Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Peninsular Rock Agama
Mains level: Not Much

A study carried out by researchers from Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, undertook to characterise urbanisation in the region and also to understand where the rock agama reside in and around Bengaluru specifically.
Why in news?
- The study examined several environmental factors that could affect the presence of the lizard and revealed that they are found mainly in rocky places and warm spots.
- Thus, the inference is that conservation efforts must point towards retaining rocky patches even while reviving landscapes by planting trees.
Peninsular Rock Agama
- The Peninsular Rock Agama (Psammophilus dorsalis) is a type of garden lizard has a strong presence in southern India.
- This lizard is a large animal, strikingly coloured in orange and black.
- They do not generate their own body heat, so they need to seek warmth from external sources like a warm rock or a sunny spot on the wall.
- They are important in ecology from different aspects — they can indicate which parts of the city are warming, and their numbers show how the food web is changing.
- Habitat loss and other such features of urbanisation have affected the presence of the animal in urban centres.
Why study them?
- Insects are critical components of a healthy ecosystem as they provide so many services, including pollination.
- So, while rock agamas are interesting in themselves, they are also a good model system to understand other aspects of the ecosystem.
- In cities such as Bengaluru, there is a lot of flora and fauna that is rapidly disappearing.
- The rock agama is one such species which is dependent on rocky scrub habitats which are being converted into buildings and plantations.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: particulars of artemis mission
Mains level: NA
NASA’s Artemis 1 mission has sought unexpected delay due to fuel leakages issue.
What is the Artemis I Mission?
- NASA’s Artemis mission is touted as the next generation of lunar exploration, and is named after the twin sister of Apollo from Greek mythology.
- Artemis is also the goddess of the moon.
- Artemis I is the first of NASA’s deep space exploration systems.
- It is an uncrewed space mission where the spacecraft will launch on SLS — the most powerful rocket in the world — and travel 2,80,000 miles from the earth for over four to six weeks during the course of the mission.
- The Orion spacecraft is going to remain in space without docking to a space station, longer than any ship for astronauts has ever done before.
- The SLS rocket has been designed for space missions beyond the low-earth orbit and can carry crew or cargo to the moon and beyond.
Key objectives of the mission
- With the Artemis Mission, NASA aims to land humans on the moon by 2024, and it also plans to land the first woman and first person of colour on the moon.
- With this mission, NASA aims to contribute to scientific discovery and economic benefits and inspire a new generation of explorers.
- NASA will establish an Artemis Base Camp on the surface and a gateway in the lunar orbit to aid exploration by robots and astronauts.
- The gateway is a critical component of NASA’s sustainable lunar operations and will serve as a multi-purpose outpost orbiting the moon.
Other agencies involved
- Other space agencies are also involved in the Artemis programme.
- The Canadian Space Agency has committed to providing advanced robotics for the gateway.
- The European Space Agency will provide the International Habitat and the ESPRIT module, which will deliver additional communications capabilities among other things.
- The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency plans to contribute habitation components and logistics resupply.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Taiwan Strait
Mains level: One China Policy

India has for the first time referred to what it called “the militarization of the Taiwan Strait”, marking a rare instance of New Delhi appearing to comment on China’s actions towards Taiwan.
What is the news?
- Two American warships have recently sailed very close to China through Taiwan Strait.
- This has intimidated the China which is already fuming due to the visit of Nancy Pelosi.
Taiwan Strait
- The Taiwan Strait is a 180-kilometer wide strait separating the island of Taiwan and continental China (and Asia of course).
- The strait is part of the South China Sea and connects to the East China Sea to the north.
- The narrowest part is 130 km wide.
Issues over Taiwan Strait
- The Taiwan Strait is itself a subject of an international dispute over its political status.
- China claims to enjoy sovereignty, sovereign rights and jurisdiction over the Taiwan Strait” and regards the waterway as “internal territorial waters” instead of being international waters.
- This means that the Chinese government denies any foreign vessel having the freedom of navigation in the strait.
- This position has drawn strong objections from the western World.
India’s change of stance
- India has followed a “One China policy” since its recognition of the PRC in 1949, and only maintains trade and cultural relations with Taiwan.
- India routinely reiterated this policy until 2008 after which it stopped mentioning it in official statements.
- This is a demand that China usually asks of most countries in official declarations.
Why is India shifting its stance?
- China often make provocative statements claiming Arunachal Pradesh.
- It often moves to issue “stapled visas” to Indian citizens in Jammu and Kashmir and Arunachal.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Gorkha regiment
Mains level: Indian Army
Nepal has postponed the recruitment rallies which were to be held in that country to recruit Gorkha soldiers for the Indian Army under the Agnipath scheme.
Why has Nepal postponed Agnipath recruitment rallies?
- Nepal is of the opinion that this new form of entry into the Indian military is not covered under the Tripartite Agreement signed between Nepal, Indian and UK governments in 1947, soon after Indian independence.
- The government feels that the Agnipath scheme must be approved by it and for that political consultations with all parties in Nepal must take place.
- This is move is visibly ‘inspired’ with inputs from China.
What was the Tripartite Agreement between India, Nepal and UK?
- Soon after Indian Independence on August 15, 1947, an agreement was reached by the governments of India, Nepal and the UK regarding the future of the Gorkha soldiers who were serving in the Indian Army.
- As per the terms of this agreement four regiments of Gorkha soldiers – 2nd, 6th, 7th and 10th – were transferred to the British Army while the rest – 1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 8th and 9th – remained with the Indian Army.
- A new Gorkha Regiment, the 11th Gorkha Rifles, was raised by India soon after Independence.
- The agreement also provides for the terms and conditions of the Nepal-domiciled Gorkha soldiers in the Indian Army and for their post-retirement benefits and pensions.
Significance of Gorkha Soldiers
- Legend has it that Hitler’s very words were, “If I had Gurkhas, no army in the world could defeat me.”
- An interesting historical aspect of Gorkha troops is that Pakistan, at the time of Independence, and China, soon after the 1962 war, had also requested Nepal for Gorkha soldiers.
- However, this request was turned down by the Nepal government.
- The largest body of Gorkha troops serves in the Indian Army while in the UK their presence has been reduced from four regiments to just two.
Can Nepalese Gorkhas in foreign Armies be called mercenaries?
- Mercenaries are understood as fighters who take part in a conflict for financial gain and usually are not parties to that conflict.
- As per the definition of the 1949 Geneva Convention, gives the officially agreed definition of a mercenary.
- It says that soldiers serving in sovereign armies are not considered mercenaries, and Gorkha soldiers cannot be called mercenaries.
- In addition, Gorkha soldiers from Nepal serve side-by-side with Gorkha soldiers who are born and brought up in India.
Have any changes been made in Gorkha unit recruitments over the years?
- There have been attempts to reduce the dependence on Nepal for the Gorkha soldiers in the Indian Army,
- To this effect, the composition has increasingly been attempted to be balanced between Indian and Nepal-domiciled troops.
