Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Mudimanikyam Temples
Mains level: Chalukyan Empire

Introduction
- Recent archaeological findings in Mudimanikyam village, Nalgonda district, unveiled two Badami Chalukya temples dating back 1,300-1,500 years and a label inscription from the 8th or 9th century AD.
- These discoveries shed light on the rich historical heritage of the region.
Ancient Mudimanikyam Temples
- Dating: The two temples, constructed between 543 AD and 750 AD, exhibit the distinctive Kadamba Nagara style in the Rekha Nagara format, a rarity in Telangana.
- Architectural Significance: Research emphasizes the importance of these temples as testimonies to the Badami Chalukya period. With minimal restoration, they can serve as valuable relics of ancient architecture in Telangana.
- Comparison: Apart from the Badami Chalukya temples at Alampur, these temples stand out as exceptional examples of architectural prowess from that era.
Details of Label Inscription
- Discovery: The label inscription, found on a pillar of a group of five temples in the village, dates back to the 8th or 9th century AD.
- Meaning: While the exact meaning of the inscription, ‘Gandaloranru,’ remains unclear, ASI suggests it may denote a heroic title, with ‘Ganda’ in Kannada meaning ‘hero.’
- Historical Context: The presence of the inscription indicates the existence of five temples, known as Panchakuta, during the late Badami Chalukya period. However, these temples are no longer in use, with one missing the Shivalinga and another containing a Vishnu idol.
Badami Chalukyas: Legacy and Achievements
- Establishment: Pulakeshin I founded the Chalukya dynasty in 550, establishing Badami (Vatapi) in present-day Karnataka as the capital.
- Extent of Empire: The Badami Chalukyas ruled over territories encompassing modern Karnataka and large parts of Andhra Pradesh.
- Pulakesi II’s Reign:
- Notable Conquests: Pulakeshin II expanded the empire northwards, halting Harsha’s advance and defeating the Vishnukundins in the southeastern Deccan.
- Diplomatic Relations: His reign saw diplomatic exchanges with Chinese and Persian empires, highlighting the dynasty’s international stature.
- Vikramaditya Dynasty: The dynasty experienced resurgence under Vikramaditya I, who expelled the Pallavas from Badami, and reached its zenith under Vikramaditya II, who conquered Kanchipuram from the Pallavas.
- Decline and End: The Rashtrakuta Dantidurga dethroned the last Badami Chalukya king, Kirtivarman I, in 753, ending the dynasty’s rule.
Cultural Feats
- Art and Architecture: The era witnessed the emergence of Vesara architecture, blending South Indian and North Indian styles, epitomized by monuments like the rock-cut temples of Pattadakal, Badami, and Aihole.
- Coinage: Unique Coinage: Chalukya coins bore legends in Nagari and Kannada scripts, featuring symbols like temples, lions, and lotuses.
- Religious Patronage: Initially adherents of Vedic Hinduism, the Chalukyas later embraced Shaivism, fostering sects like Pashupata, Kapalikas, and Kalamukhas, while also promoting Jainism.
Government and Administration:
- Military Prowess: The Chalukya army, comprising infantry, cavalry, and a formidable navy, employed innovative strategies, including intoxicating elephants before battle.
- Administrative Structure: The empire was divided into provinces, districts, and smaller administrative units, with feudal lords governing autonomous regions.
Try this PYQ from CSP 2019:
Q. Building ‘Kalyaana Mandapas’ was a notable feature in the temple construction I the kingdom of:
a) Chalukya
b) Chandela
c) Rashtrakuta
d) Vijayanagara
Post your answers here.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kittur Uprising, Rani Chennamma
Mains level: Women led armed freedom struggles

Introduction
- In 1824, a fleet of 20,000 British soldiers attempted to invade the former princely state of Karnataka, positioning themselves at the foothills of the Kittur fort.
- However, Rani Chennamma, the Queen of Kittur, led a valiant resistance, marking one of the earliest woman-led anti-colonial struggles in India.
Kittur Uprising: Historical Context
- Background: Rani Chennamma’s rebellion against the British East India Company in 1824 is celebrated as a significant event in Karnataka’s political history.
- Revolt Catalyst: The Company’s refusal to recognize Shivalingappa, adopted as the successor of Kittur under the ‘doctrine of lapse’, triggered the conflict.
- Military Confrontation: Rani Chennamma led the Kittur army in a fierce battle against the British forces, resulting in the death of British official John Thackery.
Doctrine of Lapse
- Introduced by Lord Dalhousie in 1848, the Doctrine of Lapse aimed at expanding British territories in India.
