Why in the News?
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has directed the State Environment Impact Assessment Authority (SEIAA) and the mines and geology department to stop any unlawful/illegal sand mining in the Sharavathi River coastal zone.
About National Green Tribunal (NGT)
| Description | |
| Establishment | Formed in 2010 under the National Green Tribunal Act as a statutory body. |
| Objective |
|
| Composition |
|
| Powers | Empowered to decide on questions related to various environmental laws and hear civil cases concerning environmental issues:
|
| Exceptions | Prohibited to hear any issues which are covered under:
|
| Places |
|
| Governing Principles |
|
| Review and Challenge |
|
| Jurisdiction |
|
| Disposal of Cases | Disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing of the same. |
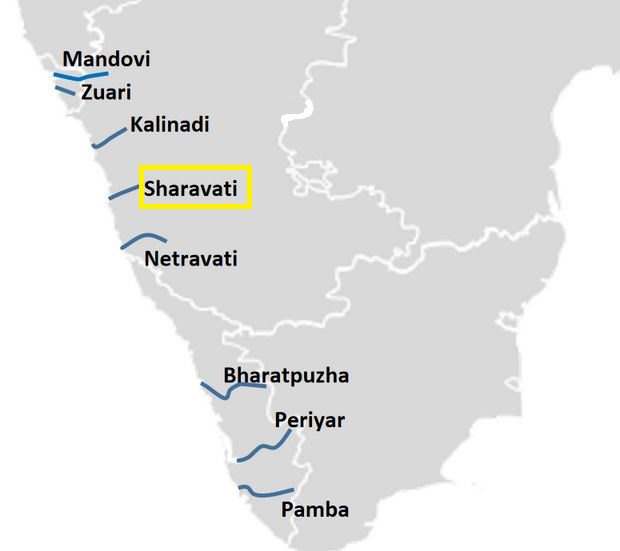
About Sharavathi River
- It originates and flows entirely within Karnataka.
- It is among the few westward-flowing rivers in the country and a significant part of its basin lies in the Western Ghats.
- Origin: The river originates at Ambutheertha in the Thirthahalli taluk.
- Legend: According to ancient legend, the god Rama shot an arrow (Ambu) into the ground to quench his wife Sita’s thirst. The water that poured out was named “Thirtha,” hence the river’s name “Sharavati,” with “Shara” meaning arrow.
Geography and Length:
- The river stretches about 128 km (80 mi) and joins the Arabian Sea at Honnavar in Uttara Kannada district.
- Jog Falls, formed by the Sharavati River, is located approximately 25 km from Siddapura.
Tributaries and Basin:
- Major tributaries: Nandihole, Haridravathi, Mavinahole, Hilkunji, Yennehole, Hurlihole, and Nagodihole.
- River basin: divided between Uttara Kannada and Shimoga districts.
- Pre-Cambrian rocks, including the Dharwar system and peninsular gneiss, dominate the basin.
Soils and Agriculture:
- Soils in the basin are predominantly lateritic and tend to be acidic, ranging from clay loamy to loamy.
- Four soil orders are found: ultisols, alfisols, inceptisols, and entisols.
Dams:
- The Linganamakki Dam, constructed in 1964, spans the Sharavati River, with a catchment area of nearly 1,991.71 km2.
- The Gerusoppa Dam, completed in 2002, primarily serves for electricity generation.
Flora and Fauna:
- The Sharavati Valley Wildlife Sanctuary declared in 1972, protects diverse ecosystems and endangered species.
- The river basin is rich in biodiversity, home to rare species of flora and fauna.
Regulation of Sand Mining in India:
|
||||||||||||||||||||
PYQ:[2018] Which of the following is/are the possible consequence/s of heavy sand mining in riverbeds?
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 [2019] With reference to the management of minor minerals in India, consider the following statements :
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 3 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 |