promoting telecom literacy, digital safety, and citizen engagement.
What is the Sanchar Mitra Scheme?
- Launching Body: An initiative by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Government of India.
- Primary Aim: To engage student volunteers as “Sanchar Mitras” or digital ambassadors to spread awareness about telecom-related issues.
- Purpose:
- Bridge the communication gap between citizens and the telecom ecosystem.
- Promote safe and informed use of telecom services.
- Encourage public participation in India’s digital transformation.
- Implementation Status:
- Piloted in select institutions.
- Now being scaled up for nationwide rollout.
Key Features and Highlights:
- Target Audience: It primarily targets students from engineering and technical backgrounds such as telecommunications, computer science, electronics, and cybersecurity.
- Selection of Volunteers: Students will be nominated as Sanchar Mitras in consultation with DoT field units and educational institutions.
- Training Modules: Volunteers will be trained to conduct grassroots campaigns on cyber fraud prevention, EMF radiation concerns, and responsible digital behavior.
- Training Institutions: Training will be delivered by the National Communications Academy–Technology (NCA-T) and the Media Wing of the DoT.
- Core Pillars: The scheme is structured around three key pillars: Connect, Educate, and Innovate.
- Tech Awareness Promotion: Sanchar Mitras will promote awareness on emerging telecom technologies like 5G, 6G, AI, and cybersecurity.
- Community Outreach: Students will engage with communities, NGOs, and schools to foster a culture of informed digital citizenship.
- Strategic Alignment: It aligns with India’s strength in the “Four Ds”: Democracy, Demography, Digitisation, and Delivery.
| [UPSC 2010] Which among the following do/does not belong/belongs to the GSM family of wireless technologies?
Options: (a) EDGE (b) LTE (c) DSL* (d) Both EDGE and LTE |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Mizoram Governor has imposed Governor’s Rule in the Chakma Autonomous District Council (CADC) due to prolonged political instability and repeated leadership changes.
About Autonomous District Councils (ADCs):
- Basis: They are local self-governing institutions established under the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- Coverage: ADCs are constituted in tribal areas of the northeastern states—Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram (ATM2).
- Purpose: These councils aim to provide autonomy to tribal communities to preserve their culture, customs, and govern their local affairs.
- Notification: Each tribal area notified under the Sixth Schedule is declared an autonomous district, governed by its respective ADC.
- Objective: The primary objectives of ADCs are to promote tribal self-governance, ensure local development, and protect tribal identity and rights.
Key Features of ADCs
- Legal Status: ADCs are formed through constitutional provisions under the Sixth Schedule and are not governed by state laws.
- Council Composition: Each ADC comprises up to 30 members, of which 26 are elected by adult suffrage and 4 are nominated by the Governor.
- Tenure: The tenure of an ADC is 5 years from the date of its constitution.
- Scope of Authority: ADCs have legislative, executive, and limited judicial powers specific to the needs of tribal communities.
- Applicability of Laws: State and Central laws do not automatically apply in ADC areas unless explicitly extended by the Governor.
Powers and Functions of ADCs:
- Law-Making Powers: ADCs can enact laws on land management, agriculture, and forest use (excluding reserved forests).
- Customary Regulations: They can regulate inheritance, marriage, divorce, and social customs, and appoint traditional chiefs and headmen.
- Local Administration: It oversee services such as primary education, dispensaries, roads, markets, and fisheries.
- Judicial Functions: Councils can establish village courts to try civil and criminal cases involving tribal members, with sentencing powers up to five years.
- Regulation of Trade: They may regulate money lending and trade by non-tribals, subject to Governor’s approval.
- Revenue Sources: It can levy taxes on professions, trades, animals, vehicles, markets, ferries, and public infrastructure like roads and schools.
Autonomy and Limitations:
- Degree of Autonomy: ADCs enjoy substantial legislative and administrative autonomy within their territorial jurisdiction.
- Non-Applicability of General Laws: Parliamentary and State laws apply only when directed by the Governor, ensuring self-rule.
- Governor’s Oversight: Despite autonomy, the Governor retains discretionary powers and can approve, modify, or annul council decisions.