- The policy was based on the principle that a princely state without a suitable heir should become part of the British Empire.
- Applied to princely states where the ruler died without a natural or legally adopted male heir, enabling the British to annex those states.
- The policy was seen as illegitimate by many Indian rulers and played a role in the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
- Several states annexed due to this Doctrine, include Satara (1848), Jaitpur (1849), Sambalpur (1849), Udaipur (1850), Jhansi (1853), and Nagpur (1854).
- Prior to the Doctrine of Lapse, princely states had a traditional practice of selecting an heir from a group of candidates known as bhajans.
- The policy was abandoned in 1859, two years after the end of the Company Rule in India.
|
Legacy of Rani Chennamma
- Political Leadership: Rani Chennamma’s role as an astute administrator and seasoned stateswoman is highlighted in historical records.
- Popular Perception: Despite her contributions, Rani Chennamma’s significance in national consciousness emerged later, as Karnataka became a state much later than other regions.
- Historical Interpretation: Folklore and local traditions fondly remember Rani Chennamma’s bravery and resilience, portraying her as a protector and guardian in Kannada lavanis or folk songs.
Post-Rebellion Period
- Imprisonment and Death: Following the British capture of Kittur Fort in 1824, Rani Chennamma and her family were imprisoned. She passed away in captivity in 1829.
- Historical Records: Historians emphasize Rani Chennamma’s commitment to serving her people, even during her imprisonment, as evidenced by her efforts to support her family and people.
Commemoration and Contemporary Relevance
- Naanoo Rani Chennamma Campaign: Social groups across India are organizing a national campaign on February 21, commemorating Rani Chennamma’s rebellion.
- Campaign Objectives: The campaign aims to mobilize women against patriarchal, anti-democratic, and casteist forces, invoking Rani Chennamma’s memory as a symbol of resistance and empowerment.
- Political Significance: The campaign underscores the need for gender equality, representation, and social justice, drawing inspiration from Rani Chennamma’s legacy of courage and leadership.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PAPA, Aditya L1, CMEs
Mains level: NA

Introduction
- India’s pioneering solar mission, Aditya-L1, has achieved a significant milestone as advanced sensors onboard successfully detected the impact of coronal mass ejections (CMEs), marking a leap forward in space exploration.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
- CMEs were discovered in 1971 and established their importance in solar-terrestrial relations later in the 1980s.
- It consists of massive clouds of solar plasma and magnetic field lines.
- It typically accompanies solar flares and filament eruptions.
- The frequency of CMEs varies with the 11-year solar cycle, with about one a week observed during solar minimum and an average of two to three CMEs per day observed near solar maximum
- They travel at thousands of km per hour.
- They can lead to geomagnetic storms, aurorae, and in extreme cases, damage to electrical power grids.
- They are primarily detected using coronagraphs aboard spacecraft such as SOHO and STEREO.
- Not all CMEs interact with Earth, but those that do can cause disruptions to satellite communications and power grids.
- Halo CMEs are Earth-directed CMEs visible as rings in white-light coronagraph observations.
|
About Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA)
- Purpose: PAPA is an energy and mass analyser tailored for in-situ measurements of solar wind electrons and ions within the low energy range.
- Sensor Composition: PAPA comprises two sensors—Solar Wind Electron Energy Probe (SWEEP) and Solar Wind Ion Composition Analyser (SWICAR)—facilitating comprehensive observations of solar phenomena.
- Functionalities: Sensors not only measure electrons and ions’ energy but also ascertain their direction of arrival, enabling a holistic understanding of solar wind dynamics.
CME Detection and Analysis
- Observations: PAPA detected CME events, notably on December 15, 2023, and during February 10-11, 2024.
- December 15, 2023: Single CME event marked by a sudden increase in electron and ion counts, aligning with solar wind parameters and magnetic field measurements.
- February 10-11, 2024: Multiple minor CME events observed, showcasing nuanced variations in electron and ion counts over time.
Performance Evaluation and Continuous Observations
- PAPA sensors are currently operational in default mode, demonstrating adherence to design specifications across all operational modes.
- Continuous observations underscore PAPA’s efficacy in monitoring space weather conditions and its adeptness in detecting and analyzing solar phenomena.
Back2Basics: Aditya-L1
- Launched successfully by ISRO on September 2.
- Orbits around the Lagrangian Point 1 (L1), maintaining a stable position 1.5 million km from Earth in the direction of the Sun.