- Also, a pure Indian Gorkha battalion was raised in 2016.
- This unit, 6th Battalion of the 1st Gorkha Rifles (6/1 GR), was raised in Subathu, in Himachal Pradesh.
- Otherwise, the ratio of Nepalese-domiciled soldiers and Indian-domiciled soldiers in a Gorkha battalion ranges from 60:40 to 70:30, though this will change further in future.
- A change was made in the recruitment rules for Gorkha Rifles recently when the Army decided that soldiers hailing from the Kumaon and Garhwal regions of Uttarakhand will also be eligible for serving in Gorkha Rifles.
What is the socio-economic impact on Nepal of Gorkha soldiers serving in the Indian Army?
- A major economic and social impact is felt in Nepal due to the Nepal-domiciled Gorkha soldiers serving in the Indian Army and much of it has to do with the remittances that they send home.
- Kathmandu receives a sustainable source of remittances from Gorkhas working in foreign armies.
- This has significantly contributed to social modernization in the isolated villages, while the financial remittances spurred entrepreneurship development thereby contributing to regional development.
Why induct Gorkha soldiers?
- Gorkha soldiers are tough. Living in the hills of Nepal makes them strong and resilient and they can stand war, climate and terrain better than most.
- No one can match their swift movement in the mountainous terrain.
- They are cheerful in disposition and nothing disturbs their equanimity.
- They are loyal to the core and fearless in battle.
- All this makes them amongst the best soldiers in the world and they are much sought after.
- Historically, they have deep rooted connection and affinity for India definitely due to cultural assimilations.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Government e-Marketplace
Mains level: Read the attached story

Government e-Marketplace (GeM), a national procurement portal, is eyeing annual procurement worth ₹2 lakh crore during FY23. Such a huge amount it is!
Government e-Marketplace
- GeM is an online platform for public procurement in India by various Government Departments / Organizations / PSUs.
- The initiative was launched on August 9, 2016 by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry with the objective to create an open and transparent procurement platform for government buyers.
- It is owned by GeM SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle) which is a 100 per cent Government-owned, non-profit company under the Ministry of Commerce and Industries
- GeM aims to enhance transparency, efficiency and speed in public procurement.
- It provides the tools of e-bidding, reverse e-auction and demand aggregation to facilitate the government users achieve the best value for their money.
- The purchases through GeM by Government users have been authorized and made mandatory by Ministry of Finance.
Note: The government has made it mandatory for sellers on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal to clarify the country of origin of their goods when registering new products.
Advantages for Buyers
- Offers rich listing of products for individual categories of Goods/Services
- Makes available search, compare, select and buy facility
- Enables buying Goods and Services online, as and when required.
- Provides transparency and ease of buying
- Ensures continuous vendor rating system
- Up-to-date user-friendly dashboard for buying, monitoring supplies and payments
- Provision of easy return policy
Advantages for Sellers
- Direct access to all Government departments.
- One-stop shop for marketing with minimal efforts
- One-stop shop for bids / reverse auction on products / services
- New Product Suggestion facility available to Sellers
- Dynamic pricing: Price can be changed based on market conditions
- Seller friendly dashboard for selling, and monitoring of supplies and payments
- Consistent and uniform purchase procedures
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Undemarcated Protected Forests
Mains level: Not Much
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has objected to the transfer of thousands of hectares of land without following due process by Chhattisgarh from its Forest to the Revenue Department for setting up industries and for building road, rail, and other infrastructure.
What is the news?
- The Union Environment Ministry has warned that the land in question is “undemarcated protected forests”, which cannot be used for non-forest purposes without clearance under the Forest Conservation (FC) Act, 1980.
‘Types of Forests’ in Law
- Broadly, state Forest Departments have jurisdiction over two types of forests notified under the Indian Forest (IF) Act, 1927:
- Reserve Forests (RF): where no rights are allowed unless specified and
- Protected Forests (PF): where no rights are barred unless specified
- Certain forests, such as village or nagarpalika forests, are managed by state Revenue Departments.
- The FC Act, 1980, applies to all kinds of forests, whether under the control of the Forest or the Revenue Department.
- It requires statutory clearance before forests can be used for any non-forest purpose such as industry, mining, or construction.
- In 1976, forests were included in List III (Concurrent List) under the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
Chhattisgarh case
- The recorded forest area in Chhattisgarh covers 44.21% of its geography.
- The state government says it is constrained by the limited availability of land, particularly in the tribal regions, for development works.
- Therefore, in May 2021, it sought a field survey to identify non-forest land — parcels smaller than 10 hectares with less than 200 trees per hectare.
Orange, a grey area
- It sought that the forests had been included by mistake in Orange Areas under the Forest Department.
- This year, it announced that over 300 sq km of “Orange” area in the Bastar region had been handed over to the Revenue Department.
- Under the zamindari system, villagers used local malguzari (livelihood concessions) forests for firewood, grazing, etc.
- When zamindari was abolished in 1951, malguzari forests came under the Revenue Department.
- In 1958, the government of undivided Madhya Pradesh notified all these areas as Protected Forest (PFs) under the Forest Department.
- Through the 1960s, ground surveys and demarcations of these PFs continued — either to form blocks of suitable patches to be declared as Reserve Forests, or to denotify and return to the Revenue Department.
- For this purpose, Madhya Pradesh amended the IF Act, 1927, in 1965 — when forests figured in the State List — to allow denotification of PFs.
- The areas yet to be surveyed — undemarcated PFs — were marked in orange on the map.
Policy jam
- Since 2003, a case has been pending in the Supreme Court on rationalising these orange areas that have remained a bone of contention between the two Departments.
- The transfer of PFs to the Revenue Department continued until 1976, when reports of illicit felling in Revenue areas prompted Madhya Pradesh to seek a fresh survey to shift quality forest patches.
- But before this survey could be undertaken, the new government that came to power in the state in 1978 switched the focus to settling encroachments.
- The FC Act came in 1980, and required central clearance for non-forest use of forest land.
- This led to a situation where the rights of lakhs of villagers, including those settled by the government through pattas, remained restricted.
After MP was split
- Carved out of Madhya Pradesh in 2000, Chhattisgarh inherited its share of ‘orange’ areas.
- Ranked second after Orissa in implementing the Forest Rights Act, 2006, the state has settled over 26,000 claims since 2019.
- The logical next step, say officials who declined to be quoted, was to find land for the economic development of the tribal belt.
- Chhattisgarh did not seek central clearance to transfer over 300 sq km to Revenue, they claim, because it did not have to.
New definition of forests
- In December 1996, the SC defined ‘forest’ after its dictionary meaning, irrespective of the status of the land it stands on.
- It also defined forestland as any land thus notified on any government record irrespective of what actually stands on that land.
- To meet this broad definition, Madhya Pradesh in 1997 framed a “practical yardstick” — an area no smaller than 10 hectares with at least 200 trees per hectare — to identify forests in Revenue areas for handing over to the Forest Department.