- Financial Constraints: ADCs often face limited revenue generation, which restricts their developmental effectiveness.
- Administrative Challenges: Operational issues include leadership instability, shortage of trained personnel, and state-level interference in council functions.
| [UPSC 2015] The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to:
Options: (a) protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes * (b) determine the boundaries between States (c) determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats (d) protect the interests of all border States |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), in its latest Frontiers 2025 report titled The Weight of Time, has warned that increased river and coastal flooding caused by climate change could unearth dangerous legacy pollutants from water bodies.
About Legacy Pollutants:
- Definition: Legacy pollutants refer to toxic substances like heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants (POPs) that continue to remain in the environment even decades after their use has been banned or restricted.
- Examples:
- Heavy Metals: Lead, Cadmium, Mercury, Arsenic.
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs):
- Pesticides: DDT (Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane), Aldrin, Endrin, Chlordane.
- Industrial Chemicals: PCBs (Polychlorinated Biphenyls), Dioxins, Furans.
- By-products: Produced from incineration, metal smelting, and waste burning.
- Persistence: These substances are highly resistant to environmental degradation and accumulate in riverbeds, lakes, estuaries, and other sediment-rich ecosystems.
- Health Hazards: Even at low exposure levels, legacy pollutants can cause: Neurotoxicity (nervous system damage), Immunotoxicity (immune disruption), Hepatotoxicity (liver damage), Reproductive toxicity (infertility, birth defects), Carcinogenicity (various cancers), Endocrine disruption etc.
- Sources:
- Past industrial practices, use of banned agricultural chemicals, and obsolete pesticide stockpiles.
- Improperly managed chemical landfills, which still hold an estimated 4.8–7 million tonnes of POP waste globally.

Key Highlights of Frontiers 2025: The Weight of Time (UNEP):
- Retreat of Toxins: Climate change-induced flooding can unearth and redistribute toxic legacy pollutants from contaminated sediments into the environment and food chain.
- How? Floodwaters re-suspend heavy metals and POPs trapped in sediment.
- Case Studies Cited:
- Hurricane Harvey (Texas, 2017): Released mercury and carcinogenic chemicals from flood-induced sediment dispersal into Galveston Bay.
- Niger Delta Floods (Nigeria, 2012): Mobilised Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) from oil-contaminated sediments.
- Pakistan Floods (2010 & 2022): Washed away obsolete pesticide stockpiles, spreading DDT and other POPs into floodwaters and soils.
- India-Specific Findings:
- Sediments of Ganga, Hindon, and Vaigai Rivers show dangerously high levels of Cadmium.
- Cadmium is a known carcinogen and endocrine disruptor, with potential to cause kidney, bone, and reproductive harm.
- Ayad and Vaigai Rivers also showed up deadly levels of Lead concentration.
| [UPSC 2016] Which of the following can be found as pollutants in the drinking water in some parts of India?
1. Arsenic 2. Sorbitol 3. Fluoride 4. Formaldehyde 5. Uranium
Options: (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2, 4 and 5 only (c) 1, 3 and 5 only* (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) and UNICEF India launched TALASH (Tribal Aptitude, Life Skills and Self-Esteem Hub), a first-of-its-kind national initiative for holistic development of tribal students in Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs).
About the TALASH Initiative:
- Overview: TALASH (Tribal Aptitude, Life Skills and Self-Esteem Hub) is a national programme launched by the National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS) in partnership with UNICEF India.
- Target Group: It is aimed at the holistic development of tribal students studying in Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs) across the country.
- Objectives: The initiative fosters self-awareness, emotional resilience, life skills, and career clarity among tribal youth.
- Focus: It is the first national initiative in India designed specifically for tribal students.
- Broader Policy: TALASH aligns with the National Education Policy 2020, promoting inclusive, equitable, and competency-based education.
- Coverage Goal: Over 1,38,336 students across 28 States and 8 Union Territories are expected to benefit.
- Implementation: By the end of 2025, TALASH aims to be implemented in all EMRSs nationwide.