- Hosts seven payloads dedicated to studying various aspects of the Sun, encompassing both remote observations and in-situ measurements.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Features of ART Regulation 2021
Mains level: Read the attached story

Introduction
- The Central government’s recent modifications to the Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules, 2022 reflect a significant shift in the legal landscape surrounding surrogacy practices in India.
- These amendments address critical issues concerning gamete usage and access to surrogacy procedures.
Why discuss this?
- Judicial Scrutiny: The Supreme Court’s involvement stems from petitions challenging the March 2023 ban on donor gametes for surrogacy, prompting the Centre to reconsider its stance.
- Public Outcry: The judiciary’s intervention follows public outcry and legal challenges from women affected by the previous rules, emphasizing the urgency of addressing surrogacy regulations.
Key Amendments on Gametes Usage
- Gamete Flexibility: The amended rules allow couples certified with medical conditions to use donor gametes for surrogacy, provided at least one gamete originates from the intending couple.
- Single Women’s Directive: Single women, including widows and divorcees, are mandated to use self-eggs and donor sperm for surrogacy, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Certification Criteria: The District Medical Board may certify the need for donor gametes based on the medical condition of either spouse in the intending couple, facilitating access to surrogacy using donor gametes.
About Altruistic Surrogacy and ART
- Definition: Altruistic surrogacy prohibits monetary compensation to the surrogate beyond medical expenses and insurance coverage, fostering ethical practices.
- ART Regulation 2021: The Act integrates Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) governance through the establishment of the National Assisted Reproductive Technology and Surrogacy Board, ensuring effective implementation and oversight.
Evolution of Surrogacy Rules and Amendments
- Ministry Initiative: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare introduced the Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules, 2022, focusing on clinic standards and personnel qualifications.
- Clinical Requirements: The rules specify staffing criteria and essential equipment, enhancing operational standards across registered surrogacy clinics.
- Medical Necessity: Surrogacy is permitted in cases of uterine abnormalities, failed IVF attempts, unexplained pregnancy losses, and pregnancy impossibility due to illness, ensuring access for couples facing diverse challenges.
Key Provisions of Surrogacy (Regulation) Rules, 2022
- Clinic Composition: Registered clinics must employ qualified professionals, including gynecologists, anesthetists, embryologists, and counselors, ensuring comprehensive care.
- Gynecologist Qualifications: Gynecologists must possess relevant post-graduate qualifications and experience in ART procedures, ensuring competency in assisted reproduction techniques.
- Insurance Coverage: Mandatory health insurance for surrogate mothers safeguards their well-being during and after pregnancy, reflecting a commitment to maternal health.
- Affidavit Requirement: Intending couples must provide a legal guarantee of compliance with surrogacy regulations, ensuring accountability and adherence to legal standards.
- Embryo Implantation Limit: Strict guidelines limit embryo implantation to minimize health risks and ethical concerns, prioritizing the well-being of both surrogate mothers and unborn children.
- Abortion Protocol: Surrogate mothers’ rights are protected through adherence to established abortion procedures, respecting their autonomy and ensuring medical safety.
Tap to read more about:
Exemptions under Surrogacy Law
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Singhbhum Craton, Archaen Eon
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
- Some recent study about the Singhbhum Craton in India, reveals that explosive volcanic eruptions were frequent around 3.5 billion years ago in regions that are also present in South Africa, and Australia.
What are Cratons?
- Cratons are stable, ancient portions of the continental lithosphere, consisting of Earth’s two topmost layers—the crust and the uppermost mantle.
- Cratons are typically found in the interiors of tectonic plates and are characterized by their ancient crystalline basement rock, often dating back to the Archean Eon.
- Mantle plume events have played a significant role in the evolution of cratons.
About Singhbhum Craton:
- The Singhbhum Craton is a geological region in India.
- Location: It is located in eastern India, covering parts of the states of Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal. The craton is separated from the Bastar Craton by the Mahanadi Graben and is in the vicinity of two Proterozoic mobile belts: the Satpura Mobile Belt and the Eastern Ghat Mobile Belt.
- Geological features:
- The rocks in the Singhbhum Craton are predominantly of Archean age, ranging from Paleoarchean to Paleoproterozoic.
- It is a part of the larger Indian Shield, which is a stable continental crust that formed during the Archean Eon.
- The Singhbhum Craton is known for its abundant occurrences of Banded Iron Formations (BIFs), which are closely associated with basic volcanic and ultrabasic intrusive. The craton is also known for its iron ore deposits, which are found in the Iron Ore Group (IOG) and are closely associated with lavas and tuffs.
- The Singhbhum Craton has undergone regional metamorphism of the amphibolite facies and is believed to have evolved as a consequence of multiple phases of compressive deformation.