- These non-forest areas, they claim, are now being identified and returned to the Revenue.
Issues with such Un-forestation
- The nature of vegetation changes over time.
- After so many years, a visual survey cannot determine if a particular piece of land did not meet the definition of forest.
- Once brought under the Forest Department, whether mistakenly or otherwise, an area gets the status of forestland as per the 1996 SC order, and hence comes under the FC Act, 1980.
Options available for CG
- Chhattisgarh, thanks to the 1965 amendment to the IF Act, can still denotify PFs unilaterally.
- It may also vest management of any land with any department since the state owns all land within its boundaries.
- But if the stated purpose is non-forest use — building industries and infrastructure — the state will anyway require central clearance under the FC Act, 1980.
What lies ahead?
- Clearance for non-forest use of forestland under the FC Act requires giving back twice the area for compensatory afforestation (CA) from Revenue to Forest.
- That would defeat the very purpose of the state government’s action.
- However, conversion of Forest to Revenue land has been exempted from CA under exceptional circumstances in the past.
- For example, when enclaves were moved out of forests, the SC allowed those to be resettled at the edge of the forests, in the absence of suitable Revenue land, as revenue villages.
- It will be a stretch, though, for such considerations to apply to thousands of hectares meant for industries.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Ozone, Ozone Hole
Mains level: Ozone recovery

The concentration of ozone-depleting substances in the atmosphere has reduced to reach a significant milestone this year.
What is Ozone and Ozone Layer?

- An ozone molecule consists of three oxygen atoms instead of the usual two (the oxygen we breathe, O2, makes up 21% of the atmosphere).
- It only exists in the atmosphere in trace quantities (less than 0.001%), but its effects are very important.
- Ozone molecules are created by the interaction of ultra-violet (UV) radiation from the Sun with O2 molecules.
- Because UV radiation is more intense at higher altitudes where the air is thinner, it is in the stratosphere where most of the ozone is produced, giving rise to what is called the ‘ozone layer’.
- The ozone layer, containing over 90% of all atmospheric ozone, extends between about 10 and 40km altitude, peaking at about 25km in Stratosphere.
Why need Ozone Layer?
- The ozone layer is very important for life on Earth because it has the property of absorbing the most damaging form of UV radiation, UV-B radiation which has a wavelength of between 280 and 315 nanometres.
- As UV radiation is absorbed by ozone in the stratosphere, it heats up the surrounding air to produce the stratospheric temperature inversion.
What is Ozone Hole?
- Each year for the past few decades during the Southern Hemisphere spring, chemical reactions involving chlorine and bromine cause ozone in the southern polar region to be destroyed rapidly and severely.
- The Dobson Unit (DU) is the unit of measure for total ozone.
- The chemicals involved ozone depletion are chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs for short), halons, and carbon tetrachloride.
- They are used for a wide range of applications, including refrigeration, air conditioning, foam packaging, and making aerosol spray cans.
- The ozone-depleted region is known as the “ozone hole”.
Tropical Ozone Hole
- According to the study, the ozone hole is located at altitudes of 10-25 km over the tropics.
- This hole is about seven times larger than Antarctica, the study suggested.
- It also appears across all seasons, unlike that of Antarctica, which is visible only in the spring.
- The hole has become significant since the 1980s. But it was not discovered until this study.
What caused an ozone hole in the tropics?
- Studies suggested another mechanism of ozone depletion: Cosmic rays.
- Chlorofluorocarbon’s (CFC) role in depleting the ozone layer is well-documented.
- The tropical stratosphere recorded a low temperature of 190-200 Kelvin (K).
- This can explain why the tropical ozone hole is constantly formed over the seasons.
Significance of the finding
- The tropical ozone hole, which makes up 50 percent of Earth’s surface, could cause a global concern due to the risks associated with it.
- It is likely to cause skin cancer, cataracts and other negative effects on the health and ecosystems in tropical regions.
Try this PYQ
Q.Consider the following statements:
Chlorofluorocarbons, known as ozone-depleting substances are used:
- In the production of plastic foams
- In the production of tubeless tyres
- In cleaning certain electronic components
- As pressurizing agents in aerosol cans
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Post your answers here
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Vishnugadh Project
Mains level: Not Much
An independent panel of the World Bank is considering a plea by residents of some village to investigate environmental damage from the under-construction Vishnugad Pipalkoti Hydro Electric Project (VPHEP).
Vishnugadh Project
- The 444-MW VPHEP is being built by the Tehri Hydropower Development Corporation (THDC), a partially State-owned enterprise.
- It is being constructed on Dhauliganga River in Chamoli District of Uttarakhand.
- The project is primarily funded by the World Bank and was sanctioned in 2011. It is proposed to be completed in June 2023.
- About 40% of the funds for the $792 million project (₹64,000 crore approx.) has already been disbursed.
Why in news now?
- Residents in their complaint have said muck dumping from the dam threatens the local Lakshmi Narayan Temple, which is deemed to be of historical and cultural importance.
- They also complained about the limited availability of water, saying that 70 of the 92 households received water only for two hours daily.
- Before the project construction, they had ready access to water.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Manusmriti
Mains level: Not Much
The Vice Chancellor of a renowned university recently criticized the Manusmriti, the ancient Sanskrit text, over its gender bias.
What is the news?
- The VC said that the Manusmriti has categorised all women as shudras, which is extraordinarily regressive.
What is Manusmriti?
- The Mānavadharmaśāstra, also known as Manusmriti or the Laws of Manu, is a Sanskrit text belonging to the Dharmaśāstra literary tradition of Hinduism.
- Composed sometime between the 2nd century BCE and 3rd century CE, the Manusmriti is written in sloka verses, containing two non-rhyming lines of 16 syllabus each.
- The text is attributed to the mythical figure of Manu, considered to be ancestor of the human race in Hinduism.
- There has been considerable debate between scholars on the authorship of the text.
- Many have argued that it was compiled by many Brahmin scholars over a period of time.
- However, Indologist Patrick Olivelle argues that Manusmṛiti’s “unique and symmetrical structure,” means that it was composed by a “single gifted individual,” or by a “strong chairman of a committee” with the aid of others.
What is the text about?
(A) Social aspects
- The Manusmriti is encyclopaedic in scope, covering subjects such as the social obligations and duties of the various castes and of individuals in different stages of life.
- It seeks to govern the suitable social and sexual relations of men and women of different castes, on taxes, the rules for kingship, on maintaining marital harmony and the procedures for settling everyday disputes.
- At its core, the Manusmriti discusses life in the world, how it is lived in reality, as well as how it ought to be.
(B) Political aspects
- They argue that the text is about dharma, which means duty, religion, law and practice.
- It also discusses aspects of the Arthashashtra, such as issues relating to statecraft and legal procedures.
- The aim of the text is to present a blueprint for a properly ordered society under the sovereignty of the king and the guidance of Brahmins.