Key Features of TALASH:
- Psychometric Assessments:
- Inspired by NCERT’s ‘Tamanna’, TALASH offers aptitude tests to help students discover their interests, abilities, and potential.
- Based on the results, students receive Career Cards suggesting suitable career options.
- Career Counselling: The platform offers structured career guidance to help students make informed decisions aligned with their strengths and aspirations.
- Life Skills & Self-Esteem Modules: TALASH teaches communication, problem-solving, emotional regulation, and self-confidence through interactive modules.
- E-Learning for Teachers:
- A dedicated online portal provides training and resources to teachers to help them mentor students effectively.
- So far, 189 teachers from 75 EMRSs have been trained to lead school-level sessions.
| [UPSC 2017] With reference to ‘National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF)’, which of the statements given below is/are correct?
1. Under NSQF, a learner can acquire the certification for competency only through formal learning.
2. An outcome expected from the implementation of NSQF is the mobility between vocational and general education.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only* (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Researchers from Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP), Lucknow, have found strong evidence that the Kashmir Valley, now cool and temperate, was once a warm, humid subtropical region.
About the Study on Fossils:
- Site of Fossil Discovery: The fossils were recovered from the Karewa sediments of the Kashmir Valley, known for preserving ancient plant remains.
- Analysis: Researchers used CLAMP (Climate Leaf Analysis Multivariate Program) to analyze fossil leaf shape, size, and margins to estimate past temperature and rainfall patterns.
- Coexistence Approach: It was also used, comparing fossil plants with their modern relatives to reconstruct the region’s ancient climate.
Key Findings:
- Past Climate Type: The Kashmir Valley once had a warm, humid subtropical climate, very different from the cool, Mediterranean-type climate it experiences today.
- Vegetation Evidence: Fossilized leaves showed diverse subtropical plant types no longer found in the region’s current vegetation.
- Role of Tectonic Uplift: The tectonic uplift of the Pir Panjal Range was identified as a key factor that blocked the Indian summer monsoon from entering the valley.
- Climatic Transition: This led to gradual drying of the region and a shift from subtropical forests to temperate ecosystems.
- Impact of Mountain-Building: The study shows that mountain-building (tectonic uplift) can directly affect climate patterns by altering monsoon routes.
- Relevance to Climate Change: The findings provide insight into natural climate shifts over millions of years, helping contextualize modern climate change.
- Ecological Vulnerability: It also highlights the fragility of mountain ecosystems like the Himalayas, which are vulnerable to both natural and human-induced environmental changes.
Back2Basics:
- Karewa Sediments: They are plateau-like terraces in the Kashmir Valley, made up of lacustrine (lake) and fluvio-glacial deposits; They are known to preserve ancient fossils, especially of plants.
- Subtropical Climate: A warm and humid climate with moderate to high rainfall, supporting dense vegetation. Ex: Climate of northeastern India.
- Mediterranean-Type Climate: Characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers; Ex: Current climate of parts of the Kashmir Valley.
|
| [UPSC 2025] Which of the following are the evidence of the phenomenon of continental drift?
I. The belt of ancient rocks from Brazil coast matches with those from Western Africa. II. The gold deposits of Ghana are derived from the Brazil plateau when the two continents lay side by side. III. The Gondwana system of sediments from India is known to have its counterparts in six different landmasses of the Southern Hemisphere.
Options: (a) I and III only (b) I and II only (c) I, II and III * (d) II and III only |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Union Home Minister recently highlighted that 83% of issues discussed in Zonal Council meetings have been resolved, reaffirming their role as effective platforms for intergovernmental cooperation.
What are Zonal Councils?
- Establishment: They are statutory bodies established under the States Reorganisation Act, 1956; they are not constitutional bodies.
- Purpose: Their main goal is to promote cooperation and coordination among states, union territories, and the central government.
- Basis for Zoning: Zones were drawn based on natural divisions, cultural and linguistic affinity, river systems, and security needs.