- The craton is made up of multiple pulses of discrete mantle plume events, resulting in a complex geological history.
Archaean Eon

- The Archaean Eon, one of the two formal divisions of Precambrian time, began about 4 billion years ago and extended to the start of the Proterozoic Eon.
- During this period, life on Earth was limited to simple single-celled organisms lacking nuclei, known as Prokaryota.
- The atmosphere lacked oxygen, and the Earth’s crust had cooled enough to allow the formation of continents.
- Volcanic activity was considerably higher than today, with numerous lava eruptions.
- The oldest rock formations exposed on Earth are from the Archaean Eon.
- The Archaean rock system includes Archaean Gneisses and Schists, which are the oldest metamorphosed rocks found in abundance in regions like the Dharwar district of Karnataka.
|
What are the recent key findings?
- Submarine Mafic Volcanism: The prevalence of submarine mafic volcanic eruptions between 3.5 and 3.3 billion years ago is documented, enriching our understanding of ancient volcanic and sedimentary processes.
- Geodynamic Insights: Comparative analysis enhances our comprehension of early Earth tectonic activities and surface/atmospheric processes during the Archaean.
Research Methodology Used:
- Field Studies and Radiometric Dating: Detailed field-based studies coupled with uranium-lead radiometric-age dating were employed to establish geological timelines and understand magma crystallization.
- Comparative Analysis: The geological similarities between the Singhbhum Craton and counterparts in South Africa and Australia were studied, focusing on volcanic eruption patterns.
Implications and Significance of the study:
- Earth’s Formative Years: Insights into Earth’s early tectonic activities contribute significantly to understanding the planet’s formative years.
- Habitable Conditions: Unique geological features, such as greenstone belts, provide invaluable information about early habitable conditions and the emergence of life.
- Global Geodynamic Processes: Comparative studies across cratons worldwide facilitate the construction of comprehensive models elucidating ancient geodynamic processes prevalent during the Archaean.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Super Pollutants types
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
- Recently, the annual meeting of the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) which took place from 21 to 23 February 2024 in Nairobi, Kenya on the margins of the Sixth session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA-6) highlighted the critical importance of international collaboration in combating short-lived climate pollutants, commonly known as “Super Pollutants.”
What are Super Pollutants?
- Super pollutants, or short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs), have a shorter atmospheric lifespan compared to CO2 but significantly impact climate change and air quality. Methane (CH4), black carbon (soot), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and tropospheric ozone (O3) are some of the major superpollutants.
Impacts of Super Pollutants
- Methane (CH 4):
- Characteristics: Potent greenhouse gas emitted from various sources such as livestock and fossil fuel production.
- Its Impact: Traps heat in the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
- Black Carbon (Soot):
- Characteristics: Fine particulate matter from incomplete combustion of fuels.
- Its Impact: Absorbs sunlight, heats the atmosphere, and accelerates the melting of snow and ice.
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs):
- Characteristics: Synthetic greenhouse gases used in refrigeration.
- Its Impact: High global warming potential despite short atmospheric lifespan.
- Tropospheric Ozone (O3):
- Characteristics: Secondary pollutants formed from VOCs and NOx.
- Its Impact: Contributes to smog, has adverse health effects, and acts as a greenhouse gas.
About Climate and Clean Air Conference 2024:
- What is the aim and objective?
- The CCAC 2024 moved the dialogue forward, focusing on the cost of inaction, highlighting ways to further scale up implementation of the Global Methane Pledge, Clean Air Flagship and Kigali Amendment, and collectively charting the course to 2025 and beyond.
- What did the CCAC 2024 Feature for?
- National policy and planning: High-level plenary sessions on global, regional and national efforts to reduce methane, black carbon, and HFCs, including the benefits of fast action, and financing for implementation.
- Science and Technology: Science Policy Dialogue sessions on latest emerging science and how new information can inform policy development. Technical sessions among CCAC Sector Hub members to showcase best practices in key emitting sectors: agriculture, cooling, fossil fuels, heavy-duty vehicles and engines, household energy, and waste.
- Focus on Implementation: Practical sessions to further refine work plans among CCAC National Consultants; Non-State Partners and Scientific Advisory Panel Members.
- What are the Functions?
- The CCAC works at the nexus of climate and air quality, to deliver multiple benefits from the fast mitigation of short-lived climate pollutants.
- Driven by policy-relevant science and pragmatism, CCAC works from the ground up, equitably and inclusively, empowering our partners to achieve their respective National Goals and catalyzing action — as well as from the top down, bringing together ministers and leaders to drive high-level ambition.