- It was meant to be read by the priestly caste and Olivelle argues that it would likely have been part of the curriculum for young Brahmin scholars at colleges.
What is its significance?
- By the early centuries of the Common Era, Manu had become, and remained, the standard source of authority in the orthodox tradition for that centrepiece of Hinduism, varṇāśrama-dharma (social and religious duties tied to class and stage of life)”.
- Indologists argue that it was a very significant text for Brahmin scholars — it attracted 9 commentaries by other writers of the tradition, and was cited by other ancient Indian texts far more frequently than other dharmaśāstra.
How did colonists consider this text?
- European Orientalists considered the Manusmṛiti to be of great historical and religious significance as well. It was the first Sanskrit text to be translated into a European language, by the British philologist Sir William Jones in 1794.
- Subsequently, it was translated into French, German, Portuguese and Russian, before being included in Max Muller’s edited volume, Sacred Books of the East in 1886.
- For colonial officials in British India, the translation of the book served a practical purpose.
- In 1772, Governor-General Warren Hastings decided to implement laws of Hindus and Muslims that they believed to be “continued, unchanged from remotest antiquity.
- For Hindus, the dharmasastras were to play a crucial role, as they were seen by the British as ‘laws,’ whether or not it was even used that way in India.
Why is it controversial?
- The ancient text has 4 major divisions: 1) Creation of the world. 2) Sources of dharma. 3) The dharma of the four social classes. 4) Law of karma, rebirth, and final liberation.
- The third section is the longest and most important section.
- The text is deeply concerned with maintaining the hierarchy of the four-fold varna system and the rules that each caste has to follow.
- Then, the Brahmin is assumed to be the perfect representative of the human race.
- While Shudras, who are relegated to the bottom of the order, are given the sole duty of serving the ‘upper’ castes.
- Some verses also contain highly prejudicial sentiments against women on the basis of their birth.
- There are many verses in the text that are considered highly controversial.
Dr. Ambedkar and Manusmriti
- On December 25, 1927, Dr B R Ambedkar had famously burned the Manusmṛiti, which he saw as a source of gender and caste oppression.
- However, he widely acknowledged that Manusmriti is NOT a religious decree but a social doctrine, manipulated since centuries to normalize oppression of the population.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: James Webb Space Telescope, Jupiter
Mains level: Not Much

The James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s latest and most powerful telescope, has captured new images of our solar system’s largest planet, Jupiter, presenting it in a never before seen light.
What is so special about snapping Jupiter?
- The photographs have captured a new view of the planet, presenting in detail its massive storms, colourful auroras, faint rings and two small moons — Amalthea and Adrastea.
- While most of us are familiar with the yellow and reddish-brown gas giant.
- The JSWT’s Near-Infrared Camera, with its specialized infrared filters, has shown Jupiter encompassed in blue, green, white, yellow and orange hues.
- Jupiter’s famous Great Red Spot, a storm so big that it could swallow Earth, appeared bright white in the image, since it was reflecting a lot of sunlight.
- The brightness here indicates high altitude — so the Great Red Spot has high-altitude hazes, as does the equatorial region.
- The numerous bright white ‘spots’ and ‘streaks’ are likely very high-altitude cloud tops of condensed convective storms.
About James Webb Space Telescope

- JWST is a space telescope jointly developed by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
- It is planned to succeed the Hubble Space Telescope as NASA’s flagship astrophysics mission.
- It will conduct a broad range of investigations across the fields of astronomy and cosmology, including:
- Observing some of the most distant events and objects in the universe such as the formation of the first galaxies
- Detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets
How is it different from other telescopes?
- JWST is much more powerful and has the ability to look in the infrared spectrum, which will allow it to peer through much deeper into the universe, and see through obstructions such as gas clouds.
- As electromagnetic waves travel for long distances, they lose energy, resulting in an increase in their wavelength.
- An ultraviolet wave, for example, can slowly move into the visible light spectrum and the infrared spectrum, and further weaken to microwaves or radio waves, as it loses energy.
- Hubble was designed to look mainly into the ultraviolet and visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- JWST is primarily an infrared telescope, the first of its kind.
Special features of JWST
(1) Time machine in space
- Powerful space telescopes, like JWST or the Hubble Telescope, are often called time machines because of their ability to view very faraway objects.
- The light coming from those objects, stars or galaxies, which is captured by these telescopes, began its journey millions of years earlier.
- Essentially, what these telescopes see are images of these stars or galaxies as they were millions of years ago.
- The more distant the planet or star, the farther back in time are the telescopes able to see.
(2) Farthest from Earth
- JWST will also be positioned much deeper into space, about a million miles from Earth, at a spot known as L2.
- It is one of the five points, known as Lagrange’s points, in any revolving two-body system like Earth and Sun, where the gravitational forces of the two large bodies cancel each other out.
- Objects placed at these positions are relatively stable and require minimal external energy to keep them there. L2 is a position directly behind Earth in the line joining the Sun and the Earth.
- It would be shielded from the Sun by the Earth as it goes around the Sun, in sync with the Earth.
(3) Engineering marvel
- JWST has one large mirror, with a diameter of 21 feet (the height of a typical two-storey building), that will capture the infra-red light coming in from the deep universe while facing away from the Sun.
- It will be shielded by a five-layer, tennis court-sized, kite-shaped sunscreen that is designed to block the heat from Sun and ensure the extremely cool temperatures that the instruments are built to operate at.
- Temperatures on the sun-facing side can get as high as 110°C, while the other side would be maintained at –200° to –230°C.
- The extremely cold temperatures are needed to detect the extremely faint heat signals from distant galaxies.
- The mirror as well as the sunscreen is so large they could not have fit into any rocket. They have been built as foldable items and would be unravelled in space.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Automatic Number Plate Reader (ANPR)
Mains level: Toll collection models in India

In light of congestion at toll plazas, the Road Transport and Highways Ministry is now moving ahead with a plan to replace toll plazas with cameras that could read number plates, also known as Automatic Number Plate Reader (ANPR) cameras.
ANPR cameras
- The plan is to remove toll plazas on national highways and instead rely on ANPR cameras, which will read vehicle number plates and automatically deduct toll from the linked bank accounts of vehicle owners.
- The model is simple: Entry and exit of toll roads will have cameras capable of reading number plates, and toll will be deducted based on these cameras.
Can all number plates be read by the cameras?
- Not all number plates in India can be read, and only those that have come after 2019 will be registered by the cameras.
- The government, in 2019, had come up with a rule mandating passenger vehicles to have company-fitted number plates, and only these number plates can be read by cameras.
- The government plans to come up with a scheme to replace older number plates.
- A pilot of this scheme is underway and legal amendments to facilitate this transition are also being moved to penalise vehicle owners who skip toll plazas and do not pay.
Current model for toll collection: FASTags
- Currently, about 97 per cent of the total toll collection of nearly Rs 40,000 crore happens though FASTags — the remaining 3 per cent pay higher than normal toll rates for not using FASTags.