- Zonal Division: India is divided into five zones—Northern, Central, Eastern, Western, and Southern—with a separate Zonal Council for each:
-
- Northern Zonal Council: Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, Delhi, Chandigarh
- Central Zonal Council: Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh
- Eastern Zonal Council: Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal
- Western Zonal Council: Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Dadra & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu
- Southern Zonal Council: Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry
Note:
- North-Eastern Council (NEC) (separate body): Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Sikkim (added in 2002)
- The union territories of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep are NOT members of any of the Zonal Councils. However, they are presently special invitees to the Southern Zonal Council.
|
Composition and Structure of Zonal Councils:
- Chairperson: Each Zonal Council is chaired by the Union Home Minister.
- State Representation: The Chief Ministers of all states in the respective zone are members of the Council.
- Additional Members: Each state nominates two additional ministers; administrators of union territories also participate.
- Vice-Chairperson Role: The role of Vice-Chairperson rotates annually among the Chief Ministers.
- Standing Committees: These are formed with Chief Secretaries of states and meet ahead of full sessions to finalize the agenda.
Functions and Responsibilities:
- Cooperation & Consensus: Promote interstate and Centre-state cooperation through dialogue and consensus-building.
- Key Issues Addressed: Economic and social planning, Border disputes, Inter-state transport, Linguistic minority concerns etc.
- Advisory Role: While the councils’ recommendations are advisory, they play a vital role in dispute resolution and coordinated policy formulation.
Recent Developments and Significance:
- Leadership in NEC: In 2018, the Union Home Minister became the Chairperson of the North Eastern Council, signaling a push for broader integration.
- Revitalization under Modi Government: Zonal Councils have evolved into dynamic, action-oriented platforms rather than passive advisory bodies.
- Strengthening Federalism: These councils now actively contribute to cooperative federalism, resolve disputes, and accelerate regional development.
- Efficacy in Implementation: With 83% of agenda issues resolved, Zonal Councils demonstrate increasing political will and effectiveness in addressing regional challenges.
| [UPSC 2013] Which of the following bodies is/are not mentioned in the Indian Constitution?
1. National Development Council 2. Planning Commission 3. Zonal Councils
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
Options: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The International Buddhist Confederation (IBC) recently celebrated Ashadha Purnima, also known as Dhammachakra Pravartana Divas at Mulagandha Kuti Vihara, Sarnath.

About Dhammachakra Pravartana Divas:
- First Sermon: It marks the day when Gautama Buddha delivered his first sermon after attaining enlightenment.
- Date of Observance: The day is observed annually on the full moon of Ashadha (Ashadha Purnima), usually in July.
- Name and Location: The sermon, called Dhammacakkappavattana Sutta, was delivered at Deer Park (Isipatana), Sarnath, near Varanasi.
- Core Teachings Introduced: It laid the foundational teachings of Buddhism by introducing the Four Noble Truths and the Noble Eightfold Path.
- Formation of Sangha: His five former ascetic companions—Kaundinya, Bhaddiya, Vappa, Mahanama, and Assaji—became the first monks of the Buddhist Sangha.
- Symbolic Representation: The Dharma Chakra (Wheel of Dharma) symbolizes this “turning of the wheel of law” and spread of the Buddha’s teachings.
- Significance:
- Monastic Practice: It marks the beginning of the Varsha Vassa, a three-month monastic retreat during the rainy season.
- Religious Importance: It is the second most important Buddhist festival after Buddha Purnima.
Modern Day Significance:
- Ambedkarite Movement: In India, it is also significant for commemorating Dr. B.R. Ambedkar’s conversion to Buddhism with his followers at Deekshabhoomi, Nagpur (14 October 1956).
- Social Commitment: On this day, millions reaffirm their commitment to Buddhist values and the 22 vows taken to renounce caste-based discrimination.
- Global Observance: The day is celebrated internationally under various names—Esala Poya (Sri Lanka), Asanha Bucha (Thailand), and Asadha Purnima (India).
|
Tap to read more about philosophical tenets of Buddhism.