- About the previous Conference:
- The CCAC 2023 was held in Bangkok.
- As an outcome of this conference, CCAC 2023 integrated planning on climate and clean air is essential to identify priority actions in key emitting sectors to scale up mitigation, and action at the national and regional level is motivating collaboration at the global scale.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AEgIS Initiative , Positronium
Mains level: NA
Why in the News?
- For the first time, an international team of physicists from the Anti-hydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy (AEgIS) collaboration has achieved a breakthrough by demonstrating the laser cooling of Positronium.
What is Positronium?
- Positronium comprises a bound electron (e-) and a positron (e+), forming a fundamental atomic system.
- What are its Properties?
- Concise (short) life where it annihilates with a half-life of 142 nanoseconds.
- Its mass is twice the electron mass, and it is considered a pure leptonic atom.
- Its hydrogen-like system, with halved frequencies for excitation, makes it ideal for attempting laser cooling and performing tests of fundamental physics theories.
About AEgIS Initiative
- Timeline: The AEgIS experiment was formally accepted by CERN in 2008, with construction and commissioning continuing through 2012-2016.
- Team: Physicists representing 19 European and one Indian research group from the AEgIS collaboration announced this scientific breakthrough.
- Experiment Location: The experiment was conducted at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Why this is significant? This experiment serves as a crucial precursor to the formation of anti-hydrogen and the measurement of Earth’s gravitational acceleration on antihydrogen in the AEgIS experiment.
Key Outcomes
- Temperature Reduction: Laser cooling initially brought Positronium atoms from ~380 Kelvin to ~170 Kelvin.
- Laser System: A 70-nanosecond pulse of the alexandrite-based laser system was used to demonstrate cooling in one dimension.
- Frequency Bands: Lasers deployed were either in the deep ultraviolet or infrared frequency bands.
Future Implications
- Spectroscopic Comparisons: Physicists expect this experiment to pave the way for performing spectroscopic comparisons required for Quantum Electrodynamics (QED).
- Potential Applications: The experiment allows for high-precision measurements of properties and gravitational behavior of Positronium, offering insights into newer physics and the production of a positronium Bose–Einstein condensate.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Food Security Act (NFSA)
Mains level: demands of farmers for a legal guarantee of Minimum Support Prices (MSP) in India

Central Idea:
The article discusses the ongoing demands of farmers for a legal guarantee of Minimum Support Prices (MSP) in India, highlighting the necessity of such a mechanism to stabilize agricultural commodity prices and support farmers’ incomes. It addresses misconceptions surrounding MSP, emphasizing its importance in insulating farmers from market price volatility and rectifying imbalances in agricultural productivity and regional procurement.
Key Highlights:
- Farmers are demanding a legal guarantee for MSP to ensure price stability and protect their incomes.
- MSP has been a longstanding mechanism in India to stabilize agricultural commodity prices, but its implementation has been limited.
- Misconceptions about the fiscal costs and operational aspects of MSP have led to hesitancy in legalizing it, despite political consensus.
- Government procurement under MSP primarily benefits consumers, not farmers, as it fulfills obligations under the National Food Security Act (NFSA).
- Expansion of MSP to cover a wider range of crops and regions is necessary to address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity and support crop diversification.
Key Challenges:
- Misunderstanding of MSP’s fiscal implications and operational requirements.
- Limited government intervention beyond rice and wheat procurement, leading to neglect of other crops and regions.
- Concerns over excessive government expenditure and market distortions.
- Ensuring effective implementation and monitoring of MSP across diverse agricultural sectors and regions.
Main Terms or keywords for answer writing:
- Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- National Food Security Act (NFSA)
- Market Price Volatility
- Agricultural Commodity Procurement
- Price Stability
- Geographical Imbalances
- Crop Diversification
Important Phrases for answer quality enrichment:
- Legal Guarantee for MSP
- Price Stability Mechanism
- Market Price Volatility
- Government Intervention in Agricultural Markets
- Regional Imbalances in Agricultural Productivity
- Income Protection for Farmers
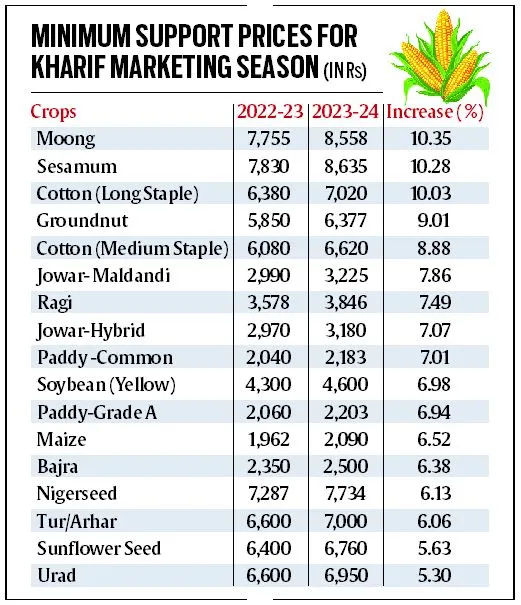
Quotes:
- “A guaranteed MSP may not solve the farmers’ problems. But it offers a good opportunity to rectify the imbalances in the MSP and procurement system.”