- With FASTags, it takes about 47 seconds per vehicle to cross a toll plaza.
- There’s a marked throughput enhancement – more than 260 vehicles can be processed per hour via electronic toll collection lane as compared to 112 vehicles per hour via manual toll collection lane, according to government data.
- While FASTags have eased traffic at toll plazas across the country, congestion is still reported as there are toll gates that need to be crossed after authentication.
Why such move?
- Congestion at toll plazas on national highways continues to impact commuters despite 97 per cent of tolling happening through FASTags.
- Apart from ANPR helping to ease congestion, the government is also looking at GPS technology as one of the options for toll collection.
Are there issues with ANPR?
- The success of ANPR cameras will depend on creating an ecosystem that is in sync with the requirements of the camera.
- The biggest problem being faced during the trials is when things are written on number plates, beyond the nine digit registration number, such as ‘Govt of India/Delhi’ etc.
- Another problem that ANPR cameras face is in reading number plates on trucks, as most of the time they are hidden or soiled etc.
- A pilot on a key expressway has found that about 10 per cent of vehicles with such number plates are being missed by the ANPR cameras.
Back2Basics: What is ‘FASTag’?
- As per Central Motor Vehicles Rules, 1989, since 1st December 2017, the FASTag had been made mandatory for all registered new four-wheelers and is being supplied by the Vehicle Manufacturer or their dealers.
- It has been mandated that the renewal of fitness certificate will be done only after the fitment of FASTag.
- For National Permit Vehicles, the fitment of FASTag was mandated since 1st October 2019.
- FASTags are stickers that are affixed to the windscreen of vehicles and use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to enable digital, contactless payment of tolls without having to stop at toll gates.
- The tags are linked to bank accounts and other payment methods.
- As a car crosses a toll plaza, the amount is automatically deducted, and a notification is sent to the registered mobile phone number.
How does it work?
- The device employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it.
- It is affixed on the windscreen, so the vehicle can drive through plazas without stopping.
- RFID technology is similar to that used in transport access-control systems, like Metro smart card.
- If the tag is linked to a prepaid account like a wallet or a debit/credit card, then owners need to recharge/top up the tag.
- If it is linked to a savings account, then money will get deducted automatically after the balance goes below a pre-defined threshold.
- Once a vehicle crosses the toll, the owner will get an SMS alert on the deduction. In that, it is like a prepaid e-wallet.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Yakshagana
Mains level: Not Much

This newscard is an excerpt of the original article published in TH.
What is Yakshagana?
- Yakshagana is a traditional theater, developed in Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and western parts of Chikmagalur districts, in the state of Karnataka and in Kasaragod district in Kerala.
- It emerged in the Vijayanagara Empire and was performed by Jakkula Varu.
- It combines dance, music, dialogue, costume, make-up, and stage techniques with a unique style and form.
- Towards the south from Dakshina Kannada to Kasaragod of Tulu Nadu region, the form of Yakshagana is called as ‘Thenku thittu’ and towards north from Udupi up to Uttara Kannada it’s called as ‘Badaga Thittu‘.
- It is sometimes simply called “Aata” or āṭa (meaning “the play”). Yakshagana is traditionally presented from dusk to dawn.
- Its stories are drawn from Ramayana, Mahabharata, Bhagavata and other epics from both Hindu and Jain and other ancient Indic traditions.
Try this question from CSP 2017:
Q.With reference to Manipuri Sankirtana, consider the following statements:
- It is a song and dance performance.
- Cymbals are the only musical instruments used in the performance.
- It is performed to narrate the life and deeds of Lord Krishna.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3.
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 only
Post your answers here.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: VL-SRSAM
Mains level: Short range missiles development

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy has successfully flight-tested the indigenously developed Vertical Launch Short Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) from the Integrated Test Range (ITR) at Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
What is Vertical Launch Short Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VLSRSAM) ?
- VL-SRSAM has been designed and developed jointly by three facilities of the DRDO for deployment of Indian Naval warships.
- The missile has the capability of neutralising various aerial threats at close ranges including sea-skimming targets.
- The tactic of sea skimming is used by various anti-ship missiles and some fighter jets to avoid being detected by the radars onboard warships.
- For this, these assets fly as close as possible to sea surface and thus are difficult to detect and neutralise.
Features of VL-SRSAM
- The missile has been designed to strike at the high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km.
- Its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.
- Two key features of the VL-SRSAM are cruciform wings and thrust vectoring.
- The cruciform wings are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- The thrust vectoring is an ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile.
- VL-SRSAM is a canisterised system, which means it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus making its transport and storage easier and improving the shelf life of weapons
Strategic significance of the missile
- The launch was conducted from a vertical launcher against an electronic target at a very low altitude.
- The flight path of the vehicle along with health parameters was monitored using a number of tracking instruments deployed by ITR, Chandipur.
- The successful testing of these systems was crucial for future launches of the missile from Indian Naval Ships.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tomato Flu
Mains level: Not Much
With cases of tomato flu reported from at least four states — Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, and Odisha — the Union Health Ministry has issued a set of guidelines on prevention, testing, and treatment of the infection.
Researchers believe that it is a different clinical presentation of hand-foot-and mouth disease (HFMD) caused by a group of enteroviruses (viruses transmitted through the intestine).
What is Tomato Flu?
- Tomato flu or tomato fever is characterized by fever, joint pain, and red, tomato-like rashes usually seen in children below the age of five years.
- This is accompanied by other symptoms of viral fevers such as diarrhoea, dehydration, nausea and vomiting, and fatigue.
- This was thought to be an aftereffect of dengue and chikungunya that is commonly seen in Kerala.
- However, researchers now believe that it is HFMD caused by enteroviruses like Coxsackievirus A-6 and A-16.
Is it very uncommon?
- Tomato flu could be an after-effect of chikungunya or dengue fever in children rather than a viral infection.
- It could also be a new variant of the viral hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common infectious disease targeting mostly children aged 1–5 years and immunocompromised adults.
- HFMD is not a new infection, we have read about it in our textbooks. It is reported from time to time across the country, but it is not very common.
Why is the infection spreading now?
- There actually are more cases or because we are more vigilant about viral infections and testing after Covid-19.
- Since the disease is self-limiting, doctors do not usually test for it.
- There are so many viral infections in children, but we cannot — and there is no need to — test for each and every one of it.
Which pathogen is causing it now? And how is the clinical presentation different?
- The current HFMD cases are mainly caused by Coxsackievirus A-6 and A-16.
- Another pathogen — Enterovirus71 — that also causes the disease is not very prevalent now, according to her.
- This is good because the pathogen was known to lead to severe neurologic symptoms, including fatal encephalitis (brain inflammation).
- In almost all cases, say 99.9% cases, the disease is self-limiting.
- But, in a small number of cases it can lead to CNS (central nervous system) complications.
Is there a treatment for the infection?