Back2Basics: Buddhist Councils
| Council |
Date & Venue |
Patron & President |
Objective |
Key Outcomes |
| 1st Buddhist Council |
483 BCE, Rajagriha (Bihar) |
Ajatashatru (Haryanka dynasty), Presided by Mahakasyapa |
To preserve the Buddha’s teachings after his Mahaparinirvana |
– Vinaya Pitaka compiled by Upali (rules for monks)
– Sutta Pitaka compiled by Ananda (discourses of Buddha) |
| 2nd Buddhist Council |
383 BCE, Vaishali (Bihar) |
Kalasoka (Shishunaga dynasty), Presided by Sabakami |
To resolve disputes over lax discipline and the ‘Ten Points’ followed by Vaishali monks |
– Split into Sthaviravadins (orthodox) and Mahasamghikas (liberal)
– Reaffirmation of stricter Vinaya rules |
| 3rd Buddhist Council |
247 BCE, Pataliputra (Patna) |
Ashoka (Maurya dynasty), Presided by Moggaliputta Tissa |
To eliminate heretical monks and consolidate Buddhist doctrine |
– Compilation of Abhidhamma Pitaka
– Composition of Kathavattu (philosophical debates)
– Launch of Buddhist missions to 9 countries |
| 4th Buddhist Council |
72 CE, Kashmir |
Kanishka (Kushan dynasty), Presided by Vasumitra (with Asvaghosha) |
To formalize doctrines and address doctrinal splits |
– Formal split into Hinayana and Mahayana schools
– Compilation of Vibhasha Sastras (commentaries) |
| 5th Buddhist Council |
1871 CE, Mandalay (Burma) |
Burmese Monarchy |
To preserve Buddhist texts |
– 729 stone slabs inscribed with the Pali Canon
– Considered a Burmese affair; not internationally recognized |
| 6th Buddhist Council |
1954 CE, Yangon (Burma) |
Burmese Govt & International Sangha |
To commemorate 2500 years of Buddhism and preserve Theravada canon |
– Global recitation and review of entire Pali Canon
– Participation from monks across Buddhist countries |
| [UPSC 2008] The concept of Eight-fold path forms the theme of-
Options: (a) Dipavamsa (b) Divyavadana (c) Mahaparinibban Sutta (d) Dharma Chakara Pravartana Sutta* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Researchers conducted the most precise global comparison of 10 Optical Atomic Clocks to pave the way for redefining the second by 2030, replacing Caesium Clocks with more accurate Optical ones.
Definition of a Second:
- The current SI unit of time is based on caesium-133 (Cs) atomic clocks.
- In 1967, one second was defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 cycles of radiation corresponding to the transition between two hyperfine levels of the ground state of a Cs-133 atom.
- In these clocks, a microwave signal is tuned until Cs atoms react maximally, ensuring the frequency is precisely 9,192,631,770 Hz.
- Frequency dividers count this microwave frequency, providing one tick per second, thus realizing the SI second.
|
About Caesium Atomic Clocks:
- Overview: Caesium atomic clocks are devices that define the current SI unit of time (second) using the oscillation frequency of caesium-133 atoms.
- SI Second Standard: One second is defined as the duration of 9,192,631,770 cycles of microwave radiation corresponding to the transition between two energy levels of the caesium-133 atom.
- Working Principle: These clocks work by tuning microwave signals to resonate with caesium atoms and then counting the resulting waves to measure time precisely.
- Stability and Usage: They are highly stable and have been used since 1967 to set international time standards.
- Applications: They are used in GPS systems, telecommunications, scientific research, and by national metrology institutions like India’s National Physical Laboratory (NPL).
- Accuracy: A typical caesium atomic clock loses about one second every 300 million years.
What are Optical Atomic Clocks?
- Overview: They are advanced timekeeping devices that use optical (visible light) frequency transitions in atoms like Strontium (Sr) or Ytterbium (Yb).
- Measurement Basis: These clocks measure time based on the oscillation of light emitted when atoms transition between energy levels at hundreds of trillions of Hz.
- Example Frequencies:
- Strontium: ~429 trillion Hz
- Ytterbium ions: over 642 trillion Hz
- Precision Tools: They require lasers and optical frequency combs to count these rapid oscillations accurately.
- Future Standard: They are being tested worldwide and are expected to replace caesium clocks by 2030 for redefining the SI second.
How Optical Atomic Clocks are Better than Caesium ones?