- “Price stability will protect the average consumer from the vagaries of inflation.”
- “Protecting the income of farmers will help revive the rural economy.”
Anecdotes:
- Instances of government procurement primarily benefiting consumers rather than farmers, highlighting the need for MSP reform.
- Farmers’ struggles with declining real incomes and wages, reflecting long-standing neglect of the agrarian economy.
Useful Statements:
- “Misconceptions surrounding the fiscal costs of MSP overlook its role in stabilizing prices and supporting farmers’ incomes.”
- “Expansion of MSP to cover a wider range of crops and regions is necessary to address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity.”
Examples and References:
- Government procurement data for rice and wheat compared to other crops, illustrating limited intervention beyond major staples.
- Comparative analysis of MSP implementation in India and other countries with similar price stabilization mechanisms.
Facts and Data:
- Government procurement figures for rice and wheat in recent years.
- Estimates of the potential fiscal costs of implementing a legal guarantee for MSP.
- Statistics on declining real incomes and wages in the agrarian sector.
Critical Analysis:
- Emphasizes the importance of MSP in stabilizing agricultural prices and supporting farmer livelihoods.
- Addresses misconceptions and challenges surrounding MSP implementation.
- Advocates for reforms to expand MSP coverage and address regional imbalances in agricultural productivity.
Way Forward:
- Implement legal guarantee for MSP to ensure price stability and support farmer incomes.
- Expand MSP coverage to include a wider range of crops and regions.
- Enhance monitoring and evaluation mechanisms to ensure effective implementation of MSP.
- Address misconceptions and concerns regarding fiscal costs and market distortions associated with MSP.
Overall, the article underscores the necessity of legalizing MSP to support farmers’ incomes, stabilize agricultural prices, and address long-standing neglect in the agrarian sector. It advocates for comprehensive reforms to expand MSP coverage and ensure its effective implementation across diverse agricultural sectors and regions.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
Mains level: challenges faced by low-income households in India in accessing LPG
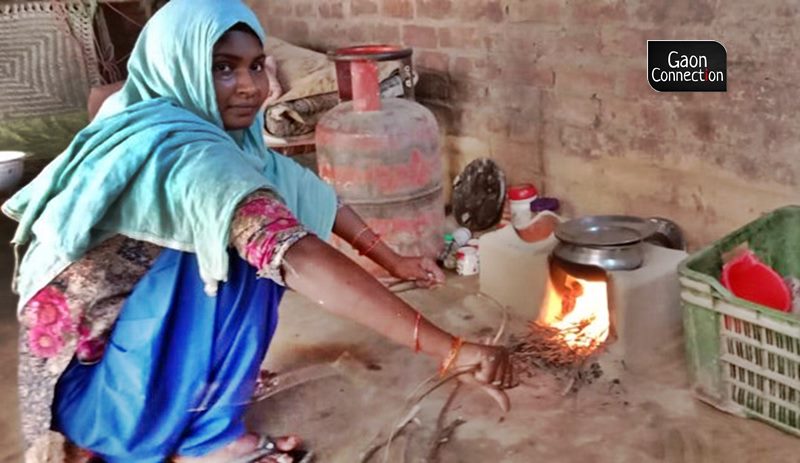

Central Idea:
The article highlights the challenges faced by low-income households in India in accessing LPG refills despite government subsidies under the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY). It suggests reforms to the existing subsidy program to make it more effective, including on-time subsidy transfers and the use of digital payment solutions.
Key Highlights:
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) aims to provide LPG access to low-income households in India.
- Despite subsidies, many households still rely on biomass for cooking due to liquidity constraints.
- Existing subsidy policies have evolved rapidly, but they may not adequately address the needs of PMUY households.
- Data analysis reveals that PMUY consumers are sensitive to the amount and timing of refill subsidies.
- Upfront subsidies, like those provided during the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY), can significantly increase LPG usage.