- There is no specific treatment or vaccine available for the disease.
- Those with the infection are treated symptomatically, such as prescription of paracetamol for fever.
How can the infection be prevented?
- As it happens mainly in children, the Centre’s advisory focuses on preventions in these age groups.
- As per the advisory, anyone suspected to have the infection should remain in isolation for five to seven days after the onset of the symptoms.
- It states that children must be educated about the infection and asked not to hug or touch other children with fever or rashes.
- The children should be encouraged to maintain hygiene, stop thumb or finger sucking, and use a handkerchief for a running nose, the advisory states.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Mains level: Prospects and challenges to CBDC
Reports have said the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) digital rupee — the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) — may be introduced in phases beginning with wholesale businesses in the current financial year.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
- CBDC is a central bank issued digital currency which is backed by some kind of assets in the form of either gold, currency reserves, bonds and other assets, recognised by the central banks as a monetary asset.
- The present concept of CBDCs was directly inspired by Bitcoin, but a CBDC is different from virtual currency and cryptocurrency.
- Cryptocurrencies are not issued by a state and lack the legal tender status declared by the government.
What is Currency chest?
Currency in India is managed by Currency chest. Currency chest is a place where the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) stocks the money meant for banks and ATMs. These chests are usually situated on the premises of different banks but administrated by the RBI.
Why India needs a digital rupee?
- Online transactions: India is a leader in digital payments, but cash remains dominant for small-value transactions.
- High currency in circulation: India has a fairly high currency-to-GDP ratio.
- Cost of currency management: An official digital currency would reduce the cost of currency management while enabling real-time payments without any inter-bank settlement.
Why is CBDC preferred over Cryptocurrency?
- Sovereign guarantee: Cryptocurrencies pose risks to consumers. They do not have any sovereign guarantee and hence are not legal tender.
- Market volatility: Their speculative nature also makes them highly volatile. For instance, the value of Bitcoin fell from USD 20,000 in December 2017 to USD 3,800 in November 2018.
- Risk in security: A user loses access to their cryptocurrency if they lose their private key (unlike traditional digital banking accounts, this password cannot be reset).
- Malware threats: In some cases, these private keys are stored by technical service providers (cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets), which are prone to malware or hacking.
- Money laundering: Cryptocurrencies are more vulnerable to criminal activity and money laundering. They provide greater anonymity than other payment methods since the public keys engaging in a transaction cannot be directly linked to an individual.
- Regulatory bypass: A central bank cannot regulate the supply of cryptocurrencies in the economy. This could pose a risk to the financial stability of the country if their use becomes widespread.
- Power consumption: Since validating transactions is energy-intensive, it may have adverse consequences for the country’s energy security (the total electricity use of bitcoin mining, in 2018, was equivalent to that of mid-sized economies such as Switzerland).
Features of CBDC
- High-security instrument: CBDC is a high-security digital instrument; like paper banknotes, it is a means of payment, a unit of account, and a store of value.
- Uniquely identifiable: And like paper currency, each unit is uniquely identifiable to prevent counterfeit.
- Liability of central bank: It is a liability of the central bank just as physical currency is.
- Transferability: It’s a digital bearer instrument that can be stored, transferred, and transmitted by all kinds of digital payment systems and services.
Key benefits offered
- Faster system: CBDC can definitely increase the transmission of money from central banks to commercial banks and end customers much faster than the present system.
- Financial inclusion: Specific use cases, like financial inclusion, can also be covered by CBDC that can benefit millions of citizens who need money and are currently unbanked or banked with limited banking services
- Monetary policy facilitation: The move to bring out a CBDC could significantly improve monetary policy development in India.
- Making of a regional currency: In the cross border payments domain, India can take a lead by leveraging digital Rupee especially in countries such as Bhutan, Saudia Arabia and Singapore where NPCI has existing arrangements.
Others:
- It is efficient than printing notes (cost of printing, transporting, and storing paper currency)
- It reduces the risk of transactions
- It makes tax collection transparent
- Prevents money laundering
Issues involved with CBDC
- Innovation with centralization: The approach of bringing a sovereign digital currency stands in stark contrast to the idea of decentralization.
- Liability on RBI: when bank customers wish to convert their deposits into digital rupee, the RBI will have to take these liabilities from the books of banks and onto its own balance sheet.
- Inflationary risk: Central banks would indulge in issuing more digital currencies which could potentially trigger higher inflation.
- User adoption: User adoption could also pose a major setback for the smooth roll out of the CBDC in India. The main challenges would always be user adoption and security.
- Reduced savings: Many, including various central bankers, fear that people may begin withdrawing money from their bank accounts as digital currencies issued by Central banks become more popular.
- Volatility: the risk is higher and there is more price volatility and lesser acceptance as a money instrument globally, unless the trust factor and investor protection factors change.
Way forward
- The launch of CBDCs may not be a smooth affair and still requires more clarity in India. There are still a lot of misconceptions about the concept of digital currency in the country.
- The effectiveness of CBDCs will depend on aspects such as privacy design and programmability.
- There is a huge opportunity for India to take a lead globally via a large-scale rollout and adoption of digital currencies.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Cloudburst
Mains level: Flash floods and cloudbursts

Over 20 people have been killed in destruction caused by cloudbursts and flash floods in different parts of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand over the last three days.
What are Cloudbursts?
- A cloudburst is a localised but intense rainfall activity.
- Short spells of very heavy rainfall over a small geographical area can cause widespread destruction, especially in hilly regions where this phenomenon is the most common.
- Not all instances of very heavy rainfall, however, are cloudbursts.
- A cloudburst has a very specific definition: Rainfall of 10 cm or more in an hour over a roughly 10 km x 10-km area is classified as a cloudburst event.
- By this definition, 5 cm of rainfall in a half-hour period over the same area would also be categorized as a cloudburst.
How is it different from normal rainfall?
- To put this in perspective, in a normal year, India, as a whole, receives about 116 cm of rainfall over the entire year.
- This means if the entire rainfall everywhere in India during a year was spread evenly over its area, the total accumulated water would be 116 cm high.
- There are, of course, huge geographical variations in rainfall within the country, and some areas receive over 10 times more than that amount in a year.
- But on average, any place in India can be expected to receive about 116 cm of rain in a year.
- During a cloudburst event, a place receives about 10% of this annual rainfall within an hour.
How common are cloudbursts?
- Cloudbursts are not uncommon events, particularly during the monsoon months.
- Most of these happen in the Himalayan states where the local topology, wind systems, and temperature gradients between the lower and upper atmosphere facilitate the occurrence of such events.
- However, not every event that is described as a cloudburst is actually, by definition, a cloudburst.
- That is because these events are highly localized.
- They take place in very small areas which are often devoid of rainfall measuring instruments.
Why are they so destructive?
- The consequences of these events, however, are not confined to small areas.
- Because of the nature of terrain, the heavy rainfall events often trigger landslides and flash floods, causing extensive destruction downstream.