- Higher Frequency Operation: Optical clocks operate at much higher frequencies, allowing division of time into finer intervals.
- Improved Precision: By counting 10,000 times more oscillations per second, optical clocks achieve significantly higher precision and stability.
- Unmatched Accuracy: An optical atomic clock using strontium reportedly drifts by less than one second in 15 billion years, compared to 300 million years for caesium clocks.
- Advanced Applications: Their precision is critical for: Next-gen GPS systems, Gravitational wave detection, Climate monitoring and research etc.
- Ultra-High Synchronization: Optical clocks enable cross-continental synchronization at 18 decimal place accuracy, essential for global time coordination.
- Noise Resilience: They offer greater resistance to environmental noise and external disturbances, improving long-term reliability.
| [UPSC 2023] Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System?
Options: (a) Australia (b) Canada (c) Israel (d) Japan* |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) negotiations are facing a credibility crisis, as years of underperformance, weak accountability, and neglect of developing countries’ concerns have created growing frustration.
About the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC):
- Overview: The UNFCCC is an international treaty adopted at the 1992 Rio Earth Summit to address climate change by stabilizing greenhouse gas (GHG) concentrations in the atmosphere.
- Entry into Force: The Convention entered into force on 21 March 1994 and currently has 197 Parties, including all UN member states.
- Governing Body – COP: The Conference of the Parties (COP) is the supreme decision-making body under the UNFCCC, which meets annually to assess progress and set new targets.
- Consensus-Based Process: The Convention operates on the principle of consensus, meaning all Parties must agree for a decision to be adopted.
- Article 2 Objective: The objective of the UNFCCC, as per Article 2, is to stabilize GHG levels at a point that prevents dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
- Key Agreements: The UNFCCC framework led to major global climate agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol (1997) and the Paris Agreement (2015).
- Institutional Structure: It has three main institutional bodies:
-
- SBSTA: Subsidiary Body for Scientific and Technological Advice
- SBI: Subsidiary Body for Implementation
- UNFCCC Secretariat: Headquartered in Bonn, Germany
- Party Classifications:
- Annex I: Developed countries (OECD + Economies in Transition); Obligated to reduce GHG emissions and submit regular reports.
- Annex II: Subset of Annex I (OECD members); Required to provide financial and technological support to developing countries.
- Non-Annex I: Developing countries; No binding emission targets but eligible for support and encouraged to act voluntarily.
- LDCs (Least Developed Countries): Low-income, highly vulnerable nations; Receive priority support under UNFCCC for adaptation and capacity building.
India and the UNFCCC:
- Ratification: India ratified the UNFCCC in 1993 and has participated actively in all COP meetings since then.
- Party Classification: India is classified as a Non- Annex I Party, meaning it has no binding emission reduction targets under the Convention.
- Paris Agreement Commitments: Under the Paris Agreement (2015), India submitted Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), including:
- Reducing emissions intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels
- Achieving 50% cumulative electric power capacity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030
- Climate Diplomacy:
- India advocates the principle of Common But Differentiated Responsibilities and Respective Capabilities (CBDR–RC) in all negotiations.
- India co-founded the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and launched the LiFE Movement (Lifestyle for Environment) to promote sustainable lifestyles.
- India has opposed unilateral trade measures such as the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) at multiple climate forums.
|
Issues with the UNFCCC Process:
- Weak Enforcement: The process lacks enforcement mechanisms; countries that fail to meet commitments face no penalties.
- Consensus Delays: The consensus-based approach often leads to delays and diluted agreements due to the ability of a few nations to block progress.
- Unmet Commitments: Developed countries have not fulfilled the promised $100 billion per year in climate finance, which was due by 2020.
- Neglected Developing Country Needs: Critical needs for adaptation finance, capacity building, and technology transfer remain largely unmet for developing nations.
- Controversial Host Nations: The selection of host countries (e.g., UAE for COP28 and Azerbaijan for COP29) has drawn criticism due to their fossil fuel dependence.
- Demand for Reforms: At the Bonn Climate Conference (2024), developing countries called for reforms such as:
- Shifting to majority-based decision-making
- Imposing limits on fossil fuel industry participation in climate talks
| [UPSC 2016] With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
2. The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2°C or even 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
3. Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
BRICS group has condemned and rejected the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and other similar climate-linked trade measures.