- Fin-tech solutions, such as electronic subsidy transfers and digital vouchers, can alleviate the financial burden of refill purchases.
Key Challenges:
- Ensuring subsidy benefits reach the intended beneficiaries without leakage.
- Addressing liquidity constraints faced by low-income households.
- Educating households about subsidy timing and logistics.
- Overcoming credit constraints, especially for daily wage earners.
- Implementing digital payment solutions effectively in rural areas.
Main Terms or keywords for answer writing:
- LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
- PMUY (Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana)
- PAHAL (Pratyaksh Hanstantrit Labh)
- PMGKY (Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana)
- Fin-tech (Financial Technology)
- e-RUPI (Electronic Rupee)

Important Phrases for quality enrichment of mains answer:
- Liquidity constraint
- Direct benefit transfer
- Upfront subsidy
- Digital voucher
- Electronic payment
- Delayed subsidy transfer

Quotes for value addition:
- “Low-income households are sensitive to the amount and timing of refill subsidy.”
- “An upfront subsidy transfer can increase the demand for LPG refills significantly.”
- “Digital payment solutions hold promise in alleviating the financial burden of refill purchases.”
Anecdotes:
- The Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) saw a spike in LPG consumption among low-income households during the period of upfront subsidy provision.
Useful Statements:
- “Ensuring subsidy benefits reach the intended beneficiaries without leakage is crucial for the success of LPG subsidy programs.”
- “Digital payment solutions can address liquidity constraints and improve access to LPG refills for low-income households.”
Examples and References:
- Data from Indore district reveals the sensitivity of PMUY consumers to refill market prices and subsidy amounts.
- The success of the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) in increasing LPG usage among low-income households serves as a relevant example.
Facts and Data:
- Before PMUY, a high percentage of rural households in India used biomass for cooking.
- PMUY households have lower LPG refill consumption compared to non-PMUY households.
- A significant increase in refill subsidy decreases monthly consumption by about 25% for PMUY consumers.
Critical Analysis:
- The article effectively identifies the challenges hindering the effectiveness of LPG subsidy programs for low-income households.
- It provides data-driven insights into consumer behavior and the impact of subsidy policies.
- The proposed fin-tech solutions offer practical approaches to address liquidity constraints and improve subsidy delivery.
Way Forward:
- Implement electronic payment solutions and digital vouchers to facilitate on-time subsidy transfers.
- Educate households about subsidy timing and logistics to improve awareness.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate subsidy programs to ensure effectiveness and address any emerging challenges.
- Collaborate between government ministries, fin-tech companies, and local stakeholders to implement reforms successfully.
By addressing these challenges and implementing innovative solutions, India can enhance LPG access for low-income households and accelerate its energy transition goals.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Exercise Dosti
Mains level: Not Much

Introduction
- Indian and Sri Lankan coast guard ships recently arrived in the Maldives to participate in the trilateral coast guard exercise Dosti 16.
Exercise Dosti
- Trilateral Collaboration: Dosti is a trilateral coast guard exercise involving India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives.
- Biennial Event: Conducted biennially, the exercise serves as a platform for enhancing cooperation and interoperability among participating nations.
- Inception: Initiated in 1991 between the Indian and Maldives Coast Guards, with Sri Lanka joining in 2012.
- Previous Editions: The exercise, last held in 2021, focuses on various maritime scenarios, including search and rescue operations and pollution response.
Objectives and Focus Areas
- Enhancing Friendship: Dosti aims to strengthen the bonds of friendship and mutual trust among the coast guards of participating nations.
- Operational Capability: The exercise emphasizes enhancing operational capability and interoperability through joint drills and exercises.
- Maritime Safety: Exercises and drills focus on providing assistance during sea accidents, combating sea pollution, and addressing challenges like oil spills.
Dosti 16: Current Edition
- Edition Details: Dosti 16 marks the 16th edition of the exercise, continuing the tradition of fostering maritime cooperation.
- Participating Forces: The coast guards of India, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives, along with observers from Bangladesh, are actively participating.
- Indian Contribution: India’s participation includes vessels like ICGS Samarth (with integral helo), ICGS Abhinav, and ICG Dornier, showcasing its commitment to regional maritime security.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: National Education Policy (NEP)
Mains level: benefits and challenges of open-book exams
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gross Domestic Product
Mains level: critique of the prevailing GDP-centric approach to economic development

Central Idea:
The central idea of the article is that traditional measures of economic growth, like GDP, are inadequate indicators of a nation’s well-being and development. Instead, the focus should shift towards inclusive and sustainable growth that prioritizes the welfare of citizens, particularly in countries like India where economic progress has not translated into improved living standards for all.