- This is the reason why every sudden downpour that leads to destruction of life and property in the hilly areas gets described as a “cloudburst”, irrespective of whether the amount of rainfall meets the defining criteria.
- At the same time, it is also possible that actual cloudburst events in remote locations aren’t recorded.
Can cloudbursts be forecasted?
- The India Meteorological Department forecasts rainfall events well in advance, but it does not predict the quantum of rainfall — in fact, no meteorological agency does.
- The forecasts can be about light, heavy, or very heavy rainfall, but weather scientists do not have the capability to predict exactly how much rain is likely to fall at any given place.
- Additionally, the forecasts are for a relatively large geographical area, usually a region, a state, a meteorological sub-division, or at best a district.
- As they zoom in over smaller areas, the forecasts get more and more uncertain.
- Theoretically, it is not impossible to forecast rainfall over a very small area as well, but it requires a very dense network of weather instruments and computing capabilities that seem unfeasible with current technologies.
- As a result, specific cloudburst events cannot be forecast. No forecast ever mentions a possibility of a cloudburst.
- But there are warnings for heavy to very heavy rainfall events, and these are routinely forecast four to five days in advance.
- Possibility of extremely heavy rainfall, which could result in cloudburst kind of situations, are forecast six to 12 hours in advance.
Are cloudburst incidents increasing?
- There is no long-term trend that suggests that cloudbursts, as defined by the IMD, are rising.
- What is well established, however, is that incidents of extreme rainfall, as also other extreme weather events, are increasing — not just in India but across the world.
- While the overall amount of rainfall in India has not changed substantially, an increasing proportion of rainfall is happening in a short span of time.
- That means that the wet spells are very wet, and are interspersed with prolonged dry spells even in the rainy season.
- This kind of pattern, attributed to climate change, does suggest that cloudburst events might also be on the rise.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Pandurang Khankhoje
Mains level: Ghadr party

Lok Sabha Speaker, who is currently in Canada for the 65th Commonwealth Parliamentary Conference, will travel to Mexico where he will unveil statues of Swami Vivekananda and Maharashtra-born freedom fighter and agriculturalist Pandurang Khankhoje.
Who was Pandurang Khankhoje (1883-1967)?
- Born in Wardha, Maharashtra, in the late 19th century, Pandurang Khankhoje came in contact with other revolutionaries early on.
- As a student, Khankhoje was an ardent admirer of the French Revolution and of the American War of Independence.
- Closer to home, the Hindu reformer Swami Dayanand and his Arya Samaj movement, which called for a spirit of reform and social change, became the hero to a young student group led by Khankhoje.
Revolutionary activities abroad
- Khankhoje decided to go abroad for further training in revolutionary methods and militaristic strategy.
- At this time, the British government’s suspicions of him were also growing due to his anti-government activities.
- Before leaving, he visited Bal Gangadhar Tilak, by whom he was inspired.
- Tilak advised him to go to Japan, which was itself a strong, anti-West Asian imperialistic force then.
- After spending time with nationalists from Japan and China, Khankhoje eventually moved to the US, where he enrolled in college as a student of agriculture.
Participation in the Indian independence movement
- Khankhoje was one of the founding members of the Ghadar Party, established by Indians living abroad in 1914, mostly belonging to Punjab.
- Its aim was to lead a revolutionary fight against the British in India.
- While in the US, Khankhoje met Lala Har Dayal, an Indian intellectual teaching at Stanford University.
- Har Dayal had begun a propaganda campaign, publishing a newspaper that featured patriotic songs and articles in the vernacular languages of India.
- This was the seed from which the Ghadar Party would emerge.
How did Khankhoje reach Mexico?
- At the military academy, Khankhoje met many people from Mexico.
- The Mexican Revolution of 1910 had led to the overthrow of the dictatorial regime, and this inspired Khankhoje.
- He also reached out to Indians working on farms in the US with the aim of discussing the idea of Indian independence with them.
- Along with the Indian workers, militant action was planned by Khankhoje in India, but the outbreak of the First World War halted these plans.
- He then reached out to Bhikaji Cama in Paris, and met with Vladimir Lenin in Russia among other leaders, seeking support for the Indian cause.
Association with Mexico
- As he was facing possible deportation from Europe and could not go to India, he sought shelter in Mexico.
- Soon, in part due to his prior friendship with Mexican revolutionaries, he was appointed a professor at the National School of Agriculture in Chapingo, near Mexico City.
- He researched corn, wheat, pulses and rubber, developing frost and drought-resistant varieties, and was part of efforts to bring in the Green Revolution in Mexico.
- Later on, the American agronomist Dr Norman Borlaug, called the Father of the Green Revolution in India, brought the Mexican wheat variety to Punjab.
- Khankhoje was revered as an agricultural scientist in Mexico.
Return to India
- Both Pandurang and Jean returned to India after 1947.
- His application for visa was initially rejected by the Indian government due to the ban by the British Indian Government, but was eventually overturned.
- He settled in Nagpur and subsequently embarked on a political career.
- Pandurang Khankhoje died on 22 January 1967.
Back2Basics: Ghadar Party
Founder: Sohan Singh Bhakna, 15 July 1913
- The Ghadar Movement was an early 20th century, international political movement founded by expatriate Indians to overthrow British rule in India.
- Earlier activists had established a ‘Swadesh Sevak Home’ in Vancouver and a ‘United India House’ in Seattle to carry out revolutionary activities. Finally, in 1913, the Ghadr was founded.
- The Ghadar Party, originally known as the Pacific Coast Hindustan Association, was founded on July 15, 1913 in the US by Lala Har Dayal, Sant Baba Wasakha Singh Dadehar, Baba Jawala Singh, Santokh Singh, and Sohan Singh Bhakna.
- The Ghadar party drew a sizable following among Indian expatriates in the United States, Canada, East Africa, and Asia.
- It fought against colonialism from 1914 to 1917, with the support of Imperial Germany and the Ottoman Empire, both of which were Central Powers opposed to the British.
- The party was organized around the weekly newspaper The Ghadar, which featured the masthead caption: Angrezi Raj Ka Dushman (an enemy of British rule); “Wanted brave soldiers to stir up rebellion in India,” the Ghadar declared.
|
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Kerala Savari
Mains level: Cab aggregators malpractices and their regulation in India

Kerala has soft launched ‘Kerala Savari’, the country’s first online taxi service owned by a State government, to ensure fair and decent service to passengers along with fair remuneration to auto-taxi workers.
What is Kerala Savari?
- Operated by the Motor Workers Welfare Board under the aegis of the Labour Department, the Kerala Savari ensures safe travel for the public at ‘government approved fares’ without any ‘surge pricing’.
- The ‘Kerala Savari’ app would be made available to the public on online platforms shortly as it is under the scrutiny of Google now.
Why such initiative?
- The alleged unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights by private app-based cab aggregators have come as a major concern for governments.