What Is the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)?
- Overview: It is a climate-related import duty imposed by the European Union on goods whose production involves higher carbon emissions than what is permitted in the EU.
- Policy Framework: CBAM is part of the EU’s “Fit for 55” climate package, aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- Scope of Coverage: The policy requires importers to declare the volume and embedded carbon emissions of certain goods, such as steel, aluminium, cement, fertiliser, hydrogen, and electricity.
- Compliance Mechanism: To offset these emissions, EU importers must surrender CBAM certificates, priced based on the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS).
- Carbon Price Adjustment: If a non-EU producer has already paid a carbon price in their country, that amount can be deducted from the CBAM charge.
- Implementation Timeline: The transitional phase of CBAM is underway from 2023 to 2025, and the definitive regime begins on January 1, 2026.
Issues with CBAM:
- Trade Discrimination Concerns: Developing countries, including India and China, argue that CBAM imposes unilateral, punitive, and discriminatory trade restrictions under the guise of environmental protection.
- Violation of Climate Agreements: It is viewed as a violation of Paris Agreement, which upholds the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities.
- Neglect of Historical Emissions: Countries in the Global South contend that climate-related trade tools like CBAM ignore historical emissions and disproportionately impact countries still reliant on carbon-intensive development.
Implications of CBAM for India:
- Impact on Exports: Indian exports, particularly in iron, steel, aluminium, and cement, will face additional scrutiny and carbon charges under CBAM, reducing their competitiveness.
- Carbon Taxation Timeline: From January 1, 2026, carbon taxes will be levied on each shipment to the EU in specific sectors, ranging from 19.8% to 52.7% in potential carbon levies.
- High Carbon Intensity Risk: India’s high carbon intensity, primarily due to its 75% dependence on coal, makes its products more vulnerable to CBAM tariffs.
| [UPSC 2023] Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: Carbon markets are likely to be one of the most widespread tools in the fight against climate change.
Statement-II: Carbon markets transfer resources from the private sector to the State.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Options: (a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I (b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I ** (c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect (d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct |
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Why in the News?
Maharashtra’s transport department has now made HSRP number plate mandatory with a final deadline set for 15 August.
What is a High-Security Registration Plate (HSRP)?
- About: It is a standardised, tamper-proof vehicle number plate mandated for all vehicles in India.
- Launch: It was officially introduced in 2001 under Rule 50 of the Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR), 1989, and later made mandatory by the Supreme Court in 2012.
- Composition: The plate is made of aluminium and includes several embedded security features to prevent counterfeiting and enhance traceability.
-
- Each HSRP is fitted with a non-removable snap lock that prevents tampering or re-use.
- The plate contains a laser-etched 10-digit unique identification number, linking it to the vehicle’s registration details.
- A chromium-based hologram of the Ashoka Chakra is embedded to authenticate the plate and prevent duplication.
- A retro-reflective film improves night-time visibility and supports automated detection systems.
- A colour-coded third registration sticker is affixed to the vehicle’s windshield displaying key information like engine number, chassis number, and registration number.
- The plate is embedded with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, allowing authorities to digitally track the vehicle for enforcement and traffic management purposes.
Compliance and Enforcement in India:
- HSRPs are mandatory for all vehicles registered after April 1, 2019, as per Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) guidelines.
- Vehicles registered before April 1, 2019 must retrofitted with HSRPs by deadlines set by respective state governments.
- The Supreme Court and Ministry of Road Transport have directed states to enforce HSRP installation strictly to enhance road safety and curb vehicle-related crimes.
- In case of non-compliance, vehicle owners are liable for a fine of ₹1,000 under Rule 50 of CMVR and Section 177 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988.
- Transport departments across states, including Maharashtra, are conducting daily enforcement drives, issuing challans and directing retrofitting at authorised centres.
- Several states have authorised zone-wise vendors to streamline installation, and vehicle owners must pre-book appointments online for HSRP fitting.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now