Key Highlights:
- Critique of GDP-centric approach: The article highlights the limitations of relying solely on GDP growth as a measure of economic health, pointing out that it doesn’t necessarily lead to increased income or well-being for citizens.
- Inequality and inequitable growth: Despite impressive GDP growth, India remains one of the most unequal countries in the world, indicating that the benefits of growth are not evenly distributed among its citizens.
- Need for a new paradigm: The article argues for a shift towards inclusive and environmentally sustainable development models, especially in the face of global challenges like climate change.
- Dependency on fossil fuels: The reliance on fossil fuels for essential materials like steel, concrete, plastics, and food production is highlighted, along with the challenges of transitioning away from them.
- Importance of local solutions: Emphasizing the significance of community-driven, local solutions, the article suggests that India should leverage its unique strengths rather than blindly following Western development models.
Key Challenges:
- Overcoming entrenched economic paradigms: Shifting away from GDP-centric models towards more inclusive and sustainable development approaches requires challenging existing economic frameworks and ideologies.
- Addressing inequality: Tackling the deep-rooted inequalities in India’s economy presents a significant challenge, especially given the historical focus on GDP growth.
- Transitioning from fossil fuels: Moving away from fossil fuel dependency poses technological, economic, and social challenges, particularly in sectors like agriculture and transportation.
- Balancing urbanization and rural development: Reconciling the push for urbanization with the need for rural development and sustainable agriculture presents complex policy dilemmas.
- Overcoming resistance to change: Convincing policymakers and society at large to embrace alternative development paradigms may face resistance from entrenched interests and ideologies.
Main Terms:
- GDP: Gross Domestic Product, a measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders.
- Inclusive growth: Economic growth that benefits all segments of society, particularly the marginalized and vulnerable.
- Sustainable development: Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Fossil fuels: Non-renewable energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas, formed from the remains of prehistoric plants and animals.
- Urbanization: The process of population concentration in urban areas, often accompanied by industrialization and economic development.
Important Phrases:
- “Increase the size of the pie before its redistribution”: Reflects the emphasis on GDP growth over equitable distribution of wealth.
- “One path for all”: Criticizes the uniform approach to development that privileges industrialization and urbanization over other forms of progress.
- “Gandhian solution”: Refers to community-driven, localized approaches to development advocated by Mahatma Gandhi.
- “Rural Bharat”: Signifies the rural heartland of India, highlighting the importance of rural communities in the country’s development.
Quotes:
- “More GDP does not improve the well-being of citizens if it does not put more income in their pockets.”
- “India must find a new paradigm of progress, for itself and for the world, for more inclusive and environmentally sustainable growth.”
- “The time has come to go back to old solutions to go to the future.”
Useful Statements:
- “Critics argue that GDP growth alone does not necessarily lead to improved living standards for citizens, particularly in countries like India where inequality persists.”
- “Transitioning away from fossil fuels presents significant challenges, but it is essential for addressing climate change and ensuring long-term sustainability.”
- “Local, community-driven solutions have the potential to address global challenges like climate change and inequitable economic growth.”
Examples and References:
- The article cites India’s experience of impressive GDP growth alongside persistent inequality as evidence of the limitations of traditional development models.
- Reference is made to the work of Vaclav Smil on the role of fossil fuels in modern economies, providing a scientific basis for understanding the challenges of transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Facts and Data:
- India’s GDP grew at 7.2% per year during both the United Progressive Alliance and National Democratic Alliance governments, yet structural conditions leading to inequitable growth remained unchanged.
- Sixty-four per cent of Indian citizens live in rural areas, highlighting the importance of rural development in India’s economic and social progress.
Critical Analysis:
The article provides a compelling critique of the prevailing GDP-centric approach to economic development, highlighting its failure to address inequality and environmental concerns. By advocating for inclusive and sustainable growth models, the article offers a nuanced perspective on the challenges facing countries like India in the 21st century. However, it could benefit from further exploration of specific policy recommendations and case studies demonstrating successful alternative development strategies.
Way Forward:
- Embrace inclusive and sustainable development models that prioritize the well-being of all citizens.
- Invest in renewable energy sources and sustainable agriculture to reduce dependency on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
- Empower local communities to drive development initiatives tailored to their unique needs and challenges.
- Reform economic policies to prioritize equitable distribution of wealth and opportunities.
- Foster international cooperation to address global challenges like climate change and inequality.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now