- Recently, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) had issued notices to cab aggregators Ola and Uber for unfair trade practices and violation of consumer rights which include:
- Charging exorbitant fares during peak hours
- Unprofessional behaviour from the part of drivers
- Lack of proper response from customer support, and
- Undue levy of cancellation charges despite the cab driver refusing to accept the ride booked by the passenger etc.
- It is against this backdrop that the Kerala government has decided to come up with an app-based platform to offer auto-taxi service for the public.
What are the main attractions of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- There will be no fluctuation in fares on Kerala Savari irrespective of day or night or rain.
- But Kerala Savari only 8% service charge in addition to the rate set by the government, whereas the private cab aggregators charge up to 20 to 30% service charge.
What are the security-related features of ‘Kerala Savari’?
- Kerala Savari is claimed as a safe and reliable online service for women, children, and senior citizens.
- This consideration has been given importance in app designing and driver registration.
- A police clearance certificate is mandatory for drivers joining the scheme apart from the required proper training.
- A panic button system has been introduced in the app.
- It has also been decided to install GPS in vehicles at a subsidised rate.
Will the new government initiative end the monopoly of private cab aggregators?
- Kerala has over five lakh autorickshaws and one lakh cabs.
- The State government plans to bring all auto-taxi workers engaged in the sector under the new platform.
- Since smartphone literacy is high in Kerala, the State is hopeful of bringing them under the scheme in a short span of time.
- In addition, the Kerala government has also decided to provide fuel, insurance, and tyre subsidies for vehicle owners in the future and has already initiated talks with major companies in this regard.
- After the evaluation of the first phase of the project in Thiruvananthapuram, it will be extended to the entire State in a phased manner.
- Kerala Savari is expected to reach Kollam, Ernakulam, Thrissur, Kozhikode, and Kannur municipal limits within a month.
Regulation of Cab Aggregators in India
- The Motor Vehicles Amendment Act 2019 seeks to regulate Cab aggregators in India
- It’s the first time cab aggregators have got statutory recognition as “digital intermediaries” or “transport aggregators”.
- They are now defined as marketplaces that can be used by passengers to connect with a driver for moving from one place to another.
- The Centre will issue broad guidelines from time to time and the states will rely on them to frame their own rules to regulate the industry.
- The aggregators will also have to comply with the provisions of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- This means they will have to follow rules on storing data safely to protect the identity of users.
|
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: Tigray Crisis
Mains level: Not Much
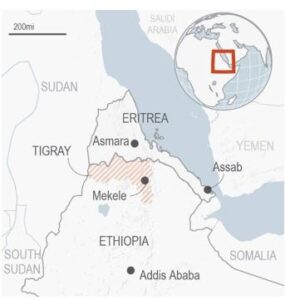
The director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), described the Tigray crisis region as the “worst humanitarian disaster on earth”.
What is the news?
- Ethiopia has been on the brink of a civil war.
- On Nov 4 2020, Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed declared war on the country’s Tigray region.
- The Tigray region is ruled by the Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF).
- The war was declared in response to the TPLF’s attack on a federal military base in Tigray.
Tigray Crisis: A backgrounder
- The animosity between Tigrayans and Eritrea goes back to the Ethiopian-Eritrean war that occurred between 1998 and 2000.
- It occurred approximately two decades ago was extremely brutal and resulted in the deaths of thousands of soldiers.
- The roots of this crisis can be traced to Ethiopia’s system of government. Since 1994, Ethiopia has had a federal system in which different ethnic groups control the affairs of 10 regions.
- The Tigray People’s Liberation Front (TPLF) – was influential in setting up this system.
- It was the leader of a four-party coalition that governed Ethiopia from 1991, when a military regime was ousted from power.
- Under the coalition, Ethiopia became more prosperous and stable, but concerns were routinely raised about human rights and the level of democracy.
How did it escalate into a crisis?
- Eventually, discontent morphed into protest, leading to a government reshuffle that saw Mr Abiy appointed PM.
- Abiy liberalized politics, set up a new party (the Prosperity Party), and removed key Tigrayan government leaders accused of corruption and repression.
- Meanwhile, Abiy ended a long-standing territorial dispute with neighbouring Eritrea, earning him a Nobel Peace Prize in 2019.
- These moves won Abiy popular acclaim, but caused unease among critics in Tigray.
- Tigray’s leaders see Abiy’s reforms as an attempt to centralize power and destroy Ethiopia’s federal system.
How bad is the humanitarian situation?
- Tigray and its neighbouring regions are facing starvation.
- There is an absence of medical facilities, no access to their own money due to shut-down banking services, ethnic and physical violence, and raids at the hands of warring forces.
- The government declared a ceasefire on humanitarian grounds but in an effort to break the TPLF in June last year, imposed a blockade on Tigray.
- This made it impossible to deliver humanitarian, economic, and medical assistance to Tigrayans.
Also read:
[Burning Issue] Ethiopian Crisis and the Geopolitics
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now
Note4Students
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: PFA, Forever Chemicals
Mains level: Residual chemicals and the pollution caused

A recent study published in Environment Science and Technology has found that rainwater from many places across the globe is contaminated with “per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances,” (PFAs) also called “forever chemicals”.
What are PFAs?
- PFAs are man-made chemicals used to make non-stick cookware, water-repellent clothing, stain-resistant fabrics, cosmetics, fire-fighting forms and many other products that resist grease, water and oil.
- They refer to a group of over 3,000 widely used human-made chemicals linked to cancer and other health risks.
- They have tendency to stick around in the atmosphere, rainwater and soil for long periods of time.
- PFAs can migrate to the soil, water and air during their production and use.
- Since most PFAs do not break down, they remain in the environment for long periods of time.
- Some of these PFAs can build up in people and animals if they are repeatedly exposed to the chemicals.
What harm do PFAs cause?
- A variety of health risks are attributed to PFA exposure, including decreased fertility, developmental effects in children, interference with body hormones, increased cholesterol levels and increased risk of some cancers.
- Recent research has also revealed that long-term low-level exposure to certain PFAs can make it difficult for humans to build antibodies after being vaccinated against various diseases.
How can these chemicals be removed from rainwater?
- There is no known method that can extract and remove PFAs from the atmosphere itself.
- There are many effective, albeit expensive, methods to remove them from rainwater that has been collected through various rainwater harvesting methods.
- One way to do this would be to use a filtration system with activated carbon.
- The activated carbon will need to be removed and replaced regularly.
- Also, the old contaminated material must be destroyed.
Remedial measures
- A cheaper method is under trial.
- The researchers first placed a PFA compound in a solvent called DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide).
- They then mixed it with sodium hydroxide (lye) in water.
- They found that when this mixture was heated up to boiling temperature, the PFA compound began to degrade.
- However, this method doesn’t work for all PFAs and only works for certain PFA subsets.
UPSC 2023 countdown has begun! Get your personal guidance plan now! (Click here)
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024
Attend Now















